Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 2.macromeasures PDF
Unit 2.macromeasures PDF
Uploaded by
Gwyneth MalagaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Bank of BarodaDocument2 pagesBank of BarodaAdventurous Freak50% (2)
- IB Economics Glossary of TermsDocument43 pagesIB Economics Glossary of Termssamira2702100% (1)
- Decision Making GuideDocument27 pagesDecision Making GuideShan Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Macro-Economics To InflationDocument5 pagesMacro-Economics To InflationGwyneth MalagaNo ratings yet
- Econ CH 13Document6 pagesEcon CH 13James HaroldNo ratings yet
- Regardless of TheirDocument11 pagesRegardless of TheirTrisha Nicole BuendiaNo ratings yet
- 08 Business Cycles, Unemployment, InflationDocument3 pages08 Business Cycles, Unemployment, Inflationcatherine tucayNo ratings yet
- Chương 1:: GDP or Gross Domestic Product 4 PartsDocument9 pagesChương 1:: GDP or Gross Domestic Product 4 PartsChi Nguyễn Thị KimNo ratings yet
- (Econ) UnemploymentDocument10 pages(Econ) UnemploymentTricia KiethNo ratings yet
- ME Cheat Sheet For FinalDocument4 pagesME Cheat Sheet For Finalkaungwaiphyo89No ratings yet
- Measuring Employment and UnemploymentDocument2 pagesMeasuring Employment and UnemploymentMohammad A. HasanNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Unemployment Review To Have For Test Fall 2020Document1 page2.3 Unemployment Review To Have For Test Fall 2020Deshay WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Theme 5 Unemployment and InflationDocument19 pagesTheme 5 Unemployment and InflationNadineNo ratings yet
- Handout 1 - Measuring Employment and UnemploymentDocument2 pagesHandout 1 - Measuring Employment and UnemploymentJntNo ratings yet
- Ms20 - MacroeconomicsDocument2 pagesMs20 - MacroeconomicsSeokjin KimNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 GDDocument32 pagesLesson1 GDPeruQuantrillNo ratings yet
- Asis 2 PEDocument21 pagesAsis 2 PELovina AishaNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics NotesDocument20 pagesMacroeconomics NotesElsa PucciniNo ratings yet
- Guided Notes Unit 5 - Macroeconomics - Economic Challenges, GDP and Growth, and LaborDocument4 pagesGuided Notes Unit 5 - Macroeconomics - Economic Challenges, GDP and Growth, and LaborNicols FleurismaNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Suggestion (Sem 5)Document38 pagesMacroeconomics Suggestion (Sem 5)Vivaan BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Macro TopicsDocument30 pagesMacro TopicsThalisson RamiresNo ratings yet
- Define 2-3 Key Terms: 0 2 / 0 6 / 2 0 1 3 S Ta R Te RDocument43 pagesDefine 2-3 Key Terms: 0 2 / 0 6 / 2 0 1 3 S Ta R Te RJowana PenasoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document13 pagesChapter 9ffffffNo ratings yet
- 06 National Income AccountingDocument4 pages06 National Income Accountingcatherine tucayNo ratings yet
- Econ Review ProjectDocument5 pagesEcon Review ProjectNing GuangNo ratings yet
- Econ100.1 ReviewerDocument9 pagesEcon100.1 Revieweranon_571264294No ratings yet
- Theories of Employment and Income: Learning ObjectivesDocument35 pagesTheories of Employment and Income: Learning Objectivesmuhammedsadiq abdullaNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic University of The Philippines Macroeconomics Reviewer 2023Document12 pagesPolytechnic University of The Philippines Macroeconomics Reviewer 2023jeferson.ordonioNo ratings yet
- Theories of Employment and Income: Learning ObjectivesDocument15 pagesTheories of Employment and Income: Learning ObjectivesBabarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MacroeconomicsDocument6 pagesIntroduction To MacroeconomicsDayangku AyusapuraNo ratings yet
- Recession and Our RoleDocument35 pagesRecession and Our RoleRegina Sharon PalletiNo ratings yet
