Professional Documents
Culture Documents
I. Assets Utilization: ROA TR/TA (Assets Utilization) - Total Expense/TA (Expense Ratio) - Taxes/TA (Tax Ratio)
I. Assets Utilization: ROA TR/TA (Assets Utilization) - Total Expense/TA (Expense Ratio) - Taxes/TA (Tax Ratio)
Uploaded by
Joele shCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Case Study - Star River Electronic LTDDocument12 pagesCase Study - Star River Electronic LTDNell Mizuno100% (2)
- Case Finland and NokiaDocument25 pagesCase Finland and NokiaJoele shNo ratings yet
- Case Finland and NokiaDocument25 pagesCase Finland and NokiaJoele shNo ratings yet
- Baf BafDocument6 pagesBaf BafJoele shNo ratings yet
- Volume of Earning AssetsDocument2 pagesVolume of Earning AssetsJoele shNo ratings yet
- Ass1 AuditDocument10 pagesAss1 AuditMoinNo ratings yet
- Liquidity Ratios: Current RatioDocument19 pagesLiquidity Ratios: Current RatiovarunNo ratings yet
- University of Swabi: Group Leader:-Awais Ali (02) Group Members: - Waqas Ali (05) Sohail IqbalDocument23 pagesUniversity of Swabi: Group Leader:-Awais Ali (02) Group Members: - Waqas Ali (05) Sohail IqbalFarhan IsrarNo ratings yet
- BankmedDocument6 pagesBankmedJoele shNo ratings yet
- Report PresentationDocument23 pagesReport PresentationdigitycoonNo ratings yet
- Faisal Spinning Mills Limited: Ratio AnalysisDocument11 pagesFaisal Spinning Mills Limited: Ratio Analysisaitzaz ahmedNo ratings yet
- GAIL 2015 Financial Ratio AnalysisDocument8 pagesGAIL 2015 Financial Ratio AnalysisVarun PatelNo ratings yet
- Days Sales Outstanding: Introduction To Business Finance Assignment No 1Document10 pagesDays Sales Outstanding: Introduction To Business Finance Assignment No 1Varisha AlamNo ratings yet
- Analysis For Dalmia Bharat LTD: Capital StructureDocument4 pagesAnalysis For Dalmia Bharat LTD: Capital Structurejaiminspatel127No ratings yet
- Dupont AnalysisDocument5 pagesDupont AnalysisNoraminah IsmailNo ratings yet
- Cia 3Document10 pagesCia 3Yashvi JainNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument10 pagesRatio AnalysisSandesha Weerasinghe0% (1)
- Aro Granite ReportDocument7 pagesAro Granite ReportsiddharthgrgNo ratings yet
- ABELLANO FRIA MAE A - PRELIM EXAM MAcctngPrEI01Document5 pagesABELLANO FRIA MAE A - PRELIM EXAM MAcctngPrEI01Nelia AbellanoNo ratings yet
- Analisis RatioDocument5 pagesAnalisis RatioKata AssalamualaikumNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio Analysis of Dabur India LTDDocument11 pagesFinancial Ratio Analysis of Dabur India LTDHarshit DalmiaNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis of Financial Statements of Hindustan Petroleum and Bharat Petroleum.Document37 pagesRatio Analysis of Financial Statements of Hindustan Petroleum and Bharat Petroleum.Kumar RitambharNo ratings yet
- Accounting Solution FinanceDocument23 pagesAccounting Solution FinancePayal PatelNo ratings yet
- Profitability RatiosDocument48 pagesProfitability RatiosMohan RajNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Ratio Analysis of Singer BangladeshDocument17 pagesAssignment On Ratio Analysis of Singer BangladeshSISohelJnu100% (2)
- Descriptive FindingsDocument8 pagesDescriptive FindingsValdi NadhifNo ratings yet
- Column1 Column2 Column3 Column1 Column 2Document3 pagesColumn1 Column2 Column3 Column1 Column 2Joele shNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of Indigo Airlines From Lender's PerspectiveDocument12 pagesFinancial Analysis of Indigo Airlines From Lender's PerspectiveAnil Kumar Reddy100% (1)
