Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Teaching Strategies LESSON 1 HEALTHED
Teaching Strategies LESSON 1 HEALTHED
Uploaded by
Angela Reyes0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pages1. The document discusses and compares traditional and activity-based teaching strategies.
2. Traditional strategies include lecturing, discussion, question and answer techniques, and use of audiovisual aids. Activity-based strategies focus more on student participation and include cooperative learning, writing to learn, concept mapping, debate, and simulations.
3. Both traditional and activity-based strategies have advantages and disadvantages. Traditional strategies can efficiently convey information but limit student interaction, while activity-based strategies enhance critical thinking and social skills but may require more class time.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document discusses and compares traditional and activity-based teaching strategies.
2. Traditional strategies include lecturing, discussion, question and answer techniques, and use of audiovisual aids. Activity-based strategies focus more on student participation and include cooperative learning, writing to learn, concept mapping, debate, and simulations.
3. Both traditional and activity-based strategies have advantages and disadvantages. Traditional strategies can efficiently convey information but limit student interaction, while activity-based strategies enhance critical thinking and social skills but may require more class time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesTeaching Strategies LESSON 1 HEALTHED
Teaching Strategies LESSON 1 HEALTHED
Uploaded by
Angela Reyes1. The document discusses and compares traditional and activity-based teaching strategies.
2. Traditional strategies include lecturing, discussion, question and answer techniques, and use of audiovisual aids. Activity-based strategies focus more on student participation and include cooperative learning, writing to learn, concept mapping, debate, and simulations.
3. Both traditional and activity-based strategies have advantages and disadvantages. Traditional strategies can efficiently convey information but limit student interaction, while activity-based strategies enhance critical thinking and social skills but may require more class time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
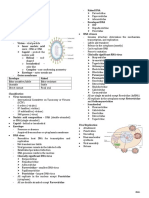
Teaching Strategies Supports students ways to develop and
evaluate their beliefs and positions
Traditional Teaching Strategies
Can foster attitudes through understanding
1. Lecturing
and allow student freedom to assert their
Most traditional method associated with opinions hence, application of new
teaching in which the teacher simply knowledge takes place.
conveys the knowledge to the students in
Many students prefer and like this method
a one-way channel of communication.
DISADVANTAGES:
Can be an efficient means of introducing
leanrers to new topics. Students use more time to think and
interact
ADVANTAGES:
Effectively only in small groups
Allows uniformity of knowledge to be
learned for all student in a class May not be an efficient way of
communicating information
Economical and cost effective
Useful only if the participants come
Helps develop students’ listening abilities
prepared with the needed background
DISADVANTAGES: information
Few teachers are good lecturers 3. Question and Answer Techniques
Initiates learning by asking students about
The lecture method lends itself to the
their insights and ideas.
teaching of facts with little emphasis
Use to assess students’ competencies and
placed on problem-solving, and transfer
baseline knowledge to find out what a
of learning
group already knows about the subject in
Not conducive to meeting students’ order to review its content.
individual learning needs Can increase motivation of learners as it
brings about eagerness to learn answers to
Allows limited attention span questions asked.
2. Discussion 7 types of questions:
Gives opportunities to share the students 1. Factual questions –demands simple
insight of understanding of the topic recall of information.
It allows teacher-student or student- 2. Probing questions –used when teacher
student interaction wants a learner to further explain an
Its purpose is to give students an answer.
opportunity to apply principles, concepts 3. Multiple choice questions –can be oral
and theories as well as clarify information or written, they usually test recall and
and concepts. can be used to begin a discussion
A topic is announced in advance and the 4. Open-ended questions –these
class is asked to take part in the discussion encompass all questions that require
by reading a certain material or watching a learners to construct an answer.
videotape among other activities. 5. Discussion-stimulating questions –help
the discussion move along for a clearer
ADVATAGES: or better view of the subject matter.
