Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter One: Acids Bases and Salts
Chapter One: Acids Bases and Salts
Uploaded by
subeer ismailOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter One: Acids Bases and Salts
Chapter One: Acids Bases and Salts
Uploaded by
subeer ismailCopyright:
Available Formats
AIDAM COLLEGE
AIDAM COLLEGE
CHEMISTRY
Chapter One: Acids Bases and Salts
1.1 Acids:
• An acid is the any substance which has sour taste.
• An acid is the covalent compound that contain hydrogen as a common element
• An acid is the substance that react with bases to produce salt and water.
1.1.1Arhenius Theory of Acid
An acid: is the any substance that dissolve with water to produce hydrogen ions.
for example:
In the reaction above hydrochloric acid dissolves in water to form hydrogen ions and chloride ions.in this
reaction the molecule decomposes completely in water forming ions.
HCl + H2O=H++Cl-
1.1.2Bronsted and Lowry of Acid
An acid is the any species that donate protons to another species in proton transfer reactions this is
called Bronsted and Lowry theory .According to this theory acids donate protons to the other substance
that is a base so acid is a proton doner.
Examples of acids:
The following substances are acids:
Name of the Acid Formula Where it is found
Hydrochloric acid HCl Stomach
Carbonic acid H2C03 Soure Drinks
Sulphuric acid H2SO4 Car batteries
Nitric acid HNO3 As fertilizers
Ascorbic acid C6H8O6 Vegetable
Citric acid C6H8O7 Lemon Juice
Lactic acid C3H6O3 Sour milk
Tannic acid C76H52O46 Tea leaf
PRE. ENG AHMED ABDI AADAN 1
AIDAM COLLEGE
AIDAM COLLEGE
CHEMISTRY
1.1.3PROPERTIES OF ACIDS
Acids have the following properties:
Acids have sour taste.
Acids turn blue litmus to red.
Acids react with bases forming salt and water.
Acids are good conductors of electricity.
They have PH less than with 7.
They are soluble in water.
They neutralizes alkalis.
1.1.4Classification of Acid :
Acids are classified into 10 many ways the most important ways are :
Classification of acids according to their sources :
Organic Acids: are acids from living things
E.g= Acids from Vinegar, Bee string, Apple, Orange , tomatoes etc.
In organic Acids: are acids from non-living things
E.g= Acids from car batteries, soft drinks and the all acids manufactured in the lab
Classification of acids according to their Basicity:
Mono basic: acids that contain one H+ ion per one molecule of acid.
E.g= HCl, HNO3 , HBr , HI , HF etc.
Di basic: acids that contain two H+ ions per one molecule of acid.
E.g= H2SO4, H2CO3 etc.
Tri basic: acids that contain three H+ ions per one molecule of acid.
E.g= H3PO4 , CH3COOH , H3COOH etc.
NOTE
Basicity of the acid : is the amount of ionisable hydrogen present with one
molecule of that acid.
Classification of acids according to their amount of water dissolved in acid:
Concentrated Acid: are acids that have high percentage of acid and low percentage of
water in their solution.
PRE. ENG AHMED ABDI AADAN 2
AIDAM COLLEGE
AIDAM COLLEGE
CHEMISTRY
Dilute Acid: are acids that have low percentage of acid and high percentage of water in
their solution.
NOTE
Dilution : is the process that that concentrated acids changed into dilute.
Classification of acids according to their number of proton donnated:
Mono protic Acid.
Di protic Acid.
Tri protic Acid.
Classification of acids according to their strength:
STRONG ACIDS
Acids that dissolve in water to produce hydrogen ions which are positive ions .In this process all the
molecule of an acid dissolves completely or partialy to form ions .The relative strength of an acid
depends the amount of hydrogen ions dissociated that acid in water.
Acids whose dissociated completely in water to form ions are called strong acids.
In strong acids all the molecule of a acid breaks down to forms hydrogen ions. when strong acids
dissolve with water they produce more ions.
examples of strong acids are:
• Nitric acid : HNO3
• hydrochloric acid : HCl
• sulphuric acid: H2SO4
HYDRONIUM ION : is the saturated ion of hydrogen in water.
The more hydrogen ions as there are in solution the more acidic it is and the lower the PH number.
PROPERTIES OF STRONG ACIDS:
1.They have pH number lower than 4.
2.They neutralize alkalis.
3.They are very corrosive.
