Professional Documents
Culture Documents
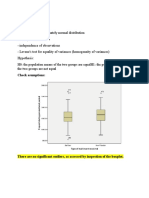
Independent Sample T Test
Independent Sample T Test
Uploaded by
Surbhî GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 1 Rep Max Chart (Epley)Document2 pages1 Rep Max Chart (Epley)RanaPuer67% (3)
- This is The Statistics Handbook your Professor Doesn't Want you to See. So Easy, it's Practically Cheating...From EverandThis is The Statistics Handbook your Professor Doesn't Want you to See. So Easy, it's Practically Cheating...Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Fvifa Tables 2Document2 pagesFvifa Tables 2Alexia100% (4)
- Maha Akhtar M57Document11 pagesMaha Akhtar M57maha AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics Assignment: Submitted ToDocument18 pagesBusiness Analytics Assignment: Submitted Tosoumya MNo ratings yet
- Output 1: Group StatisticsDocument2 pagesOutput 1: Group StatisticsluthfiyaNo ratings yet
- Hasil Output Uji T-TestDocument2 pagesHasil Output Uji T-TestAnadia RosariaNo ratings yet
- 1 - One Sample T Test.: N Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean Monthly Income 200 1.29E4 5918.521 418.503Document6 pages1 - One Sample T Test.: N Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean Monthly Income 200 1.29E4 5918.521 418.503Kazi ShuvoNo ratings yet
- T Test For AndreaDocument6 pagesT Test For AndreaEloisa EspadillaNo ratings yet
- Research Methods in Sport and Exercise TestingDocument37 pagesResearch Methods in Sport and Exercise TestingZe MelieNo ratings yet
- Group StatisticsDocument1 pageGroup StatisticsTri PurwantiNo ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument6 pagesData Analysisjiya rizviNo ratings yet
- UPDATED HYPOTHESIS TESTING in 3 STEPSDocument19 pagesUPDATED HYPOTHESIS TESTING in 3 STEPSMiguel LariosaNo ratings yet
- T Tests D.boduszekDocument20 pagesT Tests D.boduszekMano Billi100% (1)
- Class14 - Review Ttest - ANOVA - Fall10 - PostDocument34 pagesClass14 - Review Ttest - ANOVA - Fall10 - PostJM KaunazNo ratings yet
- N Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean Prelim Exam 147 83.891 10.2390 .8445Document8 pagesN Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean Prelim Exam 147 83.891 10.2390 .8445Gerald Nitz PonceNo ratings yet
- SPSS - Statistic ProjectDocument7 pagesSPSS - Statistic Projectmaha AkhtarNo ratings yet
- LovelyDocument2 pagesLovelyJovelyn CagoNo ratings yet
- Independent TestDocument1 pageIndependent Testlasali tomiaNo ratings yet
- SPSSDocument4 pagesSPSSFaryd D'Jail 'VrcNo ratings yet
- Answers To Exercises and Review Questions: T-TestDocument27 pagesAnswers To Exercises and Review Questions: T-TestAdriano ZanluchiNo ratings yet
- Uji Independen T TestDocument2 pagesUji Independen T TestHasana NurNo ratings yet
- Bài 2Document3 pagesBài 2Karachi Sơn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- KSGMDocument9 pagesKSGMKimnerly MendozaNo ratings yet
- Hasil Uji Independent T Test (Postest Konvensional Dan Postest Buzz Group)Document2 pagesHasil Uji Independent T Test (Postest Konvensional Dan Postest Buzz Group)ridhoNo ratings yet
- Spss Exercise 2 Type of Analysis For Parametric Vs Non-Parametric DataDocument21 pagesSpss Exercise 2 Type of Analysis For Parametric Vs Non-Parametric DataHong Chun YeohNo ratings yet
- SPSSDocument8 pagesSPSSAnggi LestariNo ratings yet
- SPSS T Test Lab AnswersDocument4 pagesSPSS T Test Lab AnswersSOMASUNDARAM RNo ratings yet
- Uji T (Partial/Beda) (Tidak Setara) X - YDocument4 pagesUji T (Partial/Beda) (Tidak Setara) X - YMade PradnyadiputraNo ratings yet
- ! 2 Sabarmuddin TampubolonDocument2 pages! 2 Sabarmuddin TampubolonSabar HerbalNo ratings yet
- Independent Sample T TestDocument3 pagesIndependent Sample T TestApriani SimbiNo ratings yet
- Independent Sampels TestDocument1 pageIndependent Sampels TestMuhammad RizkiNo ratings yet
- Example Independent Sample T Test PDFDocument3 pagesExample Independent Sample T Test PDFYamuna GovindarajNo ratings yet
- Chi-Square Tests: 8.611 9 .474 8.595 9 .476 10 Pvalu 0. 474Document2 pagesChi-Square Tests: 8.611 9 .474 8.595 9 .476 10 Pvalu 0. 474Dr. Mohammed MahfoozNo ratings yet
