Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organizational Theory & Design Exam #1
Organizational Theory & Design Exam #1
Uploaded by
Amit Kr GodaraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organizational Theory & Design Exam #1
Organizational Theory & Design Exam #1
Uploaded by
Amit Kr GodaraCopyright:
Available Formats
Organizational Theory & Design Exam #1
Study online at quizlet.com/_2julri
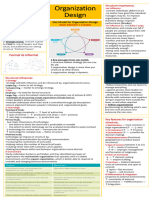
1. Adapting to -Organizations need the right fit between 7. Dimensions of -Simple, stable environment:
Complexity + internal structure + external environment Environmental uncertainty low
Dynamism -Can add positions + departments, build Uncertainty -Complex stable environment: greater
relationships, differentiation + integration, uncertainty
organic vs. mechanistic, planning, forecasting -Simple, unstable environment: even
+ responsiveness great uncertainty
-Complex, unstable environment:
2. Assessing Goal Approach: identifying an organization's
greatest uncertainty
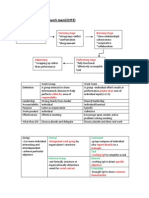
Organizational output goals + assessing how well the
Effectiveness organization has attained those goals 8. Divisional Structure -Product structure/strategic business
(profitability, market share, growth) units
-divisions organized according to
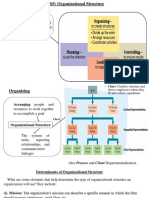
Resource-Based Approach: organizations products, services, product groups
must be successful in obtaining + managing -good for achieving coordination
valued resources in order to be effective across functional departments
because strategically valuable resources -loses economies of scale
give an organization a competitive edge -lacks technical specialization
(how well they can get resources) -eliminates economies of scale in
functional departments, poor
Internal Process Approach: effectiveness is coordination
measured as internal organization health +
9. Effectiveness The Degree to which an organization
efficiency
achieves its goals
-takes into consideration a range of
Strategic Constituents Approach:
variables at both the organizational +
effectiveness by focusing on the satisfaction
department levels
of key stakeholders
10. Efficiency Amount of resources used to achieve
3. Changing -As environment becomes more complex,
the organization's goals
Environment events become less stable, financial
-working of the organization + amount
resources become less available, level of
of resources used to produce output
uncertainty increases
11. Elements of -Uncertainty: lack of sufficient info
4. Collaborative (Dissimilar, Cooperative)
Uncertainty about environmental factors
Network -Emerging BETTER alternative to resource
-Complexity: $ + dissimilar of external
dependency
elements
-Companies join together to become more
-Dynamism: whether the organization
competitive + to share scarce resources
operates in a stable/unstable
-Alliances require managers who are good at
environment
building networks
-Companies can share risk + cooperation is a 12. Environmental Scan External/Internal
prerequisite for greater innovation, problem CEO, Top Management Team
solving, + performance Strategic Intent
Organizational Design
5. Contingency There is no "one best way", have to
Effectiveness Outcomes
customize management practice to the
-> GAP Analysis
organization
13. Framework for Inter 1) Org Relationship
-Contingency Factors Affecting Organization organizational (competitive/cooperative)
Design: Strategy, environment, technology, Relationships 2) Org Type
size/life cycle, culture (Similar, dissimilar)
6. Contingency Size 14. Functional Structure -Activities grouped by Common
Factors of Organizational Technology function
Organization Environment -specific skills + knowledge are
Design Goals + Strategy consolidated
Culture -promotes economies of scale
(outside-Influences structural dimensions) -slow response to environmental
changes, less innovation
15. Generalist Wide niche/domain, broad range of 22. Influencing -Balance linkages + independence
Strategies for products/services to a broad market Financial -Reach out + change/control elements in
survival Resources environment (establish favorable
relationships w/key elements of the
16. Geographic -Organizing to meet needs of
environment), shape the environment by
Structure users/customers by geography
influencing key sectors
-many multinational corporations are