PRE. ENG AHMED ABDI AADAN 3
AIDAM COLLEGE
AIDAM COLLEGE
CHEMISTRY
4.They are strong electrolytes.
5.They produce more hydrogen ions.
6.They are mostly mineral acids.
WEAK ACIDS
Acids whose do not completely dissolve in water are called weak acids.
In weak acids the part of the molecule dissolves in water but not at all. Weak acids produce less amount
of hydrogen ions in water .This is because of they partially Ionised.
1.1.5 REACTIONS OF ACIDS
Acids react with different substances in different proceses to produce different new susbtsances.
for example:
REACTION ON METALS
Acids react with metals to produce salt and hydrogen gas. when ever acids react with metals the
products or new substances formed during the chemical reaction are salt and hydrogen gas don’t
forget.
ACID + METAL = SALT + HYDROGEN.
ACID + IN SOLUBLE BASE = SALT +WATER.
ACID + SOLUBLE BASE= SALT + WATER NEUTRAL.
ACID + CARBONATES = SALT +WATER +CARBON DIOXIDE.
1.2 BASE
1.2.1 Definition of Base:
o Substance that have bitter taste.
PRE. ENG AHMED ABDI AADAN 4
AIDAM COLLEGE
AIDAM COLLEGE
CHEMISTRY
o Any substance that react with acids to produce salt and water.
o Any substance that receives protons in proton transfer chemical reactions.
Bases always exist in the form of:
• Metal oxides.
• Metal hydroxide.
• Metal carbonates.
• Metal hydrogen carbonates.
• Ammonia.
EXAMPLES OF BASES :
Sodium oxide,
potasium hydroxide,
lithium carbonate
ammonium hydroxide
sodium hydrogen carbonate.
ETC
Bases are type of chemical compounds.
All bases are ionic compounds except ammonia which is alkaline gas.
1.2.2 TYPES OF BASES:
There are two types of bases :
INSOLUBLE BASE:
A base that do not dissolves in water is called insoluble base .for example copper oxide is a base but it
does not dissolve in water.
PRE. ENG AHMED ABDI AADAN 5
AIDAM COLLEGE
AIDAM COLLEGE
CHEMISTRY
SOLUBLE BASE:
A base that dissolves in water is called soluble base. for example sodium hydroxide.
the typical base that dissolves in water is all called alkali or alkali is the family name of soluble. other
• A base that dissolves in water to produce hydroxide ion is called soluble base.
a compound that contain hydroxide ions is a base.
TYPES OF SOLUBLE BASE
There are two types of soluble base which are:
A) Strong soluble base:
Asoluble base that produce more amount of hydroxide ions when dissolves in water is called strong
base. strong base means strong alkali .strong bases can neutralize with acids.strong bases solution of
strong bases contain OH ions. examples of strong bases are:
• Natarium hydroxide.
• kalium hydroxide.
• lithium hydroxide.
• calcium hydroxide.
• when these bases dissolve in water all the compound decomposes to form ions which are positive ions
formed from metals and OH negative ions.
• the more OH ions there are in a solution the more alkaline it is and the greater the pH number.
B)weak soluble base:
Weak soluble base: is the base that gives up less amount of OH ions when dissolve in water. the
molecule of a weak base does not completely dissolve in water.
this means no more OH ions.the solution of weak bases contain less OH ions. An example of weak base
is ammonia.
1.2.3properties of alkalis:
PRE. ENG AHMED ABDI AADAN 6
AIDAM COLLEGE
AIDAM COLLEGE
CHEMISTRY
1.have bitter taste.
2.Turn litmus to blue.
3.Have a pH number greater than 7.
4.Neutralisez with acids.
5.Alkalis react with ammonium compounds driving it out.
SALTS:
1.3.1 Definition of Salt :
Salt : is the solid compound that formed when metal ions or ammonium ions take the position of
hydrogen in the acid.
salt is the substance that formed when metal ions or ammonium ions displace hydrogen from it( acid.
salts are generally classified in two soluble salts or insoluble salts.or salts dissolve in water and salts do
not dissolve in water.
1.3.5 Solubility rules :
1.all group one and ammonium compounds are soluble in water
2.all nitrate salts are soluble in water
3.all chloride salts are soluble in water except lead chloride and silver chloride
4.all sulphate salts are soluble in water except barium sulphate lead sulphate and calcium sulphate.
5.only group one and ammonium carbonate salts are soluble in water all other carbonates are insoluble
salts.