- Modern Labor Economics Chapter 2Document44 pagesModern Labor Economics Chapter 2As-Ad Arik AzadNo ratings yet
- ECON1102 Macroeconomics 1 CheatsheetDocument2 pagesECON1102 Macroeconomics 1 CheatsheetCarla MissionaNo ratings yet
- SV C28 UnemploymentDocument6 pagesSV C28 UnemploymentphươngNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Economic Indicators and MacroeconomicsDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Economic Indicators and MacroeconomicsAlex KohNo ratings yet
- Unemployment & Inflation: Developed By: Pup CSSD Department of EconomicsDocument7 pagesUnemployment & Inflation: Developed By: Pup CSSD Department of EconomicsMarcus MonocayNo ratings yet
- Econ Dev - Part C.2Document7 pagesEcon Dev - Part C.2Darryl LabradorNo ratings yet
- (Lecture 8.2) Chapter 12 Unemployment and Inflation (L8 - 2)Document21 pages(Lecture 8.2) Chapter 12 Unemployment and Inflation (L8 - 2)Chen Yee KhooNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Outline For Economic Concepts and TheoryDocument4 pagesComprehensive Outline For Economic Concepts and TheorycerapyaNo ratings yet
- Higher Productivity Means Higher Standard of Living: Chapter 1: Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument4 pagesHigher Productivity Means Higher Standard of Living: Chapter 1: Ten Principles of EconomicsCristina Crong MorgiaNo ratings yet
- SSM107 Lec#1 MidtermDocument5 pagesSSM107 Lec#1 MidtermMa. Krecia NicolNo ratings yet
- Intro To Macroeconomics and GDP Problem Set Answer KeyDocument5 pagesIntro To Macroeconomics and GDP Problem Set Answer KeySid JhaNo ratings yet
- Student Management SystemDocument279 pagesStudent Management System15257-Mohammed AL NomanNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Outline For Economic Concepts and TheoryDocument9 pagesComprehensive Outline For Economic Concepts and TheorycerapyaNo ratings yet
- Cosc 104Document13 pagesCosc 104Joseph KuriaNo ratings yet
- Important Basics of EconomyDocument4 pagesImportant Basics of EconomyRamana ReddyNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics PrelimDocument8 pagesApplied Economics PrelimRylyn IsabelNo ratings yet
- Indian Eco Dev 2Document11 pagesIndian Eco Dev 2Badavath JeethendraNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics 6th Edition Williamson Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesMacroeconomics 6th Edition Williamson Solutions Manualfagotbouge3q7x97% (29)
- Econ-Additional ReviewerDocument2 pagesEcon-Additional ReviewerCzarina Castillo CompleNo ratings yet
- Basic Economics With Taxation and Agrarian Reform: Dr. Vicente S. Betarmos, JRDocument6 pagesBasic Economics With Taxation and Agrarian Reform: Dr. Vicente S. Betarmos, JRPlatero RolandNo ratings yet
- Unemployment and InflationDocument45 pagesUnemployment and InflationFoni NancyNo ratings yet
- TUT 1: Measuring A Nation's Income: No Word Key Word EconomicDocument22 pagesTUT 1: Measuring A Nation's Income: No Word Key Word EconomicKim Ngọc HuyềnNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Lecture Chapter 10 GDP ComponentsDocument10 pagesMacroeconomics Lecture Chapter 10 GDP ComponentsDX 1No ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument12 pagesMeasurementRachit BhagatNo ratings yet
- Econ 214 MACRO NotesDocument48 pagesEcon 214 MACRO NotesebtreherneNo ratings yet
- Beco 2301 Macro l6 SV Ad-As Model p1Document24 pagesBeco 2301 Macro l6 SV Ad-As Model p1Ahmed MousaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document60 pagesChapter 4oakleyhouNo ratings yet
- Felicia Irene Week 10Document15 pagesFelicia Irene Week 10felicia ireneNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Note (2102)Document6 pagesMacroeconomics Note (2102)Mahmudul hasanNo ratings yet
