Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Traducir 20 PDF
Traducir 20 PDF
Uploaded by
Nora Maricela Cavazos MendozaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Traducir 20 PDF
Traducir 20 PDF
Uploaded by
Nora Maricela Cavazos MendozaCopyright:
Available Formats
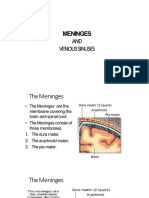
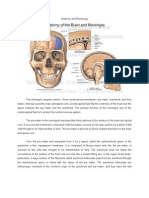
Neuroanatomy
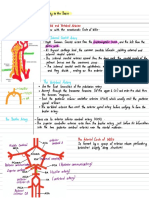
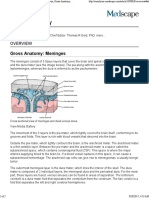
and as the falx cerebelli between the cerebellar hemispheres posterior circulation from the vertebral arteries (eFig. 9.20).
(eFig. 9.17). A smaller reflection, the diaphragm sellae, covers The internal carotid arteries arise from the branching of
the pituitary fossa and underlying pituitary gland. the common carotid arteries at the level of the fourth cervical
Deep to the dura mater is the arachnoid (from the Greek vertebra. Bilaterally the arteries course through the neck
word arachne meaning “spider’s web”) mater. The outer layer to enter the middle cranial fossa through the carotid canal.
of the arachnoid mater is composed of several layers of The arteries then make a series of turns to pass through
flattened cells that lie adjacent to the meningeal layer of the petrous portion of the temporal bone and cavernous
the dura mater (eFig. 9.19). Strands of connective tissue sinus before entering the subarachnoid space just lateral to
extend from this outer layer to form arachnoid trabeculae, the optic chiasm. Upon exiting the cavernous sinus, the
which connect internally to the pia mater (eFig. 9.19). The internal carotid artery gives rise to the ophthalmic artery
pia mater forms a thin, veil-like layer that closely follows and then continues superiorly to give off the posterior
the gyri and sulci on the surface of the brain. The pia and communicating artery and anterior choroidal arteries before
arachnoid matter are separated by a subarachnoid space terminating as the anterior and middle cerebral arteries
that contains CSF and the major blood vessels supplying (eFig. 9.21).
the brain. The two anterior cerebral arteries anastomose proximally
via the anterior communicating artery, anterior to the optic
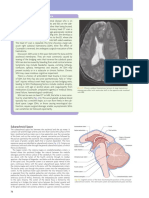
CEREBRAL VASCULATURE chiasm (eFig. 9.22). Distal to this connection, the anterior
cerebral artery (ACA) courses along the medial aspect of
Vascular supply to the brain is divided into the anterior the cerebral hemisphere within the longitudinal fissure and
circulation arising from the internal carotid arteries and follows the superior border of the corpus callosum to the
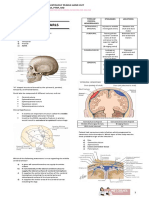
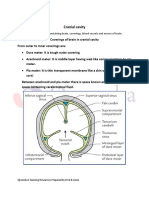
Cerebral vein Diploe Superior sagittal sinus
Epicranial aponeurosis
Sagittal suture
Scalp vessels
Skin
Emissary vein
Dura mater Periosteum
Meningeal
vessels
Arachnoid Endosteum
mater
Falx cerebri
Pia mater Calloso-
marginal
artery
Cerebral
cortex
eFig. 9.19 Coronal section of the cranial meninges: dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. (From Mtui E. Fitzgerald’s Clinical
Neuroanatomy. 7th ed., Fig. 4-5A. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2016.)
