Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Most Important Question: Click Here To View
A Most Important Question: Click Here To View
Uploaded by
Lwin Maung Maung Thike0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageThis document discusses differentiating between aberrant ventricular conduction and ventricular ectopy on an electrocardiogram. Aberrant conduction occurs when a supraventricular impulse encounters one part of the ventricular conduction system that is refractory and another that is responsive, leading to a bundle branch block pattern. Ventricular ectopy occurs when the impulse originates in the ventricles. Some clues to help differentiate the two include looking for a preceding P wave before a wide QRS complex, analyzing the length of the compensatory pause after the complex, and the long-short rule where longer cycles make aberration more likely.
Original Description:
93
Original Title
93_7-PDF_EC
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses differentiating between aberrant ventricular conduction and ventricular ectopy on an electrocardiogram. Aberrant conduction occurs when a supraventricular impulse encounters one part of the ventricular conduction system that is refractory and another that is responsive, leading to a bundle branch block pattern. Ventricular ectopy occurs when the impulse originates in the ventricles. Some clues to help differentiate the two include looking for a preceding P wave before a wide QRS complex, analyzing the length of the compensatory pause after the complex, and the long-short rule where longer cycles make aberration more likely.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageA Most Important Question: Click Here To View
A Most Important Question: Click Here To View
Uploaded by
Lwin Maung Maung ThikeThis document discusses differentiating between aberrant ventricular conduction and ventricular ectopy on an electrocardiogram. Aberrant conduction occurs when a supraventricular impulse encounters one part of the ventricular conduction system that is refractory and another that is responsive, leading to a bundle branch block pattern. Ventricular ectopy occurs when the impulse originates in the ventricles. Some clues to help differentiate the two include looking for a preceding P wave before a wide QRS complex, analyzing the length of the compensatory pause after the complex, and the long-short rule where longer cycles make aberration more likely.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Lesson V (cont)- Ventricular Arrhythmias
click here to view
2. Aberrancy vs. Ventricular Ectopy
A most important question
Aberrant Ventricular Conduction: defined as the intermittent abnormal intraventricular
conduction of a supraventricular impulse. The phenomenon comes about because of unequal
refractoriness of the bundle branches and critical prematurity of a supraventricular impulse
(see diagramof "Three Fates of PACs"). With such critical prematurity, the supraventricular
impulse encounters one bundle branch (or fascicle) which is responsive, and the other which
is refractory, and is consequently conducted with a bundle branch block or fascicular block
pattern.
ECG clues to the differential diagnosis of wide QRS premature beats:
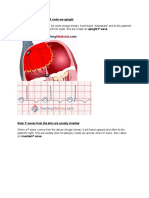
Preceding ectopic P wave (i.e., the P' of the PAC) usually hidden in the ST-T
wave of the previous beat favors aberrant ventricular conduction. In the ECG
below note the arrow pointing at a premature P wave in the ST-T segment. The
QRS has a RBBB morphology.
click here to view
Analyze the compensatory pause: A complete pause favors ventricular ectopy
(i.e., no resetting of the sinus pacemaker; next sinus impulse comes on time). An
incomplete pause favors aberration (i.e., because supraventricular prematures
are more likely to reset the sinus node's timing). Be aware of exceptions to this
simple rule because PVCs can activate the atria retrogradely and reset the sinus
node (incomplete pause), and PACs can fail to reset the sinus node (complete
pause).
