Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sensory Learning Objectives
Sensory Learning Objectives
Uploaded by
Heather Elaine Wheatley0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views4 pagesThe learning objectives cover sensory disorders related to vision and hearing/vestibular systems. For vision, topics include conjunctivitis, glaucoma, lens disorders like myopia and presbyopia, cataracts, retinopathy, papilledema, and macular degeneration. For hearing/vestibular, acute otitis media, presbycusis, conductive vs. sensorineural hearing loss, the vestibular system, Meniere's disease, and associated symptoms are discussed. No diagnostic tests or treatments will be included on the exam.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe learning objectives cover sensory disorders related to vision and hearing/vestibular systems. For vision, topics include conjunctivitis, glaucoma, lens disorders like myopia and presbyopia, cataracts, retinopathy, papilledema, and macular degeneration. For hearing/vestibular, acute otitis media, presbycusis, conductive vs. sensorineural hearing loss, the vestibular system, Meniere's disease, and associated symptoms are discussed. No diagnostic tests or treatments will be included on the exam.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views4 pagesSensory Learning Objectives
Sensory Learning Objectives
Uploaded by
Heather Elaine WheatleyThe learning objectives cover sensory disorders related to vision and hearing/vestibular systems. For vision, topics include conjunctivitis, glaucoma, lens disorders like myopia and presbyopia, cataracts, retinopathy, papilledema, and macular degeneration. For hearing/vestibular, acute otitis media, presbycusis, conductive vs. sensorineural hearing loss, the vestibular system, Meniere's disease, and associated symptoms are discussed. No diagnostic tests or treatments will be included on the exam.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
NURS 3800: Fall 2020
Learning Objectives: Sensory Disorders: Vision
No treatment or diagnostic tests will be on exam
1. Describe conjunctivitis to include its definition, clinical manifestations, and
etiology based on type of exudate present. Differentiate viral from bacterial.
Inflammation of conjunctiva
Clinical manifestations :
o Rednesss
o Tearing
o Photophobia
o Purulent drainage
o Bacterial : sticky, green/yellow discharge
o Viral : excessive tearing ; drainage minimal
o Allergic : itching
Etiology :
o Bacterial :
Streptococcus pneuoni
Staph aureus
o Viral :
Adenouris type 3
o Allergens
o Chemical / physical irritants
o Radient energy
Types :
o Hyper acute : severe infection ; loss of sight possible
o Acute : most common
o Chronic : nasal lacrimal obstruction ; can’t clear eye of irritants
2. Define normal intraocular pressure. Describe the pathophysiology of
glaucoma and the resulting clinical signs. (Do not need to know the
difference in open angle and angle-closure). Know that it is the leading
cause of preventable blindness in the US.
Normal intraocular pressure :
Glaucoma
o Patho :
Optic neuropathy accompanied by optic disc cupping &
visual field loss, associated with an increase in intraocular
pressure
Leading cause of preventable blindness
Causes :
Primary :
o No evidence of pre-existing ocular/ systemic
disease
Secondary :
o inflammatory problems of eyes
o trauma that produces hemmhorages
o tumors
o Clinical Signs :
o Risks :
Elevation of intraocular pressure
Family Hx
Age
Ethnicity (AA)
3. Compare and contrast the following lens disorders: myopia, hyperopia,
astigmatism, and presbyopia.
Myopia : near sightedness ; image focused in front of retina
Hyperopia : far sightedness ; image focused behind retina
Astigmatism : light rays aren’t focused clearly on retina -> blurred vision
Presbyopia : change in lens that occurs due to aging
4. Describe the pathophysiology of cataracts – which part of the eye is
involved and what visual changes does this cause?
Opacity in lens that interferes with transmission of light to retina
Most common cause of age-related visual loss
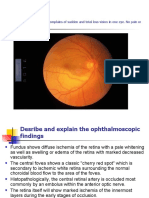
5. Describe the two types of retinopathy. Define the main pathophysiologic
problem in retinopathy – microaneurysms which bleed. Which disease
population is at risk but can be controlled with proper health habits?
6. Name the medical term for swelling of the optic disc often seen in
malignant hypertension or increased intracranial pressure.
7. Name the visual disorder which is characterized by flashing lights, floaters
and a visual defect described as a “dark veil or curtain” pulled over the
visual field.
papiledema
8. Describe the pathophysiology of macular degeneration. Which part of the
eye is involved? Is central or peripheral vision affected? Is it painful?
(Don’t need to contrast wet and dry).
Learning Objectives: Sensory Disorders: Hearing/Vestibular
1. Define acute otitis media. Name two causes of inflammation. State which
population is at greatest risk and why.