1.3.3 Preparation of soluble salts:
There are 4 general methods used to prepare soluble salts in the lab which are:
1. Action of acids on metals:
PRE. ENG AHMED ABDI AADAN 7
AIDAM COLLEGE
AIDAM COLLEGE
CHEMISTRY
This is direct combination chemical reaction that acids reacted with metals to form salt and hydrogen
gas. in this reaction metals take the position of hydrogen in the acid.
• more reactive metals are not used in this reaction with acids because it is very danger.
• less reactive metals are also exception because they cannot displace hydrogen in the acid
• mazit metals are suitable in this chemical reaction.
Example:
when magnesium is added a dilute solution of sulphuric acid the result is salt and hydrogen because of
magnesium displaces hydrogen from the acid.
magnesium +sulphuric acid = magnesium sulphate + hydrogen gas
zinc + hydrochloric acid : zinc chloride +hydrogen
2. Action of acids on insoluble base:
when acids react with insoluble base the product is water and salt.
for example: copper oxide is added with sulphuric acid and the product is copper sulphate and .water.
you can use any acid and bases with this reaction.
copper oxide + sulphuric acid = copper sulphate+ water..
The reaction is double displacement chemical reaction. copper ions attracted with sulphate ions while
hydrogen ions attracted with oxygen ions and the new substances formed are salt and water.
3. Action of acids on alkalis:
The reaction is neutralization chemical reaction when it takes place the product is normal salt and
water. in the reaction strong acids are added with strong alkalis
for example hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide the product is sodium chloride and water
because of sodium attracts with chloride ions and joined to gather to form salt while hydrogen and
hydroxide ions attract each other than joined to form a water.
PRE. ENG AHMED ABDI AADAN 8
AIDAM COLLEGE
AIDAM COLLEGE
CHEMISTRY
hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide= sodium chloride + water
4. Action of acids on carbonates:
acids react with metal carbonates to form salt, water and carbon dioxide
hydrochloric acid + sodium carbonates= sodium chloride + water + carbon dioxide.
1.3.4 Preparation of insoluble salts:
insoluble salts are prepared in the lab by the chemical reaction called precipitation reaction or methosis
reaction.
for example: a solution of magnesium chloride is added with barium sulphate and the product is two
types of salts which are soluble and insoluble reaction .in the precipitation reaction one of the products
is insoluble salt in in this reaction barium sulphate is insoluble salt.
magnesium sulphate + barium chloride= magnesium chloride + barium sulphate
1.3.2 Types of salts:
The salt is the substance formed in the direct displacemant or indirect displacement of hydrogen of an
acid from metals or ammonium ions. there are different types as following:
1.Acidic salt: is the salt formed when strong acids react with weak bases for example ammonium
chloride. sodium hydrogen carbonate, potassium hydrogen sulphate and magnesium hydrogen
carbonate are the salt that formed when only part of replaceable hydrogen are replaced.
2.Basic salt : is the salt formed when strong base reacted with weak acid.
3.Neutral salts : is the salt that formed when strong acids and strong bases reacted each other and
cancelled the typical properties of both substances. are the salts formed when all the replaceble
hydrogen ions of acids are replaced.
the end and the next chapter..
PRE. ENG AHMED ABDI AADAN 9
AIDAM COLLEGE
AIDAM COLLEGE
CHEMISTRY
1.4 NEUTRALISATION REACTION.
Is the reaction that bases react with acids .when this chemical reaction takes place the products are
neutral salt and water.
in the reaction bases contain OH- ions and acids contain H+ ions .This is because of when added both
each other the acidity and alkalinity destroyed . This reaction OH -and H+ ions attracted each other to
form a water .the typical properties of the substances are cancelled each of them
Note:
when neutralization reaction takes:
1.the pH of solution rises.
2.conductivity reaches it's lowest point when the reaction is completed.
3.the temperature of the solution rises.
1.5INDICATORS
Indicators are complex organic compound which changes color when is added both solution of an acid
or a base.
The common indicators are:
• Blue litmus which show red color of acids and blue color of bases
• Methyl organge shows pink color of acids and yellow color bases
• phenolphthalein shows colorless of acids and pink color of bases
• Blue litmus shows red color of acids and Red litmus shows blue color of bases.
1.6 PH SCAlE
PH is the measurement of power of Hydrogen ion concentration.
• Is the scale of numbers that is used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of solution
• is the measurement of acidity or alkalinity of solution
PRE. ENG AHMED ABDI AADAN 10
AIDAM COLLEGE
AIDAM COLLEGE
CHEMISTRY
• the scale runs from 0 to 14.