- Hasil DepepndentDocument1 pageHasil Depepndentrahayu ayuNo ratings yet
- Problem 1: Group N Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean Scores Type A 10 11.20 2.700 .854 Type B 10 7.20 2.044 .646Document3 pagesProblem 1: Group N Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean Scores Type A 10 11.20 2.700 .854 Type B 10 7.20 2.044 .646aaaaasssNo ratings yet
- Hasil Output Uji Independent Sample T-TestDocument1 pageHasil Output Uji Independent Sample T-TestAnadia RosariaNo ratings yet
- SPSSDocument23 pagesSPSSsuriyaNo ratings yet
- T-Test: T-Test Groups Grup (1 2) /missing Analysis /VARIABLES Variabel /CRITERIA CI (.95)Document1 pageT-Test: T-Test Groups Grup (1 2) /missing Analysis /VARIABLES Variabel /CRITERIA CI (.95)Nissa FathinNo ratings yet
- Group StatisticsDocument1 pageGroup StatisticsFikri D'el FinzNo ratings yet
- جدول الطولDocument1 pageجدول الطولllmoj1997No ratings yet
- Tugas Bu WidyaDocument4 pagesTugas Bu WidyaDevi Ayu SNo ratings yet
- Lampiran 12: Gain Penalaran Eksperimen Dan Kelas Kontrol: Independent Samples TestDocument2 pagesLampiran 12: Gain Penalaran Eksperimen Dan Kelas Kontrol: Independent Samples TestSamsul PahmiNo ratings yet
- T-Test Using SPSSDocument4 pagesT-Test Using SPSSTime SaveNo ratings yet
- T-Test: Test of Homogeneity of VariancesDocument1 pageT-Test: Test of Homogeneity of VariancesMax Double GNo ratings yet
- Ervi UjitDocument1 pageErvi UjitNurul Inayah KhairatyNo ratings yet
- Tugas Reza BiostatistikDocument1 pageTugas Reza BiostatistikSriyani SriNo ratings yet
- SPSS NotesDocument23 pagesSPSS NotesJanhavi SinghNo ratings yet
- T-Test: Group StatisticsDocument3 pagesT-Test: Group StatisticsJohn Paul A. CaldeoNo ratings yet
- Uji T-Test Sampel 15 Responden: Group StatisticsDocument2 pagesUji T-Test Sampel 15 Responden: Group StatisticsAYATULLAH HUMAININo ratings yet
- How To Analyze Data Using T-Test in SPSSDocument6 pagesHow To Analyze Data Using T-Test in SPSSGaily Jubie HontiverosNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing For Means: 8.1 One Sample T - TestDocument5 pagesHypothesis Testing For Means: 8.1 One Sample T - TestShubhankar BansalNo ratings yet
- T-Test: Group StatisticsDocument14 pagesT-Test: Group StatisticsFaisal Rachmad SyaputraNo ratings yet
- Hasil Uji Beda T-Test: Group StatisticsDocument4 pagesHasil Uji Beda T-Test: Group StatisticsBambang SatwendoNo ratings yet
- T Test, ANOVA 2Document54 pagesT Test, ANOVA 2esmeralda indrianiNo ratings yet
- Tia Sopiah - CKR0190120 - Keperawatan CDocument4 pagesTia Sopiah - CKR0190120 - Keperawatan CTedi SetiawanNo ratings yet
- UTS Aplikom Chrisensia Santika D3 Gizi 1C P17110204144Document30 pagesUTS Aplikom Chrisensia Santika D3 Gizi 1C P17110204144ChrysantikaNo ratings yet
- SPSS Outputs - Total: Group StatisticsDocument5 pagesSPSS Outputs - Total: Group StatisticsjmesafcNo ratings yet
- 5-Tests of DifferencesDocument16 pages5-Tests of DifferencesAruba AhmadNo ratings yet
- Independent Sample T Test 1Document3 pagesIndependent Sample T Test 1Teach StoryNo ratings yet
- Data Management Course Work 0173Document4 pagesData Management Course Work 0173musinguzi francisNo ratings yet
- SPSS Data Result-Group AssignmentDocument5 pagesSPSS Data Result-Group AssignmentKamaladharanii Ragu NathanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Marketing ChannelsDocument25 pagesElectronic Marketing ChannelsSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bank Performance Analysis-INDUSIND BANK: Particulars Mar-16Document26 pagesBank Performance Analysis-INDUSIND BANK: Particulars Mar-16Surbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Channels For ServicesDocument24 pagesMarketing Channels For ServicesSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Boca Vinay pgfc1948 Icici BankDocument12 pagesBoca Vinay pgfc1948 Icici BankSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Shreeya Verma (PGSF1952)Document15 pagesShreeya Verma (PGSF1952)Surbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Shreya