6. Questions that guide problem-solving –
Helps students learn the process of group
teachers need to phrase and sequence
problem-solving
questions carefully in order to guide
learners in problem-solving thinking Learning gap may exist between the fast
process. and slow learners
7. Rhetorical questions –questions for
which one expect no answers at the
time. Such questions can be used to 2. WRITING TO LEARN
stimulate thinking in the class ▪ Actively influences students’ dispositions
4. Use of Audiovisual Aids toward thinking and takes active
A traditional method that can reinforce participation in learning
teaching and learning ▪ Writing serves as a stimulus of critical
It is used as supplement to a lecture, as a thinking by immersing students in the
prelude to discussion, or a part of subject matter for utilization of knowledge
questioning strategy and effective internalization of values and
Can greatly enhance teaching and add to beliefs.
students’ interest ▪ Journal writing
▪ Creative writing assignments
Types of traditional audiovisuals:
▪ Research articles
Handouts or printed materials used to help ▪ Paper critique
communicate facts, figures and concepts 3. CONCEPT-MAPPING
Chalkboards or whiteboards are universally ▪ Lends visual assistance to students when
used in education asked to demonstrate their thinking in a
Powerpoint slides are used. graphic matter to show interconnectedness
Videotapes, films, clinical procedures of concept or ideas.
videos. 4. DEBATE
▪ A strategy that fosters critical thinking
ACTIVITY-BASED TEACHING STRATEGIES which requires in-depth recall of topics for
1. COOPERATIVE LEARNING supporting evidence and for developing
one’s position in an issue.
Students from one class are arranged into ▪ It encourages analytical skills, recognizes
small groups to facilitate learning process complex issues or concern, permits
Involves structuring small groups of students to consider alternative options
learners who work together toward shared with freedom to change one’s mind based
learning goals on information
5. SIMULATIONS
▪ Jigsaw ▪ These are exercises which learners engage
▪ Think-pair-share in to know the real world without the risks
▪ Numbered-heads together of harm or injury and make learning
▪ Talking ships enjoyable.
ADVANTAGES: ▪ Intended to help learners in decision-making
and problem-solving, develop human
Group members learn to function as part
interaction abilities and learn psychomotor
of a team
skills in a safe and controlled setting
Enhances social skills 4 types of simulation techniques:
Inculcates the spirit of team-building Simulation exercises –a controlled
representation of a piece of reality that
DISADVANTAGES:
learners can manipulate to better
Students who are fast learners may lag understand the real situation.
behind
Simulation game –represents real-life
situations in which learners compete
according to a set of rules in order to
win or achieve an object
Role-playing –form of drama in which
learners spontaneously act out roles
through interaction involving problems
or challenges in human relation.
Case study –analysis of incident or
situation in which characters and
relationships are described, factual or
hypothetical, events transpired and
problems that need to be resolved or
solved.
6. PROBLEM-BASED LEARNING
Involves confronting students with real lfie
problems which they are meant to solve on
their own.
Provides stimulus for critical thinking and
self-taught content.
Difference between PBL and simulations
7. SELF-LEARNING MODULES
▪ Also called self-directed learning modules,
self-paced learning modules, self-learning
packets, and individual learning activity
packages.
▪ Provided with the materials they needed for
the learning without the teachers
intervention.