- Working Paper EntriesDocument2 pagesWorking Paper EntriesRixer PrietoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Bulacan State University City of Malolos, Bulacan Office of The Dean of InstructionDocument8 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Bulacan State University City of Malolos, Bulacan Office of The Dean of InstructionTheresa RoqueNo ratings yet
- 1 RR 7-2009Document5 pages1 RR 7-2009JoyceNo ratings yet
- Statement 600606 35438479 2 11 2022 1 12 2022Document1 pageStatement 600606 35438479 2 11 2022 1 12 2022Orhan DagdelenNo ratings yet
- Accounting ElementsDocument21 pagesAccounting Elementsdemonking1273433No ratings yet
- EC3314 Spring PSet 4 SolutionsDocument6 pagesEC3314 Spring PSet 4 Solutionschristina0107No ratings yet
- LAW Partnership Act 1932Document10 pagesLAW Partnership Act 1932ritesh2030No ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Heirs of Sps Maglasang V Manila Banking Corp PRDocument4 pagesToaz - Info Heirs of Sps Maglasang V Manila Banking Corp PRJimi SolomonNo ratings yet
- History of Banking in The PhilippinesDocument18 pagesHistory of Banking in The PhilippinesJohn Carmelo Apilado100% (10)
- Insolvency & Bankruptcy Code, 2016Document23 pagesInsolvency & Bankruptcy Code, 2016Jeswin JohnNo ratings yet
- Revised Bharat Kosh Refund FormDocument2 pagesRevised Bharat Kosh Refund Formrd meshramNo ratings yet
- Financial Education For Working Executives: An Initiative of SEBI & NISMDocument31 pagesFinancial Education For Working Executives: An Initiative of SEBI & NISMkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Financial AccountingDocument16 pagesFinancial Accountinggarg19118No ratings yet
- BZ Payroll Slip OKT 2023-UnlockedDocument1 pageBZ Payroll Slip OKT 2023-UnlockedWidha AgustriaNo ratings yet
- Problem 2-24: © The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2010. All Rights Reserved. Solutions Manual, Chapter 2 51Document2 pagesProblem 2-24: © The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2010. All Rights Reserved. Solutions Manual, Chapter 2 51Rizky Wahyu FebriyantoNo ratings yet
- Problemas Cap 12Document5 pagesProblemas Cap 12angel guarinNo ratings yet
- Forensic Accounting in India: Problems in Detecting FraudDocument4 pagesForensic Accounting in India: Problems in Detecting FraudInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document13 pagesChapter 6ERICKA MAE NATONo ratings yet
- The Following Selected Transactions Were Completed by InterstateDocument1 pageThe Following Selected Transactions Were Completed by InterstateM Bilal SaleemNo ratings yet
- 12 BibliographyDocument8 pages12 BibliographyMotiram paudelNo ratings yet
- Strategy Tester - TAIGUNDocument90 pagesStrategy Tester - TAIGUNTeamJunTradeezNo ratings yet
- Text ResumeDocument2 pagesText Resumedilip504100% (1)
- Determinants of Financial Reporting Quality in United KingdomDocument46 pagesDeterminants of Financial Reporting Quality in United KingdomKareemEl'Bendary100% (1)
- LIC's JEEVAN VAIBHAV (UIN: 512N269V01)Document2 pagesLIC's JEEVAN VAIBHAV (UIN: 512N269V01)Sri Ram SahooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Role of GovernmentDocument21 pagesChapter 13 Role of GovernmentMuhammad Zarif IshakNo ratings yet
- IIMA Placement BrochureDocument60 pagesIIMA Placement BrochureVignesh SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Health Ensure Floater - Policy Schedule: Proposer DetailsDocument3 pagesHealth Ensure Floater - Policy Schedule: Proposer DetailsValand NileshNo ratings yet
- Account Statement: Description DateDocument3 pagesAccount Statement: Description DatevinuNo ratings yet
Unit 2.macromeasures PDF
Unit 2.macromeasures PDF
Uploaded by
Gwyneth MalagaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 2.macromeasures PDF
Unit 2.macromeasures PDF
Uploaded by
Gwyneth MalagaCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 2.