Jain - PGFC1935 - Performance AnalysisDocument13 pagesShreya Jain - PGFC1935 - Performance AnalysisSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis - CbiDocument19 pagesPerformance Analysis - CbiSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- B.O.C.A Assignment - Vishal Singh - pgsf1951 - Performance AnalysisDocument14 pagesB.O.C.A Assignment - Vishal Singh - pgsf1951 - Performance AnalysisSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bank of India Performance Analysis: Total AssetsDocument6 pagesBank of India Performance Analysis: Total AssetsSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Kotak Mahindra Bank Performance AnalysisDocument18 pagesKotak Mahindra Bank Performance AnalysisSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Shashank Malik - PGFB1944 - BOCA GR2 - Study Group 4 - Central Bank of IndiaDocument13 pagesShashank Malik - PGFB1944 - BOCA GR2 - Study Group 4 - Central Bank of IndiaSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Reshma Chauhan - PGFC1927 (BOCA)Document9 pagesReshma Chauhan - PGFC1927 (BOCA)Surbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd. Performance Analysis For The Period 2016-2020Document15 pagesKotak Mahindra Bank Ltd. Performance Analysis For The Period 2016-2020Surbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Axis Bank Ltd. Performance AnalysisDocument13 pagesAxis Bank Ltd. Performance AnalysisSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- YES Bank Performance AnalysisDocument11 pagesYES Bank Performance AnalysisSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Satyam PGSF1937 BOCA BOI BADocument15 pagesSatyam PGSF1937 BOCA BOI BASurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bank Performance Analysis - Sahil Badaya PGFB1942Document10 pagesBank Performance Analysis - Sahil Badaya PGFB1942Surbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Nitesh Khandelwal (PGFC1921) - BOCA (Central Bank of India)Document12 pagesNitesh Khandelwal (PGFC1921) - BOCA (Central Bank of India)Surbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Samarth Mehrotra - BOCADocument23 pagesSamarth Mehrotra - BOCASurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bank Performance Analysis With Risk RatiosDocument8 pagesBank Performance Analysis With Risk RatiosSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Axis Bank Ltd. Performance AnalysisDocument11 pagesAxis Bank Ltd. Performance AnalysisSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bank Performance AnalysisDocument10 pagesBank Performance AnalysisSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Rashi AggarwalDocument17 pagesRashi AggarwalSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- IDFC First Bank LTD Performance Analysis: Total AssetsDocument9 pagesIDFC First Bank LTD Performance Analysis: Total AssetsSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Priya Bansal pgfc1924Document8 pagesPriya Bansal pgfc1924Surbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Equities and Liabilities Shareholder'S Funds Mar-20 Mar-19 Total Share Capital 3,277.66 2,760.03Document11 pagesEquities and Liabilities Shareholder'S Funds Mar-20 Mar-19 Total Share Capital 3,277.66 2,760.03Surbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Assignment pgfc1913Document9 pagesAssignment pgfc1913Surbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bank Performance AnalysisDocument4 pagesBank Performance AnalysisSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- IDFC First Bank LTD Performance Analysis: Total AssetsDocument6 pagesIDFC First Bank LTD Performance Analysis: Total AssetsSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Provisions and Contingencies Include Provision For TaxDocument6 pagesProvisions and Contingencies Include Provision For TaxSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Week3 Slides Quantifying+Rewards+and+UncertaintyDocument27 pagesWeek3 Slides Quantifying+Rewards+and+UncertaintyKinnata NikkoNo ratings yet
