Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Raghu - B.Tech Project-35
Raghu - B.Tech Project-35
Uploaded by
Raghu RamanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Raghu - B.Tech Project-35
Raghu - B.Tech Project-35
Uploaded by
Raghu RamanCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 4
4. Smart Grid Technologies and Standards
4.1 Introduction:
4.1.1 Need for Smart Grids:
The electrical infrastructure of the present day has remained largely unchanged over the last
100 years. And while the grid infrastructure has been ageing, the demand for electricity has
steadily increased. The electric power distribution network of the day is very complex and ill-
suited to the needs of the 21st century.
To point out a few deficiencies: lack of automated analysis, mechanical switches causing
slow response times, lack of situational awareness, etc. [13]. These have led to blackouts
which have happened over the course of the last 40 years.
Consequently, a new grid infrastructure is essential to address the challenges such as energy
storage problems, equipment failures, the global climate change, one-way communication
and resilience problems. In the smart grid, reliable and real-time information becomes the key
factor for reliable delivery of power from the generating units to the end-users.
The impact of equipment failures, capacity constraints, and natural accidents, which cause
power disturbances and outages, can be largely avoided by online power system condition
monitoring, diagnostics and protection. [14]
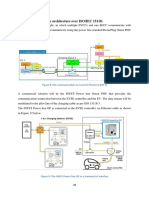
Fig 10 below shows that the Smart gird infrastructure increases the capacity and flexibility of
the network and provides advanced sensing and control through modern communications
technologies.
25
You might also like
- INSE 6680 Project Report PDFDocument30 pagesINSE 6680 Project Report PDFZaid Khan SherwaniNo ratings yet
- Gungor Smart (2011) PDFDocument10 pagesGungor Smart (2011) PDFfeku fekuNo ratings yet
- The Progressive Smart Grid System From Both Power and Communications AspectsDocument23 pagesThe Progressive Smart Grid System From Both Power and Communications AspectstaksasNo ratings yet
- IEEE Paper Smart Grid TechnologyDocument5 pagesIEEE Paper Smart Grid TechnologySujata HarugadeNo ratings yet
- Smart Grid - An Intelligent Power System: Review and Future ChallengesDocument4 pagesSmart Grid - An Intelligent Power System: Review and Future ChallengesManoj Karthik KingNo ratings yet
- Worldwide Technological Revolutions andDocument14 pagesWorldwide Technological Revolutions andgrigore mirceaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document17 pagesUnit 1Omkar Shete67% (6)
- Smart Electric Grid (15ee815) : Nitte, Karkala Nitte, KarkalaDocument124 pagesSmart Electric Grid (15ee815) : Nitte, Karkala Nitte, KarkalaDinesh ShettyNo ratings yet
- Wireless Sensor Networks For Smart Grid Applications: Melike Erol-Kantarci, Hussein T. MouftahDocument6 pagesWireless Sensor Networks For Smart Grid Applications: Melike Erol-Kantarci, Hussein T. MouftahshivaspyNo ratings yet
- An Internet of Things Solution For Real-Time Identification of Electricity Theft and Power Outrages Caused by Fault in Distribution SystemsDocument26 pagesAn Internet of Things Solution For Real-Time Identification of Electricity Theft and Power Outrages Caused by Fault in Distribution SystemsAatir MohammedNo ratings yet
- The Self-Healing Technologies of Smart Distribution Grid PDFDocument6 pagesThe Self-Healing Technologies of Smart Distribution Grid PDFedmuarizt7078No ratings yet
- Smart Grid Technology Nciaee 002Document8 pagesSmart Grid Technology Nciaee 002Mayank YadavNo ratings yet
- A Survey of The Smart Grid Technologies BackgroundDocument11 pagesA Survey of The Smart Grid Technologies BackgroundTaner YenerNo ratings yet
- Applsci 08 01320 v2Document23 pagesApplsci 08 01320 v2Amit JainNo ratings yet