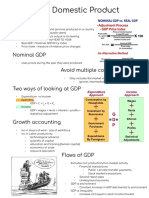
Macro Measures Add up all the spending on final goods
and services produced in a given year
3 Major Economic Goals
GDP= C + I + G + (X-M)
1. Promote economic growth
2. Limit unemployment 2. Income approach
Add up all income that resulted from
selling all final goods and services
GDP
produced in a year
dollar value of all final goods and
GDP= Rent + Wages + Interets + FP
services
anything produced by the country
Kinds of GDP
1. Nominal
GDP per capita
GDP measured in current prices
divided by population
Not account for inflation from year to
identifies how much each person year
make
2. Real
%Change in GDP = ( x 100
best measure of economic growth
GDP expressed in constant or
Not included in GDP unchanging dollars
1. Intermediate Goods Adjusts for inflation
Good inside the product don’t repeat Best way to show us through business
cycle
Price of chip inside the computer
Inflation
1. Non-production transactions
Difference between peak and line
Financial transactions (nothing is
produced)
Stocks, bonds Unemployment
Used goods Difference between line and trough in
the curve
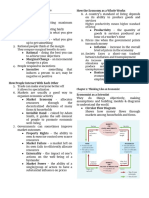
FULL EMPLOYMENT OUTPUT (Y)
2. Non-market transactions-
The Real GDP created when there is no
Black market cyclical unemployment.
Full employment
Drugs
Difference between GDP line and GDP
curve
Ways to Calculate GDP
Recession = contraction
1. Expenditure Approach
Recovery = expansion Caused recession
2. Limit unemployment Demand fails, demand for labor fails
and workers are fired
Unemployment
Goal is frictional and structural
Actively looking for a job but
unemployment. These two will always
unemployed
be between jobs or replaced by
Unemployment rate technology
Unemployed X 100 National Rate of Unemployment
labor force = Frictional + structural unemployment
Labor Force Exists when economy is healthy and
growing
No. of people willing and able to work
Real GDP
Labor Force Participation Rate
if there is no cyclical unemployment
% of population in the labor force
Criticisms of Unemployment rate
Three Types of Unemployment
UR can misdiagnose actual UR because of:
1. Frictional Employment
1. Discouraged workers
temporary unemployment or being
between jobs some people no longer looking for a
job and already given up
individuals are qualified workers with
transferable skills 2. Underemployed
wants more hours without equivalent
salary
Seasonal
-Type of frictional
Inflation
-due to time of year and nature of job
Reduce purchasing power
rising general level of prices
2. Structural Employment
each dollar of income will buy fewer
Changes in labor force make some goods than before
skills obsolete
Jobs that will never come back 3. Keep Prices stable
Workers must learn new skills to get a Unexpected inflation
job
helps borrowers
hurts lenders and people with fixed
Technological Unemployment income
-automation and machinery replace Nominal wage
human
measured by dollars rather than
purchasing power
3. Cyclical Unemployment Real wage
adjust for inflation
Nominal interest rate M- Money supply
percentage increase in money not V- Velocity
adjusting for inflation
P- Price level
real interest rate + inflation rate
Y- Quantity of output
Real interest rate
2. Demand-Pull inflation
increase in purchasing power
Demand pulls-up prices
real interest rate = inflation rate
Too many dollars chasing few goods
Real = nominal – expected inflation
Overheated economy with excessive
Consumer price index ( CPI) spending but same amount of goods
most commonly used measurement for
inflation for customers
3. Cost-Push Inflation
measures only goods bought by
customers Higher production costs - increases
prices
x 100 Negative Supply Shock
increases costs of production
forces producers to increase prices