- Classical and Modern Heuristics For The Vehicle Routing ProblemDocument17 pagesClassical and Modern Heuristics For The Vehicle Routing ProblemguidelliNo ratings yet
- Structural BreakDocument4 pagesStructural Breakmia farrowNo ratings yet
- Eco 173 Regression Part IDocument4 pagesEco 173 Regression Part INadim IslamNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Performance EvalutionDocument51 pagesPortfolio Performance EvalutionRita NyairoNo ratings yet
- Gitman Ch.5Document14 pagesGitman Ch.5Doni SujanaNo ratings yet
- SpaceDocument3 pagesSpaceNimrodBanawisNo ratings yet
- STAT 1 Course OutlineDocument1 pageSTAT 1 Course Outlinejive_gumelaNo ratings yet
- Study DesginDocument6 pagesStudy DesginRajat GoelNo ratings yet
- CH 19 Inventory TheoryDocument15 pagesCH 19 Inventory TheoryRitesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice Test Linear Regression Regression: y X y X y X X F yDocument2 pagesMultiple-Choice Test Linear Regression Regression: y X y X y X X F yMadhu CkNo ratings yet
- CVEN2002 2702 No QuestionsDocument9 pagesCVEN2002 2702 No QuestionsAbdel YazidiNo ratings yet
- Logistic RegressionDocument24 pagesLogistic RegressionVeerpal KhairaNo ratings yet
- Design of ExperimentsDocument12 pagesDesign of ExperimentsSreehari ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Assosa University School of Graduate Studies Mba ProgramDocument10 pagesAssosa University School of Graduate Studies Mba Programyeneneh meseleNo ratings yet
- BA 555 Practical Business Analysis: Linear Programming (LP)Document23 pagesBA 555 Practical Business Analysis: Linear Programming (LP)Ðệnnïs RǿmerǿNo ratings yet
- Research Methods: Inferential Statistics: Two Group DesignDocument36 pagesResearch Methods: Inferential Statistics: Two Group DesignColinNo ratings yet
- FMA Time Value of MoneyDocument5 pagesFMA Time Value of MoneyAvani TomarNo ratings yet
- Moment Generating FunctionDocument10 pagesMoment Generating FunctionRajesh DwivediNo ratings yet
- ME - St. Petersburg Paradox and Bernoulu's HypothesisDocument5 pagesME - St. Petersburg Paradox and Bernoulu's HypothesisOmkar RajmaneNo ratings yet
- Forecasting: Overview: Learning ObjectivesDocument5 pagesForecasting: Overview: Learning ObjectivesCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- MFIN6214 Lecture1 2020T3Document29 pagesMFIN6214 Lecture1 2020T3ulricaNo ratings yet
- Co-Integration and Error Correction ModelDocument4 pagesCo-Integration and Error Correction ModelSaima MunawarNo ratings yet
- Discrete Probability DistributionDocument9 pagesDiscrete Probability DistributionabdulbasitNo ratings yet
- Transportation ProblemDocument17 pagesTransportation ProblemHarjeet Kaur100% (2)
- Solution of Problem Set 1 For Purity Hydrocarbon Data PDFDocument4 pagesSolution of Problem Set 1 For Purity Hydrocarbon Data PDFDrumil TrivediNo ratings yet
- Medical Statistics From Scratch An Introduction For Health Professionals 4Th Edition David Bowers Download PDF ChapterDocument51 pagesMedical Statistics From Scratch An Introduction For Health Professionals 4Th Edition David Bowers Download PDF Chaptervicki.krause300100% (16)
- QMM5100 Multiple Regression HWDocument3 pagesQMM5100 Multiple Regression HWmanjinderchabbaNo ratings yet
Independent Sample T Test
Independent Sample T Test
Uploaded by
Surbhî GuptaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Independent Sample T Test
Independent Sample T Test
Uploaded by
Surbhî GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
Step 1- defining the variables
IV- gender (nominal)
DV- monthly income (ratio scale)
Step2 – setting null and alt hypothesis
H0- there is no significant difference between the average monthly income of male and females
H1- there is significant difference between the average monthly income of male and females
Step 3- determining the appropriate statistical test
Since we’re comparing on the basis of two mean values
X1 – avg monthly income of males
X2- avg monthly income of females
Therefore, independent sample t test is used
Step 4- we have assumed the level of significance to be 5%
α = 0.05,