• acidic substances have pH number less than 7.
• basic substances have pH number greater than 7.
• neutral substances have pH number with 7.
Note: any substance is acidic ,basic or a neutral substance.for example water can be:
• neutral when they have equal concentrarion of H +
• acidic : more H+
• basic: more OH-ions than H+
PH CAlCULATION:
Example 1
1. What is the PH of a 0.01M solution of nitric acid?
Example 2
2. What is the PH of a water solution containing 0.001M?
Example 3
3. if the PH number of hydrochloric acid solution is 2 what is the concentration of hydrogen ions?
Example 4
if the POH of aqueos solution is 8 what is the ph of this solutio n?
1.7 POH SCALE
POH: is the measurement of power of hydroxide ion concentration.
PRE. ENG AHMED ABDI AADAN 11
AIDAM COLLEGE
AIDAM COLLEGE
CHEMISTRY
Example 1 :
what is the POH of a potassium hydroxide solution that contain 1+10'13 M of hydroxide ions?
Example 2:
if the POH number of solution of sodium hydroxide is 12 what is the hydrogen ion concentration of the
solution?
Example 3:
If the pH number of a solution is 2 what is the poH of this solution containing?
---------- Forwarded message ----------
From: Ahmed Abdi adan <aabdiadan167@gmail.com>
To: Subeeeism1234@gmail.com
Cc:
Bcc:
Date: Mon, 12 Oct 2020 20:33:49 +0300
Subject:
----- Message truncated -----
PRE. ENG AHMED ABDI AADAN 12
You might also like
- Chemistry of Silica - Ralph IlerDocument790 pagesChemistry of Silica - Ralph IlerKoko200793% (14)
- Homework Assgn. Lecture 4 PDFDocument2 pagesHomework Assgn. Lecture 4 PDFMinh MinhNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument7 pagesAcids and BasesM.zuhair asifNo ratings yet
- S.2 Chemistry NsDocument61 pagesS.2 Chemistry NsTUMUSIIME INNOCENTNo ratings yet
- O Level Chemistry Teaching Note: Acids, Bases and Salts Lesson Two Chemistry DepartmentDocument13 pagesO Level Chemistry Teaching Note: Acids, Bases and Salts Lesson Two Chemistry DepartmentEli JnrNo ratings yet
- O Level Chemistry Teaching Note: Acids, Bases and Salts Lesson Two Chemistry DepartmentDocument13 pagesO Level Chemistry Teaching Note: Acids, Bases and Salts Lesson Two Chemistry DepartmentEli JnrNo ratings yet
- Abs XDocument11 pagesAbs Xkarankumar8689783No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Acids, Bases and Salts: Class - X ScienceDocument14 pagesChapter 2 - Acids, Bases and Salts: Class - X ScienceDhruv AsodariaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Acid, Base and SaltsDocument16 pagesChemistry Acid, Base and Saltsnamanpareek84No ratings yet
- Acids, Bases & OxidesDocument22 pagesAcids, Bases & OxidesMustafa ghazanfarNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter NotesDocument192 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter NotesTarunNo ratings yet
- Acid, Base, and SaltDocument12 pagesAcid, Base, and SaltTamoghna DeyNo ratings yet
- O Level Chemistry Teaching Note: Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument13 pagesO Level Chemistry Teaching Note: Acids, Bases and SaltsEli JnrNo ratings yet
- Script For The Reporting in ChemDocument11 pagesScript For The Reporting in ChemJamaica SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Project On ChemistryDocument13 pagesProject On ChemistryBadhal PaudelNo ratings yet
- Class X Subject: Chemistry Chapter 2: Acids, Bases and Salts Following Notes Till Page No: 25 of Science NCERT BookDocument5 pagesClass X Subject: Chemistry Chapter 2: Acids, Bases and Salts Following Notes Till Page No: 25 of Science NCERT Bookashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Acids PropertiesDocument12 pagesAcids Propertieshuseynovagunel2004No ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 3 Revision NotesDocument5 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Chapter 3 Revision NotesAnn Maria ThomasNo ratings yet
- Chem 2 Q2 Week 3 BRONSTED ACID BASE For StudentsDocument13 pagesChem 2 Q2 Week 3 BRONSTED ACID BASE For StudentsVince Niño M. TuldaNo ratings yet
- Acids BasesDocument25 pagesAcids BasesNermin AkberovaNo ratings yet
- Acids,+Bases+&+Salts +vocabularyDocument19 pagesAcids,+Bases+&+Salts +vocabularyunknown33No ratings yet