▪ Components of self-learning module:
o Introduction and instructions
o Behavioral objectives
o Pretest
o Learning activities
o Self evaluations
o Posttest
You might also like
- Collins Easy Learning Spanish GrammarDocument163 pagesCollins Easy Learning Spanish GrammarFaith Dawn85% (13)
- Queena Jessa D. Moratal Learning Episode 9 PDFDocument10 pagesQueena Jessa D. Moratal Learning Episode 9 PDFNelle christine Tanguilan78% (49)
- Grade 7Document6 pagesGrade 7Alecia R. CastilloNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank (2 Week) : Antibody ScreensDocument5 pagesBlood Bank (2 Week) : Antibody ScreensAngela Reyes100% (1)
- Greek Word: Lectura Read: Traditional Teaching StrategiesDocument5 pagesGreek Word: Lectura Read: Traditional Teaching StrategiesJunah DayaganonNo ratings yet
- Health EducDocument10 pagesHealth EducFlorence TimosaNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document11 pagesGroup 1Aila Erika EgrosNo ratings yet
- Cadaa - Module 4 - EDUC 126Document6 pagesCadaa - Module 4 - EDUC 126Elfe Grace L. CadaaNo ratings yet
- Identify A Teaching Approach Which Can Be Used in Accounting Classes. Give Its Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument6 pagesIdentify A Teaching Approach Which Can Be Used in Accounting Classes. Give Its Advantages and DisadvantagesCherry TeeNo ratings yet
- Iv - Methods of TeachingDocument28 pagesIv - Methods of TeachingLia ArantonNo ratings yet
- Health Education Teaching Strategies Transes PrelimsDocument54 pagesHealth Education Teaching Strategies Transes PrelimsDiana PayosNo ratings yet
- Instructional StrategiesSarahDocument47 pagesInstructional StrategiesSarahPaulo B. turaNo ratings yet
- Approaches, Techniques, Methods, & Strategies, ActivityDocument10 pagesApproaches, Techniques, Methods, & Strategies, ActivityManolo Servise HiloNo ratings yet
- The Teaching of ScienceDocument80 pagesThe Teaching of ScienceAngeles, Mark Allen C100% (1)
- Aspects Observations Strengths Areas For Improvement Action PointsDocument2 pagesAspects Observations Strengths Areas For Improvement Action PointsEJAY verj100% (1)
- WRITTEN REPORT InductiveVs - DeductiveDocument11 pagesWRITTEN REPORT InductiveVs - Deductivejmr.reposarNo ratings yet
- 2 TERM (S.Y. 2021-2022) BPHE-II: Philippine Normal University MindanaoDocument4 pages2 TERM (S.Y. 2021-2022) BPHE-II: Philippine Normal University MindanaoLovely PadernaNo ratings yet
- What Are Instructional Strategies?Document8 pagesWhat Are Instructional Strategies?jaikrishna gangala100% (1)
- Lecture and DiscussionDocument43 pagesLecture and Discussionpurvi patelNo ratings yet
- #2 Observation Checklist For FS 1topic 2Document2 pages#2 Observation Checklist For FS 1topic 2Loraine Magistrado AbonitaNo ratings yet
- Lecutre and Discussion..Document12 pagesLecutre and Discussion..prasad.4ujustNo ratings yet
- Effective Teaching Methods For Basic EducationDocument7 pagesEffective Teaching Methods For Basic EducationNsem RaoNo ratings yet
- Learning ING EPISODE 10 FINALDocument8 pagesLearning ING EPISODE 10 FINALMelvin SumalinogNo ratings yet
- Centered LearnerdDocument16 pagesCentered Learnerdrenalyne bannitNo ratings yet
- NCM102j MODULE 4Document4 pagesNCM102j MODULE 4Jenny Ruth TubanNo ratings yet
- Teaching StrategiesDocument40 pagesTeaching StrategiesjdairoNo ratings yet
- Task-4-2P-ECED-07 (JUDILLA, NEKIRYN)Document4 pagesTask-4-2P-ECED-07 (JUDILLA, NEKIRYN)nekirynNo ratings yet
- ED 213 UNIT 4 PidoDocument3 pagesED 213 UNIT 4 PidoMariter PidoNo ratings yet
- Chapt1 4Document12 pagesChapt1 4Patricia Andrea CariñoNo ratings yet
- UNIT III Lesson I Direct Expository ApproachDocument12 pagesUNIT III Lesson I Direct Expository Approachmikkajaneaguinaldo15No ratings yet