organized by country 23. Information- Provide both vertical + horizontal info flow
-focuses managers + employees on specific Sharing to accomplish organization's overall goals
geographic regions Perspective on -Traditional organization: (Vertical)
-strengths + weaknesses similar to divisional Structure efficiency, top level decision making
organization -Learning organization: (Horizontal)
communication + collaboration,
17. Goals Types -Mission, Official Goals: Communicate
decentralized authority focused on shared
+ Purposes purpose + value, bestow legitimacy
tasks + decisions
-Operating Goals: 24. Institutionalism (Similar, Cooperative)
provide employee direction + motivation, -Perspective: manage survival, balance
offer decision guidelines, define standards of expectations of environment
performance (leads to official goals) -Environment: norms + values of
stakeholders, adopt structures + processes
18. Horizontal -Horizontal linkage: coordinates activities
to please outsiders
Info Sharing across organizational departments- not
-Legitimacy: org's actions are desirable,
traditionally draw on the organization chart
proper, + appropriate
-Info system, liaison roles (located in one
department but has the responsibility for 25. Institutional -Technical structure: day to day work,
communicating + achieving coordination View + Org technology, op requirements (governed by
w/another), task forces (temp committee), Design norms + rationality of efficiency)
full-time integrator (project manager), teams
-Institutional Structure: visible to the public
19. Horizontal -Organization around core processes (tasks +
(governed by expectations of the public)
Structure activities)
-Shift toward horizontal structure during 26. Integrated Competitive values model: balance
reengineering Effectiveness concern w/various parts of the organization
-Eliminates vertical hierarchy + departmental Model
boundaries Human Relations emphasis: incorporates
-created around cross-functional processes, the values of an internal focus + flexible
self-directed teams, are dominant players, structure
people on team are given authority for
decisions Open Systems Emphasis:
-can increase organizations flexibility stability, equilibrium, communication
-culture: openness, trust, + collaboration
Internal Process Emphasis:
20. Hybrid -Combination of various structure
Stability Equilibrium, Communication
structure approaches
-tailored to specific needs
Rational Goal Emphasis: productivity,
-used in rapidly changing environments
Efficiency, profit, goal setting
-greater flexibility
27. Inter Resource transactions, flows, + linkages that
21. Importance -Means to an end
organizational occur among 2 org
of -Produce goods + services efficiently
Relationships
Organizations -Facilitates innovation
-Adapt to + influence a changing 28. Levels of External level: community
environment Analysis in Organization level: organization
-Create value for owners, customers, + Organizations Group level: Different Departments
employees Individual Level: people
-Accomodate ongoing challenges of
diversity, ethics + motivation + coordination
of employees
29. Matrix -Multifocused w/strong horizontal linkage 33. Organizational Strategic Intent: Organization's energies +
Structure -Conditions: share resources across the Purpose resources are directed toward a focused,
organization, 2 + critical outputs required unifying, + Compelling goal
(products + technical knowledge), -Mission, Competitive Advantage, Core
environment is complex + uncertain Competence
-Allows organization to meet dual demands -Operating goals: overall performance,
-Largest weakness is that employees have 2 market goals, resource goals, employee
bosses + conflicting demands development, productivity, innovation +
change goals
30. Mechanistic Mechanistic
vs. Organic -Characterized by machine-like standard 34. Organizational Contains:
rules + procedures w/clear authority Structure -Formal reporting Relationships (# of levels
-Centralized structure, specialized tasks, in hierarchy, span of control)
struck hierarchy of authority, vertical -Grouping of individuals (creation of
communication, many rules, formalized departments)
-Typical Contingency factors: large size, -Design of Systems (communication,
efficiency strategy, stable environment, rigid coordination, + integration of efforts)
culture, manufacturing technology
35. Organization Social entities that are goal-directed