Inflammation of external ear
Causes :
o Infection
o Irritation
o Allergies
o Moisture in ear
o Trauma from cleaning
2. Define presbycusis. Name 3 characteristics of the problem – hearing loss of
high pitched sounds first, difficult to hear in crowded room or with back
turned. Name which population is at greatest risk for this problem –
elderly/age related. (This question has been known to show up on the HESI
Patho Exam)
3. Differentiate between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, and state
two common causes of each disorder. (This question has been known to
show up on the HESI Patho Exam. Conductive = problem with transmission
of sound – like in external or middle ear infections. Sensorineural – problem
with auditory nerve transmission – inner ear / cochlea. There is an error in
the ECHO on the Self Assessment questions at about the 1:01 point in the
video. It is stated that presbycusis is a conductive disorder, whereas it is
actually a sensorineural disorder. Please take note of this for your exam.)
4. Name the system responsible for maintaining balance and position in space =
vestibular system – in the inner ear.
Name three common conditions associated with disorder of this system =
Meniere’s disease, motion sickness, benign paroxysmal positional vertigo .
Name the classic triad of symptoms in Meniere’s disease = vertigo, tinnitus
and hearing loss.
Name three ANS symptoms associated with disorders of this system =
nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis.
You might also like
- Test Bank For Advanced Practice Nursing in The Care of Older Adults 2nd by Kennedy Malone DownloadDocument10 pagesTest Bank For Advanced Practice Nursing in The Care of Older Adults 2nd by Kennedy Malone Downloadericgoodmanfaszgwponk100% (35)
- Ent Exam IsmDocument266 pagesEnt Exam IsmAmit BhadhanaNo ratings yet
- PEAC OphthalmologyDocument45 pagesPEAC OphthalmologySdNo ratings yet
- OphthalmologyDocument29 pagesOphthalmologyAdebisiNo ratings yet
- M11 OPHTHA Hx-Taking & Basic Ophtha Exam Team10Document6 pagesM11 OPHTHA Hx-Taking & Basic Ophtha Exam Team10Julio VernyNo ratings yet
- Homeo Eye DiseaseDocument15 pagesHomeo Eye DiseaseAlbena Trifonova100% (3)
- Redeye Mini Case 2017 Tutor's Guide PDFDocument9 pagesRedeye Mini Case 2017 Tutor's Guide PDFJoanna GarciaNo ratings yet
- NP 5Document6 pagesNP 5Ana Blesilda Cachola100% (1)
- Silo - Tips - How To Take An Ophthalmic HistoryDocument5 pagesSilo - Tips - How To Take An Ophthalmic HistorySumon SarkarNo ratings yet
- Optho HXDocument5 pagesOptho HXChris KingNo ratings yet
- Deafness, Vertigo, Conjunctivitis, Stye, Chalazion, Refractive Error, Blepharitis, Ptosis, Hoeners Syndrome-2022Document22 pagesDeafness, Vertigo, Conjunctivitis, Stye, Chalazion, Refractive Error, Blepharitis, Ptosis, Hoeners Syndrome-2022Sanjida elaNo ratings yet
- Case Report Mata 2Document4 pagesCase Report Mata 2Hanung PujanggaNo ratings yet
- Neuritis OptikusDocument17 pagesNeuritis OptikusilhamakbbarNo ratings yet
- Eye DiseasesDocument8 pagesEye DiseasesCeline de HaanNo ratings yet
- Iritis 8Document14 pagesIritis 8Alvis KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Optic Neuritis: Clinical PR ActiceDocument8 pagesOptic Neuritis: Clinical PR ActiceafbmgNo ratings yet
- MiddleEastAfrJOphthalmol19113-4844325 132723Document9 pagesMiddleEastAfrJOphthalmol19113-4844325 132723Vincent LivandyNo ratings yet
- Case 1: 70-Yr Man Complains of Sudden and Total Loss Vision in One Eye. No Pain or Other SymptomsDocument17 pagesCase 1: 70-Yr Man Complains of Sudden and Total Loss Vision in One Eye. No Pain or Other SymptomsCherry TamNo ratings yet
- History Taking& Examination of Eye: Mohamed Ahmed El - ShafieDocument38 pagesHistory Taking& Examination of Eye: Mohamed Ahmed El - ShafiesandeepNo ratings yet
- Assessment of EyeDocument15 pagesAssessment of EyegemergencycareNo ratings yet
- MYSTERY CASE: NeuroophthalmologyDocument2 pagesMYSTERY CASE: Neuroophthalmologyjuddy brownNo ratings yet
