Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cataract Surgery/ Phacoemulsification: Prepared By: Heinstein Marc C. Amparado
Cataract Surgery/ Phacoemulsification: Prepared By: Heinstein Marc C. Amparado
Uploaded by
NYENYEOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cataract Surgery/ Phacoemulsification: Prepared By: Heinstein Marc C. Amparado
Cataract Surgery/ Phacoemulsification: Prepared By: Heinstein Marc C. Amparado
Uploaded by
NYENYECopyright:
Available Formats
Cataract Surgery/ Phacoemulsification
Prepared by: Heinstein Marc C. Amparado
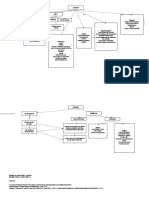
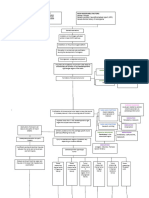
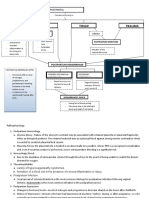
Excessive Systemic Ocular Disease
Age > 45 Genetic exposure to UV Diseases
Signs and
symptoms
Risk Factors years old light, radiation and
toxins
Complications Pathophysiology Retinitis pigmentosa,
Hexokinase Previous Ocular Myotonic dystrophy, uveitis, high myopia,
concentration Surgery Abnormal Diabetes mellitus atopic dermatitis, hereditary fundus
Medical structural changes
Types decreases Wilson's Disease dystrophies.
Management
to lens crystalline
protein
Nursing Diagnostics
Management
ATP level drops Trauma: Increase glucose in
aqueous humour
Blunt or eye injury, Stiffening, that diffuses into
chemical burn, pigmentation and lens
Nursing
Poor electrolye electrocution. increased density of
diagnosis
balance control lens material
Second osmotic
over-hydration of
Cataract Is the clouding of the lens lens
or any opacity within the lenswhich Equatorial stretching and
leads to decrease of vision. Massive influx of lens capsule damage.
water in the lens
Cataract Surgery?Isdone in order to
remove the lens of the eye that
causes a vision to be blurry, in some
Disorganization
cases it is replaced with artificial lens. of structured
protein in the
lens Opacification of
crystalline lens
Aggregation and
precipitation of
protein. Formation of Cataract
Posterior Subcapsular
Nuclear Cataract Cortical Cataract Congenital Cataract
Cataract
Natural lens slowly
loss its transparency Blurred Vision
Visual Acuity Test
Decreased Contrast
Hardening of cental Sensitivity
lens nucleus
Nearsightedness
Glare and halos
around lights Lights starts to scatter
Lens of the eye Surgical Intervention:
Retinal Exam
becomes milky Phacoemulsification
·Anxiety related to possibility
of loss of vision as Risk for injury related ·Risk for infection related
evidenced by expressed to invasive surgical to surgical procedure
concern regarding changes procedure (Phacoemulsification).
in life events.
-Instruct the patient to
-Provide accurate, honest -Make sure to check
wear glasses during the
information. Discuss the OR equipments
are on its best day and wear eye
probability that careful
treatment can prevent function. protection at night.
further loss of vision. -Assist the surgeon -Give eye drops / eye
-Assess anxiety level and on providing the ointment suitable doctor
degree of knowledge of exact equipments advice.
condition. used for the -Advise the patient not to
-provide mental relaxation procedure. rub the eyes to prevent
techniques as well as -Position OR lights on
infection.
support involving elements the area the surgeon
will be working . -Instruct client to wash
of religious.
hands before applying eye
ointment/drops.