- Application of Internet of Things: Last Meter Smart Grid and Smart Energy Efficient SystemDocument6 pagesApplication of Internet of Things: Last Meter Smart Grid and Smart Energy Efficient SystemJose María CotesNo ratings yet
- The Effects of The Smart Grid System On (Autosaved)Document14 pagesThe Effects of The Smart Grid System On (Autosaved)vignesh waranNo ratings yet
- Developing A Communication Infrastructure For The Smart GridDocument7 pagesDeveloping A Communication Infrastructure For The Smart GridAkshatha NaikNo ratings yet
- Energy-Theft Detection Issues For Advanced Metering Infrastructure in Smart GridDocument16 pagesEnergy-Theft Detection Issues For Advanced Metering Infrastructure in Smart GridArydj DjabarNo ratings yet
- Smart Grid TechnologyDocument5 pagesSmart Grid TechnologyKinza MallickNo ratings yet
- On The Communication Requirements For The Smart Grid: Mohamed Daoud, Xavier FernandoDocument8 pagesOn The Communication Requirements For The Smart Grid: Mohamed Daoud, Xavier Fernandoellie210879No ratings yet
- Smart Grid Technology1Document11 pagesSmart Grid Technology1Bhumika ThummaNo ratings yet
- Smart Grid Challenges, Issues and Solutions: C. P. Vineetha and C.A. BabuDocument4 pagesSmart Grid Challenges, Issues and Solutions: C. P. Vineetha and C.A. BabuTabhiNo ratings yet
- Smart Grid12 09Document11 pagesSmart Grid12 09Akshatha NaikNo ratings yet
- Smart Grid Architecture For Power Control Report WritingDocument8 pagesSmart Grid Architecture For Power Control Report WritingSagnik BasuNo ratings yet
- Smart Grid Security Issues: Vasco Delgado-Gomes, Jo Ao F. Martins, Celson Lima and Paul Nicolae BorzaDocument5 pagesSmart Grid Security Issues: Vasco Delgado-Gomes, Jo Ao F. Martins, Celson Lima and Paul Nicolae BorzaMatthew SimeonNo ratings yet
- Working Smarter, Not Harder: An Introduction To The "Smart Grid"Document5 pagesWorking Smarter, Not Harder: An Introduction To The "Smart Grid"Aisha SulubNo ratings yet
- Abstract:: Zihan XuDocument9 pagesAbstract:: Zihan XuIkhlas KittaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Introduction (Smart Grid)Document57 pagesUnit-1 Introduction (Smart Grid)sujithNo ratings yet
- Altera Overcoming Smart Grid Equipment Design Challenges With FPGAsDocument20 pagesAltera Overcoming Smart Grid Equipment Design Challenges With FPGAskn65238859No ratings yet
- FOX615 2013 Low PDFDocument12 pagesFOX615 2013 Low PDFNeelakandan Masilamani100% (1)
- Project3 PDFDocument162 pagesProject3 PDFBhautikgiri Goswami (Giri)No ratings yet
- Securing The Grid PDF 1696181801Document48 pagesSecuring The Grid PDF 1696181801Vitor Dos Santos FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Report 11Document19 pagesReport 11balaji xeroxNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Technical and Non Technical Losses On Power Outages in NigeriaDocument5 pagesThe Effects of Technical and Non Technical Losses On Power Outages in NigeriaASHISHNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0142061514003743 Main PDFDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0142061514003743 Main PDFSamuel TesfayNo ratings yet
- Complete Proposal For ShokDocument20 pagesComplete Proposal For ShokManuNo ratings yet
- Los Efectos de La Inteligente Cuadrícula Sistema Nacional de La GridsDocument5 pagesLos Efectos de La Inteligente Cuadrícula Sistema Nacional de La GridsPamela Alexandra Hermoza VivancoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To SmartGridDocument21 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To SmartGridGaylethunder007No ratings yet
- An Advanced Protection Scheme For Enabling An LVDC Last Mile Distribution NetworkDocument8 pagesAn Advanced Protection Scheme For Enabling An LVDC Last Mile Distribution Networkmusharraf saeedNo ratings yet
- Effect of Renewable Energy and Electric Vehicles On Smart GridDocument11 pagesEffect of Renewable Energy and Electric Vehicles On Smart GridArmando MaloneNo ratings yet
