Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RSW Spec
RSW Spec
Uploaded by
Cherrie PedritoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RSW Spec
RSW Spec
Uploaded by
Cherrie PedritoCopyright:
Available Formats
HISTORY OF ARCHITECTURE
Pre-Historic Architecture
NEOLITHIC AGE OR STONE AGE (8000-3000 BC)
According to Crave, J. (2020), structures are
in geometric forms created by earth and
stone. Created by our earliest human-made
formations. Their way of construction is
megalithic (large stones), and their usual
materials are animal skins, wooden frames,
and bones ( Espina, K. (n/a) )
(picture on the left)
Dolmen
Pairs of upright stone capped with
horizontal slab (Espina, K. (n/a)).
Pre-Classical Architecture
A. West Asiantic Architecture
50000-2000BC
It has 3-periods: Mesopotamian, Assyrian,
and Persian. Materials they used for
constructions are materials readily
available which was clay, soil, reeds, and
rushes. Some are bricks, timbers, copper,
tin, lead, gold, and imported silvers
(Espina, K. (n/a)).
(picture on the left)
Ziggurats
-Ziggurat of Ur
Religious buildings built next to temples
with 7 stages (Espina, K. (n/a)).
Egyptian Architecture
3200 BC – 1 AD
It has a centralized omnipotent authority of
the Pharaoh, there structures are
characterized by simplicity, massiveness,
and monumentality. Their construction
systems are columnar and trabeated, which
usually made of stone (abundant) (Espina, K.
(n/a).)
(picture on the left)
Pyramids
-Pyramid at Gizeh
massive funerary structure of stone or brick
of Pharaohs (Espina, K. (n/a).)
Classical Architecture
Classical architecture refers to the style
and design of buildings in ancient Greece and ancient Rome, from the rise of ancient Greece until the
fall of the Roman empire (Craven, J. 2020.)
A. Aegean and Greek Architecture
Developed Doric, Ionic, and Composite
column (Crave, J. 2020).
Their buildings are characterized by
simplicity and harmony, with purity of line,
perfect proportions, define details,
monumental, formal, static, and columnar.
Their designs are usually windowless, door-
square head, and marble roof.
(picture on the left)
Temples
-The Parthenon, Acropolis
Chief building type with 12 columns (Espina, K. (n/a)).
B. Etruscan and Roman Architecture
The Romans borrowed heavily from the
earlier Greek and Hellenistic styles, but their
buildings were more highly ornamented
(Craven, J. 2020). their system of
construction are arctuated and trabeated, with
wall surfacing, buttresses, semi-circular
openings, vaulted roof, and mouldings
(Espina, K. (n/a)).
(picture on the left)
Theaters and Amphitheaters
-Colosseum, Rome
Gladiators trained to fight each others at
organized contests (Espina, K. (n/a)).
Early Christian Architecture
It was highly-influenced by Roman art and
Architecture. Early christians’ structure are
characterized by simplicity and horizontally,
with arcaded and trabeated system of
construction (Espina, K. (n/a)).
(picture on the left)
Churches (Basilican Church)
A building to shelter worshipers of Christians
(Espina, K. (n/a)).
Byzantine Architecture
Official style for Orthodox Churches. Style was
centralized and domed characterized by simple
exterior, and rich interior (Espina, K. (n/a)).
(picture on the left)
Churches
-Hagia Sophia, Constantinople
Distinction of Early Christian Churches to Byzantine, are Early Chirstian Churches are horizontally
plan, while Byzantine is Domed and Centralized.
Romanesque Architecture
Religious fervor expressed in arts, cathedrals, and monastic buildings (Espina, K. (n/a)).
Cathedrals
Gothic Architecture
Characterized by departure from classic lines, identified by the general use of pointed arch, and also
called Medieval Architecture (Espina, K. (n/a)).