Definition -Designed as deliberately structured +
Organic
coordinated activity systems
-Design of organization is looser, free-
-Linked to the external Environment
flowing, + adaptive
-OPEN SYSTEM (inputs: raw materials,
-Decentralized structure, empowered roles,
people info->transformation process-
collaborative teamwork, horizontal
>Outputs: Products + services)
communication, few rules, informal
-Typical contingency factors: small size, 36. Organization -Required Work Activities: as organizations
innovation strategy, changing environment, Design grow more, more functions will need to be
adaptive culture, service technology Alternatives performed
-Reporting Relationships: Chain of
BOTH depend on: structure, tasks/roles, Command
system formality, communication, hierarchy - Departmental Grouping Options:
vs. Collaboration 1) Functional Grouping: places together
employees who perform similar knowledge
31. Miles + Snow's Formulate strategy that matches the
+ skills (all marketing together)
Strategy demands of the external environment
2) Divisional Grouping: organized according
Typology -Prospector: fluid, creativity, risk-taker,
to what the organization produces (product
innovative, decentralized
division 1)
-Defender: efficiency, centralized authority +
2) Multi-focused grouping: embraces 2 +
tight cost control
structural grouping alternatives (product
-Analyzer: balances efficiency + learning,
division 1 + marketing)
tight cost control w/flexibility + adaptability,
3) Horizontal grouping: grouped around
creative, research, risk-taking
core work processes ( HR, Finance, with
-Reactor: no clear organizational approach,
Core Process 1 across)
reacts to market place (bad)
4) Virtual Network Grouping: loosely
32. Organizational System formed by the interaction of a connected cluster of separate components
ecosystem community of organizations + their
37. Organization All the elements that exist outside the
environment
Environment boundary of the organization
-Domain: chosen environmental field of
action
-Sectors: (Subdivisions) contain simliar
elements
38. Population (Similar, Competitive) 45. Strategy Plan for interacting w/the competitive
Ecology -Org diversity + adaptation within a environment
population of organizations -Models exist to aid in formulating strategy:
-Population is a set of org engaged in similar Porter's 5 Forces, Miles + Snow's Strategy
activities Typology
-Theory notes that large, established org's -Strategy impacts internal organization
often become dinosaurs (difficulty adapting, characteristics, managers must design the
changing environment determines organization to support the firm's
survival/failure) competitive strategy
-Heavy investments can limit org adaptation
46. Structural Formalization
-Model looks at org form
Dimensions of Specialization
-Org nice can help aid in survival of an org
Organization Hierarchy of Authority
-VARIATION->SELECTION->RETENTION
Design Complexity
39. Porter's Differentiation strategy: distinguish Centralization
Competitive products/services from others in the industry
47. Symptoms of -Decision making is delayed/lacking quality
Strategies (creates hook)
Structural -Organization cannot meet changing needs
Deficiency -Employee performance declines, needs are
Low-Cost Leadership: increase market share
not met
by keeping costs low compared to
-too much conflict
competitors (efficiency)
48. Task Sectors that the organization interacts
can choose to focus broad/narrow in Environment w/directly to achieve goals
reaching multiple markets -ex: industry, raw materials, market, human
resources sectors
40. Relational -High level of horizontal coordination
Coordination -Frequent, timely, problem-solving 49. Vertical Info -Vertical linkages: coordinate activities
communication Sharing between the top + bottom of organization
-Relationships of shared goals, shared -Hierarchical referral: vertical lines which
knowledge + mutual respect identify the chain of command
-Rules + plans: create vertical Links
41. Resource (Dissimilar, Competitive)
-Vertical info systems: reports, computer
Dependence -Org's minimize their dependence on other
systems, written info
orgs for the supply of resources
-org's succeed by striving for autonomy 50. Virtual -Extend horizontal coordination beyond
-org's alter independent relationships through Networks + boundaries of organization
ownership, contracts, + joint ventures Outsourcing -Most common strategy: outsourcing
