Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atomic Structure: AUFBAU Principle - As The Electrons
Atomic Structure: AUFBAU Principle - As The Electrons
Uploaded by
MarkLawrenceMagsombol0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views2 pagesAtoms consist of protons, electrons, and neutrons. J.J. Thomson created the Plum Pudding model which viewed atoms as a positively charged fluid containing negatively charged electrons. Niels Bohr proposed the planetary model where electrons orbit the nucleus in distinct energy levels, absorbing or emitting radiation when changing orbits. The atomic number equals the number of protons which equals the number of electrons.
Original Description:
Original Title
Atomic Structure
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAtoms consist of protons, electrons, and neutrons. J.J. Thomson created the Plum Pudding model which viewed atoms as a positively charged fluid containing negatively charged electrons. Niels Bohr proposed the planetary model where electrons orbit the nucleus in distinct energy levels, absorbing or emitting radiation when changing orbits. The atomic number equals the number of protons which equals the number of electrons.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views2 pagesAtomic Structure: AUFBAU Principle - As The Electrons
Atomic Structure: AUFBAU Principle - As The Electrons
Uploaded by
MarkLawrenceMagsombolAtoms consist of protons, electrons, and neutrons. J.J. Thomson created the Plum Pudding model which viewed atoms as a positively charged fluid containing negatively charged electrons. Niels Bohr proposed the planetary model where electrons orbit the nucleus in distinct energy levels, absorbing or emitting radiation when changing orbits. The atomic number equals the number of protons which equals the number of electrons.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Atomic Structure
Atoms consist of three basic particles: protons, electrons, and neutrons. The outermost regions of the
atoms are called electron shells and contain the electrons.
Plum Pudding Theory
J.J. Thomson created this theory.
As each atom was a sphere filled with a
positively charged fluid, known as the
“pudding”. Scattered in this fluid were
negatively charged electrons, those
were the “plums” in the pudding.
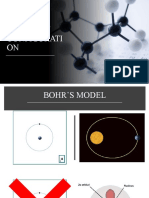
Bohr Planetary Model
The Bohr Model is a planetary
model in which the negatively charged
electrons orbit a small, positively charged
nucleus similar to the planets orbiting the
sun (except that the orbits are not planar).
Electrons orbit the nucleus in orbits that
have a set size and energy. The energy of
the orbit is related to its size. The lowest
energy is found in the smallest orbit.
Radiation is absorbed or emitted when an
electron moves from one orbit to another.
In atom, the atomic number of protons =
number of electrons
AUFBAU Principle - As the electrons
move away from the nucleus, the greater
energy they have which means building
up.
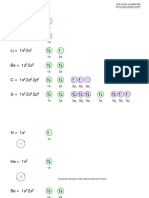
MEL (n) Max # of e # of subtotal Sub-level # of orbitals
n designation
−¿¿
Electronic Configuration – distribution of e in different sublevels of orbitals
CHONSPX – elements usually found in organic compounds
X – halogens (F, Cl, Br, I)
Number of unpaired electrons
1
1s 1
1 s 2 s 2 2 p2 or
2
2
2 2 1 1
1 s 2 s 2 px 2 p y
1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p1x 2 p 1y 2 p 1z 2
1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p1x 2 p 1y 2 p 1z 3
1
You might also like
- Module Two Lesson Three Guided Notes PDFDocument4 pagesModule Two Lesson Three Guided Notes PDFMadera HarrisNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument19 pagesReviewerJulia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table: Electron StructuresDocument58 pagesPeriodic Table: Electron StructuresVimanan A/L S. VelangganiNo ratings yet