- Activity 1 FS 1Document8 pagesActivity 1 FS 121bgu0195msNo ratings yet
- FLCT Review Material For Distribution 2024 2Document9 pagesFLCT Review Material For Distribution 2024 2danllyodangelo.sambajonNo ratings yet
- UNIT III Lesson I Direct Expository ApproachDocument12 pagesUNIT III Lesson I Direct Expository Approachmikkajaneaguinaldo15No ratings yet
- Seven JumpDocument22 pagesSeven JumpMoch. Ivan KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Integrative ReviewerDocument6 pagesIntegrative ReviewerMontecer, Donnalyn S. BSE SOCIAL STUDIES 2ENo ratings yet
- Some Models of Teaching: By: Xyrille Yves Zaide BSED IIDocument25 pagesSome Models of Teaching: By: Xyrille Yves Zaide BSED IILiezel LebarnesNo ratings yet
- FS2 - Learning Episode 7 Guiding Principles in The Selection and Use of Teaching MethodsDocument10 pagesFS2 - Learning Episode 7 Guiding Principles in The Selection and Use of Teaching Methodssheilajanedlasala100% (1)
- Formative Assessment Leaflet PDFDocument2 pagesFormative Assessment Leaflet PDFGabriel 15 MoseyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 FLCT. HANDOUTDocument32 pagesLesson 1 FLCT. HANDOUTKc BalderamaNo ratings yet
- College of Teacher Education: Technology For Teaching and Learning IIDocument3 pagesCollege of Teacher Education: Technology For Teaching and Learning IIapi-750865366No ratings yet
- Problem-Based Learning: Sri Sundari Medu Fkik UmyDocument25 pagesProblem-Based Learning: Sri Sundari Medu Fkik UmyArio Anindito PNo ratings yet
- PBL - TutorialDocument47 pagesPBL - TutorialVieraChNo ratings yet
- EPP W ENTREP-LPDocument7 pagesEPP W ENTREP-LP202100133No ratings yet
- Traditional Teaching Method: Health Education Methods/StrategiesDocument18 pagesTraditional Teaching Method: Health Education Methods/StrategiesNichole ShaineNo ratings yet
- Principles of LCT (SCT)Document4 pagesPrinciples of LCT (SCT)Chaé RiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Ma'Am EyoDocument7 pagesReviewer Ma'Am EyoAliya JimenezNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 5 PDFDocument14 pagesStudy Guide 5 PDFqhafjthelin waybNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document26 pagesModule 5Merry Grace TamundongNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 TeachersDocument5 pagesUnit 3 TeachersbalajoberrylkateNo ratings yet
- Scientific Approach & Quantum Learning-2Document36 pagesScientific Approach & Quantum Learning-2Noob GamersNo ratings yet
- Dawal, Angelika O. Bsed Math 4 (Performance Task 7) - 105605Document3 pagesDawal, Angelika O. Bsed Math 4 (Performance Task 7) - 105605ghela0511No ratings yet
- JENNY EDFX343 Week 2 TutorialDocument19 pagesJENNY EDFX343 Week 2 TutorialjayNo ratings yet
- Organization and Managements of Learner-Centered Classrooms: Study Guide For Module No. 3Document13 pagesOrganization and Managements of Learner-Centered Classrooms: Study Guide For Module No. 3Ace ManicaoNo ratings yet
- Tsos Final Exam NotesDocument6 pagesTsos Final Exam NotesAleslie ReforealNo ratings yet
- Tsos Final Exam NotesDocument10 pagesTsos Final Exam NotesAleslie ReforealNo ratings yet
- New Module Lesson 1Document13 pagesNew Module Lesson 1CABELA, TRICIA ANN T.No ratings yet
- Tubigan - Modern Approaches Applicable To College TeachingDocument4 pagesTubigan - Modern Approaches Applicable To College TeachingihlaNo ratings yet
- Lec RecitDocument1 pageLec RecitElkana Jelai BarbaNo ratings yet
- Difference of Passive and Active Learning Advantages & Disadvantages of Teaching MethodsDocument3 pagesDifference of Passive and Active Learning Advantages & Disadvantages of Teaching MethodsジェスNo ratings yet