- Power Quality and EMC in Smart GridDocument6 pagesPower Quality and EMC in Smart GridMohammed MansoorNo ratings yet
- Smart Power Grid: Name - Shubham Jindal Year - 3 Branch - EN Roll No. - 1503021055Document15 pagesSmart Power Grid: Name - Shubham Jindal Year - 3 Branch - EN Roll No. - 1503021055shivam guptaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2772671123000165 MainDocument16 pages1 s2.0 S2772671123000165 MainArif TirtaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security and Privacy Issues in SmaDocument17 pagesCyber Security and Privacy Issues in SmasbaaliaNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Asif Rabbani-Smart Grids and Photovoltaic Integration-Analysis of Residential Grid Connected System in North CyprusDocument6 pagesMuhammad Asif Rabbani-Smart Grids and Photovoltaic Integration-Analysis of Residential Grid Connected System in North CyprusAsif RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Power Quality and EMC in Smart GridDocument6 pagesPower Quality and EMC in Smart GridBernardMightNo ratings yet
- Power Grid Monitoring Based On Machine Learning AnDocument17 pagesPower Grid Monitoring Based On Machine Learning AnMaestria en Instrumentación y Control. Facultad de Ingeniería.No ratings yet
- Networking The Smart Grid: A Tropos Networks White PaperDocument11 pagesNetworking The Smart Grid: A Tropos Networks White PaperRavi Kiran GoudNo ratings yet
- A Proposed Communications Infrastructure For The PDFDocument5 pagesA Proposed Communications Infrastructure For The PDFAlane RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Smart Grids: Under The Esteem Guidance of MR - Srinath SirDocument7 pagesSmart Grids: Under The Esteem Guidance of MR - Srinath SirSubhashini Pulathota0% (1)
- Smart Grid - WikipediaDocument48 pagesSmart Grid - WikipediaBablu VermaNo ratings yet
- 210-04.12.2012-Smart Grid in TransmissionDocument2 pages210-04.12.2012-Smart Grid in Transmissionvimal240388No ratings yet
- Power Digitization Unveiled: Navigating the Digital Frontier of EnergyFrom EverandPower Digitization Unveiled: Navigating the Digital Frontier of EnergyNo ratings yet
- WSN Based Smart Grid ApplicationDocument24 pagesWSN Based Smart Grid Applicationsarath1998shajiNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report Artificial Intelligence in Power StationDocument32 pagesSeminar Report Artificial Intelligence in Power StationxzcNo ratings yet
- Physical Layer Security in Wireless Smart Grid: Special Issue PaperDocument9 pagesPhysical Layer Security in Wireless Smart Grid: Special Issue Paperrazanafees853No ratings yet
- Auto-Recloser Circuit Breaker in Power System Based On Internet of Things For Smart GridDocument7 pagesAuto-Recloser Circuit Breaker in Power System Based On Internet of Things For Smart GridjiregnaNo ratings yet
- ECv3i1 Energy Transformation TechnologiesDocument4 pagesECv3i1 Energy Transformation TechnologiesSreenu ThejaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security For Smart Grid Systems: Status, Challenges and PerspectivesDocument6 pagesCyber Security For Smart Grid Systems: Status, Challenges and PerspectivesChetan KotwalNo ratings yet
- 1N4148 (Do-35) 1N4148. 1N4148 1N4148 A0Document6 pages1N4148 (Do-35) 1N4148. 1N4148 1N4148 A0Raghu RamanNo ratings yet
- Raghu - B.Tech Project-55Document1 pageRaghu - B.Tech Project-55Raghu RamanNo ratings yet
- Raghu - B.Tech Project-65Document1 pageRaghu - B.Tech Project-65Raghu RamanNo ratings yet
- 6.5 Gobetwino: Arduino Communicating With Excel: Figure 21: Gobetwino Working ExplanationDocument1 page6.5 Gobetwino: Arduino Communicating With Excel: Figure 21: Gobetwino Working ExplanationRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
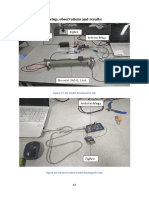
- 6.4 Experimental Setup, Observations and Results:: Figure 17: EV Model Developed in LabDocument1 page6.4 Experimental Setup, Observations and Results:: Figure 17: EV Model Developed in LabRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
