Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aggabao Pharma Cholinergicdrugs PDF
Aggabao Pharma Cholinergicdrugs PDF
Uploaded by
Ivy Aggabao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageOriginal Title
AGGABAO-PHARMA-CHOLINERGICDRUGS.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageAggabao Pharma Cholinergicdrugs PDF
Aggabao Pharma Cholinergicdrugs PDF
Uploaded by
Ivy AggabaoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
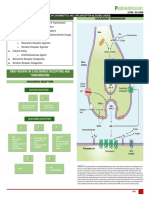
CHOLINOMIMETIC (CHOLINERGIC) DRUGS
DIRECT-ACTING INDIRECT ACTING
MUSCARINIC NICOTINIC ORGANOPHOSPHATE
S
Ex. Echothiophate
Ex. Nicotine
CHOLINE ESTER
Ex. Carbachol • IRREVERSIBLE ANTICHOLINESTERASE
• Ligand gated ion channel. • covalently binds via its phosphate group to
• Binds two ACh molecules elicits a the serine-OH group at the active site of
ALKALOID conformational change → allows the acetylcholinesterase→ enzyme is
Ex. Atropine entry of sodium ions → permanently inactivated.
depolarization of the effector cell → • Inhibits acetylcholinesterase for a longer
mediate fast excitatory synaptic duration
• binds to M1, M3, and M5 receptors
transmission.
→ activates the inositol
• Related in structure and sequence to
trisphosphatem (IP3), diacylglycerol
(DAG) cascade→ DAG open smooth
receptors of GABA, glycine, 5HT3, CARBAMATES
glutamate.
muscle calcium channels→IP3
releases calcium from endoplasmic Ex. Neostigmine
and sarcoplasmic reticulum→increase
cellular cGMP • MEDIUM DURATION ANTICHOLINESTERASE
concentration,→increases potassium • Increase the concentration of endogenous
flux across cardiac cell membranes acetylcholine at cholinoreceptors by inhibiting
and decreases it in ganglion and acetylcholinesterase.
smooth muscle cells→attenuate the • Undergoes two-step hydrolysis that allow
activation of adenylyl cyclase and covalent bond formation→ reversible
modulate the increase in cAMP levels carbamylation of acetylcholinesterase →
induced by hormones such as accumulation of acetylcholine.
catecholamines→reduce the • 30 mins-6 hrs
physiologic response of the organ to
stimulatory hormones.
•
EDROPHONIUM
Ex. Tensilon
• SHORT ACTING ANTICHOLINESTERASE
• Bind reversibly to the anionic active site of
AChE→ ionic bond formed→preventing
hydrolysis of ACh
• 10 to 20 minutes
SUBMITTED BY: AGGABAO. IVY
D.
You might also like
- Psychopharmacology Drugs, The Brain, and BehaviorDocument13 pagesPsychopharmacology Drugs, The Brain, and Behavior陳琮方5% (21)
- Psychological and Behavioral Effects of Hyperinsulinism in GoldfishDocument3 pagesPsychological and Behavioral Effects of Hyperinsulinism in GoldfishIvy Aggabao100% (1)
- Experiment 4 PhysioDocument2 pagesExperiment 4 PhysioIvy AggabaoNo ratings yet
- NPB 107 SyllabusDocument2 pagesNPB 107 SyllabusApril MartínezNo ratings yet
- Cholinoreceptor Blockers and Cholinesterase Regenerators: Submitted By: Aggabao, Ivy D. MED-2 Assignment #2 9/17/20Document1 pageCholinoreceptor Blockers and Cholinesterase Regenerators: Submitted By: Aggabao, Ivy D. MED-2 Assignment #2 9/17/20Ivy AggabaoNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic ReceptorsDocument32 pagesCholinergic Receptorskishoranande8010No ratings yet
- Harmacology: Brief Review On Cholinergic Receptors and TransmissionDocument10 pagesHarmacology: Brief Review On Cholinergic Receptors and TransmissionMa. Mil Adrianne PamaNo ratings yet
- 3 Cholinergic SystemDocument14 pages3 Cholinergic SystemAli EllaffiNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemKC PalattaoNo ratings yet
