Professional Documents
Culture Documents
James Watt PDF
James Watt PDF
Uploaded by
Divya DarshiniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
James Watt PDF
James Watt PDF
Uploaded by
Divya DarshiniCopyright:
Available Formats
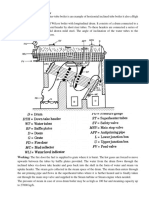
JAMES WATT - 1736 – 1819.
Born on 19 January 1736 in Greenock, Scotland, James Watt was a scientist , best known as an
inventor and mechanic rather than a theorist who, had a tremendous impact on the shape of modern
society. Watt did not invent the first steam engine, but his improvements to the design of the steam
engine turned it from a water pump for coal mines with few other applications into the source of
motive power that drove the Industrial Revolution.
James Watt didn’t make any direct contributions to the
field of electricity. He worked on steam engines. Steam
engines that existed prior to Watt’s innovations condensed
the steam in the cylinder by injecting cold water. This
created a pressure difference, driving the piston, but it
also cooled down the cylinder. Much energy was wasted
heating up the cylinder again with each cycle. Watt
realized this and solved the problem by adding
a separate condenser, external to the cylinder,
so that the cylinder could be kept hot.
This made the engine much more
efficient.
When the Watt engine was paired with Thomas Edison’s electrical generator in the late 19th century,
the generation of electricity on a large scale was possible for the first time. Soon after, the streets of
New York and other cities were illuminated with electric lamps. Many other uses for electricity were
developed in the following years, so that it has become thoroughly integrated into the daily lives of
people around the world.
Most electric power plants use steam power, so in a sense you could say that they also inherited some of
the legacy of Watt’s engine, even though the design is very different. (Instead of a reciprocating piston,
power plants use steam turbines.) The development of the steam engine and the formal study of
thermodynamics were closely linked, and an understanding of thermodynamics is essential for
designing electrical machines
During the course of his work with the steam engine, Watt developed the concept of horsepower as a
unit of power output. In honor of his work related to efficiency and power, a unit of power in the
International System of Units (SI) commonly used for both electricity and mechanics, the watt (equal to
one joule of work performed per second (or 1/746 horsepower)), seen in the context of electricity was
named after him.
DIVYA DARSHINI A- 1RW18AT035
SANJANA RAO -1RW18AT098
You might also like
- Wind Turbine Project ReportDocument19 pagesWind Turbine Project ReportMuaz Fabregas100% (2)
- PowerDocument2 pagesPowerraymond baliteNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument5 pagesINTRODUCTIONAkrfwNo ratings yet
- DC and AcDocument3 pagesDC and Acshyamu rathoreNo ratings yet
- The First Commutator DC Electric Motor Capable of Turning Machinery Was Invented by The British Scientist William Sturgeon in 1832Document2 pagesThe First Commutator DC Electric Motor Capable of Turning Machinery Was Invented by The British Scientist William Sturgeon in 1832mbajlo00No ratings yet
- Vaclav Smil - Energy Transitions - History, Requirements, Prospects (2010) (001-100) (051-100)Document50 pagesVaclav Smil - Energy Transitions - History, Requirements, Prospects (2010) (001-100) (051-100)Alonso TobonNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor - HistoryDocument5 pagesElectric Motor - HistoryNiel BrianNo ratings yet
- Electric MotorDocument20 pagesElectric MotorAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Jacob S. Gibbs Brinsley ColeberdDocument6 pagesJacob S. Gibbs Brinsley Coleberdjolly antNo ratings yet
- History of The Steam Engine ReadingDocument5 pagesHistory of The Steam Engine ReadingGiang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Steam EngineDocument2 pagesSteam EnginemartaNo ratings yet
- For Other Kinds of Motors, See - For A Railroad Electric Engine, SeeDocument6 pagesFor Other Kinds of Motors, See - For A Railroad Electric Engine, SeeSubramanian SakthivelNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument25 pagesSeminar ReportYogesh RathiNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy TechnologyDocument31 pagesWind Energy TechnologyAjay VermaNo ratings yet
