Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chap05-A 6
Chap05-A 6
Uploaded by
S M B0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
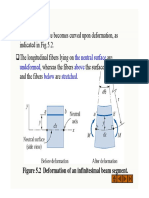
10 views1 pageThe cross sections of a beam rotate rigidly about the neutral axis, which passes through the beam's axis and is perpendicular to the plane of symmetry. The neutral axis exists for each cross section and all neutral axes combined define the neutral surface, which contains them and lies in the xz-plane.
Original Description:
a
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe cross sections of a beam rotate rigidly about the neutral axis, which passes through the beam's axis and is perpendicular to the plane of symmetry. The neutral axis exists for each cross section and all neutral axes combined define the neutral surface, which contains them and lies in the xz-plane.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageChap05-A 6
Chap05-A 6
Uploaded by
S M BThe cross sections of a beam rotate rigidly about the neutral axis, which passes through the beam's axis and is perpendicular to the plane of symmetry. The neutral axis exists for each cross section and all neutral axes combined define the neutral surface, which contains them and lies in the xz-plane.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
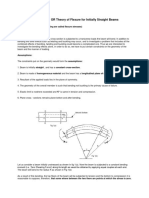
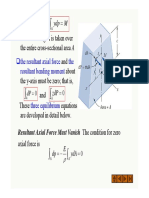
The above assumptions lead us to the following conclusion:
Each cross section of the beam rotates as a rigid entity about a
line called the neutral axis of the cross section.
The neutral axis passes through the axis of the beam and is
perpendicular to the plane of symmetry, as shown in Fig. 5.1.
The xz-plane that contains the neutral axes of all the cross
sections is known as the neutral surface of the beam.
You might also like
- Fibres: Named After The Swiss Jacob Bernoulli (1654-1705), From A Famous Family of Mathematicians and PhysicistsDocument1 pageFibres: Named After The Swiss Jacob Bernoulli (1654-1705), From A Famous Family of Mathematicians and Physicistsdruwid6No ratings yet
- Simple Bending TheoryDocument11 pagesSimple Bending TheoryAnonymous 2RduvkjgZNo ratings yet
- IC24Document7 pagesIC24DrSn PadhiNo ratings yet
- Stress in BeamsDocument48 pagesStress in BeamsPaulina Wahyu HariyaniNo ratings yet
- Shear Centre - With Examples: Curved BeamsDocument3 pagesShear Centre - With Examples: Curved BeamsAmlanNo ratings yet
- Afd Note05Document3 pagesAfd Note05zcap excelNo ratings yet
- Unsymmetrical BendingDocument12 pagesUnsymmetrical BendingDej AdmasuNo ratings yet
- LectureDocument8 pagesLectureRohit PareekNo ratings yet
- Stresses in BeamDocument13 pagesStresses in BeammaloyNo ratings yet
- Module 13 - Stresses in BeamsDocument29 pagesModule 13 - Stresses in BeamsKd CaisedoNo ratings yet
- Simple Bending1Document10 pagesSimple Bending1programmingprofessor01No ratings yet
- Affine TransformationDocument6 pagesAffine Transformationbrown222No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 (151-154)Document4 pagesChapter 11 (151-154)fitri auliaNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Beams For Bending: Chapter 5 - 5-A. Symmetric Member in Pure BendingDocument16 pagesAnalysis and Design of Beams For Bending: Chapter 5 - 5-A. Symmetric Member in Pure BendingAaron CansinoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2SOPHIA JERARINo ratings yet
- 5 Bending StressDocument23 pages5 Bending Stressmuhamadsaidi100% (1)
- زينبDocument6 pagesزينببراق احمد حسين مودرNo ratings yet
- Beam BendingDocument46 pagesBeam BendingAditya RatleyNo ratings yet
- Powder Technology, 9: EisevierDocument9 pagesPowder Technology, 9: EisevierRodolfo Morales GálvezNo ratings yet
- Arbitrary Objects: Is Identical To The Motion of The ObjectDocument2 pagesArbitrary Objects: Is Identical To The Motion of The ObjectKacou FatimNo ratings yet