- CholinomimeticsDocument20 pagesCholinomimeticsAhmed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Excitation of Skeletal MusclesDocument15 pagesExcitation of Skeletal Musclesrahma sajjadNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic and Anticholinergic Drugs and Neuromuscular BockersDocument32 pagesCholinergic and Anticholinergic Drugs and Neuromuscular Bockersvyast8069No ratings yet
- Cholinergic Agents: Pharmaceutical Chemistry 2Document64 pagesCholinergic Agents: Pharmaceutical Chemistry 2ahmed hotyNo ratings yet
- Unit 8. Cholinergic and AnticholinergicsDocument50 pagesUnit 8. Cholinergic and AnticholinergicsApril Mergelle LapuzNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Section 05 - Cholinergic Transmission 1 (Cholinomimetics and Antimuscarinics)Document5 pagesPharmacology - Section 05 - Cholinergic Transmission 1 (Cholinomimetics and Antimuscarinics)Pathalee ThalpavilaNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Drugs - TablesDocument7 pagesCholinergic Drugs - TablesThuan Tăng NguyenNo ratings yet
- 18 Smooth MuscleDocument3 pages18 Smooth Muscleمحمود محمدNo ratings yet
- 2 (1) - 1Document66 pages2 (1) - 1ahmed hotyNo ratings yet
- (Cholinergic System) Model Questions and AnswersDocument45 pages(Cholinergic System) Model Questions and AnswersAjay SinghNo ratings yet
- CholinomimeticsDocument64 pagesCholinomimeticsMariyam HanifNo ratings yet
- Outline CH 12 Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs (NMBDS) and Reversal AgentsDocument36 pagesOutline CH 12 Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs (NMBDS) and Reversal AgentsCinthia Gonzalez NunezNo ratings yet
- Cholinergics Part IDocument48 pagesCholinergics Part IYaman Adnan QabajaNo ratings yet
- NMJ 1Document40 pagesNMJ 1Zainab AshroffNo ratings yet
- Лекция № 6Document63 pagesЛекция № 6C Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Agents: Cholinergic Receptors Types of Receptor Muscarinic Receptor Nicotinic ReceptorDocument4 pagesCholinergic Agents: Cholinergic Receptors Types of Receptor Muscarinic Receptor Nicotinic ReceptorDonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives: Drugs That Enhance Cholinergic TransmissionDocument3 pagesLearning Objectives: Drugs That Enhance Cholinergic TransmissionSamer FarhanNo ratings yet
- Direct Acting Muscarinic AgonistDocument6 pagesDirect Acting Muscarinic AgonistDeia ArahmanNo ratings yet
- Direct Acting Muscarinic AgonistDocument6 pagesDirect Acting Muscarinic AgonistDeia ArahmanNo ratings yet
- Direct Acting Muscarinic AgonistDocument6 pagesDirect Acting Muscarinic AgonistDeia ArahmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 Cholinergic TransmissionDocument20 pagesLecture 15 Cholinergic TransmissionSamer FarhanNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic DrugsDocument22 pagesCholinergic Drugsmug ashNo ratings yet
- Biochemsitry Pharmacy Nervous System 2014Document36 pagesBiochemsitry Pharmacy Nervous System 2014Sardar jiNo ratings yet
- Cholinoceptor - Activating (Cholinergic Agonist) and Cholinesterase - Inhibiting DrugsDocument53 pagesCholinoceptor - Activating (Cholinergic Agonist) and Cholinesterase - Inhibiting DrugsDan FabrosNo ratings yet
- By Duy Thai, 1997: Choline AcetyltransferaseDocument4 pagesBy Duy Thai, 1997: Choline Acetyltransferaseravi2likeNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic System and DrugsDocument42 pagesCholinergic System and DrugsIgnatius MicahelNo ratings yet
