Professional Documents
Culture Documents
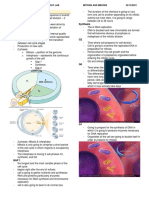
Union of Egg and Sperm Cell in The Fallopian Tube, Producing A Zygote (The First Cell of The New Offspring)
Union of Egg and Sperm Cell in The Fallopian Tube, Producing A Zygote (The First Cell of The New Offspring)
Uploaded by
AIMEE MARGARET FLORESOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Union of Egg and Sperm Cell in The Fallopian Tube, Producing A Zygote (The First Cell of The New Offspring)
Union of Egg and Sperm Cell in The Fallopian Tube, Producing A Zygote (The First Cell of The New Offspring)
Uploaded by
AIMEE MARGARET FLORESCopyright:
Available Formats
oxygen pressurizes the cell making it enucleated - apoptosis - cell suicide/programmed death
bio longtest #2 no oxygen = death 1. genetic mutation- occurs when cells don’t divide
cell modification, mitosis, meiosis absence of nucleus: 2. sunburn- to avoid cancer
- adaptation of the red blood cell 3. embryo webbing- formation and structure of our hands and feet
cell modification - allows the red blood cell to contain more hemoglobin 4. nerve cells- if they won’t die, they may cause epilepsy
- carry more oxygen molecules
cilia flagella microvilli - distinctive bi-concave shape which aids in diffusion - capases - enzymes; disintegration and digestion of worn out cells
- projects from the - 1 per cell - extension of the cell cycle and cell division * random mutation
surface of the cell cell membrane that * replication - is a must before cell division - foundation of evolution
- composed of are supported by - each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic ** DNA - double helix; identity, genomes
microtubules which microfilaments information ** RNA - single helix; sequence of protein, uracil is found here
are in the cell - abundant on the - if DNA is not replicated, meiosis & mitosis would slowly halve
membrane surface of cell the size of the genome until each cell would die
- transports mucus ** absorption - * most important cycle for growth and reproduction
(WBC) in which dust important function * cancer - unregulated cell division dna replication precedes cell division
particles are -> intestines ** Walther Flemming- used dye to identify DNA/nucleus cell division:
embedded upward - duplication of DNA
and away reproduction growth & tissue renewal - distribution of identical genetic material
development - allocation of 2 copies to opposite ends of the cell
- splits into 2 cells
form fits its functions: - an amoeba, a - fertilized egg - cells will give rise to
* e.g: tail (balance), hair (warmth) single-celled divided forming 2 new blood cells genome:
organism, is dividing cells - it becomes a protein - consists of all the cell’s genetic material
anatomy study of parts and structures of organisms
into 2 cells ** necrosis - death when it dies - cookbook containing recipes
- each new cell will of a cell caused by - bacteria have a - consists of one or more chromosomes
physiolog the way in which a living organism or bodily part be an indiv organism an injury circular DNA
y functions
** bacteria - 99.9% lang palagi yung mga panglinis somatic cells germ cells
- 1% - resistance of the bacteria itself + all bacteria have a circular DNA,
tissue specialized cell that have similar structure and same
therefore, can facilitate horizontal gene transfer - body cells - responsible for reproduction
function
- SEX PILUS - conjugative pill for the transfer of DNA between bacteria, in
the process of bacterial cojugation.
organs interaction, they do not interfere with another’s organ’s -> they allow for the exchange of genes via the formation of mating pairs
function - amoxicillin (antibiotic) - pag-ininom na ito, magkakaroon ng sex pilus so chromatin chromatid
** helping each other next time hindi na siya masyadong makakaffect kaya magtatake ka ng
new meds - found in the nuclear pore - condensed chromosome
- resting state of - bago mag divide
arrangement of layers
* HOW DO CELL KEEP THEIR IDENTITY? chromosomes * ase- enzyme
squamous cuboidal columnar - they have DNA; new cells get a complete set of DNA molecule - unwound * ose- sugar
- cell's DNA & associated
* structure of the DNA proteins
- flat, no storage - square - pillar-like - nucleases - nitrogen-based (nitrogenous bases)
- diffusion - high to - secrets and - secretes, absorbs, - nucleotide - building blocks of the DNA and RNA
low (solutes) absorbs water sweeps ** DNA - double helix
- osmosis - low to - nephron - gastrointestinal tract centromere chromosomes
high (water) (kidney) - stomach secretes * regeneration
** location: blood ** location: (HCL) - because of the cell cycle - small section of - individual molecules of DNA with their
cells, alveoli, kidney tubules, ** location: digestive - eg. lizards can regenerate when they’re cut DNA and associated proteins
lymphatic vessels, small glands, tract line, gallbladder and associated proteins - has genetic codes
lining of the heart ovary surface excretory glands, small that attaches the ** first 22 pairs of chromosomes- autosomes
bronchi, respiratory tract, sister chromatids to * xx- female
nephron mitosis meiosis each other * xy- male
- same - specialized type of cell division that gives rises to
* bakit mas maraming babae?