- Profitability Ratios: Return On Asset (ROA)Document11 pagesProfitability Ratios: Return On Asset (ROA)Saddam Hossain EmonNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sample 1Document22 pagesAssignment Sample 1Nguyen GingNo ratings yet
- Liquidity Market Performance AnalysisDocument4 pagesLiquidity Market Performance AnalysisJessicaNo ratings yet
- Course Project Week 11,12Document5 pagesCourse Project Week 11,12Nae InsaengNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument23 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisRajkamalChichaNo ratings yet
- Pakistan State Oil: Analysis ReportDocument17 pagesPakistan State Oil: Analysis ReportKhushbakht FarrukhNo ratings yet
- Written Assignment Week 1Document6 pagesWritten Assignment Week 1MaylynNo ratings yet
- AirtelDocument13 pagesAirtelRohan ChandnaNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio Analysis of HealthsouthDocument11 pagesFinancial Ratio Analysis of Healthsouthfarha tabassumNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements of NordstromDocument16 pagesFinancial Statements of NordstromAnkita JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 Data Analysis & InterpretationDocument52 pagesChapter - 6 Data Analysis & InterpretationAbhilash JackNo ratings yet
- Capitaland CoDocument11 pagesCapitaland CoLucas ThuitaNo ratings yet
- Trend Ratios EDITEDDocument10 pagesTrend Ratios EDITEDClaudine Anne AguiatanNo ratings yet
- K ElectricDocument9 pagesK ElectricAyesha Bareen.No ratings yet
- Deptor Turn Over RatioDocument2 pagesDeptor Turn Over RatioananthakumarNo ratings yet
- Company Overview: Sun Pharmaceutical Industries LimitedDocument1 pageCompany Overview: Sun Pharmaceutical Industries LimitedDeepikaNo ratings yet
- Financial Management and ControlDocument18 pagesFinancial Management and ControlcrystalNo ratings yet
- Spicejet: Hot. Spicy. Spicejet Names All Its Aircraft With The Name of An IndianDocument5 pagesSpicejet: Hot. Spicy. Spicejet Names All Its Aircraft With The Name of An IndianBraveenvarmaNo ratings yet
- Steel Authority of India Limited SAILDocument21 pagesSteel Authority of India Limited SAILShambhavi SinhaNo ratings yet
- Chandrasekaran.M Rebaccal.A ,: A Study On Capital BudgetingDocument11 pagesChandrasekaran.M Rebaccal.A ,: A Study On Capital Budgetingharisshaikh7070No ratings yet
- "Current Issues and Practices of Finance": A Seminar Paper OnDocument14 pages"Current Issues and Practices of Finance": A Seminar Paper Onnotes.mcpuNo ratings yet
- Project Financial RatiosDocument25 pagesProject Financial RatiosParthiv MistryNo ratings yet
- Return On Total Assets (ROA)Document3 pagesReturn On Total Assets (ROA)Anonymous zphhAI652lNo ratings yet
- Pakistan State Oil: Analysis ReportDocument17 pagesPakistan State Oil: Analysis ReportMaaz HanifNo ratings yet
- Vertical Analysis FinalDocument8 pagesVertical Analysis FinalLiya JahanNo ratings yet
- DD Finance ReportDocument25 pagesDD Finance ReportVishwasKariyaNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis P&GDocument10 pagesFinancial Analysis P&Gsayko88No ratings yet
- Shahzad PainDocument17 pagesShahzad PainRana TayyabNo ratings yet
- Hup Seng IndustryDocument4 pagesHup Seng IndustryMuhamad Uzayr Syahmi RohaizamNo ratings yet
- Abellano Fria Mae A - Prelim Exam Macctngprei01Document4 pagesAbellano Fria Mae A - Prelim Exam Macctngprei01Nelia AbellanoNo ratings yet
- Profitability of The CompanyDocument10 pagesProfitability of The CompanyAscia SummerNo ratings yet