- British Culture and Civilisation Project - James Watt and The Steam EngineDocument5 pagesBritish Culture and Civilisation Project - James Watt and The Steam EngineAlexandru OrghiciNo ratings yet
- How HVAC&R Changed The WorldDocument10 pagesHow HVAC&R Changed The WorldNguyễn Thành NamNo ratings yet
- Steam Engine: "Steam Machine" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, See - For The Railway Engine, SeeDocument2 pagesSteam Engine: "Steam Machine" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, See - For The Railway Engine, SeedabdfbiNo ratings yet
- Electric MotorDocument25 pagesElectric Motorstevensteeler083No ratings yet
- Steam Turbine - Wikipedia PDFDocument62 pagesSteam Turbine - Wikipedia PDFMohit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Advances in Wind EnergyDocument66 pagesAdvances in Wind EnergyArshadali Ansari100% (2)
- Electric Motor: Cleanup Quality StandardsDocument20 pagesElectric Motor: Cleanup Quality StandardsAmruthesh_Hp_2617No ratings yet
- Electric Motor Wikipedia PDFDocument138 pagesElectric Motor Wikipedia PDFHoppohigdi786 Hoppohigdi786No ratings yet
- Wind TurbineDocument12 pagesWind TurbineDhesa HidayatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 . . . .1Document18 pagesChapter 01 . . . .1Kapeel KumarNo ratings yet
- The Current WarDocument13 pagesThe Current WarKhaled TamerNo ratings yet
- Wind TurbineDocument18 pagesWind TurbineDinesh Inavolu50% (2)
- DynamoDocument28 pagesDynamoChris McLean0% (1)
- Wind CompilationDocument31 pagesWind CompilationMohd. Mustakim Bin Ahmad OthmanNo ratings yet
- History of The Steam EngineDocument3 pagesHistory of The Steam Engineakmo alimbayNo ratings yet
- TeslaDocument3 pagesTeslaKESH MusicNo ratings yet
- Teslaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa PDFDocument3 pagesTeslaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa PDFKESH MusicNo ratings yet
- Reading PracticeDocument3 pagesReading PracticeHueyjieeeNo ratings yet
- Invention of The Ac MotorDocument3 pagesInvention of The Ac MotorAlonso FloresNo ratings yet
- Turbo Electric GeneratorsDocument3 pagesTurbo Electric GeneratorsKripakar Kalavagunta100% (2)
- ScibdDocument8 pagesScibdPascu IonutNo ratings yet
- Electric MotorDocument30 pagesElectric MotorBob100% (1)
- Abigail Flores Activity 1Document1 pageAbigail Flores Activity 1Angela Abigail Flores CambiNo ratings yet
- Franklin Institute Museum: A. C. Carlton, Executive Director J A M E S WATT (1736-1819)Document2 pagesFranklin Institute Museum: A. C. Carlton, Executive Director J A M E S WATT (1736-1819)cassandraNo ratings yet
- James WattDocument5 pagesJames WattweldharishNo ratings yet
- Wind TurbineDocument3 pagesWind TurbineKhelidja DhmNo ratings yet
- Looking Back To Electric Cars: September 2012Document7 pagesLooking Back To Electric Cars: September 2012UnknownNo ratings yet
- Vertical Axis Wind Turbine - A StudyDocument14 pagesVertical Axis Wind Turbine - A Studystealth376No ratings yet
- Electric MotorDocument25 pagesElectric MotorKulwant SinghNo ratings yet
- Engineering 130Document11 pagesEngineering 130dean_mahdiNo ratings yet
- Engine - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument12 pagesEngine - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShumway GordonNo ratings yet
- History: Dynamos and Engine Installed at Edison General Electric Company, New York 1895Document4 pagesHistory: Dynamos and Engine Installed at Edison General Electric Company, New York 1895mrjunoonNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor - Test ADocument29 pagesElectric Motor - Test AJemeraldNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesElectric Motor - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediad_richard_dNo ratings yet
- Tong - Quat LânDocument6 pagesTong - Quat LânQuốc HuyNo ratings yet
- Essay Power ElectronicDocument15 pagesEssay Power Electronicmutun66No ratings yet
- DynamoDocument7 pagesDynamoArun PrabakaranNo ratings yet
- Wind TurbineDocument24 pagesWind TurbinerjiyfrauefaboovyohNo ratings yet
- EE527ASSIGNMENTNO.1 - JalandoniDocument13 pagesEE527ASSIGNMENTNO.1 - JalandoniElrich Joseph JalandoniNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument14 pagesSteam Turbinemivano100% (2)