- Project in Biology POWERPOINTDocument39 pagesProject in Biology POWERPOINTJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Acids - NotesDocument16 pagesAcids - Notesvarun puriNo ratings yet
- Acid Bases and SaltsDocument26 pagesAcid Bases and SaltsTracy ChangNo ratings yet
- Acids - Bases - Salts: Classes of CompoundsDocument32 pagesAcids - Bases - Salts: Classes of CompoundsBamz GeeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes: Acid Base and SaltsDocument2 pagesChemistry Notes: Acid Base and SaltsZain BadshahNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases&Salts NotesDocument12 pagesAcids Bases&Salts NotesAngelic Shine100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Acids, Bases and SaltsSmrita SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Acids, Bases and SaltsDileep Singh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument34 pagesAcids, Bases and SaltsV de VendettaNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases Chapter - A4 - v1Document27 pagesAcids and Bases Chapter - A4 - v1markmchemNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 2 Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument11 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 2 Acids, Bases and Saltsmilind dhamaniyaNo ratings yet
- 10 Chemistry - Acids, Bases and Salts - NotesDocument12 pages10 Chemistry - Acids, Bases and Salts - NotesaaravgggoswamiNo ratings yet
- 05 Acid Base and Redox 2009 IncDocument8 pages05 Acid Base and Redox 2009 Incapi-27085921No ratings yet
- CHM 101Document12 pagesCHM 101preciousoyibakporNo ratings yet
- Acid Base and SaltDocument15 pagesAcid Base and SaltMr. Sujan LamsalNo ratings yet
- ERT CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science ChemistryDocument8 pagesERT CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science ChemistryshanthaNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument25 pagesAcids, Bases and SaltsAnthonya KnightNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts Class10Document7 pagesAcids Bases and Salts Class10aanbalanNo ratings yet
- Chem Module Acid BaseDocument12 pagesChem Module Acid BaseRANJEET SHARMANo ratings yet
- Acids, Base and SaltsDocument20 pagesAcids, Base and SaltsTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 10Document29 pagesChemistry 10Javed QasimNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and SaltsDocument6 pagesAcids Bases and SaltsHanaa AbouziedNo ratings yet
- Notes Ch-Acids and Bases-1 - 240530 - 174138Document12 pagesNotes Ch-Acids and Bases-1 - 240530 - 174138Anjani RathoreNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Cellular CompoundsDocument2 pagesModule 2 Cellular CompoundsBonjour IgbalicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11.Document45 pagesChapter 11.HalaNo ratings yet
- Acid, Base and Salt at UNIDELDocument13 pagesAcid, Base and Salt at UNIDELFamous IteNo ratings yet
- Acids and Alkalis: Learning ObjectivesDocument23 pagesAcids and Alkalis: Learning ObjectivesOsmany MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument11 pagesAcids and BasesDarla GreyNo ratings yet
- Asm1 52315Document8 pagesAsm1 52315krishna.madhan2009No ratings yet
- X - SM - Sci - Acid Bases SaltsDocument14 pagesX - SM - Sci - Acid Bases SaltsKabir AroraNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases..Document5 pagesAcids and Bases..rachelNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases - An IntroductionDocument84 pagesAcids and Bases - An Introductionapi-239884728No ratings yet
- Acid Bases and SaltsDocument70 pagesAcid Bases and Saltscampbelltyesha4No ratings yet
- Chemistry: Acids, Bases & SaltsDocument3 pagesChemistry: Acids, Bases & SaltsSarvesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts (BBC Site)Document6 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts (BBC Site)Ramesh GoldbergNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts 3BDocument34 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts 3Bkesiangeorge07No ratings yet
- Plan 26Document2 pagesPlan 26api-19964534No ratings yet