- Term Paper - Accounting and FinanceDocument3 pagesTerm Paper - Accounting and FinanceJayNo ratings yet
- How To Start A Payroll & Bookkeeping Service: A Complete Payroll & Bookkeeping Service Business PlanFrom EverandHow To Start A Payroll & Bookkeeping Service: A Complete Payroll & Bookkeeping Service Business PlanNo ratings yet
- Viii. Growth RatiosDocument2 pagesViii. Growth RatiosJoele shNo ratings yet
- Collective LearningDocument1 pageCollective LearningJoele shNo ratings yet
- 1-Computer Ethics For Computer Professionals: 1.1 - The ACM Code of ConductDocument2 pages1-Computer Ethics For Computer Professionals: 1.1 - The ACM Code of ConductJoele shNo ratings yet
- OperatingDocument2 pagesOperatingJoele shNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1-Code of Conduct For Institute For Certification of Computing ProfessionalsDocument2 pages1.1.1-Code of Conduct For Institute For Certification of Computing ProfessionalsJoele shNo ratings yet
- FinancialDocument1 pageFinancialJoele shNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis:: Year 2010 2011 2012Document2 pagesRatio Analysis:: Year 2010 2011 2012Joele shNo ratings yet
- Expense ControlDocument1 pageExpense ControlJoele shNo ratings yet
- B-Preparation For Future Losses PLL/ Total Loans&leases: Year 2010 2011 2012Document2 pagesB-Preparation For Future Losses PLL/ Total Loans&leases: Year 2010 2011 2012Joele shNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate RiskDocument2 pagesInterest Rate RiskJoele shNo ratings yet
- Tax RatioDocument1 pageTax RatioJoele shNo ratings yet
- ThirdDocument1 pageThirdJoele shNo ratings yet
- Non-Int exp/TA Depends On: Each item/TA2013 Each item/TA2014Document1 pageNon-Int exp/TA Depends On: Each item/TA2013 Each item/TA2014Joele shNo ratings yet
I. Assets Utilization: ROA TR/TA (Assets Utilization) - Total Expense/TA (Expense Ratio) - Taxes/TA (Tax Ratio)
I. Assets Utilization: ROA TR/TA (Assets Utilization) - Total Expense/TA (Expense Ratio) - Taxes/TA (Tax Ratio)
Uploaded by
Joele shOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
I. Assets Utilization: ROA TR/TA (Assets Utilization) - Total Expense/TA (Expense Ratio) - Taxes/TA (Tax Ratio)
I. Assets Utilization: ROA TR/TA (Assets Utilization) - Total Expense/TA (Expense Ratio) - Taxes/TA (Tax Ratio)
Uploaded by
Joele shCopyright:
Available Formats
EM didn’t change from 2013 to 2014 and remained constant at a multiplier of 11.1.
However,
ROA (2014) is less than ROA (2013). Therefore, the decrease of ROE is mainly due to low
ROA.
ROA is a broad concept that depends on many factors such as revenues, expenses and taxes.
ROA= TR/TA (assets utilization) – Total Expense/TA (expense ratio) – Taxes/TA (tax ratio)
I. Assets utilization
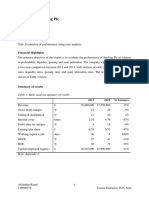
AU TOTAL YEAR
REVENUES
6.25% 2013
2,464,145
6.11% 2,578,239 2014
Table 4: AU
As we can see in table 4 above, asset utilization decreased from 2013 to 2014 which
partially explains the decrease of ROA and in turn ROE. To see what factor or ratio that
pushed asset utilization to be low in 2014 and high in 2013, we should decompose it
more.
AU=Int. income/TA +Non int. income/TA + SG/TA.
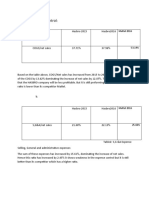
First: interest income ratio
2014 2013
5.113% 5.112% interest income/total assets
Table 5: interest ratio
Interest income increased slightly from 2013 to 2014 however AU decreased from 2013 to 2014.
Therefore, it didn’t have any clear impact on AU and then ROA.