- 2 - Atoms and The PeriodicTableDocument48 pages2 - Atoms and The PeriodicTableTaryhana FitzgerlandNo ratings yet
- QMech HomeworkSolutions PDFDocument31 pagesQMech HomeworkSolutions PDFSankha100% (1)
- QMech HomeworkSolutionsDocument31 pagesQMech HomeworkSolutionsJimmy ShamsiNo ratings yet
- Las 9 Q2Document4 pagesLas 9 Q2Jonah Labine Jabulin-RadazaNo ratings yet
- CHE 110 Molecular Orbital Practice Problems Answers PDFDocument3 pagesCHE 110 Molecular Orbital Practice Problems Answers PDFynottripNo ratings yet
- AP Chem 2 WorksheetDocument9 pagesAP Chem 2 WorksheetJane IvanovaNo ratings yet
- 2a Atoms and Molecules PostDocument30 pages2a Atoms and Molecules Postapi-3767370No ratings yet
- Crystal Lattice Vibrations: Phonons: Introduction To Solid State PhysicsDocument25 pagesCrystal Lattice Vibrations: Phonons: Introduction To Solid State PhysicsJack CaoNo ratings yet
- Siruri: I. Calculati Limitele Sirului Cu Termen GeneralDocument6 pagesSiruri: I. Calculati Limitele Sirului Cu Termen Generalv1or3laNo ratings yet
- Ch05 1 DiatomicMODocument19 pagesCh05 1 DiatomicMOKaPíl JêThwañìNo ratings yet
- Electron Configuration (Kimia) PDFDocument20 pagesElectron Configuration (Kimia) PDFalbertNo ratings yet
- Angle Is The Angle That The String Makes With The Vertical When Released From Rest Will Affect TheDocument8 pagesAngle Is The Angle That The String Makes With The Vertical When Released From Rest Will Affect TheHidayah SakinahNo ratings yet
- Chpater 1 - 1.1 Electronic ConfigurationDocument7 pagesChpater 1 - 1.1 Electronic ConfigurationSyafiyatulMunawarahNo ratings yet
- L2 - Electron ConfigurationDocument26 pagesL2 - Electron ConfigurationHommer CorderoNo ratings yet
- Chap2 Estimation Procedures 201213Document26 pagesChap2 Estimation Procedures 201213aieyinHengNo ratings yet
- Electron ConfigurationDocument28 pagesElectron ConfigurationJoanna PoshnjaNo ratings yet
- Problem42 21Document1 pageProblem42 21IENCSNo ratings yet
- Lecture-10: An Alternate Way of Finding The Equation of Conic Section For Motion Under GravityDocument10 pagesLecture-10: An Alternate Way of Finding The Equation of Conic Section For Motion Under GravityAshutosh singhNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of Hydrogen Electronic Structure of HydrogenDocument9 pagesElectronic Structure of Hydrogen Electronic Structure of HydrogenRaja Muda Raja NgahNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Review of Atomic Structure and Chemical BondingDocument53 pagesUnit 2 Review of Atomic Structure and Chemical BondingYna MillamaNo ratings yet
- Electron ConfigurationsDocument52 pagesElectron ConfigurationsMarivic CabatcheteNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument108 pagesMatterArshe OmaguingNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of MatterDocument47 pagesElectronic Structure of MatterMary Rose Lepardo - RosanesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Periodic Table)Document46 pagesChapter 4 (Periodic Table)Tunku Hilman Al-nordinNo ratings yet
- Electron Configuration and Quantum NumbersDocument41 pagesElectron Configuration and Quantum NumbersgallosaaronmatthewNo ratings yet
- American DivisionDocument5 pagesAmerican DivisionTarek FaramawyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document25 pagesLecture 8yalavarthi vishalNo ratings yet
- STAT 2601 Test 3 Formula Sheet (Official)Document1 pageSTAT 2601 Test 3 Formula Sheet (Official)subui613No ratings yet
- Analytic GeometryDocument53 pagesAnalytic GeometrySupriyo ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 - : SolutionDocument2 pagesQuiz 3 - : SolutionRiley mooreoNo ratings yet
