Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hormones, Particularly .: Ureters Scrotum
Hormones, Particularly .: Ureters Scrotum
Uploaded by
Fatima Doran Pandaog0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesThe document describes the male reproductive system and its functions. It discusses the roles of the ureters, urethra, seminal vesicles, penis, prepuce, urinary bladder, testes, scrotum, epididymis, ductus deferens, anus, rectum, ejaculatory duct, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands. The ureters carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The urethra carries urine from the bladder outside the body. The seminal vesicles and prostate gland secrete fluids that compose semen. The testes produce sperm and hormones. Together these structures work to transport and store sperm and secrete fluids for ejaculation
Original Description:
Original Title
male reproductiv.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the male reproductive system and its functions. It discusses the roles of the ureters, urethra, seminal vesicles, penis, prepuce, urinary bladder, testes, scrotum, epididymis, ductus deferens, anus, rectum, ejaculatory duct, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands. The ureters carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The urethra carries urine from the bladder outside the body. The seminal vesicles and prostate gland secrete fluids that compose semen. The testes produce sperm and hormones. Together these structures work to transport and store sperm and secrete fluids for ejaculation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesHormones, Particularly .: Ureters Scrotum
Hormones, Particularly .: Ureters Scrotum
Uploaded by
Fatima Doran PandaogThe document describes the male reproductive system and its functions. It discusses the roles of the ureters, urethra, seminal vesicles, penis, prepuce, urinary bladder, testes, scrotum, epididymis, ductus deferens, anus, rectum, ejaculatory duct, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands. The ureters carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The urethra carries urine from the bladder outside the body. The seminal vesicles and prostate gland secrete fluids that compose semen. The testes produce sperm and hormones. Together these structures work to transport and store sperm and secrete fluids for ejaculation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
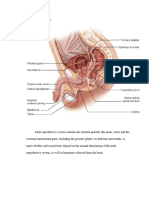
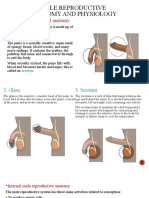
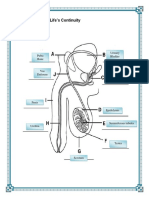
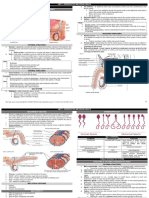
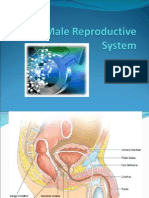
Ureters hormones,
carry the urine away particularly testosterone.
from kidneys to the Scrotum
urinary bladder, which is a The scrotum has a
temporary reservoir for the urine. protective function and acts as a
climate control system for the
Urethra testes.
is a tubular structure that carries Epididymis
the urine from the It functions in the carrying and
urinary bladder to the outside. storage of the sperm cells that
are produced in the testes.
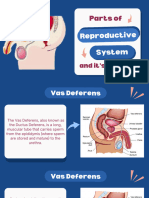
Seminal vesicle Ductus deferens
glands are an androgen is 30-45 cm in length
dependent organ that secretes a serves to transport sperms cells
significant fraction of the fluid that from the respective epididymis to
eventually the ipsilateral ejaculatory duct.
becomes semen (seminal fluid). Anus
They secrete fluid that partly is the external opening of
composes the semen. the rectum.
Penis Two sphincters control the exit
The function of the penis is to of feces from the body during an
provide a means of urination and act of defecation, which is the
sexual function. primary function of the anus.
In addition, the penis functions by Rectum
filling with blood during an is the final straight portion of
erection to enable penetrative the large intestine in humans and
sexual intercourse some other mammals, and
Prepuce the gut in others.
The male prepuce also provides acts as a temporary storage site
adequate mucosa and skin to for feces.
cover the entire penis during The rectum receives faecal
erection. material from the descending
Urinary bladder colon, transmitted through regular
The urinary bladder functions as muscle contractions
a storage vessel for urine to called peristalsis. As the rectal
delay the frequency of urination. walls expand due to the materials
It is one of the most elastic filling it from within, stretch
organs of the body and can receptors from the nervous
increase its volume greatly to system located in the rectal walls
accommodate up to 800 mL stimulate the desire to pass
of urine at maximum capacity in feces, a process
adults. called defecation.
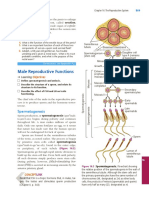
Testes Ejaculatory duct
Testes have two functions – to The ejaculatory duct delivers
produce sperm and to produce sperm into the urethra, adding
secretions and additives from
the prostate necessary for sperm
function, while providing an
interface between the
reproductive and urinary systems
in men.