therefore, confidence level becomes 95%
step 5- set the decision rule p value
if p <= 0.05, accept H1
otherwise accept H0
step 6- calculations and reports generated through SPSS
Group Statistics
gender N Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean
female 6 3.00 1.095 .447
income
male 4 2.00 1.155 .577
Independent Samples Test
Levene's Test for t-test for Equality of Means
Equality of
Variances
F Sig. t df Sig. (2- Mean Std. Error 95% Confidence
tailed) Difference Difference Interval of the
Difference
Lower Upper
Equal
variances . . 1.386 8 .203 1.000 .722 -.664 2.664
assumed
income
Equal
variances not 1.369 6.316 .218 1.000 .730 -.766 2.766
assumed
Step 7- conclusive findings
From the 1st table we find that,
N1=6
N2=4
X1>X2 = 3.00>2.00
SD1<SD2 = 1.095<1.155
Therefore we calculate coeff of variation = (SD/Mean)*100
CV1 = 0.365
CV2 = 0.577
Since CV1<CV2, males have more monthly income than that of females
From 2nd table
P value is 0.203 >0.05, therefore , null hypothesis is accepted
We conclude that there is no significant difference between the avg monthly income of males and
females
You might also like
- 1 Rep Max Chart (Epley)Document2 pages1 Rep Max Chart (Epley)RanaPuer67% (3)
- This is The Statistics Handbook your Professor Doesn't Want you to See. So Easy, it's Practically Cheating...From EverandThis is The Statistics Handbook your Professor Doesn't Want you to See. So Easy, it's Practically Cheating...Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Fvifa Tables 2Document2 pagesFvifa Tables 2Alexia100% (4)
- Maha Akhtar M57Document11 pagesMaha Akhtar M57maha AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics Assignment: Submitted ToDocument18 pagesBusiness Analytics Assignment: Submitted Tosoumya MNo ratings yet
- Output 1: Group StatisticsDocument2 pagesOutput 1: Group StatisticsluthfiyaNo ratings yet
- Hasil Output Uji T-TestDocument2 pagesHasil Output Uji T-TestAnadia RosariaNo ratings yet
- 1 - One Sample T Test.: N Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean Monthly Income 200 1.29E4 5918.521 418.503Document6 pages1 - One Sample T Test.: N Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean Monthly Income 200 1.29E4 5918.521 418.503Kazi ShuvoNo ratings yet
- T Test For AndreaDocument6 pagesT Test For AndreaEloisa EspadillaNo ratings yet
- Research Methods in Sport and Exercise TestingDocument37 pagesResearch Methods in Sport and Exercise TestingZe MelieNo ratings yet
- Group StatisticsDocument1 pageGroup StatisticsTri PurwantiNo ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument6 pagesData Analysisjiya rizviNo ratings yet
- UPDATED HYPOTHESIS TESTING in 3 STEPSDocument19 pagesUPDATED HYPOTHESIS TESTING in 3 STEPSMiguel LariosaNo ratings yet
- T Tests D.boduszekDocument20 pagesT Tests D.boduszekMano Billi100% (1)
- Class14 - Review Ttest - ANOVA - Fall10 - PostDocument34 pagesClass14 - Review Ttest - ANOVA - Fall10 - PostJM KaunazNo ratings yet
- N Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean Prelim Exam 147 83.891 10.2390 .8445Document8 pagesN Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean Prelim Exam 147 83.891 10.2390 .8445Gerald Nitz PonceNo ratings yet
- SPSS - Statistic ProjectDocument7 pagesSPSS - Statistic Projectmaha AkhtarNo ratings yet
- LovelyDocument2 pagesLovelyJovelyn CagoNo ratings yet
- Independent TestDocument1 pageIndependent Testlasali tomiaNo ratings yet
- SPSSDocument4 pagesSPSSFaryd D'Jail 'VrcNo ratings yet
- Answers To Exercises and Review Questions: T-TestDocument27 pagesAnswers To Exercises and Review Questions: T-TestAdriano ZanluchiNo ratings yet
- Uji Independen T TestDocument2 pagesUji Independen T TestHasana NurNo ratings yet
- Bài 2Document3 pagesBài 2Karachi Sơn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- KSGMDocument9 pagesKSGMKimnerly MendozaNo ratings yet
- Hasil Uji Independent T Test (Postest Konvensional Dan Postest Buzz Group)Document2 pagesHasil Uji Independent T Test (Postest Konvensional Dan Postest Buzz Group)ridhoNo ratings yet
