Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answers
Answers
Uploaded by
Priya KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (350)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Core Practical 13a and 13b RevisionDocument15 pagesCore Practical 13a and 13b RevisionPriya KumarNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Biology B - Paper 1 (9BI0 - 01)Document40 pagesBiology B - Paper 1 (9BI0 - 01)Priya Kumar100% (1)
- The Crimean War & The Charge of The Light Brigade: History & FilmDocument6 pagesThe Crimean War & The Charge of The Light Brigade: History & FilmPriya KumarNo ratings yet
- Jury AttentionDocument2 pagesJury AttentionPriya KumarNo ratings yet
- 2007 (Slightly Adapted) Prose Composition: Suggested AnswerDocument3 pages2007 (Slightly Adapted) Prose Composition: Suggested AnswerPriya KumarNo ratings yet
- News Article Analysis WorksheetDocument2 pagesNews Article Analysis WorksheetPriya KumarNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE: Monday 23 January 2012 Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesDocument6 pagesEdexcel GCE: Monday 23 January 2012 Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesPriya KumarNo ratings yet
- VCE Chemistry Study Design - Units 1 and 2 Sample Assessment Tasks 2007-2014Document8 pagesVCE Chemistry Study Design - Units 1 and 2 Sample Assessment Tasks 2007-2014Priya KumarNo ratings yet
- Book 10 - Thematic NotesDocument28 pagesBook 10 - Thematic NotesPriya KumarNo ratings yet
- Milone To What Extent Does Clodius Fit This Description?: Mad, Bad and Dangerous To Know'. From Your Reading of ProDocument2 pagesMilone To What Extent Does Clodius Fit This Description?: Mad, Bad and Dangerous To Know'. From Your Reading of ProPriya KumarNo ratings yet
- Microscope Workshop - Calibrating An Eye Piece GraticuleDocument3 pagesMicroscope Workshop - Calibrating An Eye Piece GraticulePriya KumarNo ratings yet
- ES&S Ecology (Topic 2) Question Set #1 Name(s) - 1Document3 pagesES&S Ecology (Topic 2) Question Set #1 Name(s) - 1Priya KumarNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 RespirationDocument11 pagesTopic 5 RespirationPriya Kumar100% (1)
- Haemoglobin: Partial Pressure of OxygenDocument3 pagesHaemoglobin: Partial Pressure of OxygenPriya KumarNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Halogens (As Aqueous Solutions)Document4 pagesReactions of Halogens (As Aqueous Solutions)Priya KumarNo ratings yet
Answers
Answers
Uploaded by
Priya KumarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answers
Answers
Uploaded by
Priya KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Answers:
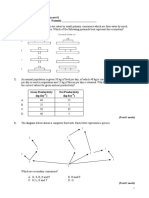
1) 47- Lower Right Molar/ Mandibular Third Molar
26- Upper Left Molar/ Maxillary First Molar
15- Upper Right Premolar/ Maxillary Second Premolar
2) (i) A - Chewing/ biting down on his cheeks
(ii) A - As a result of chewing his cheeks, the body reacts to this trauma by producing keratin
cells, which forms a protective coating on the cheeks. This layer of keratin forms a hard patch
on the cheeks with the aim of protecting the soft tissues in that area. This process is known as
hyperkeratosis.
3)(i) Streptococcus mutans. Its spherical or round in shape
(ii) Gram positive.
(iii) Gram staining is the process which separates bacteria into two groups, gram positive and
gram negative bacteria. The procedure includes several steps:
1-fixation of the bacterial cells by heating or using methanol.
2-application of primary stains (crystal violet) staining all cells blue/purple.
3-application of mordat (iodine solution) cells still appear blue/purple.
4-decolorization (extraction of blue dye) by using alcohol or acetone, this distinguishes gram
negative bacteria (appears colourless) and gram positive bacteria (appears blue).
5-application of counter stain (safranin) its red dye stains gram negative bacteria red/pink.
4(i) Lidocaine is used as a local anaesthetic
(ii) Lidocaine stops nerve conduction by blocking the Na+ channels so Na+ cant enter the cell
and thus no action potential can travel to brain to record pain.
(iii) He wanted to wait for the lidocaine to take full effect as there are many different nerves in
the oral cavity. Some are myelinated and some are not be thus the speed of impulse
transmission may differ.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (350)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Core Practical 13a and 13b RevisionDocument15 pagesCore Practical 13a and 13b RevisionPriya KumarNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Biology B - Paper 1 (9BI0 - 01)Document40 pagesBiology B - Paper 1 (9BI0 - 01)Priya Kumar100% (1)
- The Crimean War & The Charge of The Light Brigade: History & FilmDocument6 pagesThe Crimean War & The Charge of The Light Brigade: History & FilmPriya KumarNo ratings yet
- Jury AttentionDocument2 pagesJury AttentionPriya KumarNo ratings yet
- 2007 (Slightly Adapted) Prose Composition: Suggested AnswerDocument3 pages2007 (Slightly Adapted) Prose Composition: Suggested AnswerPriya KumarNo ratings yet
- News Article Analysis WorksheetDocument2 pagesNews Article Analysis WorksheetPriya KumarNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE: Monday 23 January 2012 Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesDocument6 pagesEdexcel GCE: Monday 23 January 2012 Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesPriya KumarNo ratings yet
- VCE Chemistry Study Design - Units 1 and 2 Sample Assessment Tasks 2007-2014Document8 pagesVCE Chemistry Study Design - Units 1 and 2 Sample Assessment Tasks 2007-2014Priya KumarNo ratings yet
- Book 10 - Thematic NotesDocument28 pagesBook 10 - Thematic NotesPriya KumarNo ratings yet
- Milone To What Extent Does Clodius Fit This Description?: Mad, Bad and Dangerous To Know'. From Your Reading of ProDocument2 pagesMilone To What Extent Does Clodius Fit This Description?: Mad, Bad and Dangerous To Know'. From Your Reading of ProPriya KumarNo ratings yet
- Microscope Workshop - Calibrating An Eye Piece GraticuleDocument3 pagesMicroscope Workshop - Calibrating An Eye Piece GraticulePriya KumarNo ratings yet
- ES&S Ecology (Topic 2) Question Set #1 Name(s) - 1Document3 pagesES&S Ecology (Topic 2) Question Set #1 Name(s) - 1Priya KumarNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 RespirationDocument11 pagesTopic 5 RespirationPriya Kumar100% (1)
- Haemoglobin: Partial Pressure of OxygenDocument3 pagesHaemoglobin: Partial Pressure of OxygenPriya KumarNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Halogens (As Aqueous Solutions)Document4 pagesReactions of Halogens (As Aqueous Solutions)Priya KumarNo ratings yet