GDP Deflator
measures all goods produced
domestically
Imported Goods
Not part of GDP
Don't show up in GDP deflator
Formula of GDP Deflator
GDP Deflator = x 100
3 Causes of Inflation
1. Government prints TOO MUCH money
(Quantity theory)
results to hyperinflation
•Quantity theory of money identity
MxV=PxY
You might also like
- Bank of BarodaDocument2 pagesBank of BarodaAdventurous Freak50% (2)
- IB Economics Glossary of TermsDocument43 pagesIB Economics Glossary of Termssamira2702100% (1)
- Decision Making GuideDocument27 pagesDecision Making GuideShan Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Macro-Economics To InflationDocument5 pagesMacro-Economics To InflationGwyneth MalagaNo ratings yet
- Econ CH 13Document6 pagesEcon CH 13James HaroldNo ratings yet
- Regardless of TheirDocument11 pagesRegardless of TheirTrisha Nicole BuendiaNo ratings yet
- 08 Business Cycles, Unemployment, InflationDocument3 pages08 Business Cycles, Unemployment, Inflationcatherine tucayNo ratings yet
- Chương 1:: GDP or Gross Domestic Product 4 PartsDocument9 pagesChương 1:: GDP or Gross Domestic Product 4 PartsChi Nguyễn Thị KimNo ratings yet
- (Econ) UnemploymentDocument10 pages(Econ) UnemploymentTricia KiethNo ratings yet
- ME Cheat Sheet For FinalDocument4 pagesME Cheat Sheet For Finalkaungwaiphyo89No ratings yet
- Measuring Employment and UnemploymentDocument2 pagesMeasuring Employment and UnemploymentMohammad A. HasanNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Unemployment Review To Have For Test Fall 2020Document1 page2.3 Unemployment Review To Have For Test Fall 2020Deshay WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Theme 5 Unemployment and InflationDocument19 pagesTheme 5 Unemployment and InflationNadineNo ratings yet
- Handout 1 - Measuring Employment and UnemploymentDocument2 pagesHandout 1 - Measuring Employment and UnemploymentJntNo ratings yet
- Ms20 - MacroeconomicsDocument2 pagesMs20 - MacroeconomicsSeokjin KimNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 GDDocument32 pagesLesson1 GDPeruQuantrillNo ratings yet
- Asis 2 PEDocument21 pagesAsis 2 PELovina AishaNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics NotesDocument20 pagesMacroeconomics NotesElsa PucciniNo ratings yet
- Guided Notes Unit 5 - Macroeconomics - Economic Challenges, GDP and Growth, and LaborDocument4 pagesGuided Notes Unit 5 - Macroeconomics - Economic Challenges, GDP and Growth, and LaborNicols FleurismaNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Suggestion (Sem 5)Document38 pagesMacroeconomics Suggestion (Sem 5)Vivaan BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Macro TopicsDocument30 pagesMacro TopicsThalisson RamiresNo ratings yet
- Define 2-3 Key Terms: 0 2 / 0 6 / 2 0 1 3 S Ta R Te RDocument43 pagesDefine 2-3 Key Terms: 0 2 / 0 6 / 2 0 1 3 S Ta R Te RJowana PenasoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document13 pagesChapter 9ffffffNo ratings yet
- 06 National Income AccountingDocument4 pages06 National Income Accountingcatherine tucayNo ratings yet
- Econ Review ProjectDocument5 pagesEcon Review ProjectNing GuangNo ratings yet
- Econ100.1 ReviewerDocument9 pagesEcon100.1 Revieweranon_571264294No ratings yet
- Theories of Employment and Income: Learning ObjectivesDocument35 pagesTheories of Employment and Income: Learning Objectivesmuhammedsadiq abdullaNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic University of The Philippines Macroeconomics Reviewer 2023Document12 pagesPolytechnic University of The Philippines Macroeconomics Reviewer 2023jeferson.ordonioNo ratings yet
- Theories of Employment and Income: Learning ObjectivesDocument15 pagesTheories of Employment and Income: Learning ObjectivesBabarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MacroeconomicsDocument6 pagesIntroduction To MacroeconomicsDayangku AyusapuraNo ratings yet