- 7a System of Particles and Rotational MotionDocument39 pages7a System of Particles and Rotational Motionved tankNo ratings yet
- Vlasov Computation of Prismatic SHellsDocument53 pagesVlasov Computation of Prismatic SHellsMaliOdKužineNo ratings yet
- Articulo de ThompsonDocument3 pagesArticulo de ThompsonSalim BravoNo ratings yet
- Tugas KINEMATIC RELATIONSHIP FOR BEAMDocument8 pagesTugas KINEMATIC RELATIONSHIP FOR BEAMdhiafahheraNo ratings yet
- BendingDocument10 pagesBendinglaunchermaaitah2No ratings yet
- Bending 6.3-6.4: Longitudinal Strain Flexure FormulaDocument33 pagesBending 6.3-6.4: Longitudinal Strain Flexure FormulaPrasad GNNo ratings yet
- Lobatchewsky, The Origins of Non-Euclidean GeometriesDocument16 pagesLobatchewsky, The Origins of Non-Euclidean GeometriesGeorge Mpantes mathematics teacher100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Stresses in Beam (Basic Topics) : M Constant V DM / DX 0Document1 pageChapter 5 Stresses in Beam (Basic Topics) : M Constant V DM / DX 0Pavan KishoreNo ratings yet
- System of Practicles and Rotational MotionDocument39 pagesSystem of Practicles and Rotational MotionKashyap Patel89% (9)
- A Geometrical Background For de Sitter's World by H.S.M. CoxeterDocument13 pagesA Geometrical Background For de Sitter's World by H.S.M. CoxeterTomás CampoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Ending StressesDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 3 Ending StresseshaymanotNo ratings yet
- Physics 10th Class NotesDocument88 pagesPhysics 10th Class NotesM.Latif SajidNo ratings yet
- Wa0005.Document4 pagesWa0005.ME-6 Ganesh NerkarNo ratings yet
- Stiffness Method of Thin-Walled Beams With Closed Cross-SectionDocument13 pagesStiffness Method of Thin-Walled Beams With Closed Cross-SectionKhalil DeghoumNo ratings yet
- Bending of Curved Beams 12012020Document8 pagesBending of Curved Beams 12012020The YogiNo ratings yet
- PrismatoidsDocument6 pagesPrismatoidsmyasweet22No ratings yet
- Beams On Elastic Foundation: I. Basic ConceptsDocument1 pageBeams On Elastic Foundation: I. Basic ConceptsIt'x PathanNo ratings yet
- Beam DeflectionDocument10 pagesBeam Deflectioncarlo manabatNo ratings yet
- Figure 1 Curved Beam CurvatureDocument2 pagesFigure 1 Curved Beam CurvaturePrashannaNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Thin Plate Theory, Structural InstabilityDocument78 pagesUnit-I Thin Plate Theory, Structural InstabilityNirav LakhaniNo ratings yet
- FM Lecture 2Document8 pagesFM Lecture 2prasanna footballNo ratings yet
- Simplebending March 17 and 24Document23 pagesSimplebending March 17 and 24Tugce ZorluNo ratings yet
- CH-3 Strength of MaterialsDocument33 pagesCH-3 Strength of Materialsethiopia ethiopia100% (2)
- UNIT-3 Strength of MaterialDocument127 pagesUNIT-3 Strength of Materialakashtripathi0292No ratings yet
- Cross Section (Geometry) - WikipediaDocument5 pagesCross Section (Geometry) - Wikipediaramthecharm_46098467No ratings yet
- Space Frames: I. Basic ConceptsDocument14 pagesSpace Frames: I. Basic ConceptscurlyjockeyNo ratings yet
- Game Engine Programming 2 Week 3 Module 3Document25 pagesGame Engine Programming 2 Week 3 Module 3Dean LevyNo ratings yet
- Bending StressDocument16 pagesBending Stresspalash1401No ratings yet
- Unit-II: Bending and Shear and Torsion of Thin Walled BeamsDocument63 pagesUnit-II: Bending and Shear and Torsion of Thin Walled BeamsSwethaNo ratings yet
- Vibration 2Document68 pagesVibration 2Asong, Daniel LorenzNo ratings yet
- Bridges2021 7Document8 pagesBridges2021 7Paco TorresNo ratings yet
- flightDynamicsFullVersion PDFDocument51 pagesflightDynamicsFullVersion PDFKarthikeya SrivathsavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Strength of materialDocument25 pagesChapter 4 Strength of materialsamiasefa27No ratings yet
- Un SymmetricalDocument2 pagesUn SymmetricaljaihogoluNo ratings yet