- Cataract PTDocument9 pagesCataract PTPreeti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cataract PTDocument9 pagesCataract PTpreeti sharmaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Assessing EyeDocument13 pages3 - Assessing EyeFrancine Julia MorilloNo ratings yet
- PtosisDocument23 pagesPtosisSunny jaiswalNo ratings yet
- 1-8 Eyelid DisordersDocument6 pages1-8 Eyelid Disorderssien99100% (1)
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi KorneaDocument133 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi KorneaAriyanie NurtaniaNo ratings yet
- Graves 508Document6 pagesGraves 508VellaNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro Ocular Pathology OghreDocument23 pages1 Intro Ocular Pathology OghreUyigue EuniceNo ratings yet
- Preseptal CellulitisDocument4 pagesPreseptal CellulitisKm PlegariaNo ratings yet
- PBL Modul Blindness KLP 14Document25 pagesPBL Modul Blindness KLP 14033010969No ratings yet
- PrintDocument32 pagesPrintnewtonNo ratings yet
- Symposium Toxic Optic Neuropathy: Pradeep Sharma, Reena SharmaDocument5 pagesSymposium Toxic Optic Neuropathy: Pradeep Sharma, Reena SharmaCony NurbayyiniNo ratings yet
- Feline UveitesDocument9 pagesFeline UveitesErick ConfickeerzNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Sensory Problems Care of Clients With Sensory ProblemsDocument82 pagesCare of Clients With Sensory Problems Care of Clients With Sensory Problemssnpjavier100% (1)
- Bell'S Palsy: Villanueva, Relyssa Ashley L. BSNDocument6 pagesBell'S Palsy: Villanueva, Relyssa Ashley L. BSNAshley VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- CD 2Document14 pagesCD 2Amira AlmutairiNo ratings yet
- Sympathetic Uveitis/ Ophthalmia: PG CornerDocument4 pagesSympathetic Uveitis/ Ophthalmia: PG CornerVincent LivandyNo ratings yet
- American Journal of Ophthalmology Case Reports: Bilal Rana, David M. Hinkle TDocument2 pagesAmerican Journal of Ophthalmology Case Reports: Bilal Rana, David M. Hinkle TDaniel GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Bell's PalsyDocument17 pagesBell's PalsyFree ZingNo ratings yet
- Red EyeDocument1 pageRed EyeSirAdjeteyNo ratings yet
- Red Eye CheckDocument3 pagesRed Eye CheckkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Cervoni2017 4Document5 pagesCervoni2017 4ekanovicaNo ratings yet
- Divine Intervention Episode 36 Usmle OphthalmologyDocument15 pagesDivine Intervention Episode 36 Usmle OphthalmologySwisskelly1No ratings yet
- Module Opthalmology Corneal Ulcer: Group 7 Wulan-Fadzely-Arif Amri-Safuan Arif-Nadiah-Insyira-Fatimah-Andi AbsharinaDocument19 pagesModule Opthalmology Corneal Ulcer: Group 7 Wulan-Fadzely-Arif Amri-Safuan Arif-Nadiah-Insyira-Fatimah-Andi Absharinaarifamri92No ratings yet
- Bright Eyes - The Treatment of Eye Diseases by AcupucntureDocument8 pagesBright Eyes - The Treatment of Eye Diseases by AcupucntureElizabeth Durkee Neil100% (1)
- 1 - Orientation, History Taking and ExaminationDocument96 pages1 - Orientation, History Taking and ExaminationHari ShresthaNo ratings yet
- A Review of Neuro-Ophthalmologic EmergenciesDocument5 pagesA Review of Neuro-Ophthalmologic EmergenciesZakiyul FuadNo ratings yet
- Okap Samson Uveitis PDFDocument12 pagesOkap Samson Uveitis PDFsharu4291No ratings yet
- Bell Palsy: Clinical Examination and Management: ReviewDocument8 pagesBell Palsy: Clinical Examination and Management: ReviewCitraNo ratings yet
- Bells PalsyDocument6 pagesBells PalsyCastay GuerraNo ratings yet
- Disturbance in Sensory PerceptionDocument48 pagesDisturbance in Sensory PerceptionKristine Louise JavierNo ratings yet
- Sympathetic OphthalmiaDocument27 pagesSympathetic OphthalmiaAnish KumarNo ratings yet
- Neuro Ophthalmology Matthew J Thurtell Download PDF ChapterDocument51 pagesNeuro Ophthalmology Matthew J Thurtell Download PDF Chapterkenneth.mcculough280100% (5)
- Case Report PresentationDocument34 pagesCase Report PresentationDwi Permana PutraNo ratings yet