Cathedrals
Architecture in the Renaissance Period
Baroque and Rococo Architecture
Architecture during the growth of the European States
Architecture in Colonial & Post Colonial America
Architecture in the Industrial Revolution
Architecture at the beginning of the twentieth Century
The International Style and Modernism
Contempory Architecture
You might also like
- Romanian Horezu RoosterDocument1 pageRomanian Horezu RoostermamakingNo ratings yet
- How To Paint Citadel Miniatures - DeathwatchDocument36 pagesHow To Paint Citadel Miniatures - Deathwatchwilly trancoso100% (3)
- History of Architecture FEU-ALE Reviewer PDFDocument65 pagesHistory of Architecture FEU-ALE Reviewer PDFJheyneii100% (5)
- Magic: A History: From Alchemy to Witchcraft, from the Ice Age to the PresentFrom EverandMagic: A History: From Alchemy to Witchcraft, from the Ice Age to the PresentRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (15)
- 1ST Term J1 Fine Art-1Document22 pages1ST Term J1 Fine Art-1Peter Omovigho Dugbo100% (1)
- History of Architecture (Timeline) : Prehistoric ByzantineDocument3 pagesHistory of Architecture (Timeline) : Prehistoric Byzantinejohn rheuven bentulan100% (2)
- Roman Architecture Part 1 and 2Document10 pagesRoman Architecture Part 1 and 2Christal Canuto MacatimpagNo ratings yet
- Iljuwas Bill Reid: Life & Work by Gerald McMasterDocument164 pagesIljuwas Bill Reid: Life & Work by Gerald McMasterArt Canada InstituteNo ratings yet
- National Museum of Cambodia BoardDocument1 pageNational Museum of Cambodia Boardloeundalin080402No ratings yet
- Columbu 2018 Volcanic NoraDocument19 pagesColumbu 2018 Volcanic NoraNicola NorìoNo ratings yet
- Art History Timeline of Western World AnDocument8 pagesArt History Timeline of Western World AnEstrella Esperanza Montoya PantojaNo ratings yet
- Roman ArchitectureDocument4 pagesRoman ArchitectureChristal Canuto MacatimpagNo ratings yet
- History of ArchitectureDocument75 pagesHistory of Architectureranel jamarolinNo ratings yet
- Neroso Hoa NotesDocument10 pagesNeroso Hoa NotesSeth Jaycee GalvanNo ratings yet
- The Monument StoneDocument12 pagesThe Monument StonecsreejithNo ratings yet
- Secondary Arts 9 Q1 Module5Document13 pagesSecondary Arts 9 Q1 Module5Rona RuizNo ratings yet
- Ee297050043 232253179 1125 History of Architecture Reviewer Perez PDFDocument10 pagesEe297050043 232253179 1125 History of Architecture Reviewer Perez PDFMarivicNo ratings yet
- Cultures of Glass Architecture - (1 Glassworks The History of Glass and Its Architectural Identity)Document16 pagesCultures of Glass Architecture - (1 Glassworks The History of Glass and Its Architectural Identity)Sen MingNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument11 pagesArt AppreciationMary Grace TolentinoNo ratings yet
- HOA 1 SummaryDocument10 pagesHOA 1 SummaryNicole Osuna Dichoso100% (1)
- Architectural Design AssessmentDocument6 pagesArchitectural Design AssessmentShyra Mae NavarroNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Architecture Orientalizing To ArchaicDocument3 pagesEvolution of Architecture Orientalizing To ArchaicpringlebobNo ratings yet
- Structural Assessment of Ancient Buildin PDFDocument8 pagesStructural Assessment of Ancient Buildin PDFkptandreasNo ratings yet
- Ancient Period Art App.Document3 pagesAncient Period Art App.evonpallasNo ratings yet
- Western Classical ArchitectureDocument8 pagesWestern Classical ArchitectureSheriyanfsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 ArchitectureDocument24 pagesLesson 5 ArchitectureTitser JoNo ratings yet
- Art AppDocument4 pagesArt AppShyra MangawitNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6.ArtsAppreciation 075455Document64 pagesCHAPTER 6.ArtsAppreciation 075455April Rose Pabadora RojasNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greek ArchitectureDocument8 pagesAncient Greek ArchitectureFrancis Reese Benette DianasasNo ratings yet
- Arts Written Work #1Document4 pagesArts Written Work #1Georgie CatalanNo ratings yet
- GREEK ART ROMAN ART 1 - CompressedDocument29 pagesGREEK ART ROMAN ART 1 - Compressedacenavalta19No ratings yet