- Recession and Our RoleDocument35 pagesRecession and Our RoleRegina Sharon PalletiNo ratings yet
- Modern Labor Economics Chapter 2Document44 pagesModern Labor Economics Chapter 2As-Ad Arik AzadNo ratings yet
- ECON1102 Macroeconomics 1 CheatsheetDocument2 pagesECON1102 Macroeconomics 1 CheatsheetCarla MissionaNo ratings yet
- SV C28 UnemploymentDocument6 pagesSV C28 UnemploymentphươngNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Economic Indicators and MacroeconomicsDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Economic Indicators and MacroeconomicsAlex KohNo ratings yet
- Unemployment & Inflation: Developed By: Pup CSSD Department of EconomicsDocument7 pagesUnemployment & Inflation: Developed By: Pup CSSD Department of EconomicsMarcus MonocayNo ratings yet
- Econ Dev - Part C.2Document7 pagesEcon Dev - Part C.2Darryl LabradorNo ratings yet
- (Lecture 8.2) Chapter 12 Unemployment and Inflation (L8 - 2)Document21 pages(Lecture 8.2) Chapter 12 Unemployment and Inflation (L8 - 2)Chen Yee KhooNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Outline For Economic Concepts and TheoryDocument4 pagesComprehensive Outline For Economic Concepts and TheorycerapyaNo ratings yet
- Higher Productivity Means Higher Standard of Living: Chapter 1: Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument4 pagesHigher Productivity Means Higher Standard of Living: Chapter 1: Ten Principles of EconomicsCristina Crong MorgiaNo ratings yet
- SSM107 Lec#1 MidtermDocument5 pagesSSM107 Lec#1 MidtermMa. Krecia NicolNo ratings yet
- Intro To Macroeconomics and GDP Problem Set Answer KeyDocument5 pagesIntro To Macroeconomics and GDP Problem Set Answer KeySid JhaNo ratings yet
- Student Management SystemDocument279 pagesStudent Management System15257-Mohammed AL NomanNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Outline For Economic Concepts and TheoryDocument9 pagesComprehensive Outline For Economic Concepts and TheorycerapyaNo ratings yet
- Cosc 104Document13 pagesCosc 104Joseph KuriaNo ratings yet
- Important Basics of EconomyDocument4 pagesImportant Basics of EconomyRamana ReddyNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics PrelimDocument8 pagesApplied Economics PrelimRylyn IsabelNo ratings yet
- Indian Eco Dev 2Document11 pagesIndian Eco Dev 2Badavath JeethendraNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics 6th Edition Williamson Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesMacroeconomics 6th Edition Williamson Solutions Manualfagotbouge3q7x97% (29)
- Econ-Additional ReviewerDocument2 pagesEcon-Additional ReviewerCzarina Castillo CompleNo ratings yet
- Basic Economics With Taxation and Agrarian Reform: Dr. Vicente S. Betarmos, JRDocument6 pagesBasic Economics With Taxation and Agrarian Reform: Dr. Vicente S. Betarmos, JRPlatero RolandNo ratings yet
- Unemployment and InflationDocument45 pagesUnemployment and InflationFoni NancyNo ratings yet
- TUT 1: Measuring A Nation's Income: No Word Key Word EconomicDocument22 pagesTUT 1: Measuring A Nation's Income: No Word Key Word EconomicKim Ngọc HuyềnNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Lecture Chapter 10 GDP ComponentsDocument10 pagesMacroeconomics Lecture Chapter 10 GDP ComponentsDX 1No ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument12 pagesMeasurementRachit BhagatNo ratings yet
- Econ 214 MACRO NotesDocument48 pagesEcon 214 MACRO NotesebtreherneNo ratings yet
- Beco 2301 Macro l6 SV Ad-As Model p1Document24 pagesBeco 2301 Macro l6 SV Ad-As Model p1Ahmed MousaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document60 pagesChapter 4oakleyhouNo ratings yet