You might also like
- FINAL EXAM Advanced Health Assessment and Diagnostic ReasoningDocument15 pagesFINAL EXAM Advanced Health Assessment and Diagnostic ReasoningGeorge Ekai100% (2)
- How To Survive Hospital StayDocument38 pagesHow To Survive Hospital StayLaurentiu M.No ratings yet
- Gender and Body Hair Constructing The Feminine WomanDocument12 pagesGender and Body Hair Constructing The Feminine Womaninfected mushroomNo ratings yet
- Nagle Notes On PharmacologyDocument263 pagesNagle Notes On PharmacologyrelyessNo ratings yet
- The Feasibility of Using Hibiscus RosaDocument20 pagesThe Feasibility of Using Hibiscus RosaChristianjames DiamanteNo ratings yet
- Seminar ActivityDocument2 pagesSeminar ActivityStephen YorNo ratings yet
- The Little Black Book of Ecg Secrets PDFDocument12 pagesThe Little Black Book of Ecg Secrets PDFamaandreiNo ratings yet
- Cataract Week 13Document9 pagesCataract Week 13Janselle H ArmaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map CATARACTDocument2 pagesConcept Map CATARACTJrBong Semanero100% (1)
- Jpaquit Patho For CataractDocument4 pagesJpaquit Patho For CataractJon Gab PaquitNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Primary Cataract: Saint Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing S.Y. 2021-2022Document3 pagesPathophysiology of Primary Cataract: Saint Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing S.Y. 2021-2022zoie ziazzetteNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Primary Cataract: Saint Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing S.Y. 2021-2022Document3 pagesPathophysiology of Primary Cataract: Saint Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing S.Y. 2021-2022zoie ziazzetteNo ratings yet
- Occupational Hazards in Dental, Textile Industry and MechanicDocument20 pagesOccupational Hazards in Dental, Textile Industry and MechanicimtahifNo ratings yet
- Retinal Detachment: Traction Retinal Detachment Rhegmatogenous Detachment Exudative/Serous Retinal DetachmentDocument3 pagesRetinal Detachment: Traction Retinal Detachment Rhegmatogenous Detachment Exudative/Serous Retinal DetachmentJordz Placi100% (1)
- (Ophtha) Ocular Emergenices - Dr. VillalvaDocument6 pages(Ophtha) Ocular Emergenices - Dr. VillalvaPatricia ManaliliNo ratings yet
- Cataract Cataracts CataractDocument6 pagesCataract Cataracts Cataractta CNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade Maths 3Document1 page6th Grade Maths 3Khofifah Suci ANo ratings yet
- Lens and Cataract Group 7Document66 pagesLens and Cataract Group 7Symon MillarNo ratings yet
- Materi Bimbingan Kepaniteraan Klinik Ilmu Penyakit Mata: No Pembimbing Topik Sub TopikDocument2 pagesMateri Bimbingan Kepaniteraan Klinik Ilmu Penyakit Mata: No Pembimbing Topik Sub TopikRizka ChairaniNo ratings yet
- Type and Cause Refractive ErrorDocument7 pagesType and Cause Refractive ErrorShi YingNo ratings yet
- Red EyeDocument54 pagesRed EyeT786 kharNo ratings yet
- Ophtha ReviewerDocument3 pagesOphtha ReviewerToni Sy EncinaresNo ratings yet
- CataractDocument24 pagesCataractNeela Kandan100% (1)
- Disorders of The EyeDocument15 pagesDisorders of The EyeVinz Khyl G. Castillon100% (2)
- NCM 116 Lect Visual PerceptionDocument45 pagesNCM 116 Lect Visual PerceptionMariano MarbellaNo ratings yet
- Corneal Dystrophies: Retinal DetachmentDocument5 pagesCorneal Dystrophies: Retinal DetachmentCake ManNo ratings yet
- GLAUCOMA Revised Concept MapDocument5 pagesGLAUCOMA Revised Concept MapJanselle H ArmaNo ratings yet
- EYE Checklist by Dr. AnushDocument3 pagesEYE Checklist by Dr. AnushTemplifyITNo ratings yet
- E-Book Ophthalmology Referral Guide For GPsDocument11 pagesE-Book Ophthalmology Referral Guide For GPsnaravichandran3662No ratings yet
- Disease Cheat SheetDocument393 pagesDisease Cheat Sheetsurviving nursing school50% (2)
- Science Newspaper ArticleDocument4 pagesScience Newspaper ArticleLyndon AciertoNo ratings yet