stratified squamous - protection areas prone to genetic nuclei that are genetically different from one another
- the female organ is acidic
abrasion make-up - new organism
2 types of sperms :
** location: esophagus lining, - growth, - combination of gametes (sperm & egg)
1. slow but big & strong - usually female/ x
epidermis, vagina, anus, mouth development - fertilization
2. Fast but small & weak- - usually male/ y
and repair * can be fertilized by 2 sperm cells pero it will die
stratified cuboidal - protection; secretion GAMETES: sperm & egg ; produced by germ cells
** location: urinary bladder, * fertilization
urethra - union of egg and sperm cell in the fallopian tube, producing a zygote (the first cell of HISTONES: proteins, DNA tightly coiled around this
the new offspring)
stratified columnar - protection DNA: double helix composing nucleotides
** location: largest glands, cell death is a part of life
sweat, mammary, salivary glands - trisomy 21 - down syndrome ; extra chromosome HELICASES: unzips the double-stranded DNA into single strands
- cell production = cell death allowing each strand to be copied
** ** if puro production lang, growth of tumor
RBC : no nucleus to give way to hemoglobin (carries oxygen)
DNA POLYMERASE: creates complimentary DNA, makes a partner for S-evere weight loss
helices
cells # of germ cells gametes
meiosis chromosomes
LIGASE: form covalent bonds between adjacent DNA segments - cell cycle by which we create an egg cell and a sperm cell (gametes)
- proofreads, discarding mismatched nucleotides and inserting correct - n = set = 23 single chromosomes
ones - haploid = n = egg & sperm cell somatic cells 46 single spermatogoniu sperm = 23
- diploid = 2n = 1 set each from mama & papa = forms zygote diploid 23 pairs m single
MUTATION: change in a cell’s DNA structure, happens because of a - sexual reproduction 23 pairs = 46
mistake in cell’s DNA sequence - creates an entirely different cell = new organism egg = 23
single
TELOMERE: sequence of genes, codes found at the end of our goal:
chromosomes - reduction - from 46 to 23 single chromosomes (IMPORTANT) zygote 46 pairs oogonium diploid ; 2n=46
- as we grow older, telomeres at the end of our chromosomes shrink - genetic variation - no 2 persons are exactly the same diploid 23 pairs 23 pairs = 46 haploid ; n=23
- major depression- shorter telomeres; accelerated aging - production of gametes
/ - creates 4 haploid cells
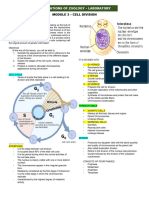
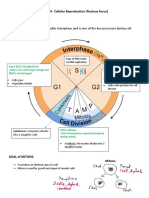
mitosis ** SUMMARY * plasma membrane
3 PHASES OF THE CELL CYCLE - meiosis consists of 2 divisions, which introduces variation and reduce - outermost part of the cell
1. interphase number of chromosomes in daughter cells - protection of the cell
- errors during mitosis may result in offsprings with abnormal number of - transport substances in and out of the cell
G1 S G2 chromosomes
* selective permeability
- cell grows - enzymes replicate the cell’s - cell grows more ** CELLS - plasma membrane is selective of substance that come in and out of the
physically genetic material and repair but also prepares 1. somatic cells (diploid) cell
larger, copies damage DNA to divide - everything inside our body
organelles, and - duplicates centrosome - produces - 23 pairs of chromosomes * protein
makes the (microtubule-organizing proteins that will - code of the cell
molecular center) help coordinate 2. zygote (diploid) - major component of our body
building blocks - centrosomes help separate mitosis - 23 pairs of chromosomes - eg. nails and hair - keratin
it will need in the DNA during mitotic - reorganize its - mRNA - through the rough endoplasmic reticulum, the golgi bodies
later steps phase (mitosis and contents for 3. germ cells transport substances outside the body
- checkpoint cytokinesis) mitosis - diploid cells that would perform meiosis to form gametes - these are also embedded to the plasma membrane
for damaged ** at the end: each - check point - germinate - grow
DNA chromosome consists of 2 - 4-6 hours, most
- 5-6 hours, attached sister chromatids active ** spermatogonium