-Central hub
42. Resource- Organizations depend on the environment
-managers don't have hands on control
Dependence -Strive to acquire control over resources to
over activities/employees
Perspective minimize dependence
-org's are vulnerable if resources are
controlled by other org's
-Minimize vulnerabilities
-Will team up w/others when resources are
scarce
43. Specialist Narrow range of goods/services that serve a
Strategies narrow market
for survival
44. Stakeholder Balancing the needs of groups in + outside of
Approach the organization that has a stake in the
organization's performance
You might also like
- Finding The Right Remedy For Poor Organizational PerformanceDocument12 pagesFinding The Right Remedy For Poor Organizational PerformancePaula FerrazNo ratings yet
- Delegation and Delegation ErrorsDocument14 pagesDelegation and Delegation Errorsniraj benu100% (3)
- Nature of Internal Audit: The Functions of Management Consist of Five Basic ActivitiesDocument5 pagesNature of Internal Audit: The Functions of Management Consist of Five Basic ActivitiesJere Mae Bertuso TaganasNo ratings yet
- Session 7: Environment - Strategy - Structure: Prof. Pavni Kaushiva DWO 2021-22Document9 pagesSession 7: Environment - Strategy - Structure: Prof. Pavni Kaushiva DWO 2021-22NIKAM PRANITA GORAKHNATHNo ratings yet
- MAPR Notes PDFDocument8 pagesMAPR Notes PDFgigihdNo ratings yet
- Strategy Implementation: HCAD 5390Document36 pagesStrategy Implementation: HCAD 5390Vignesh VSNo ratings yet
- Strategyimplementation 4Document36 pagesStrategyimplementation 4Eunice Eidelwiess AraniegoNo ratings yet
- Kalo Mau Sebar Bilang Dlu Yaaaa, Love:)Document7 pagesKalo Mau Sebar Bilang Dlu Yaaaa, Love:)caseyNo ratings yet
- Strategik Management (Done)Document24 pagesStrategik Management (Done)Nur ZulaikhaNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management Grade 12 UST SHS ReviewerDocument11 pagesOrganization and Management Grade 12 UST SHS ReviewerTRISHA MAE ABOC100% (13)
- Strategy Implementation: HCAD 5390Document75 pagesStrategy Implementation: HCAD 53903azozNo ratings yet
- Mind Map Module 6Document1 pageMind Map Module 6hesham.ashraf86No ratings yet
- Organizational Effectiveness & EfficiencyDocument24 pagesOrganizational Effectiveness & EfficiencyDr. Sujoy SenNo ratings yet
- Organizational Structure by Burns & Stalker (1961)Document5 pagesOrganizational Structure by Burns & Stalker (1961)Erika Joille PatayonNo ratings yet
- STRATEGIC ImplementationDocument35 pagesSTRATEGIC ImplementationhjkdskjchNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Organizational SystemsDocument4 pagesChapter 6 Organizational SystemsKaito ShinichiNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management ReviewerDocument3 pagesOrganization and Management ReviewerRoanaNo ratings yet
- Group Behaviour (CHP 3)Document2 pagesGroup Behaviour (CHP 3)Annie Wong Chin YiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Implementing The StrategyDocument75 pagesChapter 9 - Implementing The StrategyAmit Khundia0% (1)
- Chapter-3-Orgman 2Document15 pagesChapter-3-Orgman 2Erica VillaesterNo ratings yet
- 3 - Corporate Strategy and Long Range Planning: Strategic Management LessonDocument8 pages3 - Corporate Strategy and Long Range Planning: Strategic Management LessonMich AlbaniaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Implimentation-Organising For ActionDocument35 pagesStrategic Implimentation-Organising For ActionhjkdskjchNo ratings yet
- KA1 - Business Analysis Planning & MonitoringDocument2 pagesKA1 - Business Analysis Planning & MonitoringSaurabh MehtaNo ratings yet
- Engr301 ReviewDocument5 pagesEngr301 ReviewthomasNo ratings yet
- PAL Medical Travel Grants Program: Soaring Towards Good Health and WellbeingDocument8 pagesPAL Medical Travel Grants Program: Soaring Towards Good Health and WellbeingAngelica BaesNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management CH-4Document9 pagesStrategic Management CH-4padmNo ratings yet
- Purpose: To Exploit and Create New and Different: Chapter 1 - The Nature of Strategic ManagementDocument3 pagesPurpose: To Exploit and Create New and Different: Chapter 1 - The Nature of Strategic ManagementJanelle MendozaNo ratings yet
- 1 Design of Organizational StructureDocument33 pages1 Design of Organizational StructureJustine MangubatNo ratings yet