e16
booksmedicos.org
You might also like
- Anatomy and Pathophysiology of Stroke: Eitan AurielDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Pathophysiology of Stroke: Eitan AurielZenithaMeidaNo ratings yet
- Netter NeuroScience VasculatureDocument32 pagesNetter NeuroScience VasculaturesilvianpasNo ratings yet
- The Meninges and The Cerebrospinal Fluid: Bagian Anatomi Fkik-Uin Alauddin MakassarDocument23 pagesThe Meninges and The Cerebrospinal Fluid: Bagian Anatomi Fkik-Uin Alauddin MakassaryuyuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document5 pagesLecture 10bibifamelaganieNo ratings yet
- HerniaDocument13 pagesHerniarmt_01No ratings yet
- Step 1: Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesStep 1: Lecture NotesHo Hoang VuNo ratings yet
- 05 Cranial Cavity in Part 1Document27 pages05 Cranial Cavity in Part 1ilagernischit321No ratings yet
- MeningesDocument43 pagesMeningesRehab NaeemNo ratings yet
- Brain Spinal Cord Cerebrospinal Fluid Nervous System Pia Mater Membrane TissueDocument2 pagesBrain Spinal Cord Cerebrospinal Fluid Nervous System Pia Mater Membrane TissuelecturioNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis NOTESDocument5 pagesCase Analysis NOTESneehoshiNo ratings yet
- BI 232 Lab 9Document17 pagesBI 232 Lab 9Cj LinceNo ratings yet
- Nervioso First AidDocument62 pagesNervioso First Aidadrenalina1238No ratings yet
- Meninges of The BrainDocument42 pagesMeninges of The Brainchochojk36No ratings yet
- The Meninges and Blood Vessels of Brain and Spinal Cord, and The Cerebrospinal FluidDocument39 pagesThe Meninges and Blood Vessels of Brain and Spinal Cord, and The Cerebrospinal Fluidnurul rezki fitrianiazisNo ratings yet
- Arteries of The Brain: N N N N N N N NDocument2 pagesArteries of The Brain: N N N N N N N NjihadNo ratings yet
- 4 Blood Supply, Meninges and Cerebrospinal Fluid CirculationDocument17 pages4 Blood Supply, Meninges and Cerebrospinal Fluid CirculationPepeeNo ratings yet
- Meninges: Consist of Three LayersDocument23 pagesMeninges: Consist of Three LayersShantu ShirurmathNo ratings yet
- Bau Dent2008 Meninges and Venous Sinuses 2023Document33 pagesBau Dent2008 Meninges and Venous Sinuses 2023rozhinajalili1381turkeyNo ratings yet
- Meninges & VascularDocument39 pagesMeninges & VascularAriandindi AriandiNo ratings yet
- The Meninges and The Cerebrospinal FluidDocument39 pagesThe Meninges and The Cerebrospinal FluidAfdalia AmandaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Pearls: Jimffel A. Tejada, PTRP, MDDocument13 pagesAnatomy Pearls: Jimffel A. Tejada, PTRP, MDSanielle Karla Garcia Lorenzo100% (1)
- Brain and MeningesDocument5 pagesBrain and Meningesr74k8zgg8rNo ratings yet
- Clinical Neuroanatomical TechniquesDocument6 pagesClinical Neuroanatomical TechniquesMWNo ratings yet
- NVS MeningesDocument5 pagesNVS Meningesdncm.alejandroNo ratings yet
- Updated - CHAPTER 2 PART BDocument43 pagesUpdated - CHAPTER 2 PART Bdeela decemberNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Circulation and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) : By: Biruk A September, 2021Document37 pagesCerebral Circulation and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) : By: Biruk A September, 2021ሌናፍ ኡሉምNo ratings yet
- ICBA NotesDocument60 pagesICBA NotesAndrew EldeiryNo ratings yet
- MeningensDocument2 pagesMeningenslianurliaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyKamille Jeane Stice CavalidaNo ratings yet