most active - 10-12 hours, most - found in testes
important - 23 pairs of chromosomes
- will undergo spermatogenesis in meiosis to form 4 sperm cells
S PHASE (animal cell): duplication of the centrosome **oogonium
- centrosomes- structures that organize the mitotic spindle - found in ov ry
- spindle- set of microtubule proteins that coordinate the movements of the - 23 pairs of chromosomes
chromosomes during mitosis - will undergo oogenesis in meiosis to form 1 egg cell because the 3
** plant cells: lack centrosomes; they organize their spindle fibers becomes polar bodies kasi they don’t have the right ingredients to form an
throughout the cell egg cell
checkpoints: 4.gametes (haploid = 23 single chromosomes)
G!: apoptosis can occur if DNA is damaged beyond repair - sperm cells
S: - - egg cells
G2: mitosis will not occur until DNA has replicated
M: mitosis stops until chromosomes are properly aligned COMPARISON OF DIVISIONS
G0: resting face (nerve/brain cells)
mitosis meiosis
** cancer
- metastasis - spread of cancer # of divisions 1 2
** tumor
1. malignant - restless, mabilis # of daughter cells 2 4
2. benign - mabagal lumaki
genetically identical yes no
** risk factors: environment, lifestyle, family
7 warning signs (prolonged and painful) chromosome # same as parent 2n half as parent n
C-hange in bowel/bladder habits
A-sore that doesn't heal
U-nusual/prolonged bleeding where somatic cells germ cells
T-hickness/lump elsewhere
I-ndigestion/difficulty swallowing when throughout life sexual maturity
O-bvious change in warts/moles
N-agging cough
role growth & repair sexual reproduction
U-nexplained anemia
You might also like
- BIOB10 Full Study Guide PDFDocument121 pagesBIOB10 Full Study Guide PDFnadaNo ratings yet
- M2-L2-Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument2 pagesM2-L2-Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionAira Estandian GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Meiosis GIZMODocument9 pagesMeiosis GIZMOYeet ThisbichemptyNo ratings yet
- Strawberry Dna Lab and Analysis QuestionsDocument5 pagesStrawberry Dna Lab and Analysis Questionsapi-354423730No ratings yet
- Bio11 Campbell Chapter 12Document4 pagesBio11 Campbell Chapter 12ChristineNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet Bio L2Document7 pagesFact Sheet Bio L2Jodi Kryztel JosolNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics - Lesson 4 - Mitosis - MeiosisDocument11 pagesCytogenetics - Lesson 4 - Mitosis - MeiosisAli TaguibaoNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesCell DivisionMEDRANO, Hana Jhiemyka O.No ratings yet
- General Biology - Cell ReproductionDocument5 pagesGeneral Biology - Cell Reproductionlol okNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle & Cell Division: Has One Centromere and Two ChromatidsDocument4 pagesThe Cell Cycle & Cell Division: Has One Centromere and Two ChromatidsMnemo SyneNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For General Biology (Mitosis, Meiosis, Etc.) : Grade 11 STEMDocument20 pagesReviewer For General Biology (Mitosis, Meiosis, Etc.) : Grade 11 STEMYanni SerenoNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method: Fransisco RediDocument9 pagesScientific Method: Fransisco RediEduardo ZaldivarNo ratings yet
- Gzoo Prelim ReviewerDocument14 pagesGzoo Prelim Reviewermerry joy gadgudeNo ratings yet
- GEN. ZOO (Midterms)Document8 pagesGEN. ZOO (Midterms)mimiNo ratings yet
- General Biology (2nd Quarter Reviewer)Document18 pagesGeneral Biology (2nd Quarter Reviewer)Kimberly DalagNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Basic Biology Lyst7818Document34 pagesLesson 2 - Basic Biology Lyst7818sudhansusharma74No ratings yet
- Cell BIOLOGYDocument4 pagesCell BIOLOGYAria Moon100% (1)
- 3 Cell Populations Static-It Does Not Undergo Dna SynthesisDocument4 pages3 Cell Populations Static-It Does Not Undergo Dna SynthesisZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- 3 Cell Populations Static-It Does Not Undergo Dna SynthesisDocument4 pages3 Cell Populations Static-It Does Not Undergo Dna SynthesisZHIARA MAE FACUNNo ratings yet