- Spss Exercise 2 Type of Analysis For Parametric Vs Non-Parametric DataDocument21 pagesSpss Exercise 2 Type of Analysis For Parametric Vs Non-Parametric DataHong Chun YeohNo ratings yet
- SPSSDocument8 pagesSPSSAnggi LestariNo ratings yet
- SPSS T Test Lab AnswersDocument4 pagesSPSS T Test Lab AnswersSOMASUNDARAM RNo ratings yet
- Uji T (Partial/Beda) (Tidak Setara) X - YDocument4 pagesUji T (Partial/Beda) (Tidak Setara) X - YMade PradnyadiputraNo ratings yet
- ! 2 Sabarmuddin TampubolonDocument2 pages! 2 Sabarmuddin TampubolonSabar HerbalNo ratings yet
- Independent Sample T TestDocument3 pagesIndependent Sample T TestApriani SimbiNo ratings yet
- Independent Sampels TestDocument1 pageIndependent Sampels TestMuhammad RizkiNo ratings yet
- Example Independent Sample T Test PDFDocument3 pagesExample Independent Sample T Test PDFYamuna GovindarajNo ratings yet
- Chi-Square Tests: 8.611 9 .474 8.595 9 .476 10 Pvalu 0. 474Document2 pagesChi-Square Tests: 8.611 9 .474 8.595 9 .476 10 Pvalu 0. 474Dr. Mohammed MahfoozNo ratings yet
- Hasil DepepndentDocument1 pageHasil Depepndentrahayu ayuNo ratings yet
- Problem 1: Group N Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean Scores Type A 10 11.20 2.700 .854 Type B 10 7.20 2.044 .646Document3 pagesProblem 1: Group N Mean Std. Deviation Std. Error Mean Scores Type A 10 11.20 2.700 .854 Type B 10 7.20 2.044 .646aaaaasssNo ratings yet
- Hasil Output Uji Independent Sample T-TestDocument1 pageHasil Output Uji Independent Sample T-TestAnadia RosariaNo ratings yet
- SPSSDocument23 pagesSPSSsuriyaNo ratings yet
- T-Test: T-Test Groups Grup (1 2) /missing Analysis /VARIABLES Variabel /CRITERIA CI (.95)Document1 pageT-Test: T-Test Groups Grup (1 2) /missing Analysis /VARIABLES Variabel /CRITERIA CI (.95)Nissa FathinNo ratings yet
- Group StatisticsDocument1 pageGroup StatisticsFikri D'el FinzNo ratings yet
- جدول الطولDocument1 pageجدول الطولllmoj1997No ratings yet
- Tugas Bu WidyaDocument4 pagesTugas Bu WidyaDevi Ayu SNo ratings yet
- Lampiran 12: Gain Penalaran Eksperimen Dan Kelas Kontrol: Independent Samples TestDocument2 pagesLampiran 12: Gain Penalaran Eksperimen Dan Kelas Kontrol: Independent Samples TestSamsul PahmiNo ratings yet
- T-Test Using SPSSDocument4 pagesT-Test Using SPSSTime SaveNo ratings yet
- T-Test: Test of Homogeneity of VariancesDocument1 pageT-Test: Test of Homogeneity of VariancesMax Double GNo ratings yet
- Ervi UjitDocument1 pageErvi UjitNurul Inayah KhairatyNo ratings yet
- Tugas Reza BiostatistikDocument1 pageTugas Reza BiostatistikSriyani SriNo ratings yet
- SPSS NotesDocument23 pagesSPSS NotesJanhavi SinghNo ratings yet
- T-Test: Group StatisticsDocument3 pagesT-Test: Group StatisticsJohn Paul A. CaldeoNo ratings yet
- Uji T-Test Sampel 15 Responden: Group StatisticsDocument2 pagesUji T-Test Sampel 15 Responden: Group StatisticsAYATULLAH HUMAININo ratings yet
- How To Analyze Data Using T-Test in SPSSDocument6 pagesHow To Analyze Data Using T-Test in SPSSGaily Jubie HontiverosNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing For Means: 8.1 One Sample T - TestDocument5 pagesHypothesis Testing For Means: 8.1 One Sample T - TestShubhankar BansalNo ratings yet
- T-Test: Group StatisticsDocument14 pagesT-Test: Group StatisticsFaisal Rachmad SyaputraNo ratings yet
- Hasil Uji Beda T-Test: Group StatisticsDocument4 pagesHasil Uji Beda T-Test: Group StatisticsBambang SatwendoNo ratings yet
- T Test, ANOVA 2Document54 pagesT Test, ANOVA 2esmeralda indrianiNo ratings yet
- Tia Sopiah - CKR0190120 - Keperawatan CDocument4 pagesTia Sopiah - CKR0190120 - Keperawatan CTedi SetiawanNo ratings yet
- UTS Aplikom Chrisensia Santika D3 Gizi 1C P17110204144Document30 pagesUTS Aplikom Chrisensia Santika D3 Gizi 1C P17110204144ChrysantikaNo ratings yet
- SPSS Outputs - Total: Group StatisticsDocument5 pagesSPSS Outputs - Total: Group StatisticsjmesafcNo ratings yet
- 5-Tests of DifferencesDocument16 pages5-Tests of DifferencesAruba AhmadNo ratings yet
- Independent Sample T Test 1Document3 pagesIndependent Sample T Test 1Teach StoryNo ratings yet