Long-Short Rule (Ashman Phenomenon): The earlier in the cycle a PAC
occurs and the longer the preceding cycle, the more likely the PAC will be
conducted with aberration (see diagram "The Three Fates of PACs"). This is
because the refractory period of the ventricular conduction system is proportional
to cycle length or heart rate; the longer the cycle length or slower the heart rate,
the longer the recovery time of the conduction system. In most individuals the
right bundle normally recovers more slowly than the left bundle, and a critically
http://library.med.utah.edu/kw/ecg/ecg_outline/Lesson5/ventricular.html (4 of 10) [5/11/2006 9:39:47 AM]
You might also like
- ECG InterpretationDocument1 pageECG InterpretationCecil-An DalanonNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Biology FGS0044 Answer All Questions. Diagram of An Animal Cell. Label The PartsDocument3 pagesTutorial Biology FGS0044 Answer All Questions. Diagram of An Animal Cell. Label The PartsPreeti RajasegarNo ratings yet
- Supraventricular Tachycardia: Arun Umesh Mahtani,, Devi Gopinath NairDocument17 pagesSupraventricular Tachycardia: Arun Umesh Mahtani,, Devi Gopinath Nairwindar baquero100% (1)
- Bureau GrotDocument4 pagesBureau GrotMay KrivanishNo ratings yet
- Aberrant Ventricular Conduction Types and Concealed ConductionDocument25 pagesAberrant Ventricular Conduction Types and Concealed ConductionTemptationNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 ArrhythmiaDocument32 pagesUnit 7 ArrhythmiaJack TomarNo ratings yet
- PrintDocument21 pagesPrintSamsudin YahyaNo ratings yet
- 11 AvrtDocument32 pages11 AvrtthetlwinagNo ratings yet
- Click Here To View: 3. Atrial Fibrillation (A-Fib)Document1 pageClick Here To View: 3. Atrial Fibrillation (A-Fib)Lwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Click Here To View: 6. Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT) and RhythmDocument1 pageClick Here To View: 6. Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT) and RhythmLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial RhythmDocument12 pagesAtrial RhythmCarlo Domingo LadieroNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Conduction Disturbances: Bundle Branch Blocks and Related AbnormalitiesDocument12 pagesVentricular Conduction Disturbances: Bundle Branch Blocks and Related AbnormalitiesFelipe GallardoNo ratings yet
- Geekymedics.com-How to Read an ECGDocument15 pagesGeekymedics.com-How to Read an ECGSravya ValisettiNo ratings yet
- Catheter Ablation of Fascicular Ventricular Tachycardia: Review ArticleDocument9 pagesCatheter Ablation of Fascicular Ventricular Tachycardia: Review Articleapi-26166949No ratings yet
- Gold BergDocument14 pagesGold BergNico DwikiNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Sense ResponseDocument3 pagesVentricular Sense ResponseDaniel Banina AguerreNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument21 pagesHow To Read An ECGSlychenkoNo ratings yet
- 35 7-PDF EcDocument1 page35 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Heart Block PPT by SibaDocument36 pagesHeart Block PPT by Sibaritumitu_ritumitu100% (1)
- Ecg Junctionalventriculararrhythmias 140109180429 Phpapp02Document21 pagesEcg Junctionalventriculararrhythmias 140109180429 Phpapp02Morad KananNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Electrophysiology Basics (RL-204-Tn)Document5 pagesCardiac Electrophysiology Basics (RL-204-Tn)Navojit ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia: Dian Pratiwi Cardiology Department Chasan Boesoerie HospitalDocument73 pagesArrhythmia: Dian Pratiwi Cardiology Department Chasan Boesoerie HospitalummuabNo ratings yet
- EP NotesDocument5 pagesEP NotesHasan AshrafNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECGSarah RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Supraventricular Tachycardia - Life in The Fast Lane ECG LibraryDocument29 pagesSupraventricular Tachycardia - Life in The Fast Lane ECG LibraryYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- 18cardiac Arrhythmias Part 3Document8 pages18cardiac Arrhythmias Part 3Jaydave PatelNo ratings yet
- Bagliani G. Atrioventricular Nodal Conduction Disease. Javier Antico Gonzalez LopezDocument13 pagesBagliani G. Atrioventricular Nodal Conduction Disease. Javier Antico Gonzalez Lopezsonia isanamiNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmia: Prepared By: Charina Gail O. Baloy, RPH, Msc. (C.)Document44 pagesCardiac Arrhythmia: Prepared By: Charina Gail O. Baloy, RPH, Msc. (C.)Chinenye Akwue100% (1)
- Premature - Atrial - Complex FinalDocument16 pagesPremature - Atrial - Complex FinalBat ManNo ratings yet
- 83 7-PDF EcDocument1 page83 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Basic EP IntervalsDocument13 pagesBasic EP IntervalsdrharoonmohdNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECGcharlyn206No ratings yet