- Raghu - B.Tech Project-53Document1 pageRaghu - B.Tech Project-53Raghu RamanNo ratings yet
- 6.2.3 Interfacing The Zigbee Transceivers With The ArduinoDocument1 page6.2.3 Interfacing The Zigbee Transceivers With The ArduinoRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
- Raghu - B.Tech Project-56 PDFDocument1 pageRaghu - B.Tech Project-56 PDFRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
- Raghu - B.Tech Project-49Document1 pageRaghu - B.Tech Project-49Raghu RamanNo ratings yet
- 6.3.3 Explanation of The Program On EVDocument1 page6.3.3 Explanation of The Program On EVRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
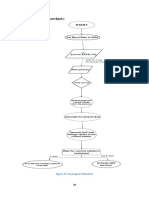
- Figure 16: Control Station Program (Flowchart)Document1 pageFigure 16: Control Station Program (Flowchart)Raghu RamanNo ratings yet
- 5.3 The State of Charge Estimating Methods For Battery:: 5.3.1 Definition and Classification of SOC EstimationDocument1 page5.3 The State of Charge Estimating Methods For Battery:: 5.3.1 Definition and Classification of SOC EstimationRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
- 5.2 State of Charge:: Figure 12: General Layout of An OCV-curveDocument1 page5.2 State of Charge:: Figure 12: General Layout of An OCV-curveRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
- Figure 13: Block Diagram Representing The Two Way Communication Between The EV and The Smart Grid ServerDocument1 pageFigure 13: Block Diagram Representing The Two Way Communication Between The EV and The Smart Grid ServerRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
- 6.2.2 Configuring The Zigbee TransceiversDocument1 page6.2.2 Configuring The Zigbee TransceiversRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
- Establishment of A Two Way Communication System Using ZigbeeDocument1 pageEstablishment of A Two Way Communication System Using ZigbeeRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
- Raghu - B.Tech Project-48 PDFDocument1 pageRaghu - B.Tech Project-48 PDFRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
- 3.5.3 Proposal of Basic Architecture Over ISO/IEC 15118:: Figure 8: PLC Communication On Control Pilot Line (CPLT)Document1 page3.5.3 Proposal of Basic Architecture Over ISO/IEC 15118:: Figure 8: PLC Communication On Control Pilot Line (CPLT)Raghu RamanNo ratings yet
- 6.2 Hardware Implementation of The Two-Way Communication:: 6.2.1 Apparatus UsedDocument1 page6.2 Hardware Implementation of The Two-Way Communication:: 6.2.1 Apparatus UsedRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Overview of SOC Estimating Mathematical Methods:: 5.4.1 Open Circuit Voltage MethodDocument1 page5.4 Overview of SOC Estimating Mathematical Methods:: 5.4.1 Open Circuit Voltage MethodRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
- 3.5.2 Architecture of Iso/Iec 15118 V2Iog:: Figure 6: Pilot Signal StatesDocument1 page3.5.2 Architecture of Iso/Iec 15118 V2Iog:: Figure 6: Pilot Signal StatesRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
- Figure 11: Block Diagram of A Battery SystemDocument1 pageFigure 11: Block Diagram of A Battery SystemRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
- 5.4.2 Terminal Voltage MethodDocument1 page5.4.2 Terminal Voltage MethodRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
- Raghu - B.Tech Project-29Document1 pageRaghu - B.Tech Project-29Raghu RamanNo ratings yet
- 4.2.3 Cellular Network Communication:: Table 4: Smart Gird Communications TechnologiesDocument1 page4.2.3 Cellular Network Communication:: Table 4: Smart Gird Communications TechnologiesRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Communications Technologies Available For Smart Grids:: 4.2.1 ZigbeeDocument1 page4.2 Communications Technologies Available For Smart Grids:: 4.2.1 ZigbeeRaghu RamanNo ratings yet