To see how the company is operating regarding its interest income, we should evaluate three
factors that influence how much the bank is generating income from his assets, the three factors
You might also like
- Case Study - Star River Electronic LTDDocument12 pagesCase Study - Star River Electronic LTDNell Mizuno100% (2)
- Case Finland and NokiaDocument25 pagesCase Finland and NokiaJoele shNo ratings yet
- Case Finland and NokiaDocument25 pagesCase Finland and NokiaJoele shNo ratings yet
- Baf BafDocument6 pagesBaf BafJoele shNo ratings yet
- Volume of Earning AssetsDocument2 pagesVolume of Earning AssetsJoele shNo ratings yet
- Ass1 AuditDocument10 pagesAss1 AuditMoinNo ratings yet
- Liquidity Ratios: Current RatioDocument19 pagesLiquidity Ratios: Current RatiovarunNo ratings yet
- University of Swabi: Group Leader:-Awais Ali (02) Group Members: - Waqas Ali (05) Sohail IqbalDocument23 pagesUniversity of Swabi: Group Leader:-Awais Ali (02) Group Members: - Waqas Ali (05) Sohail IqbalFarhan IsrarNo ratings yet
- BankmedDocument6 pagesBankmedJoele shNo ratings yet
- Report PresentationDocument23 pagesReport PresentationdigitycoonNo ratings yet
- Faisal Spinning Mills Limited: Ratio AnalysisDocument11 pagesFaisal Spinning Mills Limited: Ratio Analysisaitzaz ahmedNo ratings yet
- GAIL 2015 Financial Ratio AnalysisDocument8 pagesGAIL 2015 Financial Ratio AnalysisVarun PatelNo ratings yet
- Days Sales Outstanding: Introduction To Business Finance Assignment No 1Document10 pagesDays Sales Outstanding: Introduction To Business Finance Assignment No 1Varisha AlamNo ratings yet
- Analysis For Dalmia Bharat LTD: Capital StructureDocument4 pagesAnalysis For Dalmia Bharat LTD: Capital Structurejaiminspatel127No ratings yet
- Dupont AnalysisDocument5 pagesDupont AnalysisNoraminah IsmailNo ratings yet
- Cia 3Document10 pagesCia 3Yashvi JainNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument10 pagesRatio AnalysisSandesha Weerasinghe0% (1)
- Aro Granite ReportDocument7 pagesAro Granite ReportsiddharthgrgNo ratings yet
- ABELLANO FRIA MAE A - PRELIM EXAM MAcctngPrEI01Document5 pagesABELLANO FRIA MAE A - PRELIM EXAM MAcctngPrEI01Nelia AbellanoNo ratings yet
- Analisis RatioDocument5 pagesAnalisis RatioKata AssalamualaikumNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio Analysis of Dabur India LTDDocument11 pagesFinancial Ratio Analysis of Dabur India LTDHarshit DalmiaNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis of Financial Statements of Hindustan Petroleum and Bharat Petroleum.Document37 pagesRatio Analysis of Financial Statements of Hindustan Petroleum and Bharat Petroleum.Kumar RitambharNo ratings yet
- Accounting Solution FinanceDocument23 pagesAccounting Solution FinancePayal PatelNo ratings yet
- Profitability RatiosDocument48 pagesProfitability RatiosMohan RajNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Ratio Analysis of Singer BangladeshDocument17 pagesAssignment On Ratio Analysis of Singer BangladeshSISohelJnu100% (2)
- Descriptive FindingsDocument8 pagesDescriptive FindingsValdi NadhifNo ratings yet
- Column1 Column2 Column3 Column1 Column 2Document3 pagesColumn1 Column2 Column3 Column1 Column 2Joele shNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of Indigo Airlines From Lender's PerspectiveDocument12 pagesFinancial Analysis of Indigo Airlines From Lender's PerspectiveAnil Kumar Reddy100% (1)
- Profitability Ratios: Return On Asset (ROA)Document11 pagesProfitability Ratios: Return On Asset (ROA)Saddam Hossain EmonNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sample 1Document22 pagesAssignment Sample 1Nguyen GingNo ratings yet
- Liquidity Market Performance AnalysisDocument4 pagesLiquidity Market Performance AnalysisJessicaNo ratings yet
- Course Project Week 11,12Document5 pagesCourse Project Week 11,12Nae InsaengNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument23 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisRajkamalChichaNo ratings yet
- Pakistan State Oil: Analysis ReportDocument17 pagesPakistan State Oil: Analysis ReportKhushbakht FarrukhNo ratings yet
- Written Assignment Week 1Document6 pagesWritten Assignment Week 1MaylynNo ratings yet