- Flexural Stresses or Bending Stresses in Beams (Derivation of Bending Stress Equation)Document3 pagesFlexural Stresses or Bending Stresses in Beams (Derivation of Bending Stress Equation)Muhammad Jawad IsmaeelNo ratings yet
- Plane Stress and Plane StrainDocument44 pagesPlane Stress and Plane StrainManiNo ratings yet
- Robotics Kinematics and DynamicsDocument24 pagesRobotics Kinematics and Dynamicsأحمد دعبسNo ratings yet
- Neutral AxisDocument3 pagesNeutral Axishaseeb ansariNo ratings yet
- Lec 5 - BendingDocument20 pagesLec 5 - BendingWilliam LeongNo ratings yet
- Problem 7.7Document2 pagesProblem 7.7S M BNo ratings yet
- Chap05-A 9Document1 pageChap05-A 9S M BNo ratings yet
- C. Equilibrium: Da. - (E/) YDocument1 pageC. Equilibrium: Da. - (E/) YS M BNo ratings yet
- Chap05-A 7Document1 pageChap05-A 7S M BNo ratings yet
- Chap05-A 11Document1 pageChap05-A 11S M BNo ratings yet
- Because E / ρ ≠ 0, this equation can be satisfied only if (b) .Document1 page Because E / ρ ≠ 0, this equation can be satisfied only if (b) .S M BNo ratings yet
- Spring Design GuideDocument9 pagesSpring Design GuideS M BNo ratings yet
- Plane of The Symmetry: Applied Loads Perpendicular To The Beam (The X-Axis)Document1 pagePlane of The Symmetry: Applied Loads Perpendicular To The Beam (The X-Axis)S M BNo ratings yet
- The fiber form are arc a' b' of radius (ρ-y) , subtended by the angle dθ, its deformed length is The original length of this fiber is of the fiberDocument1 page The fiber form are arc a' b' of radius (ρ-y) , subtended by the angle dθ, its deformed length is The original length of this fiber is of the fiberS M BNo ratings yet
- Applied Strength of Materials - Robert L. Mott and Joseph A. Untener 6e SI 2018 SCF03Document2 pagesApplied Strength of Materials - Robert L. Mott and Joseph A. Untener 6e SI 2018 SCF03S M BNo ratings yet
- Square With Corners Uniformly Loaded: Abound RoundedDocument256 pagesSquare With Corners Uniformly Loaded: Abound RoundedS M BNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials: Stresses in BeamsDocument1 pageMechanics of Materials: Stresses in BeamsS M BNo ratings yet
- Stress-Concentration Factors For Rounded Rectangular Holes in Infinite SheetsDocument16 pagesStress-Concentration Factors For Rounded Rectangular Holes in Infinite SheetsS M BNo ratings yet
- PS8Document13 pagesPS8S M BNo ratings yet
- Determination of Minimised K Values and Boundary Shapes For A Class of Quasi-Rectangular Holes in Infinite PlatesDocument59 pagesDetermination of Minimised K Values and Boundary Shapes For A Class of Quasi-Rectangular Holes in Infinite PlatesS M BNo ratings yet
- Age 8 9 Vol1 Print Learn CenterDocument101 pagesAge 8 9 Vol1 Print Learn CenterS M BNo ratings yet
- DTMB 1959 1290 PDFDocument26 pagesDTMB 1959 1290 PDFS M BNo ratings yet
- PS9Document10 pagesPS9S M BNo ratings yet
- PS5Document9 pagesPS5S M BNo ratings yet
- DTMB 1957 1149 PDFDocument44 pagesDTMB 1957 1149 PDFS M BNo ratings yet
- DTMB 1959 1311Document34 pagesDTMB 1959 1311S M BNo ratings yet
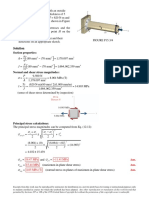
- Solution: P15.2 A Solid 19-Mm-Diameter Aluminum AlloyDocument2 pagesSolution: P15.2 A Solid 19-Mm-Diameter Aluminum AlloyS M BNo ratings yet
- Solution: L 130 Mm. Determine The Normal and Shear StressesDocument2 pagesSolution: L 130 Mm. Determine The Normal and Shear StressesS M BNo ratings yet
- Solution: P15.4 A Hollow Bronze Shaft With An OutsideDocument2 pagesSolution: P15.4 A Hollow Bronze Shaft With An OutsideS M BNo ratings yet
- Solution: P15.59 A Pressurized Pipe With An Outside Diameter of 355Document2 pagesSolution: P15.59 A Pressurized Pipe With An Outside Diameter of 355S M BNo ratings yet
- Devi StuthiDocument1 pageDevi StuthiS M BNo ratings yet
- 766 1557771239 PDFDocument14 pages766 1557771239 PDFS M BNo ratings yet
- Circle DividedDocument1 pageCircle DividedS M BNo ratings yet
- Divisions 4cdBW ModelDocument1 pageDivisions 4cdBW ModelS M BNo ratings yet
- Another Mechanical ToyDocument4 pagesAnother Mechanical ToyS M BNo ratings yet