- Data Management Course Work 0173Document4 pagesData Management Course Work 0173musinguzi francisNo ratings yet
- SPSS Data Result-Group AssignmentDocument5 pagesSPSS Data Result-Group AssignmentKamaladharanii Ragu NathanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Marketing ChannelsDocument25 pagesElectronic Marketing ChannelsSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bank Performance Analysis-INDUSIND BANK: Particulars Mar-16Document26 pagesBank Performance Analysis-INDUSIND BANK: Particulars Mar-16Surbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Channels For ServicesDocument24 pagesMarketing Channels For ServicesSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Boca Vinay pgfc1948 Icici BankDocument12 pagesBoca Vinay pgfc1948 Icici BankSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Shreeya Verma (PGSF1952)Document15 pagesShreeya Verma (PGSF1952)Surbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Shreya Jain - PGFC1935 - Performance AnalysisDocument13 pagesShreya Jain - PGFC1935 - Performance AnalysisSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis - CbiDocument19 pagesPerformance Analysis - CbiSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- B.O.C.A Assignment - Vishal Singh - pgsf1951 - Performance AnalysisDocument14 pagesB.O.C.A Assignment - Vishal Singh - pgsf1951 - Performance AnalysisSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bank of India Performance Analysis: Total AssetsDocument6 pagesBank of India Performance Analysis: Total AssetsSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Kotak Mahindra Bank Performance AnalysisDocument18 pagesKotak Mahindra Bank Performance AnalysisSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Shashank Malik - PGFB1944 - BOCA GR2 - Study Group 4 - Central Bank of IndiaDocument13 pagesShashank Malik - PGFB1944 - BOCA GR2 - Study Group 4 - Central Bank of IndiaSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Reshma Chauhan - PGFC1927 (BOCA)Document9 pagesReshma Chauhan - PGFC1927 (BOCA)Surbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd. Performance Analysis For The Period 2016-2020Document15 pagesKotak Mahindra Bank Ltd. Performance Analysis For The Period 2016-2020Surbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Axis Bank Ltd. Performance AnalysisDocument13 pagesAxis Bank Ltd. Performance AnalysisSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- YES Bank Performance AnalysisDocument11 pagesYES Bank Performance AnalysisSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Satyam PGSF1937 BOCA BOI BADocument15 pagesSatyam PGSF1937 BOCA BOI BASurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bank Performance Analysis - Sahil Badaya PGFB1942Document10 pagesBank Performance Analysis - Sahil Badaya PGFB1942Surbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Nitesh Khandelwal (PGFC1921) - BOCA (Central Bank of India)Document12 pagesNitesh Khandelwal (PGFC1921) - BOCA (Central Bank of India)Surbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Samarth Mehrotra - BOCADocument23 pagesSamarth Mehrotra - BOCASurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bank Performance Analysis With Risk RatiosDocument8 pagesBank Performance Analysis With Risk RatiosSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Axis Bank Ltd. Performance AnalysisDocument11 pagesAxis Bank Ltd. Performance AnalysisSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bank Performance AnalysisDocument10 pagesBank Performance AnalysisSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Rashi AggarwalDocument17 pagesRashi AggarwalSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- IDFC First Bank LTD Performance Analysis: Total AssetsDocument9 pagesIDFC First Bank LTD Performance Analysis: Total AssetsSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Priya Bansal pgfc1924Document8 pagesPriya Bansal pgfc1924Surbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Equities and Liabilities Shareholder'S Funds Mar-20 Mar-19 Total Share Capital 3,277.66 2,760.03Document11 pagesEquities and