Prostate gland
The prostate’s most important
function is the production of a fluid
that, together with sperm cells from
the testicles and fluids from other
glands, makes up semen.
The muscles of the prostate also
ensure that the semen is forcefully
pressed into the urethra and then
expelled outwards during
ejaculation.
Bulbourethral glands
The bulbourethral glands function
to lubricate the
spongy urethra for the passage
of the ejaculate. Due to the
alkaline pH of the excreted fluid,
they also act to neutralize
residual acidic urine that remains
in the spongy urethra.
You might also like
- QuestionnairesDocument13 pagesQuestionnairesFatima Doran Pandaog86% (7)
- Affairs in The Philipinas Islands (1582-1583) : by Fray Domingo de SalazarDocument31 pagesAffairs in The Philipinas Islands (1582-1583) : by Fray Domingo de SalazarFatima Doran PandaogNo ratings yet
- Instructions of Governor Sande To Captain FigueroaDocument13 pagesInstructions of Governor Sande To Captain FigueroaFatima Doran Pandaog100% (1)
- Bobiles Edwin Activity No 2Document3 pagesBobiles Edwin Activity No 2Edwin BobilesNo ratings yet
- LECTURE NO 3 - Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesLECTURE NO 3 - Reproductive SystemRebell AeonNo ratings yet
- Human Male and Female Reproductive System (Reviewer)Document8 pagesHuman Male and Female Reproductive System (Reviewer)Justine Yuan DoradoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesReproductive SystemaynNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystembDocument23 pagesMale Reproductive SystembMECHIE ALQUEZANo ratings yet
- Delamide, Reproductive System Anaphy LabDocument5 pagesDelamide, Reproductive System Anaphy LabKristine Lorainne DelamideNo ratings yet
- MCN LEC (Prelims)Document19 pagesMCN LEC (Prelims)BIANCA ANGELICA GERARDONo ratings yet
- Biomedicalperspective in Gender and Sexuality: Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument29 pagesBiomedicalperspective in Gender and Sexuality: Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionBrian CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Activity-Gee 7Document6 pagesActivity-Gee 7Justin DomacenaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Supplementary Activity 1 - Parts and Function Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesWeek 2 Supplementary Activity 1 - Parts and Function Reproductive SystemBernadette Vidon-PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesReproductive SystemMikaella ViadorNo ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesThe Male Reproductive SystemJrp AneworNo ratings yet
- Liver: Loop of Henle. After The Loop of Henle, The Tubule Coils Once More As The Distal Tubule. It ThenDocument3 pagesLiver: Loop of Henle. After The Loop of Henle, The Tubule Coils Once More As The Distal Tubule. It ThenKush KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology: 1. PenisDocument7 pagesMale Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology: 1. PenisMhiahLine TolentinoNo ratings yet
- MCN ReviewerDocument10 pagesMCN ReviewerFatrick BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Life's Continuity - WORKSHEET - 6 (CHRESTINE)Document11 pagesLife's Continuity - WORKSHEET - 6 (CHRESTINE)Patricio IsaranNo ratings yet
- Science Presentation: By: Beam BorachoDocument33 pagesScience Presentation: By: Beam BorachoPEMAR ACOSTANo ratings yet
- GenBio 2 Notes Male ReproductionDocument1 pageGenBio 2 Notes Male ReproductionSTEM STUDENTSNo ratings yet
- Unit 12: - Reproductive SystemDocument18 pagesUnit 12: - Reproductive SystemgilissaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document7 pagesChapter 4melanielampera17No ratings yet
- Urinary System: Cabrera Chunga Geraldinne. Grández Nuncira Claudia. Mundaca Rojas Cesar. Niquén Fiestas SthefanyDocument13 pagesUrinary System: Cabrera Chunga Geraldinne. Grández Nuncira Claudia. Mundaca Rojas Cesar. Niquén Fiestas SthefanyPamela Galvez VasquezNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesParts of The Male Reproductive SystemEris MolenoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Sa ScienceDocument15 pagesReviewer Sa Sciencecjosh9975No ratings yet
- Science ReviewDocument3 pagesScience ReviewAinieNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document158 pagesWeek 4Qossay WaxNo ratings yet
- Bahan UASDocument4 pagesBahan UASislamiah sybNo ratings yet
- OB 1st SemDocument4 pagesOB 1st SemMai CarbonNo ratings yet