- Causes of Eye DischargeDocument4 pagesCauses of Eye Dischargeabed alawiNo ratings yet
- Red FlagDocument14 pagesRed FlagAsem AlmeerabiNo ratings yet
- AnisocoriaDocument11 pagesAnisocoriaChaturangaNSenerathNo ratings yet
- Health Asme 7Document4 pagesHealth Asme 7Harmin HawkinsNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve Palsy: Dr. Saud AlromaihDocument74 pagesFacial Nerve Palsy: Dr. Saud AlromaihChandra ManapaNo ratings yet
- Drooping Eyelid, (Ptosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDrooping Eyelid, (Ptosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Eent Post Test Final DipologDocument6 pagesEent Post Test Final DipologJan Joseph BanzuelaNo ratings yet
- TR-SENSES MercadoDocument174 pagesTR-SENSES MercadoroseNo ratings yet
- What Is VertigoDocument12 pagesWhat Is VertigoManayu WidaswariNo ratings yet
- Guy Kawasaki - The Art of Innovation, Speech (ENG)Document30 pagesGuy Kawasaki - The Art of Innovation, Speech (ENG)lishugo100% (3)
- Ears Lecture GuideDocument56 pagesEars Lecture GuidemajNo ratings yet
- VertigoDocument50 pagesVertigosaltoftheearthlightoftheworld506No ratings yet
- Meniere DiseaseDocument6 pagesMeniere Diseasefirza yoga baskoroNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument66 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentSisir Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- Meniere's DiseaseDocument46 pagesMeniere's Diseaseabhinay_1712No ratings yet
- Kahoot (1) MergedDocument8 pagesKahoot (1) MergedNathaly MoraNo ratings yet
- The Spectrum of Vestibular MigraineDocument14 pagesThe Spectrum of Vestibular MigraineRudolfGerNo ratings yet
- Hiperakusis Dan TinnitusDocument11 pagesHiperakusis Dan TinnitusavininditaNo ratings yet
- Meniere's Disease: Leona Šupljika GabelicaDocument17 pagesMeniere's Disease: Leona Šupljika GabelicaAlvarendra RationoNo ratings yet
- Meniere's DiseaseDocument32 pagesMeniere's DiseaseMOISED MOisedm100% (1)
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Hearing and Balance Disorders WebDocument36 pagesAssessment and Management of Patients With Hearing and Balance Disorders Webmalinda0% (1)
- Approach To The History and Evaluation of Vertigo and DizzinessDocument24 pagesApproach To The History and Evaluation of Vertigo and DizzinessPAULA GABRIELA ABAD POLONo ratings yet
- MSN Question Bank-Unit 1 - Ent: Long Essay 5MDocument31 pagesMSN Question Bank-Unit 1 - Ent: Long Essay 5Mkiran kumarNo ratings yet
- Genta Transtimpanica 1Document7 pagesGenta Transtimpanica 1natalia.gallinoNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Vertigo and Dizziness Syndrome in A Neurological Outpatient ClinicDocument8 pagesDiagnosis of Vertigo and Dizziness Syndrome in A Neurological Outpatient ClinicnoorlitaNo ratings yet
- FlashcardsDocument140 pagesFlashcardsDoodNo ratings yet
- Vertigo and DizzinessDocument14 pagesVertigo and Dizzinessa7mad thunaibatNo ratings yet
- Vestibular Paroxysmia: Diagnostic CriteriaDocument7 pagesVestibular Paroxysmia: Diagnostic CriteriaSadiah Hasyim AlweiniNo ratings yet
- Meniere's DiseaseDocument26 pagesMeniere's DiseasenandaanggiNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Nclex Questions Neuro1Document13 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Nclex Questions Neuro1dee_day_80% (1)
- 160 Nursing Bullets: Medical-Surgical Nursing Reviewer: Nursing Diagnosis Care Plan NCLEX Questions Exam QuestionDocument16 pages160 Nursing Bullets: Medical-Surgical Nursing Reviewer: Nursing Diagnosis Care Plan NCLEX Questions Exam Questionvarshasharma05100% (4)
- Assessment: Vestibular Testing Techniques in Adults and ChildrenDocument13 pagesAssessment: Vestibular Testing Techniques in Adults and ChildrenpuputNo ratings yet
- Ménière's Disease Treatment: A Patient-Centered Systematic ReviewDocument13 pagesMénière's Disease Treatment: A Patient-Centered Systematic ReviewAulia NurrahmahNo ratings yet
- Betahistine Used in VertigoDocument8 pagesBetahistine Used in VertigoMuhammad Faisal EffendiNo ratings yet