- Sunday Academic Meet-13 240428 083750Document9 pagesSunday Academic Meet-13 240428 083750lakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Supraventricular TachyarrythmiasDocument172 pagesSupraventricular TachyarrythmiasAbnet WondimuNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument24 pagesHow To Read An ECGredroseeeeeeNo ratings yet
- Dissertation EkgDocument6 pagesDissertation EkgBuyACollegePaperOnlineMilwaukee100% (1)
- Physiology Lecture - Dr. Dominguez: Slow FastDocument3 pagesPhysiology Lecture - Dr. Dominguez: Slow FastJayricDepalobosNo ratings yet
- Ablation Above The Semilunar Valves: When, Why, and How?: Mahmoud Suleiman, MD, Samuel J. Asirvatham, MDDocument6 pagesAblation Above The Semilunar Valves: When, Why, and How?: Mahmoud Suleiman, MD, Samuel J. Asirvatham, MDkaushikNo ratings yet
- Rule: P Waves From The SA Node Are UprightDocument13 pagesRule: P Waves From The SA Node Are UprightredroseeeeeeNo ratings yet
- 2019 WellSpan CV Symposium SVTDocument46 pages2019 WellSpan CV Symposium SVThawaig8No ratings yet
- Bradydysrhythmias and Atrioventricular Conduction BlocksDocument9 pagesBradydysrhythmias and Atrioventricular Conduction BlocksMariPaty LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Estimulação Transcutânea Não InvasivaDocument10 pagesEstimulação Transcutânea Não InvasivaMarcos AcioliNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias 101Document59 pagesArrhythmias 101Abdiwahab ShahnizzleNo ratings yet
- Arritmias Supraventriculares .Document8 pagesArritmias Supraventriculares .fh2301lrNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Pacing Maneuvers For Supraventricular Tachycardia - Part 2Document13 pagesDiagnostic Pacing Maneuvers For Supraventricular Tachycardia - Part 2aafagihNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Pacing Maneuvers Part 1Document16 pagesDiagnostic Pacing Maneuvers Part 1chirudarsiNo ratings yet
- Conductive Systemof The HeartDocument25 pagesConductive Systemof The HeartShreeya PooniaNo ratings yet
- Seminar Conduction System of HeartDocument61 pagesSeminar Conduction System of HeartKirtishAcharyaNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECG: Confirm DetailsDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECG: Confirm DetailsRinothja RajaratnamNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Wide QRS TachycardiasDocument6 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Wide QRS TachycardiasKev Jose Ruiz RojasNo ratings yet
- Beta's Short RP.: Click Here To ViewDocument1 pageBeta's Short RP.: Click Here To ViewLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 01 Bradydysrhythmias and Atrioventricular Conduction Blocks 1-9Document9 pages01 Bradydysrhythmias and Atrioventricular Conduction Blocks 1-9Amar TalatiNo ratings yet
- QRS ComplexDocument7 pagesQRS Complexchiusavi77No ratings yet
- Tachycardia Which Fast Is Too FuriousDocument79 pagesTachycardia Which Fast Is Too FuriousEstiningtiyas RahayuNo ratings yet
- Basics of The 12-Lead ECG - CE Article - NursingCenterDocument13 pagesBasics of The 12-Lead ECG - CE Article - NursingCenterتمارا مقداديNo ratings yet
- Supraventricular TachycardiDocument8 pagesSupraventricular TachycardiHairunisa 0049No ratings yet
- Escape Pacemaker Takes Over by Default:: 1. Slowing of The Primary Pacemaker (I.e., SA Node) SubsidiaryDocument1 pageEscape Pacemaker Takes Over by Default:: 1. Slowing of The Primary Pacemaker (I.e., SA Node) SubsidiaryLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- ECG of The Month: DiscussionDocument2 pagesECG of The Month: DiscussionKrlÖz Ändrz Hërëdîa ÖpzNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECGCFTCNo ratings yet
- Approach To Ventricular Tachyarrythmias and SCDDocument151 pagesApproach To Ventricular Tachyarrythmias and SCDAbnet WondimuNo ratings yet
- EKG - Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCS)Document8 pagesEKG - Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCS)SAM dabombdigNo ratings yet
- ST Segment Depression-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageST Segment Depression-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 137 7-PDF Ec PDFDocument1 page137 7-PDF Ec PDFLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 142 7-PDF EcDocument1 page142 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- A Very Subtle 1st Degree AV BlockDocument1 pageA Very Subtle 1st Degree AV BlockLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
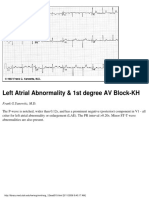
- Left Atrial Abnormality & 1st Degree AV Block-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageLeft Atrial Abnormality & 1st Degree AV Block-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
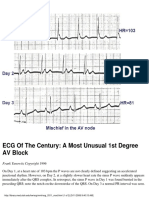
- ECG of The Century: A Most Unusual 1st Degree AV BlockDocument1 pageECG of The Century: A Most Unusual 1st Degree AV BlockLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
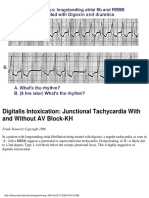
- Digitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without AV Block-KHDocument1 pageDigitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without AV Block-KHLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 135 7-PDF EcDocument1 page135 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
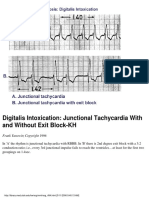
- Digitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without Exit Block-KHDocument1 pageDigitalis Intoxication: Junctional Tachycardia With and Without Exit Block-KHLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 129 7-PDF Ec PDFDocument1 page129 7-PDF Ec PDFLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 130 7-PDF EcDocument1 page130 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 129 7-PDF EcDocument1 page129 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
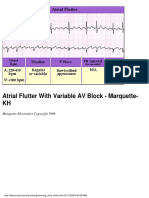
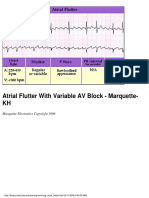
- Atrial Flutter With Variable AV Block - Marquette-KHDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With Variable AV Block - Marquette-KHLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 126 7-PDF Ec PDFDocument1 page126 7-PDF Ec PDFLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flutter With 2:1 Conduction: Leads II, III, V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With 2:1 Conduction: Leads II, III, V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 128 7-PDF EcDocument1 page128 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction: Lead V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DDocument1 pageAtrial Flutter With 2:1 AV Conduction: Lead V1-KH: Frank G.Yanowitz, M.DLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- PROTEIN SynthesisDocument37 pagesPROTEIN SynthesisChirag KothariNo ratings yet
- Network Marketing Opportunity - Vestige Marketing Plan URTSAM - +919711572735Document16 pagesNetwork Marketing Opportunity - Vestige Marketing Plan URTSAM - +919711572735Samir K Mishra100% (1)
- Perkins 60 Kva Silent StamfordDocument3 pagesPerkins 60 Kva Silent StamfordM. Rizky FauziNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Olds Maternal Newborn Nursing and Womens Health Across The Lifespan 11th Edition by DavidsonDocument31 pagesTest Bank For Olds Maternal Newborn Nursing and Womens Health Across The Lifespan 11th Edition by DavidsonMartin Courser100% (38)
- CBSE Schools and KV Class VII SA I Science Model Question Paper 2015Document4 pagesCBSE Schools and KV Class VII SA I Science Model Question Paper 2015Amrita SenNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Medicare Insurance PlanDocument7 pagesDifferent Types of Medicare Insurance PlanGetmy PolicyNo ratings yet
- Kellogg v. Energy Safety Services Inc., 544 F.3d 1121, 10th Cir. (2008)Document23 pagesKellogg v. Energy Safety Services Inc., 544 F.3d 1121, 10th Cir. (2008)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Report137 Pretreatment & Design Considerations - Large Scale Seawater FacilitiesDocument197 pagesReport137 Pretreatment & Design Considerations - Large Scale Seawater FacilitiesLTE002No ratings yet
- Certificate of EmploymentDocument3 pagesCertificate of EmploymentDiana Ley Supnet Madriaga100% (1)
- Reactive Dyes AnswersDocument14 pagesReactive Dyes AnswerstusharNo ratings yet
- Common Factors in PsychotherapyDocument11 pagesCommon Factors in Psychotherapydrc.psyNo ratings yet
- SteroidsDocument2 pagesSteroidsShawn FreemanNo ratings yet
- Risk PDFDocument48 pagesRisk PDFusljebrka.milosNo ratings yet
- Adaptation CardsDocument17 pagesAdaptation CardsNubar MammadovaNo ratings yet
- 13-Incident Investigation and Corrective ActionREVISED PDFDocument56 pages13-Incident Investigation and Corrective ActionREVISED PDFSafiuddin Afdal LaudinNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report Format 2019 Phas 4Document39 pagesSummer Training Report Format 2019 Phas 4Gokul VasanNo ratings yet
- AA V6 I1 High Fidelity FSIDocument3 pagesAA V6 I1 High Fidelity FSIpriyankar007No ratings yet
- Final Paper 1Document27 pagesFinal Paper 1api-315734227No ratings yet
- Alumni - 2016Document198 pagesAlumni - 2016GSL Medical College0% (1)
- Material Master Configuration - 10.07.2022Document13 pagesMaterial Master Configuration - 10.07.2022DeepakNo ratings yet
- Marketing Report TarangDocument19 pagesMarketing Report TarangKaran KumarNo ratings yet
- Datasheet - Burndy - YA6CTC10Document2 pagesDatasheet - Burndy - YA6CTC10Ariel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Parents Angry As COVID. Ex 1-5.Document2 pagesParents Angry As COVID. Ex 1-5.Chirtoacă IonNo ratings yet
- IPPAThirdWorldCongressProgram PDFDocument136 pagesIPPAThirdWorldCongressProgram PDFCristian FerradaNo ratings yet
- CH2 Electric Potential and Capacitance 2019Document6 pagesCH2 Electric Potential and Capacitance 2019PrachiNo ratings yet
- Subanen HistoryDocument14 pagesSubanen HistoryAllan Mangangot100% (1)
- Berihun Project-2-1Document36 pagesBerihun Project-2-1yirga assefaNo ratings yet
- 1-Science Lab RulesDocument11 pages1-Science Lab RuleseyydaNo ratings yet