- Felicia Irene Week 10Document15 pagesFelicia Irene Week 10felicia ireneNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Note (2102)Document6 pagesMacroeconomics Note (2102)Mahmudul hasanNo ratings yet
- Working Paper EntriesDocument2 pagesWorking Paper EntriesRixer PrietoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Bulacan State University City of Malolos, Bulacan Office of The Dean of InstructionDocument8 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Bulacan State University City of Malolos, Bulacan Office of The Dean of InstructionTheresa RoqueNo ratings yet
- 1 RR 7-2009Document5 pages1 RR 7-2009JoyceNo ratings yet
- Statement 600606 35438479 2 11 2022 1 12 2022Document1 pageStatement 600606 35438479 2 11 2022 1 12 2022Orhan DagdelenNo ratings yet
- Accounting ElementsDocument21 pagesAccounting Elementsdemonking1273433No ratings yet
- EC3314 Spring PSet 4 SolutionsDocument6 pagesEC3314 Spring PSet 4 Solutionschristina0107No ratings yet
- LAW Partnership Act 1932Document10 pagesLAW Partnership Act 1932ritesh2030No ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Heirs of Sps Maglasang V Manila Banking Corp PRDocument4 pagesToaz - Info Heirs of Sps Maglasang V Manila Banking Corp PRJimi SolomonNo ratings yet
- History of Banking in The PhilippinesDocument18 pagesHistory of Banking in The PhilippinesJohn Carmelo Apilado100% (10)
- Insolvency & Bankruptcy Code, 2016Document23 pagesInsolvency & Bankruptcy Code, 2016Jeswin JohnNo ratings yet
- Revised Bharat Kosh Refund FormDocument2 pagesRevised Bharat Kosh Refund Formrd meshramNo ratings yet
- Financial Education For Working Executives: An Initiative of SEBI & NISMDocument31 pagesFinancial Education For Working Executives: An Initiative of SEBI & NISMkalirajgurusamyNo ratings yet
- Financial AccountingDocument16 pagesFinancial Accountinggarg19118No ratings yet
- BZ Payroll Slip OKT 2023-UnlockedDocument1 pageBZ Payroll Slip OKT 2023-UnlockedWidha AgustriaNo ratings yet
- Problem 2-24: © The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2010. All Rights Reserved. Solutions Manual, Chapter 2 51Document2 pagesProblem 2-24: © The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2010. All Rights Reserved. Solutions Manual, Chapter 2 51Rizky Wahyu FebriyantoNo ratings yet
- Problemas Cap 12Document5 pagesProblemas Cap 12angel guarinNo ratings yet
- Forensic Accounting in India: Problems in Detecting FraudDocument4 pagesForensic Accounting in India: Problems in Detecting FraudInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document13 pagesChapter 6ERICKA MAE NATONo ratings yet
- The Following Selected Transactions Were Completed by InterstateDocument1 pageThe Following Selected Transactions Were Completed by InterstateM Bilal SaleemNo ratings yet
- 12 BibliographyDocument8 pages12 BibliographyMotiram paudelNo ratings yet
- Strategy Tester - TAIGUNDocument90 pagesStrategy Tester - TAIGUNTeamJunTradeezNo ratings yet
- Text ResumeDocument2 pagesText Resumedilip504100% (1)
- Determinants of Financial Reporting Quality in United KingdomDocument46 pagesDeterminants of Financial Reporting Quality in United KingdomKareemEl'Bendary100% (1)
- LIC's JEEVAN VAIBHAV (UIN: 512N269V01)Document2 pagesLIC's JEEVAN VAIBHAV (UIN: 512N269V01)Sri Ram SahooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Role of GovernmentDocument21 pagesChapter 13 Role of GovernmentMuhammad Zarif IshakNo ratings yet
- IIMA Placement BrochureDocument60 pagesIIMA Placement BrochureVignesh SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Health Ensure Floater - Policy Schedule: Proposer DetailsDocument3 pagesHealth Ensure Floater - Policy Schedule: Proposer DetailsValand NileshNo ratings yet
- Account Statement: Description DateDocument3 pagesAccount Statement: Description DatevinuNo ratings yet