- Aternal &: Seminal VesiclesDocument7 pagesAternal &: Seminal VesiclesKyle FernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16. The Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 16. The Reproductive SystemScianna Christel LastimosaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 REPORTDocument5 pagesGeneral Biology 2 REPORTFaustino, Jayreign MaeNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesReproductive SystemJC MangaoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesReproductive Systemcollege code - 5No ratings yet
- Parenthood and Family RelationsDocument2 pagesParenthood and Family RelationsSakshi TyagiNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesReproductive SystemkhakimagdalenaNo ratings yet
- Report Sheet The Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesReport Sheet The Male and Female Reproductive SystemFelix HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System Female Reproductive SystemDocument1 pageMale Reproductive System Female Reproductive SystemEunimae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Science 5 ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience 5 ReviewerAlexandra Pauline DimayugaNo ratings yet
- SXSXDocument27 pagesSXSXJoevany E. BigorniaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System NotesDocument2 pagesReproductive System NotesPhenominNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument71 pagesMale Reproductive Systemאילן גרינולדNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesReproductive SystemMatt MasilonganNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument11 pagesUrinary SystemYomira Balvin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Human Male Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesHuman Male Reproductive Systemmilviepaz100% (1)
- Reproductive SystemDocument37 pagesReproductive Systemqfqxvbb5v2No ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive SystemDocument22 pagesMale and Female Reproductive SystemRhod Vincent Jamolod TayongNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2.1 Antepartum - Pregnancy NURSING NOTESDocument11 pagesMODULE 2.1 Antepartum - Pregnancy NURSING NOTESQwer TyNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Nursing SystemDocument17 pagesReproductive Nursing SystemBobby Dwi PutraNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument6 pagesHistologyarezoo bahramiNo ratings yet
- Fantiyao Reproductive System Group 2Document4 pagesFantiyao Reproductive System Group 2Jushelle Anne Tigoy PilareNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Melanie Arangel, Lecture Notes & Activities (Online) 2Document6 pagesWeek 1 - Melanie Arangel, Lecture Notes & Activities (Online) 2Makspeyn del Valle - MoonNo ratings yet
- Excretory System 2021Document27 pagesExcretory System 2021fashion20trendsNo ratings yet
- Bovine Male GenitaliaDocument48 pagesBovine Male Genitaliaಮನೋಜ್ ಭಾರದ್ವಾಜ್No ratings yet
- Workbook Activity #21: Male Reproductive System General ObjectiveDocument3 pagesWorkbook Activity #21: Male Reproductive System General ObjectiveAmbaw PutiiNo ratings yet
- ANPH M3 CU14. Reproductive SystemDocument22 pagesANPH M3 CU14. Reproductive Systemmark tuazonNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesReproductive SystemShekinah AsebuqueNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document11 pagesPresentation 1Mariel Anne AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Group3 ReproductivesystemDocument19 pagesGroup3 ReproductivesystemLeonie OngNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 Module 7.11.2 Male Reproductive System PDFDocument8 pagesGenbio2 Module 7.11.2 Male Reproductive System PDFYsabelle RamosNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument16 pagesMale Reproductive SystemJeric FranzNo ratings yet
- AutobioDocument4 pagesAutobioFatima Doran PandaogNo ratings yet
- Nineteenth Century CE Architectur1Document3 pagesNineteenth Century CE Architectur1Fatima Doran PandaogNo ratings yet
- Patient Scenario, Chapter 15, Nursing Care of A Family During Labor and BirthDocument3 pagesPatient Scenario, Chapter 15, Nursing Care of A Family During Labor and BirthFatima Doran PandaogNo ratings yet
- Receiving Concurrent Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Erythromycin, Saquinavir, Verapamil, Fluconazole) - 25 MG Once Daily InitiallyDocument272 pagesReceiving Concurrent Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Erythromycin, Saquinavir, Verapamil, Fluconazole) - 25 MG Once Daily InitiallyFatima Doran PandaogNo ratings yet
- Respiration Pulse SitesDocument2 pagesRespiration Pulse SitesFatima Doran PandaogNo ratings yet