- ACCA SBL Unit of Innovation, Performance Excellence and Change Management 2021Document255 pagesACCA SBL Unit of Innovation, Performance Excellence and Change Management 2021Quensteen LimNo ratings yet
- Page 570 For Features of DecentralizationDocument5 pagesPage 570 For Features of DecentralizationSARGAM JAINNo ratings yet
- 7s Model and Org StructureDocument40 pages7s Model and Org StructureMudit KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Contemporary Concepts of ManagementDocument7 pagesModule 1 Contemporary Concepts of ManagementMarla Brigitte GalvanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Aligning Training With Strategy: Effective Training: Systems, Strategies,& Practices, 4 EditionDocument12 pagesChapter Two Aligning Training With Strategy: Effective Training: Systems, Strategies,& Practices, 4 EditionahmadkamranNo ratings yet
- Finals ReviewerDocument6 pagesFinals ReviewerDharnel Jude EpeNo ratings yet
- Week 11: Strategic Control and Corporate GovernanceDocument9 pagesWeek 11: Strategic Control and Corporate Governancesunshine mydayNo ratings yet
- Pa 111 NotesDocument13 pagesPa 111 NotesMara JavierNo ratings yet
- Erm Reviewer Group 5-6Document6 pagesErm Reviewer Group 5-6Veerna LanaqueNo ratings yet
- PGP21-OBII - Session 2 PDFDocument22 pagesPGP21-OBII - Session 2 PDFMegha SinhaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Fundamentals of Organization StructureDocument33 pagesModule 4 Fundamentals of Organization StructureAbsar SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- MKTG 8 (Lesso 1-2) PDFDocument9 pagesMKTG 8 (Lesso 1-2) PDFmeyyyyyyyyyyNo ratings yet
- Module 7 PlanningDocument6 pagesModule 7 PlanningMarla Brigitte GalvanNo ratings yet
- MPE 505 Organizatonal StructureDocument20 pagesMPE 505 Organizatonal StructureMwaura MouriceNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of Solution Manual For Canadian Organizational Behaviour, 10th Edition Steven McShane Kevin Tasa All ChapterDocument63 pagesFull Download PDF of Solution Manual For Canadian Organizational Behaviour, 10th Edition Steven McShane Kevin Tasa All Chapterpompeabxss100% (4)
- Chapter 6: Structure and Control: Structure Follows Strategy (Chandler)Document30 pagesChapter 6: Structure and Control: Structure Follows Strategy (Chandler)kadbroniNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 - Cabrera 2Document31 pagesChapter-4 - Cabrera 2Justine Chile PanopioNo ratings yet
- Organizational DesignDocument30 pagesOrganizational DesignFun Toosh345No ratings yet
- The Organisation and Its EnvironmentDocument33 pagesThe Organisation and Its EnvironmentMarioNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Internal AnalysisDocument9 pagesGroup 4 Internal AnalysisDarlene CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Organising, NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Organising, NotesMayank DuhalniNo ratings yet
- Acccob 3 Q1 ReviewerDocument11 pagesAcccob 3 Q1 ReviewertrishadatuNo ratings yet
- BU1104Document72 pagesBU1104dashidalgoNo ratings yet
- Mintzberg-1Document17 pagesMintzberg-1Inna JoraNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis - Appex Corp - Group 6Document4 pagesCase Analysis - Appex Corp - Group 6payalkhndlwl100% (1)
- MODERN-APPROACH BbookletDocument5 pagesMODERN-APPROACH BbookletPoppy MooreNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument14 pagesReviewerAlvarez FraizerNo ratings yet
- 3-4 July-Fundamentals of ORGANIZATION Structure-Cha14engelskDocument22 pages3-4 July-Fundamentals of ORGANIZATION Structure-Cha14engelskarunesh shrivastavaNo ratings yet
- ACCA BT Topic 13.1Document4 pagesACCA BT Topic 13.1عمر اعظمNo ratings yet
- TM251 - Valerio - Study Questions Page 288Document3 pagesTM251 - Valerio - Study Questions Page 288Howard Lee ValerioNo ratings yet
- Sesssion # 5Document30 pagesSesssion # 5Muhammad Hasan QadriNo ratings yet
- EVALUATING THE ROLE OF CORE COMPETENCIES IN IMPROVING PERFORMANCE OF MANUFACTURING INDUSTRIESFrom EverandEVALUATING THE ROLE OF CORE COMPETENCIES IN IMPROVING PERFORMANCE OF MANUFACTURING INDUSTRIESNo ratings yet