Liabilities Shareholder'S Funds Mar-20 Mar-19 Total Share Capital 3,277.66 2,760.03Surbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Assignment pgfc1913Document9 pagesAssignment pgfc1913Surbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bank Performance AnalysisDocument4 pagesBank Performance AnalysisSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- IDFC First Bank LTD Performance Analysis: Total AssetsDocument6 pagesIDFC First Bank LTD Performance Analysis: Total AssetsSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Provisions and Contingencies Include Provision For TaxDocument6 pagesProvisions and Contingencies Include Provision For TaxSurbhî GuptaNo ratings yet
- Week3 Slides Quantifying+Rewards+and+UncertaintyDocument27 pagesWeek3 Slides Quantifying+Rewards+and+UncertaintyKinnata NikkoNo ratings yet
- Classical and Modern Heuristics For The Vehicle Routing ProblemDocument17 pagesClassical and Modern Heuristics For The Vehicle Routing ProblemguidelliNo ratings yet
- Structural BreakDocument4 pagesStructural Breakmia farrowNo ratings yet
- Eco 173 Regression Part IDocument4 pagesEco 173 Regression Part INadim IslamNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Performance EvalutionDocument51 pagesPortfolio Performance EvalutionRita NyairoNo ratings yet
- Gitman Ch.5Document14 pagesGitman Ch.5Doni SujanaNo ratings yet
- SpaceDocument3 pagesSpaceNimrodBanawisNo ratings yet
- STAT 1 Course OutlineDocument1 pageSTAT 1 Course Outlinejive_gumelaNo ratings yet
- Study DesginDocument6 pagesStudy DesginRajat GoelNo ratings yet
- CH 19 Inventory TheoryDocument15 pagesCH 19 Inventory TheoryRitesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice Test Linear Regression Regression: y X y X y X X F yDocument2 pagesMultiple-Choice Test Linear Regression Regression: y X y X y X X F yMadhu CkNo ratings yet
- CVEN2002 2702 No QuestionsDocument9 pagesCVEN2002 2702 No QuestionsAbdel YazidiNo ratings yet
- Logistic RegressionDocument24 pagesLogistic RegressionVeerpal KhairaNo ratings yet
- Design of ExperimentsDocument12 pagesDesign of ExperimentsSreehari ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Assosa University School of Graduate Studies Mba ProgramDocument10 pagesAssosa University School of Graduate Studies Mba Programyeneneh meseleNo ratings yet
- BA 555 Practical Business Analysis: Linear Programming (LP)Document23 pagesBA 555 Practical Business Analysis: Linear Programming (LP)Ðệnnïs RǿmerǿNo ratings yet
- Research Methods: Inferential Statistics: Two Group DesignDocument36 pagesResearch Methods: Inferential Statistics: Two Group DesignColinNo ratings yet
- FMA Time Value of MoneyDocument5 pagesFMA Time Value of MoneyAvani TomarNo ratings yet
- Moment Generating FunctionDocument10 pagesMoment Generating FunctionRajesh DwivediNo ratings yet
- ME - St. Petersburg Paradox and Bernoulu's HypothesisDocument5 pagesME - St. Petersburg Paradox and Bernoulu's HypothesisOmkar RajmaneNo ratings yet
- Forecasting: Overview: Learning ObjectivesDocument5 pagesForecasting: Overview: Learning ObjectivesCharice Anne VillamarinNo ratings yet
- MFIN6214 Lecture1 2020T3Document29 pagesMFIN6214 Lecture1 2020T3ulricaNo ratings yet
- Co-Integration and Error Correction ModelDocument4 pagesCo-Integration and Error Correction ModelSaima MunawarNo ratings yet
- Discrete Probability DistributionDocument9 pagesDiscrete Probability DistributionabdulbasitNo ratings yet
- Transportation ProblemDocument17 pagesTransportation ProblemHarjeet Kaur100% (2)
- Solution of Problem Set 1 For Purity Hydrocarbon Data PDFDocument4 pagesSolution of Problem Set 1 For Purity Hydrocarbon Data PDFDrumil TrivediNo ratings yet
- Medical Statistics From Scratch An Introduction For Health Professionals 4Th Edition David Bowers Download PDF ChapterDocument51 pagesMedical Statistics From Scratch An Introduction For Health Professionals 4Th Edition David Bowers Download PDF Chaptervicki.krause300100% (16)
- QMM5100 Multiple Regression HWDocument3 pagesQMM5100 Multiple Regression HWmanjinderchabbaNo ratings yet