- Jessen2015 Article TheGlymphaticSystemABeginnerSGDocument17 pagesJessen2015 Article TheGlymphaticSystemABeginnerSGAhmad Al-HusainNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular NotesDocument11 pagesCardiovascular NotesJireh Acabal100% (1)
- Subarachnoid BlockDocument25 pagesSubarachnoid BlockScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- The Meninges and Blood Vessels of Brain and Spinal Cord, and The Cerebrospinal FluidDocument39 pagesThe Meninges and Blood Vessels of Brain and Spinal Cord, and The Cerebrospinal FluidPraneetha NouduriNo ratings yet
- Netter's Anatomy Coloring 2345Document1 pageNetter's Anatomy Coloring 2345Andreea GheorgheNo ratings yet
- General Organization of The Brain Gross Anatomy ofDocument36 pagesGeneral Organization of The Brain Gross Anatomy ofJoebeth Narte VillegasNo ratings yet
- 7 The Meninges, CSFDocument22 pages7 The Meninges, CSFDavid KleinNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of The BrainDocument2 pagesBlood Supply of The BrainCiven AremufNo ratings yet
- Case 3 S H: Ubdural AematomaDocument9 pagesCase 3 S H: Ubdural AematomaAndreea LăzăroiuNo ratings yet
- Brain AtlasDocument11 pagesBrain AtlasPriya HaloiNo ratings yet
- 01 Neuroscience: Gross Anatomy of The BrainDocument5 pages01 Neuroscience: Gross Anatomy of The BrainAsh CansanayNo ratings yet
- MeningesDocument25 pagesMeningesAsad OsmanNo ratings yet
- The SkullDocument6 pagesThe SkullKeeping up with ania kokoNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of The Brain: Gigi Fernandez-Agbisit, MD Pediatric NeurologistDocument40 pagesBlood Supply of The Brain: Gigi Fernandez-Agbisit, MD Pediatric NeurologistVivien EnriquezNo ratings yet
- 2-Meninges and SinusesDocument62 pages2-Meninges and SinusesMajd HallakNo ratings yet
- 10a Folds of Dura Matter-Dr-GosaiDocument5 pages10a Folds of Dura Matter-Dr-GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 THE MENINGESDocument16 pagesChapter 7 THE MENINGESRoger Fernando Abril DiazNo ratings yet
- The Paranasal Sinuses: Shyam Prasad AravindakshaDocument8 pagesThe Paranasal Sinuses: Shyam Prasad AravindakshakhanhlinhNo ratings yet
- Lecture Outline: See Separate Powerpoint Slides For All Figures and Tables Pre-Inserted Into Powerpoint Without NotesDocument65 pagesLecture Outline: See Separate Powerpoint Slides For All Figures and Tables Pre-Inserted Into Powerpoint Without Notesellie marcusNo ratings yet
- Tiếng Anh Chuyên Ngành - Trắc Nghiệm 2Document3 pagesTiếng Anh Chuyên Ngành - Trắc Nghiệm 2Nguyễn Thiện LuânNo ratings yet
- Anatomia para Estética Parte 1Document45 pagesAnatomia para Estética Parte 1Rodolpho VilelaNo ratings yet
- GRDA Intro Brain Cranial Nerves P2Document7 pagesGRDA Intro Brain Cranial Nerves P2KingNo ratings yet
- De Vries 2019 TSVCDocument14 pagesDe Vries 2019 TSVCJimmy Pino CoricazaNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 4 Saraf C2Document111 pagesPemicu 4 Saraf C2CcNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument26 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYCNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument26 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreJSlinkNYNo ratings yet
- MeningesDocument23 pagesMeningeskainat karimNo ratings yet
- GONZALES DENT 2D M13 Post Task Lesson 1 The Blood Supply of The Head and NeckDocument2 pagesGONZALES DENT 2D M13 Post Task Lesson 1 The Blood Supply of The Head and NeckJeo GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Cranial Meninges)Document78 pagesCranial Meninges)Mustafa IbrahimNo ratings yet
- MENINGES - Anatomy of Dura Matter, Pia MatterDocument34 pagesMENINGES - Anatomy of Dura Matter, Pia MatterfidhavfathimaNo ratings yet