- Acid and BasesDocument80 pagesAcid and BasesMenaga IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Soaps and Salts - Chemistry Book for Beginners | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Soaps and Salts - Chemistry Book for Beginners | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Biopolymers: R.M. Johnson, L.Y. Mwaikambo and N. TuckerDocument159 pagesBiopolymers: R.M. Johnson, L.Y. Mwaikambo and N. TuckerYasser BayoumiNo ratings yet
- The Nutritional Properties of Palm Oil: Professor Tom SandersDocument23 pagesThe Nutritional Properties of Palm Oil: Professor Tom Sandersghost2011No ratings yet
- Studies On The Detection and Spectrophotometric Determination of Organic Compounds and The Synthesis of A New Inorganic Ion-ExchangerDocument132 pagesStudies On The Detection and Spectrophotometric Determination of Organic Compounds and The Synthesis of A New Inorganic Ion-ExchangerSaif AnwarNo ratings yet
- Decompositions of Di-t-Alkyl Peroxides. I. Kinetics: Frederick F. EDocument7 pagesDecompositions of Di-t-Alkyl Peroxides. I. Kinetics: Frederick F. Emartinml_1191No ratings yet
- Chapter 17 StrawberryDocument11 pagesChapter 17 StrawberrycesarNo ratings yet
- A-L-Rhamnosyl-B-D-Glucosidase (Rutinosidase) From AspergillusDocument11 pagesA-L-Rhamnosyl-B-D-Glucosidase (Rutinosidase) From AspergilluskateNo ratings yet
- Anti Baldwin CyclizationDocument14 pagesAnti Baldwin CyclizationNguyễn Khánh PhươngNo ratings yet
- Chili Pepper Research StudiesDocument5 pagesChili Pepper Research StudiesSodiu ThoriumNo ratings yet
- Material SelectionDocument4 pagesMaterial SelectionSofwan JuewekNo ratings yet
- Psychedelic ChemistryDocument125 pagesPsychedelic ChemistryKathy LongressNo ratings yet
- Examples of Applicable Steels For Typical ProductsDocument1 pageExamples of Applicable Steels For Typical Productsapi-3848892No ratings yet
- Nomenclature For Organic Polymers: Robert B. Fox and Edward S. WilksDocument4 pagesNomenclature For Organic Polymers: Robert B. Fox and Edward S. WilksantonioNo ratings yet
- (Alfred Rudin (Auth.) ) Solutions Manual For The ElDocument61 pages(Alfred Rudin (Auth.) ) Solutions Manual For The ElMahmood KhanNo ratings yet
- Color ChemistryDocument15 pagesColor ChemistryZeeshan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Storage Tanks: Technical Guidance Package For: Hemical SourcesDocument57 pagesStorage Tanks: Technical Guidance Package For: Hemical SourcesMurali Muthu100% (1)
- Pyrolysis of Plastic Waste - Opportunities and ChallengesDocument17 pagesPyrolysis of Plastic Waste - Opportunities and Challengesgavin meadeNo ratings yet
- Overview of Standard WeightsDocument16 pagesOverview of Standard WeightsAnonymous 1gbsuaafddNo ratings yet
- LSCO. RSL 2020 - Highlights of ChangesDocument14 pagesLSCO. RSL 2020 - Highlights of ChangesDebashishDolonNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Handout - 1Document62 pagesCell Biology Handout - 1Dewi Lasimpara100% (1)
- Assignment-1 231111 210733Document3 pagesAssignment-1 231111 210733mamon137No ratings yet
- Biofumigation: A Potential Aspect For Suppression of Plant-Parasitic NematodesDocument7 pagesBiofumigation: A Potential Aspect For Suppression of Plant-Parasitic NematodesIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Vitamin A RM COADocument2 pagesVitamin A RM COAASHOK KUMAR LENKANo ratings yet
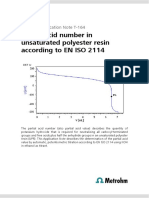
- Partial Acid Number in Unsaturated Polyester Resin According To EN ISO 2114Document2 pagesPartial Acid Number in Unsaturated Polyester Resin According To EN ISO 2114Mamoon ShahidNo ratings yet
- Afa HBSDD 0013 01 Aa enDocument117 pagesAfa HBSDD 0013 01 Aa enVictor CastrejonNo ratings yet
- QuimicaDocument422 pagesQuimicaVernon SandovalNo ratings yet
- Bossolani Et Al. - FPS - 2021 PDFDocument20 pagesBossolani Et Al. - FPS - 2021 PDFJoao William BossolaniNo ratings yet
- Stability of Vitamin C Derivatives in Solution and Topical FormulationsDocument7 pagesStability of Vitamin C Derivatives in Solution and Topical FormulationsBobbyGunarsoNo ratings yet
- Org Chem 6Document45 pagesOrg Chem 6tyron9520No ratings yet