- Teaching Strategies: Ncm102/N: Health EducationDocument48 pagesTeaching Strategies: Ncm102/N: Health EducationCasey Wruble100% (1)
- Learner-Centered ApproachDocument13 pagesLearner-Centered ApproachAbdelmalek ElboudaryNo ratings yet
- Learning How to Learn: ‘A Guide to Effective Teaching and Learning Strategies’From EverandLearning How to Learn: ‘A Guide to Effective Teaching and Learning Strategies’Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- MYCODocument59 pagesMYCOAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- HEMA-1 Up To PG 30.-1-31Document31 pagesHEMA-1 Up To PG 30.-1-31Angela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Tumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenDocument5 pagesTumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Hema DagdagDocument1 pageHema DagdagAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Pedigree Analysis WorksheetDocument3 pagesPedigree Analysis WorksheetAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Urine Sediment ConstituentsDocument12 pagesUrine Sediment ConstituentsAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Finals - VirologyDocument14 pagesFinals - VirologyAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Hema 2Document35 pagesHema 2Angela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Assignment#1 - 3a - Group 7Document20 pagesAssignment#1 - 3a - Group 7Angela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument56 pagesIlovepdf MergedAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Myco LQDocument37 pagesMyco LQAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Blue. 1 or 2 HoursDocument5 pagesBlue. 1 or 2 HoursAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument31 pagesIlovepdf MergedAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Coagulation Screening Procedures:: RD THDocument2 pagesCoagulation Screening Procedures:: RD THAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- 1 Hema LecDocument5 pages1 Hema LecAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Aubf Lec (2 Week) Physical Examination of Urine: Color, Clarity Specific GravityDocument38 pagesAubf Lec (2 Week) Physical Examination of Urine: Color, Clarity Specific GravityAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: T. VaginalisDocument78 pagesMicrobiology: T. VaginalisAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Midterms - MycologyDocument17 pagesMidterms - MycologyAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- 1 Hema LecDocument5 pages1 Hema LecAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- BLOOD COLLECTION Part 1 Hema LabDocument7 pagesBLOOD COLLECTION Part 1 Hema LabAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Finals - ImmunohematologyDocument20 pagesFinals - ImmunohematologyAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Phagocyte System.: Innate/non-Specific Immune SystemDocument6 pagesPhagocyte System.: Innate/non-Specific Immune SystemAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- 5TH Week Hematocrit DeterminationDocument24 pages5TH Week Hematocrit DeterminationAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Tests: JAPAY, Princess Agatha Mei R. BS Medical Technology 3ADocument5 pagesBiochemical Tests: JAPAY, Princess Agatha Mei R. BS Medical Technology 3AAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lec (Module 2) : Cellular Adaptations, Cellular Injury and Cell DeathDocument5 pagesHistopath Lec (Module 2) : Cellular Adaptations, Cellular Injury and Cell DeathAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lec (Module 1) : Iintroduction To PathologyDocument17 pagesHistopath Lec (Module 1) : Iintroduction To PathologyAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Biochem Test 1.2Document9 pagesBiochem Test 1.2Angela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lab (Module 2) : Receiving, Accessioning and Gross Examination of Tissue SamplesDocument5 pagesHistopath Lab (Module 2) : Receiving, Accessioning and Gross Examination of Tissue SamplesAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cclec MidtermsDocument65 pagesCclec MidtermsAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Concepts and Recent TrendsDocument38 pagesPreliminary Concepts and Recent TrendsLiz DenillaNo ratings yet