- Steam Engine Project ReportDocument47 pagesSteam Engine Project Reportpurushottamdeshpande113No ratings yet
- Guarnieri 2011Document2 pagesGuarnieri 2011Marcos Fortaleza de Sousa SilvaNo ratings yet
- James Watt ProjectDocument11 pagesJames Watt ProjectOmarDeebNo ratings yet
- Project On Savonious Wind Turbine (L.C.I.T BhanduDocument33 pagesProject On Savonious Wind Turbine (L.C.I.T Bhandupatel ketanNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet FC SIDocument2 pagesData Sheet FC SIAndrea AtzeniNo ratings yet
- AEE311L Experiment 7 8Document8 pagesAEE311L Experiment 7 8Fe BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Philippine Agricultural Engineering Standard Paes 117: 2000 Agricultural Machinery - Small Engine - Methods of TestDocument16 pagesPhilippine Agricultural Engineering Standard Paes 117: 2000 Agricultural Machinery - Small Engine - Methods of TestJerard BalalaNo ratings yet
- 04 - SONAR 5K WPV GuidanceDocument22 pages04 - SONAR 5K WPV Guidancetran vinhNo ratings yet
- 1MRG008027 - Review of IED670 Configuration Developed by ABB India - 05Document29 pages1MRG008027 - Review of IED670 Configuration Developed by ABB India - 05Jayam kondanNo ratings yet
- Analysis On Bidirectional Interactive Electric Vehicles Operation Modes Vehicle-To-Grid (V2G) and Gridto-Vehicle (G2V) Variations Within Smart GridDocument26 pagesAnalysis On Bidirectional Interactive Electric Vehicles Operation Modes Vehicle-To-Grid (V2G) and Gridto-Vehicle (G2V) Variations Within Smart Gridsuman shahNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission in Pakistan and LossesDocument11 pagesPower Transmission in Pakistan and LossesWASIF KHANNo ratings yet
- WATER TUBE BOILER and Fire Tube BoilerDocument3 pagesWATER TUBE BOILER and Fire Tube Boilerashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- CB Test CertificateDocument2 pagesCB Test Certificatedgatos dgatosNo ratings yet
- Sample Calculations of Boiler Pumps and IDDocument5 pagesSample Calculations of Boiler Pumps and IDMelvinDapitanonNo ratings yet
- Allen Bradley 700 Td552 - en PDocument6 pagesAllen Bradley 700 Td552 - en PsayedNo ratings yet
- Enron Wınd: Specifications - Enron Wind 750i KW SeriesDocument4 pagesEnron Wınd: Specifications - Enron Wind 750i KW SeriesAkash RockNo ratings yet
- Sample - Solution Power Electronics Original Daniel HartDocument8 pagesSample - Solution Power Electronics Original Daniel HartAdel HabibiNo ratings yet
- Electric Traction: LocomotionDocument29 pagesElectric Traction: LocomotionRaja SekaranNo ratings yet
- User Manual of The TENMA 72-7245 PDFDocument15 pagesUser Manual of The TENMA 72-7245 PDFHashan PereraNo ratings yet
- 60 AnalysingDocument8 pages60 AnalysingscribsunilNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase TransfomersDocument10 pagesThree-Phase TransfomersAhmad AbunassarNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics (1) - ELE221: DR./ Abdelhady GhanemDocument13 pagesPower Electronics (1) - ELE221: DR./ Abdelhady GhanemAhmad Ash SharkawiNo ratings yet
- Chain Test RigDocument6 pagesChain Test RigService MMINo ratings yet
- Generator Automatic Voltage Regulator Operation ManualDocument9 pagesGenerator Automatic Voltage Regulator Operation Manualsabrahima100% (1)
- AG Akım Gerilim TRFDocument12 pagesAG Akım Gerilim TRFkgskgmNo ratings yet
- Ee8401 - em Ii - Question Bank - Unit2Document4 pagesEe8401 - em Ii - Question Bank - Unit2DEVINo ratings yet
- Overview of Multi MW Wind Turbines and Wind ParksDocument15 pagesOverview of Multi MW Wind Turbines and Wind ParksGanesh SuraboinaNo ratings yet
- Yc1-16024-Tr Set Ga-Rev-01Document6 pagesYc1-16024-Tr Set Ga-Rev-01VirgilioNo ratings yet
- IUIa GiV EnglDocument3 pagesIUIa GiV EnglJavierNo ratings yet
- Syntron Price List Wef 9TH Aug 2012Document2 pagesSyntron Price List Wef 9TH Aug 2012saurabhjerps231221No ratings yet
- Fairchild Display Power SolutionDocument58 pagesFairchild Display Power SolutionFrancisco Antonio100% (1)
- Liebert High Efficiency Modes of Operation WP en Emea VertivDocument14 pagesLiebert High Efficiency Modes of Operation WP en Emea VertivThe Quan BuiNo ratings yet
- AccuSine Selection ToolDocument34 pagesAccuSine Selection ToolMohamed SamyNo ratings yet