- Art App Part 56 ReviewerDocument9 pagesArt App Part 56 ReviewerBela BellsNo ratings yet
- Byblos An Ancient Capital of The LevantDocument24 pagesByblos An Ancient Capital of The LevantBassem KamelNo ratings yet
- GEC8 Midterm Examination Rev.Document3 pagesGEC8 Midterm Examination Rev.monicashayephNo ratings yet
- Art History Timeline Art Periods/ Movements Dates Chief Artists and Major Works Characteristics Historical EventsDocument11 pagesArt History Timeline Art Periods/ Movements Dates Chief Artists and Major Works Characteristics Historical EventsRegine YuNo ratings yet
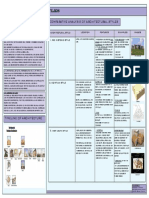
- Architectu Re Perio D Place Style Great Architects Famous Buildings Special Features Evolution Advancement ImportanceDocument4 pagesArchitectu Re Perio D Place Style Great Architects Famous Buildings Special Features Evolution Advancement ImportanceSreejith ChandranNo ratings yet
- Architectural Styles Comparative Analysis of Architectural StylesDocument1 pageArchitectural Styles Comparative Analysis of Architectural StylesJaskiratNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greek ArchitectureDocument35 pagesAncient Greek ArchitectureAnupam SinghNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 9 HandoutDocument8 pagesMapeh 9 HandoutAngelica Dyan MendozaNo ratings yet
- Art App Part 56 ReviewerDocument10 pagesArt App Part 56 ReviewerOnyx CuevasNo ratings yet
- AR2222 Lecture 1 - Ancient Greece and RomeDocument85 pagesAR2222 Lecture 1 - Ancient Greece and RomeSim Yee ShuangNo ratings yet
- Arts and HumanitiesDocument2 pagesArts and HumanitiesHannah Urmeneta HerreriaNo ratings yet
- Triptych of GreeceDocument2 pagesTriptych of GreeceScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- A Companion To Roman Architecture - (A Companion To Roman Architecture)Document4 pagesA Companion To Roman Architecture - (A Companion To Roman Architecture)enrajb.roinNo ratings yet
- ADA Assignment-IDocument10 pagesADA Assignment-I0549 Pranjal NigamNo ratings yet
- Beams Arches DomesDocument13 pagesBeams Arches DomesIngeniero EstructuralNo ratings yet
- Ancient ArtDocument4 pagesAncient ArtNikki LacuarinNo ratings yet
- Holocene Fault Scarps at Mycenae GreeceDocument12 pagesHolocene Fault Scarps at Mycenae Greeceoliveiralivvia2016No ratings yet
- 4 Greek Arch HandoutDocument19 pages4 Greek Arch HandoutVincent CastorNo ratings yet
- Greek ArchitectureDocument1 pageGreek ArchitectureRyn LahoylahoyNo ratings yet
- Ancient GreekDocument94 pagesAncient Greekwai hang chooNo ratings yet
- History 101Document2 pagesHistory 101Eu EuNo ratings yet
- MAA - Kuzmanovska, Stankovski PDFDocument11 pagesMAA - Kuzmanovska, Stankovski PDFmad astronomyNo ratings yet
- History of Interior Design 1 Booklet PDFDocument56 pagesHistory of Interior Design 1 Booklet PDFDelia GozmanNo ratings yet
- 555555Document5 pages555555Lhea Dacillo San JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Mapeh Sculpture2sDocument2 pagesMapeh Sculpture2sjisa52053No ratings yet
- Greek Architecture: PhasesDocument37 pagesGreek Architecture: PhasesChristian MaquilanNo ratings yet
- A Review Analysis of Ancient Greek Architecture: November 2014Document10 pagesA Review Analysis of Ancient Greek Architecture: November 2014anon_535400813No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document4 pagesChapter 6Yo MamaNo ratings yet
- Artandarch AssignmentDocument15 pagesArtandarch AssignmentYeasfi ArafNo ratings yet
- Greek I PDFDocument29 pagesGreek I PDFkitston100% (1)
- FullDocument6 pagesFullRaduan KrauseNo ratings yet
- Prehistoric Egyptian (5000 BC) New East (Mesopotamia) (4000 BC)Document29 pagesPrehistoric Egyptian (5000 BC) New East (Mesopotamia) (4000 BC)Gina Ann MaderaNo ratings yet
- Handout#2 Lesson 2 MESOPOTAMIAN AND EGYPTIANDocument3 pagesHandout#2 Lesson 2 MESOPOTAMIAN AND EGYPTIANJohn Dale AmaguinNo ratings yet
- Philippines - HTML Products/covid-19-Lab-SuppliesDocument1 pagePhilippines - HTML Products/covid-19-Lab-SuppliesCherrie PedritoNo ratings yet
- Land Degradation PDFDocument4 pagesLand Degradation PDFCherrie PedritoNo ratings yet