- AirtelDocument13 pagesAirtelRohan ChandnaNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio Analysis of HealthsouthDocument11 pagesFinancial Ratio Analysis of Healthsouthfarha tabassumNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements of NordstromDocument16 pagesFinancial Statements of NordstromAnkita JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 Data Analysis & InterpretationDocument52 pagesChapter - 6 Data Analysis & InterpretationAbhilash JackNo ratings yet
- Capitaland CoDocument11 pagesCapitaland CoLucas ThuitaNo ratings yet
- Trend Ratios EDITEDDocument10 pagesTrend Ratios EDITEDClaudine Anne AguiatanNo ratings yet
- K ElectricDocument9 pagesK ElectricAyesha Bareen.No ratings yet
- Deptor Turn Over RatioDocument2 pagesDeptor Turn Over RatioananthakumarNo ratings yet
- Company Overview: Sun Pharmaceutical Industries LimitedDocument1 pageCompany Overview: Sun Pharmaceutical Industries LimitedDeepikaNo ratings yet
- Financial Management and ControlDocument18 pagesFinancial Management and ControlcrystalNo ratings yet
- Spicejet: Hot. Spicy. Spicejet Names All Its Aircraft With The Name of An IndianDocument5 pagesSpicejet: Hot. Spicy. Spicejet Names All Its Aircraft With The Name of An IndianBraveenvarmaNo ratings yet
- Steel Authority of India Limited SAILDocument21 pagesSteel Authority of India Limited SAILShambhavi SinhaNo ratings yet
- Chandrasekaran.M Rebaccal.A ,: A Study On Capital BudgetingDocument11 pagesChandrasekaran.M Rebaccal.A ,: A Study On Capital Budgetingharisshaikh7070No ratings yet
- "Current Issues and Practices of Finance": A Seminar Paper OnDocument14 pages"Current Issues and Practices of Finance": A Seminar Paper Onnotes.mcpuNo ratings yet
- Project Financial RatiosDocument25 pagesProject Financial RatiosParthiv MistryNo ratings yet
- Return On Total Assets (ROA)Document3 pagesReturn On Total Assets (ROA)Anonymous zphhAI652lNo ratings yet
- Pakistan State Oil: Analysis ReportDocument17 pagesPakistan State Oil: Analysis ReportMaaz HanifNo ratings yet
- Vertical Analysis FinalDocument8 pagesVertical Analysis FinalLiya JahanNo ratings yet
- DD Finance ReportDocument25 pagesDD Finance ReportVishwasKariyaNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis P&GDocument10 pagesFinancial Analysis P&Gsayko88No ratings yet
- Shahzad PainDocument17 pagesShahzad PainRana TayyabNo ratings yet
- Hup Seng IndustryDocument4 pagesHup Seng IndustryMuhamad Uzayr Syahmi RohaizamNo ratings yet
- Abellano Fria Mae A - Prelim Exam Macctngprei01Document4 pagesAbellano Fria Mae A - Prelim Exam Macctngprei01Nelia AbellanoNo ratings yet
- Profitability of The CompanyDocument10 pagesProfitability of The CompanyAscia SummerNo ratings yet
- Term Paper - Accounting and FinanceDocument3 pagesTerm Paper - Accounting and FinanceJayNo ratings yet
- How To Start A Payroll & Bookkeeping Service: A Complete Payroll & Bookkeeping Service Business PlanFrom EverandHow To Start A Payroll & Bookkeeping Service: A Complete Payroll & Bookkeeping Service Business PlanNo ratings yet
- Viii. Growth RatiosDocument2 pagesViii. Growth RatiosJoele shNo ratings yet
- Collective LearningDocument1 pageCollective LearningJoele shNo ratings yet
- 1-Computer Ethics For Computer Professionals: 1.1 - The ACM Code of ConductDocument2 pages1-Computer Ethics For Computer Professionals: 1.1 - The ACM Code of ConductJoele shNo ratings yet
- OperatingDocument2 pagesOperatingJoele shNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1-Code of Conduct For Institute For Certification of Computing ProfessionalsDocument2 pages1.1.1-Code of Conduct For Institute For Certification of Computing ProfessionalsJoele shNo ratings yet
- FinancialDocument1 pageFinancialJoele shNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis:: Year 2010 2011 2012Document2 pagesRatio Analysis:: Year 2010 2011 2012Joele shNo ratings yet
- Expense ControlDocument1 pageExpense ControlJoele shNo ratings yet
- B-Preparation For Future Losses PLL/ Total Loans&leases: Year 2010 2011 2012Document2 pagesB-Preparation For Future Losses PLL/ Total Loans&leases: Year 2010 2011 2012Joele shNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate RiskDocument2 pagesInterest Rate RiskJoele shNo ratings yet
- Tax RatioDocument1 pageTax RatioJoele shNo ratings yet
- ThirdDocument1 pageThirdJoele shNo ratings yet
- Non-Int exp/TA Depends On: Each item/TA2013 Each item/TA2014Document1 pageNon-Int exp/TA Depends On: Each item/TA2013 Each item/TA2014Joele shNo ratings yet