- Case Bacterial MeningitisDocument29 pagesCase Bacterial MeningitisMika SaldanaNo ratings yet
- Retinal Detachment: Jama Patient PageDocument1 pageRetinal Detachment: Jama Patient PageKemal TaufikNo ratings yet
- Complications DiabetesDocument5 pagesComplications DiabetesMicah James MaravillasNo ratings yet
- Ocular Emergencies-Sept2013 PDFDocument22 pagesOcular Emergencies-Sept2013 PDFKaramsi Gopinath NaikNo ratings yet
- Science Daily Newspaper: GlaucomaDocument4 pagesScience Daily Newspaper: GlaucomaLyndon AciertoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Eye Health GuideDocument24 pagesDiabetes Eye Health GuideAnh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Corneal Dystrophy and Keratoconus Concept Map/ PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesCorneal Dystrophy and Keratoconus Concept Map/ PathophysiologyBadgal BazingaNo ratings yet
- Corneal Dystrophies: Retinal DetachmentDocument6 pagesCorneal Dystrophies: Retinal DetachmentMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- Medical History Taking Project Ppt-Converted NoDocument17 pagesMedical History Taking Project Ppt-Converted Noabdul qayyumNo ratings yet
- Aphakia and Ectopia LentisDocument34 pagesAphakia and Ectopia LentisMaham RehmanNo ratings yet
- ติว NL2 ปี 5 2022 outlineDocument49 pagesติว NL2 ปี 5 2022 outlineSugus PichayaNo ratings yet
- Red-Eye - Vanilla DrJAMDocument40 pagesRed-Eye - Vanilla DrJAMDr J A M “JAYGOUR”No ratings yet
- Corneoscleral Laceration Differential DiagnosesDocument1 pageCorneoscleral Laceration Differential DiagnosesPuddingNo ratings yet
- Sensory Perception System EnglishDocument10 pagesSensory Perception System EnglishDian WalineloNo ratings yet
- Eyes Lecture 2Document4 pagesEyes Lecture 2Rue Cheng MaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology (Final 1)Document3 pagesPathophysiology (Final 1)Clarence BravioNo ratings yet
- About The Authors: Lai Ling TanDocument12 pagesAbout The Authors: Lai Ling TanStrawberry ShortcakeNo ratings yet
- Uw - Elseby Notes PediatricsDocument218 pagesUw - Elseby Notes PediatricsIvy QueenNo ratings yet
- Sensory Perception System: Group 9Document10 pagesSensory Perception System: Group 9Dian WalineloNo ratings yet
- The Eye VisionDocument7 pagesThe Eye VisionJean ReyesNo ratings yet
- Bhavna, M Optom, FASCO. Faculty, Sankara College of Optometry, BangaloreDocument9 pagesBhavna, M Optom, FASCO. Faculty, Sankara College of Optometry, BangaloreBHUVANANo ratings yet
- Epithelial Skin Tumor Poster 2Document1 pageEpithelial Skin Tumor Poster 2Htet Htet AungNo ratings yet
- Retinitis Pigmentosa HandoutDocument1 pageRetinitis Pigmentosa Handoutskeleronnn14No ratings yet
- Dry Eye DiseaseDocument8 pagesDry Eye DiseaseaNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis, Clinical Features and Management of Recurrent Corneal ErosionsDocument10 pagesPathogenesis, Clinical Features and Management of Recurrent Corneal Erosionsyoan rahmahNo ratings yet
- CataractsDocument2 pagesCataractsKevin EndravianNo ratings yet
- Eor CataractDocument3 pagesEor CataractDaneva ReyesNo ratings yet
- Gel OftalmicDocument38 pagesGel OftalmicDiana LeonNo ratings yet
- Retinal Vein Occlusion Concept MapDocument2 pagesRetinal Vein Occlusion Concept MapJoe RealNo ratings yet
- Ambasan, Eg (Bsn3a) - Age-Related Macular DegenerationDocument1 pageAmbasan, Eg (Bsn3a) - Age-Related Macular DegenerationEllen Grace AmbasanNo ratings yet
- Paralisis FacialDocument25 pagesParalisis FacialItzel Estephany ANo ratings yet
- 2021-Conrady Et Al-Ocular Drug Delivery For Uveitis Pharmaceutics-13-01224-V2Document17 pages2021-Conrady Et Al-Ocular Drug Delivery For Uveitis Pharmaceutics-13-01224-V2Richard GabrielNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study (Open Glaucoma)Document4 pagesDrug-Study (Open Glaucoma)aliannaNo ratings yet