- Lecture/Week 2/ Pre-Recorded Lecture BasedDocument6 pagesLecture/Week 2/ Pre-Recorded Lecture Basedmaria apolonia vergaraNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument3 pagesCell Cycle and MitosisalxndrasenalesNo ratings yet
- Chromosome: - To Efficiently Package DNA Into Smaller Volumes ToDocument10 pagesChromosome: - To Efficiently Package DNA Into Smaller Volumes ToCarmela Cordon FelixNo ratings yet
- Word CycleDocument3 pagesWord CycleNday GwapaKUNONo ratings yet
- Biology Periodic ReviewerDocument6 pagesBiology Periodic ReviewerLanz NicoleiNo ratings yet
- General Biology Reviewer 2nd QRTRDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology Reviewer 2nd QRTRAlfer JaoNo ratings yet
- Semi-Finals Science 08Document9 pagesSemi-Finals Science 08rr.qtieeNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviewerDocument2 pagesBio ReviewerA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Biology (Mitosis Cell Division)Document3 pagesBiology (Mitosis Cell Division)Harry ParconNo ratings yet
- Biology (Mitosis Cell Division)Document3 pagesBiology (Mitosis Cell Division)Harry ParconNo ratings yet
- CELL ORGANELLES-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesCELL ORGANELLES-WPS OfficePaul TormonNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument8 pagesMitosisMilongy JavierNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division22-50863No ratings yet
- The Cell:: Fundamental Medical Science 1 CytologyDocument16 pagesThe Cell:: Fundamental Medical Science 1 CytologyezebelluciNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle: Histology Lab Mitosis and Meiosis 02/10/2021Document8 pagesCell Cycle: Histology Lab Mitosis and Meiosis 02/10/2021Danielle Anne Zamora-Matillosa LambanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Cell DivisionDocument9 pagesLecture 3 Cell DivisionSalim HudheifaNo ratings yet
- Year 1 Biology: Chapter 2 Revision: State The Cell TheoryDocument16 pagesYear 1 Biology: Chapter 2 Revision: State The Cell TheoryOlivia YinNo ratings yet
- Foz Lab M3Document7 pagesFoz Lab M3jsbitsoflyfNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio-1st Sem (Darlene Palanca 11sf-Stem)Document20 pagesGen Bio-1st Sem (Darlene Palanca 11sf-Stem)dcp.marie98No ratings yet
- Foz Lec M3Document9 pagesFoz Lec M3jsbitsoflyfNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Topic 3Document4 pagesAnaphy Topic 3RAYNE CHLOIE LASTANo ratings yet
- C MitosisDocument3 pagesC Mitosisapi-606777952No ratings yet
- Pro Bef Ore Karyotic Nucleus: BloodDocument5 pagesPro Bef Ore Karyotic Nucleus: BloodDanielle Anne Zamora-Matillosa LambanNo ratings yet
- Mitotic Cell Cycle + InheritanceDocument11 pagesMitotic Cell Cycle + InheritanceNezza WidarkoNo ratings yet
- Bio C6 NotesDocument13 pagesBio C6 NotesTHEN YUE PINGNo ratings yet
- To Appreciate The Animations and Explanations, PLS. Download As A Power Point. ThanksDocument34 pagesTo Appreciate The Animations and Explanations, PLS. Download As A Power Point. ThanksPawpaw Chan0% (1)
- The Cell: Exercise 2Document5 pagesThe Cell: Exercise 2Jasmine Nicole EnriquezNo ratings yet
- 1st Summative Exam - General BiologyDocument12 pages1st Summative Exam - General BiologyAgatha AquinoNo ratings yet
- Biology CellsDocument7 pagesBiology Cellsperaltasabina70No ratings yet
- Ana CellsDocument4 pagesAna CellsDCRUZNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument10 pagesCell StructureririNo ratings yet
- CELL OVERVIEW PREVENTION Notes 2015Document7 pagesCELL OVERVIEW PREVENTION Notes 2015Alexander LukashenkoNo ratings yet
- BIOL-1110 - Unit 3 - Study GuideDocument3 pagesBIOL-1110 - Unit 3 - Study GuideOmarNo ratings yet
- Biology F4C6 WatermarkDocument9 pagesBiology F4C6 Watermarkpitopi7277No ratings yet
- Bio Rev 2Document3 pagesBio Rev 2mailforprinting101No ratings yet
- Bio CH 9 Study GuideDocument3 pagesBio CH 9 Study Guidelunarkat2027No ratings yet