- I.Nutrition and Electrolytes A. Vitamins Classification: Fat Soluble Vitamin Generic Name: Vitamin E BRAND NAME: Aquasol EDocument176 pagesI.Nutrition and Electrolytes A. Vitamins Classification: Fat Soluble Vitamin Generic Name: Vitamin E BRAND NAME: Aquasol EFatima Doran PandaogNo ratings yet
- 7 - Amplitude Modulation - Part 2Document35 pages7 - Amplitude Modulation - Part 2Fatima Doran PandaogNo ratings yet
- My Fib Poem I Am Going To Have A Mathematical Fib Poem and You Will Be Amazed Because The Poem Follows The Fibonacci Sequence. Nasirin, Arjay D. BseeDocument1 pageMy Fib Poem I Am Going To Have A Mathematical Fib Poem and You Will Be Amazed Because The Poem Follows The Fibonacci Sequence. Nasirin, Arjay D. BseeFatima Doran PandaogNo ratings yet
- AbduaDocument2 pagesAbduaFatima Doran PandaogNo ratings yet
- Advent of Spanish Colonization: An Antonio de Morga'S AccountDocument35 pagesAdvent of Spanish Colonization: An Antonio de Morga'S AccountFatima Doran PandaogNo ratings yet
- Abdilla, Saidahmae P.Document2 pagesAbdilla, Saidahmae P.Fatima Doran PandaogNo ratings yet
- 28-01 - The Reproductive SystemDocument18 pages28-01 - The Reproductive SystemMelinda AprilyaNo ratings yet
- A0230048 PDFDocument33 pagesA0230048 PDFNathaniel LyngdohNo ratings yet
- G10 Science Q3 - Week 1 - Male Reproductive SystemDocument18 pagesG10 Science Q3 - Week 1 - Male Reproductive SystemKlent CalunsagNo ratings yet
- Pene Palmeado Una Nueva ClasificacionDocument9 pagesPene Palmeado Una Nueva ClasificacionJorgy Ayala PinedaNo ratings yet
- Foreskin Man No. 1Document12 pagesForeskin Man No. 1Matthew Hess83% (12)
- Anatomy Lab. (2) - WorksheetsDocument8 pagesAnatomy Lab. (2) - WorksheetsHamzeh SandoukaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesMale Reproductive SystemShayu ShaNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Intrauterine Insemination Time On Semen ParametersDocument4 pagesThe Effect of Intrauterine Insemination Time On Semen ParametersRamadhan AkmalNo ratings yet
- Practica Reproducitve Systme and PresentDocument10 pagesPractica Reproducitve Systme and PresentLauris CassoNo ratings yet
- AndrologyDocument57 pagesAndrologyaginche amareNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Gross AnatomyDocument13 pagesVeterinary Gross AnatomyTatenda MagejaNo ratings yet
- 176-Article Text-478-1-10-20140830Document5 pages176-Article Text-478-1-10-20140830Ikrimah FithriyandiniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 009Document8 pagesChapter 009api-281340024No ratings yet
- Male Reproductive Functions: Did You Get It?Document1 pageMale Reproductive Functions: Did You Get It?Krizziane Ivy CuajotorNo ratings yet
- Pathologic and Physiologic PhimosisDocument4 pagesPathologic and Physiologic PhimosisJuwita PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Sperma Bab IvDocument7 pagesSperma Bab IvAmelia nur safitri100% (1)
- Semen Analysis Corner Stone in Evaluating Infertility: MethodsDocument8 pagesSemen Analysis Corner Stone in Evaluating Infertility: MethodsHamid IqbalNo ratings yet
- Mind Map Male Reproductive SystemDocument1 pageMind Map Male Reproductive SystemFuzna DahliaNo ratings yet
- Pamphlet TseDocument2 pagesPamphlet TseMuhamad AkmalNo ratings yet
- Histology of TestisDocument2 pagesHistology of TestisyolandadwiooNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemAdor AbuanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument101 pagesUntitledb.makesan100% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S0093691X18306071 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0093691X18306071 MainAntonia Piedrahita MolinaNo ratings yet
- Different Forms of Infertility in MaleDocument36 pagesDifferent Forms of Infertility in MaleSheikh QasimNo ratings yet
- YL Anatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument22 pagesYL Anatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemdrnyolNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument49 pagesMale Reproductive SystemRinkish Dalliah50% (2)
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument27 pagesMale Reproductive System金 Abigail RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Bull Semen Collection and Analysis For ArtificialDocument11 pagesBull Semen Collection and Analysis For ArtificialAdleend RandabungaNo ratings yet
- 170031-Article Text-437088-1-10-20180420Document6 pages170031-Article Text-437088-1-10-20180420Ghani Ikhsan MajidNo ratings yet
- Reproductive OrgansDocument8 pagesReproductive OrgansSelim HanNo ratings yet