- Respiratory: CycleDocument12 pagesRespiratory: CycleGourav SinghNo ratings yet
- .Respiration in Plants ?Document12 pages.Respiration in Plants ?Omm SuvamNo ratings yet
- Pcol Finals CompreDocument17 pagesPcol Finals CompreAbby LumanglasNo ratings yet
- 5.neuromuscular JunctionDocument32 pages5.neuromuscular Junction234820No ratings yet
- 2cholinergic Drugs - MahDocument56 pages2cholinergic Drugs - Mahعلي الكوافيNo ratings yet
- BLOK 12 - IT 5 - Obat Otonom Antikolinergik - MTKDocument58 pagesBLOK 12 - IT 5 - Obat Otonom Antikolinergik - MTKtattosssNo ratings yet
- Acetylcholine ReceptorDocument1 pageAcetylcholine Receptorsai calderNo ratings yet
- L8 - Cholinergic Neurotransmission and The Skeletal NMJDocument8 pagesL8 - Cholinergic Neurotransmission and The Skeletal NMJlaylahd2003No ratings yet
- b8 - Ache InhibitorsDocument16 pagesb8 - Ache InhibitorsNav ThiranNo ratings yet
- New-NUB - Skeletal Muscle RelaxantsDocument47 pagesNew-NUB - Skeletal Muscle Relaxantsطه طارقNo ratings yet
- Direct Acting Cholinomimetics - BSN - 23Document28 pagesDirect Acting Cholinomimetics - BSN - 23KAMAU FRANCIS GATHUTHINo ratings yet
- Summaries of ToxologyDocument10 pagesSummaries of ToxologyAJ AYNo ratings yet
- 16-K-Ca ImbalanceDocument11 pages16-K-Ca Imbalanceمصطفى محمد جواد كاظمNo ratings yet
- NP2 PDFDocument27 pagesNP2 PDFRajat AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Agonists: Prepared by: Sevan M. Rustum 07512491694 يسيردتلا رجفلا دهعمDocument41 pagesCholinergic Agonists: Prepared by: Sevan M. Rustum 07512491694 يسيردتلا رجفلا دهعمAhmed MohamadNo ratings yet
- Parasympathomimetic AgentsDocument26 pagesParasympathomimetic Agentsrushikesh ugaleNo ratings yet
- Salivation: Done By: Fatima Ammash & Malak RizkDocument20 pagesSalivation: Done By: Fatima Ammash & Malak RizkAbeda AmmashNo ratings yet
- Stimulants of M ReceptorsDocument4 pagesStimulants of M ReceptorsYeshaa MiraniNo ratings yet
- CHOLINOCEPTORSDocument20 pagesCHOLINOCEPTORSLaura AweleNo ratings yet
- Patra 2018Document7 pagesPatra 2018Bei26No ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Common Drugs and AntidotesDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Common Drugs and AntidotesAnaliza Kitongan LantayanNo ratings yet
- LIFE1051 Neurochemistry 2Document47 pagesLIFE1051 Neurochemistry 2harienNo ratings yet
- PHARMA SupertableDocument2 pagesPHARMA SupertablelpanatalioNo ratings yet
- Pnas 86 13 5159Document4 pagesPnas 86 13 5159dai itakoNo ratings yet
- b8 - Anticholinesterase DrugsDocument11 pagesb8 - Anticholinesterase DrugsNav ThiranNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Midterm RecallsDocument3 pagesBiochemistry Midterm Recallssuper novaNo ratings yet
- 2 Cholinoceptors Activating Drugs.Document48 pages2 Cholinoceptors Activating Drugs.Vaidehi ParekhNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular JunctionDocument6 pagesNeuromuscular JunctionManish GujjarNo ratings yet
- The Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsFrom EverandThe Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsJohn ApSimonNo ratings yet
- Cholinoreceptor Blockers and Cholinesterase Regenerators: Submitted By: Aggabao, Ivy D. MED-2 Assignment #2 9/17/20Document1 pageCholinoreceptor Blockers and Cholinesterase Regenerators: Submitted By: Aggabao, Ivy D. MED-2 Assignment #2 9/17/20Ivy AggabaoNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid MetabolismDocument10 pagesNucleic Acid MetabolismIvy Aggabao100% (1)
- Bio621 Chapter 3Document109 pagesBio621 Chapter 3MizahNo ratings yet