- Lecture (1) MVCSDocument21 pagesLecture (1) MVCSTelal MohammedNo ratings yet
- ELECTRIC FLUX 1 Chapter1 04Document57 pagesELECTRIC FLUX 1 Chapter1 04Shubham TiwariNo ratings yet
- Orthogonal Arrays: How To Construct?Document17 pagesOrthogonal Arrays: How To Construct?ThaiHuynhNgocNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips The Root Locus TechniqueDocument21 pagesDokumen - Tips The Root Locus TechniqueSolid Work and Mechanical software TutorialNo ratings yet
- 2014 H2 C1 Promo SolutionsDocument10 pages2014 H2 C1 Promo SolutionsMe4d SHiV23No ratings yet
- 8.4. The Exclusion Principle and The Periodic TableDocument3 pages8.4. The Exclusion Principle and The Periodic TablesebastianNo ratings yet
- CIVL Pablo Hurtado AssignmentDocument4 pagesCIVL Pablo Hurtado AssignmentPablo Esteban Hurtado OjedaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 03 RCDocument12 pagesAssignment 03 RCHidden TalentNo ratings yet
- 03 NonStandardGalerkinDocument16 pages03 NonStandardGalerkinPandit.Venkata RamanaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry-Part I-Chapter 2-Periodic Relationships Among The Elements-Student's NotesDocument8 pagesGeneral Chemistry-Part I-Chapter 2-Periodic Relationships Among The Elements-Student's NotesHuyền Đỗ KhánhNo ratings yet
- 3 PolarcoordinatesDocument26 pages3 PolarcoordinatesWan SyazwanNo ratings yet
- B - Lecture10 The Root Locus Rules Automatic Control SystemDocument31 pagesB - Lecture10 The Root Locus Rules Automatic Control SystemAbaziz Mousa OutlawZzNo ratings yet
- Electron ConfigurationDocument33 pagesElectron ConfigurationArnel BaradiNo ratings yet
- XT e E: 1. (A) and (B)Document19 pagesXT e E: 1. (A) and (B)Anonymous 0MQ3zRNo ratings yet
- 3 - The Quantum Mechanical Model of The Atom (Structure 1.3.3 and 1.3.4)Document12 pages3 - The Quantum Mechanical Model of The Atom (Structure 1.3.3 and 1.3.4)JouliesNo ratings yet
- QP6PPT 2015Document33 pagesQP6PPT 2015Johnny BraveNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 33 Quantum NumbersDocument14 pagesTUTORIAL 33 Quantum NumbersDYES Motion GraphicsNo ratings yet
- Spect Rosco Pie 7Document13 pagesSpect Rosco Pie 7LumyNo ratings yet
- MOT Part 2Document24 pagesMOT Part 2suka11blyatNo ratings yet
- S6 Revision For Pure Mathematics Allow Me To Discuss This Dozen of Questions With YouDocument7 pagesS6 Revision For Pure Mathematics Allow Me To Discuss This Dozen of Questions With Youkaziba stephenNo ratings yet
- 3 Module Two Lesson Three Guided NotesDocument4 pages3 Module Two Lesson Three Guided NotesJoelle MatarNo ratings yet
- Materials Science - Physics - Atomic Structure and BondingDocument6 pagesMaterials Science - Physics - Atomic Structure and BondingczeraldguevarraNo ratings yet
- Quantum Theory and The Electronic Structure of AtomsDocument28 pagesQuantum Theory and The Electronic Structure of AtomsVimanan A/L S. VelangganiNo ratings yet
- Math GTM QP 20-12-23Document4 pagesMath GTM QP 20-12-23sbpathuriNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument22 pagesNotesBrian WambuaNo ratings yet
- 1204 - The Global CityDocument58 pages1204 - The Global CityMarkLawrenceMagsombolNo ratings yet
- Musical Arts Instrumental Solo (2019 - PIANO)Document1 pageMusical Arts Instrumental Solo (2019 - PIANO)MarkLawrenceMagsombolNo ratings yet
- Nature of MathematicsDocument1 pageNature of MathematicsMarkLawrenceMagsombolNo ratings yet
- Balmes, John Vincent A.Document13 pagesBalmes, John Vincent A.MarkLawrenceMagsombolNo ratings yet
- Cyber BullyingDocument6 pagesCyber BullyingMarkLawrenceMagsombolNo ratings yet
- FDocument70 pagesFMarkLawrenceMagsombolNo ratings yet
- Claude Debussy: A Biography PresentationDocument3 pagesClaude Debussy: A Biography PresentationMarkLawrenceMagsombolNo ratings yet