- Cell DivisonsDocument2 pagesCell DivisonsharlyNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Cell Growth, Division and ReproductionDocument6 pages10.1 Cell Growth, Division and ReproductionJJNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesBiology ReviewerLycaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Mitosis and MeiosisDocument19 pagesUnit 2 Mitosis and MeiosisErnest TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Genetic Control of Systems, Cell Cycle and FunctionsDocument5 pagesGenetic Control of Systems, Cell Cycle and Functionsangeltheegg123No ratings yet
- Gene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyFrom EverandGene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Naoba BiologyDocument11 pagesNaoba BiologyCEO IMPHAL SMARTCITYNo ratings yet
- Biology Practicals PDFDocument23 pagesBiology Practicals PDFLalitha SrinuNo ratings yet
- CytogeneticsDocument9 pagesCytogeneticsnaiktariq00No ratings yet
- CH 45 MeiosisDocument17 pagesCH 45 MeiosiserichaasNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division-1Document35 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division-1shaikh mohammadNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Scientific SelfDocument8 pagesMODULE 2 Scientific SelfAsh FellNo ratings yet
- Ebook Human Genetics PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Human Genetics PDF Full Chapter PDFallen.elliott147100% (38)
- Genetics: Analysis of Genes and Genomes, Ninth Edition: Includes Navigate 2 Advantage AccessDocument7 pagesGenetics: Analysis of Genes and Genomes, Ninth Edition: Includes Navigate 2 Advantage AccessVims BatchNo ratings yet
- MudicraouioDocument44 pagesMudicraouioSunita KumarNo ratings yet
- Santrock Powerpoint Chapter 2Document32 pagesSantrock Powerpoint Chapter 2shaigest100% (1)
- (Series in Positive Psychology.) Pluess, Michael - Genetics of Psychological Well-Being - The Role of Heritability and Genetics in Positive Psychology-Oxford UniveDocument317 pages(Series in Positive Psychology.) Pluess, Michael - Genetics of Psychological Well-Being - The Role of Heritability and Genetics in Positive Psychology-Oxford UniveLaura Quintero100% (1)
- Igenetics Pearson New International Edition A Molecular Approach Ebook PDFDocument41 pagesIgenetics Pearson New International Edition A Molecular Approach Ebook PDFkathleen.watts301100% (41)
- Module 11Document64 pagesModule 11Andrew Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology and HSB Cell Divsion NotesDocument10 pagesCSEC Biology and HSB Cell Divsion NotesAnasha Éttienne-Taylor100% (2)
- Mitosis MeiosisDocument10 pagesMitosis MeiosisGurpreet NuriNo ratings yet
- 07 Chapter 1Document144 pages07 Chapter 1anon_315634141No ratings yet
- Meiosis Worksheet 13 KeyDocument2 pagesMeiosis Worksheet 13 KeyFarhan Pranadarmesta Merch100% (1)
- K-2813 (Life Science) (Paper-II)Document8 pagesK-2813 (Life Science) (Paper-II)Mehedi HossainNo ratings yet
- B.SC., 2 Year, 3 Semester Paper-III: Cell Biology, Genetics and Immunology Cell DivisionDocument24 pagesB.SC., 2 Year, 3 Semester Paper-III: Cell Biology, Genetics and Immunology Cell DivisionLAZY I LEoPARDNo ratings yet
- Report of Biological Practical LessonDocument118 pagesReport of Biological Practical Lessonpmm23d177No ratings yet
- What Is A Gene - Genetics Home ReferenceDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Gene - Genetics Home ReferenceAmit KaushikNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Vs Meiosis Card SortDocument2 pagesMitosis Vs Meiosis Card SortLisa MillardNo ratings yet
- Mutation: Prof. Harshraj. S. Shinde K. K. Wagh College of Agril. Biotech, Nashik. IndiaDocument24 pagesMutation: Prof. Harshraj. S. Shinde K. K. Wagh College of Agril. Biotech, Nashik. IndiaMonika shankarNo ratings yet
- q4wk1 Grade 8 ScienceDocument8 pagesq4wk1 Grade 8 ScienceRoxanne QuebadaNo ratings yet
- Bio 123 Qa PHG SPM 09-1Document105 pagesBio 123 Qa PHG SPM 09-1Masitah AmzalNo ratings yet
- Question Bank IX CH-5 CELL - THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFEDocument18 pagesQuestion Bank IX CH-5 CELL - THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFENoel MammenNo ratings yet
- Genome Organization in ProkaryotesDocument8 pagesGenome Organization in ProkaryotesVijay Kishore75% (4)
- CUCET 2020 Model Paper UG PDFDocument11 pagesCUCET 2020 Model Paper UG PDFsonu peterNo ratings yet