- IT GOVERNANCE APPROACHES FOR AGILE SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT INVESTMENTSFrom EverandIT GOVERNANCE APPROACHES FOR AGILE SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT INVESTMENTSRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Modification of ProteinsDocument39 pagesModification of ProteinsAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- 13 - Data For Query FunctionDocument30 pages13 - Data For Query FunctionAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Amit KR Godara P41003Document7 pagesAmit KR Godara P41003Amit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Amit KR Godara - P41003 - SSMDDocument3 pagesAmit KR Godara - P41003 - SSMDAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9Document4 pagesLesson 9Amit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- MODULE 7 Food Additives Lesson M-VII.18. Aroma Compounds in Food & Flavour Enhancers - Monosodium Glutamate, NucleotidesDocument5 pagesMODULE 7 Food Additives Lesson M-VII.18. Aroma Compounds in Food & Flavour Enhancers - Monosodium Glutamate, NucleotidesAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Que No 5 B) Influence of Water Activity On Food Spoilage Reations Ans - Water Activity & Microbial GrowthDocument11 pagesQue No 5 B) Influence of Water Activity On Food Spoilage Reations Ans - Water Activity & Microbial GrowthAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Modification of Proteins: Bimlesh MannDocument30 pagesModification of Proteins: Bimlesh MannAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Antinutritional Factors and Food Contaminant Lesson-M-VIII.21 Toxic Trace Elements, RadionuclidesDocument7 pagesAntinutritional Factors and Food Contaminant Lesson-M-VIII.21 Toxic Trace Elements, RadionuclidesAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Module: 3 Food Lipids Lesson M-III.8: Edible Fats and Oils - Classification and Chemical CompositionDocument7 pagesModule: 3 Food Lipids Lesson M-III.8: Edible Fats and Oils - Classification and Chemical CompositionAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Module: 3 Food Lipids Lesson M.III.10Document4 pagesModule: 3 Food Lipids Lesson M.III.10Amit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Freezing Point Depression of A Mix Prof. H. Douglas Goff, University of GuelphDocument4 pagesCalculation of Freezing Point Depression of A Mix Prof. H. Douglas Goff, University of GuelphAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Course - CHEESE TECHNOLOGYDocument5 pagesCourse - CHEESE TECHNOLOGYAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Cereals: - : IntroductionDocument8 pagesCereals: - : IntroductionAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- DE-13 - Quiz 14Document2 pagesDE-13 - Quiz 14Amit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Dairy Engineering: 6.2 Soaker Type Bottle Washers 6.3 Description of Operation 6.4 MaintenanceDocument4 pagesDairy Engineering: 6.2 Soaker Type Bottle Washers 6.3 Description of Operation 6.4 MaintenanceAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- DE-13 - Quiz 17Document2 pagesDE-13 - Quiz 17Amit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Cheese Technology: Module 14. Packaging, Storage and Distribution of CheeseDocument3 pagesCheese Technology: Module 14. Packaging, Storage and Distribution of CheeseAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Cheese Technology: Module 14. Packaging, Storage and Distribution of CheeseDocument8 pagesCheese Technology: Module 14. Packaging, Storage and Distribution of CheeseAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- DE-13 - Quiz 9Document3 pagesDE-13 - Quiz 9Amit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Cheese Technology: Module 15. Accelerated Ripening of CheeseDocument10 pagesCheese Technology: Module 15. Accelerated Ripening of CheeseAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- DE-13 - Quiz 6Document2 pagesDE-13 - Quiz 6Amit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- 8static Characteristics of Measuring Instruments - Iii PDFDocument4 pages8static Characteristics of Measuring Instruments - Iii PDFAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- DE-13 - Quiz 8Document2 pagesDE-13 - Quiz 8Amit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- 18 Electrical Transducers Inductive Transducer PDFDocument7 pages18 Electrical Transducers Inductive Transducer PDFAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- 6 Static Characteristics of Measuring InstrumentsDocument5 pages6 Static Characteristics of Measuring InstrumentsAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- 9 Dynamic Characteristics of Measuring InstrumentsDocument6 pages9 Dynamic Characteristics of Measuring InstrumentsAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- 3classification of InstrumentsDocument5 pages3classification of InstrumentsAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Course Module Tourism Planning PrelimDocument7 pagesCourse Module Tourism Planning PrelimRalph Centeno100% (1)