- Cobra VenomDocument29 pagesCobra VenomJohn ShaprioNo ratings yet
- 126-Article Text-513-1-10-20170524Document10 pages126-Article Text-513-1-10-20170524Yosia KevinNo ratings yet
- Respon UroDocument20 pagesRespon UroNurul FajrinaNo ratings yet
- NeurotransmittersDocument1 pageNeurotransmittersmegs13045No ratings yet
- Nervous CoordinationDocument45 pagesNervous CoordinationTajXNo ratings yet
- End-Plate PotentialDocument7 pagesEnd-Plate PotentialSitrak OnyNo ratings yet
- Katzung & Trevor's Pharmacology - Examination & Board Review, 11e-Serotonin 5-Hydroxytryptamine 5-Ht and Related AgonistsDocument3 pagesKatzung & Trevor's Pharmacology - Examination & Board Review, 11e-Serotonin 5-Hydroxytryptamine 5-Ht and Related Agonistsfreemind323No ratings yet
- 1Document6 pages1Jude Matthew Diokno BernalNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Medicine Sci - 2022 - Saberfard - Effect of Medetomidine Midazolam Ketamine Propofol and Isoflurane OnDocument9 pagesVeterinary Medicine Sci - 2022 - Saberfard - Effect of Medetomidine Midazolam Ketamine Propofol and Isoflurane OnZanuba Ulya Haura cellinNo ratings yet
- Nervous System MartiniDocument66 pagesNervous System MartiniHilma Halimatusy SyfaNo ratings yet
- PHAR2821: Drug Discovery IIIDocument52 pagesPHAR2821: Drug Discovery IIISophia LiuNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs To Treat Psychiatric DisordersDocument435 pagesAntiepileptic Drugs To Treat Psychiatric DisordersHugo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Module 2.1 The Concept of The SynapseDocument4 pagesModule 2.1 The Concept of The SynapseArcanus LorreynNo ratings yet
- Unit 8. Cholinergic and AnticholinergicsDocument50 pagesUnit 8. Cholinergic and AnticholinergicsApril Mergelle LapuzNo ratings yet
- .25 - Endocannabinoids and ExerciseDocument6 pages.25 - Endocannabinoids and ExerciseIago LinsNo ratings yet
- 48 - Lecture - Presentation - 0 2Document56 pages48 - Lecture - Presentation - 0 2shea studiesNo ratings yet
- Neuro Muscular Junction NNDocument68 pagesNeuro Muscular Junction NNAnak AyamNo ratings yet
- Mubarek Aplied Neuroscience PPT Lecture NoteDocument50 pagesMubarek Aplied Neuroscience PPT Lecture NoteAklile TsegaNo ratings yet
- Gustatory (Taste) Receptors: Dr. Rusdi, M.BiomedDocument16 pagesGustatory (Taste) Receptors: Dr. Rusdi, M.BiomedNahla FaridaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry and Cell Biology of Dopaminergic NeurotransmissionDocument18 pagesBiochemistry and Cell Biology of Dopaminergic NeurotransmissionOneng IfayaniNo ratings yet
- BIBLIOGRAFIE Neural Conduction Synaptic TransmisionDocument16 pagesBIBLIOGRAFIE Neural Conduction Synaptic TransmisionMirela GiurgeaNo ratings yet
- Farmacologia de La KetaminaDocument11 pagesFarmacologia de La KetaminaMarjorie Lisseth Calderón LozanoNo ratings yet
- Assessing Newborn Re Exes: Tonic Neck Re Ex (Fencing Re Ex)Document4 pagesAssessing Newborn Re Exes: Tonic Neck Re Ex (Fencing Re Ex)Mariah Blez BognotNo ratings yet
- Tripartite SynapseDocument1 pageTripartite SynapseYusuf JunetNo ratings yet
- The Neuron: Vce Psychology - Unit 3 Aos 1Document22 pagesThe Neuron: Vce Psychology - Unit 3 Aos 1C0SMICALCHEMISTNo ratings yet
- VO Basics of Neuroscience WS 22Document4 pagesVO Basics of Neuroscience WS 22Sina HsNo ratings yet
- Drug Receptors and Pharmacodynamics: D. Structural ProteinsDocument6 pagesDrug Receptors and Pharmacodynamics: D. Structural ProteinsJennifer HerediaNo ratings yet