- True LoveDocument4 pagesTrue Lovelena100% (2)
- Andrew N. Meltzoff, Wolfgang Prinz - The Imitative Mind - Development, Evolution and Brain Bases-Cambridge University Press (2002)Document365 pagesAndrew N. Meltzoff, Wolfgang Prinz - The Imitative Mind - Development, Evolution and Brain Bases-Cambridge University Press (2002)Tláloc González EstradaNo ratings yet
- Ielts Reading QuestionsDocument3 pagesIelts Reading QuestionsLê HiếnNo ratings yet
- Shklovski y BakhtinDocument28 pagesShklovski y BakhtinConstanza LeonNo ratings yet
- Grade 10Document2 pagesGrade 10Nicolai VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Geralyn Presentation Selection of ContentDocument17 pagesGeralyn Presentation Selection of ContentGeralyn Valdriz RamosNo ratings yet
- Success Factors in Project Management: Key Words: Projects ProjectDocument17 pagesSuccess Factors in Project Management: Key Words: Projects Projectbeast mickeyNo ratings yet
- The Imperative - Easy Learning Grammar: Commands and OrdersDocument2 pagesThe Imperative - Easy Learning Grammar: Commands and OrdersRaviNo ratings yet
- Present Tenses: Become A REPORTED SPEECH Genius!Document3 pagesPresent Tenses: Become A REPORTED SPEECH Genius!TommyNo ratings yet
- PT and Cur DevDocument28 pagesPT and Cur DevECE CAPILINo ratings yet
- Use of Suggestopedia To Improve StudentsDocument5 pagesUse of Suggestopedia To Improve StudentsButsayamas S.No ratings yet
- TPGPDocument3 pagesTPGPapi-313793865No ratings yet
- DLL English Quarter 1 WEEK 1-10Document35 pagesDLL English Quarter 1 WEEK 1-10Ken-bee BangcaNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning Lab ManualDocument38 pagesMachine Learning Lab ManualabdulNo ratings yet
- Keats As Romantic PoetDocument14 pagesKeats As Romantic PoetTaibur Rahaman100% (2)
- PM Question PaperDocument2 pagesPM Question PaperSwathi Jampala100% (3)
- Teacher TalkDocument6 pagesTeacher TalkGloria GinevraNo ratings yet
- Task 1 - What's The Real Meaning?Document6 pagesTask 1 - What's The Real Meaning?gogolee2013No ratings yet
- TNCT Lesson 4Document18 pagesTNCT Lesson 4Krys shaine ValdezNo ratings yet
- Egyptian Arabic Lesson 1 Introductions: EA1 Main Dialogue: Listen online Vocabulary تادﺮﻔﳌاDocument3 pagesEgyptian Arabic Lesson 1 Introductions: EA1 Main Dialogue: Listen online Vocabulary تادﺮﻔﳌاPakar Kuda LautNo ratings yet
- Secrets of Happy BrainDocument4 pagesSecrets of Happy BrainLaura SandovalNo ratings yet
- Feedback & Reflection POWERPOINTDocument52 pagesFeedback & Reflection POWERPOINTAmal SaeedNo ratings yet
- NỘI DUNG ÔN THI HỌC KÌ MÔN TIẾNG ANH 11Document8 pagesNỘI DUNG ÔN THI HỌC KÌ MÔN TIẾNG ANH 11Thiện MinhhNo ratings yet
- EDUC 17 SyllabusDocument3 pagesEDUC 17 SyllabusHanna Sharleen FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Holy Cross College, Inc.: Sta. Ana, PampangaDocument13 pagesHoly Cross College, Inc.: Sta. Ana, PampangaMary Catherine Shire MusniNo ratings yet
- L The Processes of Instruction-LDocument12 pagesL The Processes of Instruction-Lapi-247091657No ratings yet
- Evaluating Creative Multimedia FormDocument3 pagesEvaluating Creative Multimedia FormLonil Bayongawan100% (1)