- 01 Self Management Skills II Revision NotesDocument5 pages01 Self Management Skills II Revision Notessurjeetkumar32222No ratings yet
- Diversity Best Practices: D&I Strategic Plans and Maturity Models Presented To Kaiser PermanenteDocument30 pagesDiversity Best Practices: D&I Strategic Plans and Maturity Models Presented To Kaiser PermanenteRick dhar0% (1)
- 10 5923 J HRMR 20170702 03Document7 pages10 5923 J HRMR 20170702 03Meena SivasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Sisay Research ProposalDocument25 pagesSisay Research ProposalDereje ZegeyeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Understanding Groups and Managing Work Teams: Learning OutcomesDocument16 pagesChapter 9 - Understanding Groups and Managing Work Teams: Learning OutcomesSindhu Nath ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Leadership and Organizational Behavior: Lob-Mm Ukwms Smt1 Paruh 1 Dr. Fenika Wulani, CHCMDocument13 pagesLeadership and Organizational Behavior: Lob-Mm Ukwms Smt1 Paruh 1 Dr. Fenika Wulani, CHCMSereza FebrianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document32 pagesChapter 6ViaNo ratings yet
- Level of Effectiveness On The Practices of Sales Force Management of Honda Cars BatangasDocument9 pagesLevel of Effectiveness On The Practices of Sales Force Management of Honda Cars BatangasAsia Pacific Journal of Multidisciplinary ResearchNo ratings yet
- Strategic ControlDocument8 pagesStrategic ControlDECIPOLO, KENNETH JOHN E.No ratings yet
- Awareness, Acceptability, and Relevance of The Vision, Mission, Goals, and Objectives of The Programs of Naval State University Graduate SchoolDocument26 pagesAwareness, Acceptability, and Relevance of The Vision, Mission, Goals, and Objectives of The Programs of Naval State University Graduate SchooljhungutierrezNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - STRAMA PDFDocument19 pagesReviewer - STRAMA PDFKristelle LlegaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Strategy 2nd Edition Grant Test BankDocument9 pagesFoundations of Strategy 2nd Edition Grant Test BankDina Wegman100% (38)
- Identification of Change Initiative Within The Organization: A Discussion On Why Change Is SignificantDocument7 pagesIdentification of Change Initiative Within The Organization: A Discussion On Why Change Is SignificantPitez NyambuzNo ratings yet
- Thematic Unit MatrixDocument5 pagesThematic Unit Matrixapi-242501884No ratings yet
- AppendixD.3 PartII CompetenciesDocument1 pageAppendixD.3 PartII CompetenciesRamil Tuason100% (1)
- The Partnering ToolbookDocument45 pagesThe Partnering ToolbooklenaNo ratings yet
- Community Based Watershed Management in BangladeshDocument7 pagesCommunity Based Watershed Management in BangladeshAli Azam Khan100% (1)
- BSC - Basic ConceptsDocument24 pagesBSC - Basic ConceptssugabossNo ratings yet
- 100 Life Goals (The Ultimate Personal Goals To Achieve in Your Lifetime)Document18 pages100 Life Goals (The Ultimate Personal Goals To Achieve in Your Lifetime)zgh zghNo ratings yet
- 1Document5 pages1Waad MajidNo ratings yet
- Vision Ans MissionDocument11 pagesVision Ans MissionValarmathiNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management MethodologyDocument203 pagesStrategic Management MethodologyChristophe LacourNo ratings yet
- Coaching PhilosophyDocument24 pagesCoaching PhilosophySim BuenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Challenge of ManagementDocument24 pagesChapter 1 The Challenge of Managementjeff leonenNo ratings yet
- Create Money Before Christmas by Carl James Harvey (Slides)Document143 pagesCreate Money Before Christmas by Carl James Harvey (Slides)Nguyen Hong Ha50% (2)
- TR-Mechatronics Servicing NC IV PDFDocument108 pagesTR-Mechatronics Servicing NC IV PDFPaul BautistaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management:: Dr. Dennis Anthony A. Kilongkilong, PIE, ASEAN EngrDocument32 pagesStrategic Management:: Dr. Dennis Anthony A. Kilongkilong, PIE, ASEAN EngrJeramz QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Event Sponsorship Taaras As at 21 JuneDocument10 pagesEvent Sponsorship Taaras As at 21 JuneMichael MolloyNo ratings yet