- Ocular Chemical Burns From Accidental Exposure To.28Document2 pagesOcular Chemical Burns From Accidental Exposure To.28qalbiNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Eye: Presbyo PiaDocument16 pagesDisorders of The Eye: Presbyo PiaPadmavathi CNo ratings yet
- Thrombosis Tone Tissue Trauma: Postpartal ComplicationsDocument6 pagesThrombosis Tone Tissue Trauma: Postpartal ComplicationsNYENYENo ratings yet
- Paper Work No. 2: Curriculum and Assessment For Physical Education and Health EducationDocument5 pagesPaper Work No. 2: Curriculum and Assessment For Physical Education and Health EducationNYENYENo ratings yet
- Heinstein Marc C. Amparado November 20, 2020 BSN III-C2 Asst. Prof Kathleah CaluscusanDocument2 pagesHeinstein Marc C. Amparado November 20, 2020 BSN III-C2 Asst. Prof Kathleah CaluscusanNYENYENo ratings yet
- John Clienton B. Babor: Career Objec VeDocument3 pagesJohn Clienton B. Babor: Career Objec VeNYENYENo ratings yet
- Silliman University Dumaguete City: SY 2020-2021 College of NursingDocument14 pagesSilliman University Dumaguete City: SY 2020-2021 College of NursingNYENYENo ratings yet
- Ward Class in Myasthenia GravisDocument17 pagesWard Class in Myasthenia GravisNYENYENo ratings yet
- Ecological ProjectDocument2 pagesEcological ProjectNYENYENo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper On "Flatten The Curve... "Document1 pageReflection Paper On "Flatten The Curve... "NYENYENo ratings yet
- World Obesity Atlas 2023 ReportDocument232 pagesWorld Obesity Atlas 2023 ReportVozMediaNo ratings yet
- Werner Mork: Excerpts From The Memoirs ofDocument21 pagesWerner Mork: Excerpts From The Memoirs ofnorman0303No ratings yet
- Preterm Labor Case AnalysisDocument2 pagesPreterm Labor Case AnalysisJOPAR JOSE C. RAMOSNo ratings yet
- Wildlife Fact File - Mammals Pgs. 301-310Document20 pagesWildlife Fact File - Mammals Pgs. 301-310ClearMind84100% (1)
- Review Article: Cluster Headache-Acute and Prophylactic TherapyDocument24 pagesReview Article: Cluster Headache-Acute and Prophylactic TherapyPurna Adi PutraNo ratings yet
- 13 Approved Herbal Plants From DOHDocument2 pages13 Approved Herbal Plants From DOHRIK HAROLD GATPANDANNo ratings yet
- 23 and MeDocument17 pages23 and Mewilliam919No ratings yet
- CI M Chapter12Document15 pagesCI M Chapter12Silvio FaveroNo ratings yet
- Pudina MintDocument10 pagesPudina MintjunaidNo ratings yet
- Warm Muscles Before Exercisestretch Out Stretchtire Out ExhaustmusclesDocument1 pageWarm Muscles Before Exercisestretch Out Stretchtire Out Exhaustmuscleskarla duarteNo ratings yet
- 12 Aerobic Gram-Positive BacilliDocument68 pages12 Aerobic Gram-Positive BacilliClarence SantosNo ratings yet
- PORNOGRAPHYDocument3 pagesPORNOGRAPHYFaizan KhalidNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cancer Antigen (Ca-125) : Enzyme Immunoassay Test Kit Catalog Number: 10103Document2 pagesOvarian Cancer Antigen (Ca-125) : Enzyme Immunoassay Test Kit Catalog Number: 10103yousrazeidan1979No ratings yet
- Dementia and COVID-19 Lockdown More Than A Double Blow For Patients and CaregiversDocument5 pagesDementia and COVID-19 Lockdown More Than A Double Blow For Patients and CaregiversIraNo ratings yet
- DoH BP Leaflet - Web VersionDocument2 pagesDoH BP Leaflet - Web Versionpatburchall6278No ratings yet
- OB-assessment OutputDocument14 pagesOB-assessment OutputKaren TangNo ratings yet
- Fatal Vision GogglesDocument26 pagesFatal Vision Gogglesapi-282144674No ratings yet
- PAMI Pain Mangement and Dosing Guide 02282017Document2 pagesPAMI Pain Mangement and Dosing Guide 02282017Hawsin100% (1)
- Jurnal GadarDocument10 pagesJurnal GadarRiandini PandansariNo ratings yet
- CarcinogenDocument196 pagesCarcinogenJosé RamírezNo ratings yet
- Chagas DiseaseDocument6 pagesChagas DiseaseFranciscoNo ratings yet
- Definition of JVPDocument16 pagesDefinition of JVPMimi ChukwuNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR) - The... Download Scientific DiagramDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR) - The... Download Scientific DiagramNajla As'ariNo ratings yet