- Baguio Museum - Home of Baguio's Cultural & Historical Heritage - Philippine PrimerDocument14 pagesBaguio Museum - Home of Baguio's Cultural & Historical Heritage - Philippine PrimerCherrie PedritoNo ratings yet
- Baguio City Market HistoryDocument4 pagesBaguio City Market HistoryCherrie PedritoNo ratings yet
- References:: 80 Inspirational Education Quotes For Students and TeachersDocument4 pagesReferences:: 80 Inspirational Education Quotes For Students and TeachersCherrie PedritoNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument2 pagesReview of Related LiteratureCherrie PedritoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2. Biodiversity and The Healthy Society PDFDocument9 pagesUnit 2. Biodiversity and The Healthy Society PDFCherrie PedritoNo ratings yet
- A Case Study Research Presented To The College of Engineering and ArchitectureDocument21 pagesA Case Study Research Presented To The College of Engineering and ArchitectureCherrie PedritoNo ratings yet
- Container VanDocument11 pagesContainer VanCherrie PedritoNo ratings yet
- Overall EWD Vehicle Exterior Rear Window DefoggerDocument1 pageOverall EWD Vehicle Exterior Rear Window Defoggergabrielzinho43No ratings yet
- Electrical LayoutDocument1 pageElectrical LayoutNiroshan JayawickramaNo ratings yet
- Guion InglésDocument3 pagesGuion InglésALNo ratings yet
- 4 Periods in Art History (Part 1)Document55 pages4 Periods in Art History (Part 1)Kiel JohnNo ratings yet
- Zerokorr - Method StatementDocument8 pagesZerokorr - Method StatementAshif AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Timeliness - The Images Have Meaning In: PhotojournalismDocument9 pagesTimeliness - The Images Have Meaning In: PhotojournalismOmar FermosoNo ratings yet
- (PaperzoneVN - Com) - SantaClaus v2Document30 pages(PaperzoneVN - Com) - SantaClaus v2John Castillo RojasNo ratings yet
- Kangaroo 3,4th Grade 2020Document6 pagesKangaroo 3,4th Grade 2020Devil InsideNo ratings yet
- EXPRESSIONISM: A Bold New Movement: Arts 10Document14 pagesEXPRESSIONISM: A Bold New Movement: Arts 10Anela KimNo ratings yet
- Blender & Z BrushDocument20 pagesBlender & Z BrushKurniawan SusiloNo ratings yet
- Wendy Cheesman FosterDocument2 pagesWendy Cheesman FosterirfanmNo ratings yet
- The Collected Home by Darryl CarterDocument23 pagesThe Collected Home by Darryl CarterCrown Publishing GroupNo ratings yet
- 20 Spaceman - Quentin TrollipDocument5 pages20 Spaceman - Quentin TrollipJuan Carlos CocaNo ratings yet
- Artists and ArtisansDocument19 pagesArtists and ArtisansKaye PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Datamodel For StudentsDocument59 pagesDatamodel For StudentshqfNo ratings yet
- The Idea of The Primary Stage in Alvar Aalto's Drawings Through The Analysis of The Design Process of "Vuoksenniska Church (1955 - 1958) "Document11 pagesThe Idea of The Primary Stage in Alvar Aalto's Drawings Through The Analysis of The Design Process of "Vuoksenniska Church (1955 - 1958) "Abreu IzaNo ratings yet
- Gawad Sa Manlilikha NG Bayan (GAMABA)Document47 pagesGawad Sa Manlilikha NG Bayan (GAMABA)Micah GalangNo ratings yet
- Baroque ArtistDocument34 pagesBaroque ArtistGenelNo ratings yet
- Fine Arts EventsDocument3 pagesFine Arts EventsMilton Mj Too CxNo ratings yet
- 2018 BuildCrete Stucco Plaster Pool Plaster Brochure 1Document2 pages2018 BuildCrete Stucco Plaster Pool Plaster Brochure 1ProvincianosNo ratings yet
- Magsaysay Ave. Karangalan Village, Manggahan Pasig CityDocument5 pagesMagsaysay Ave. Karangalan Village, Manggahan Pasig CityJamie FernandezNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Cathy Lawday Get Set Go 1 Workbook PRDocument106 pagesToaz - Info Cathy Lawday Get Set Go 1 Workbook PRАнастасия ЯковенкоNo ratings yet
- James Stirling Rakesh 29Document11 pagesJames Stirling Rakesh 29merakiNo ratings yet
- Ancient Egyptian Art: Similar Art For Over 3000 YearsDocument5 pagesAncient Egyptian Art: Similar Art For Over 3000 YearsDina HushamNo ratings yet
- Cpar 2Document96 pagesCpar 2Ruby BieNo ratings yet
- FCM - Fixed Skylight in Profiled Metal Roof - July 2023Document1 pageFCM - Fixed Skylight in Profiled Metal Roof - July 2023deanNo ratings yet