Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Long Wavelength: Low Frequency & Low Energy
Long Wavelength: Low Frequency & Low Energy
Uploaded by
Guki SuzukiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Philippine History: Spaces For Conflict and ControversiesDocument74 pagesPhilippine History: Spaces For Conflict and ControversiesGuki Suzuki80% (10)
- SCIENCE REVIEWER FinalDocument8 pagesSCIENCE REVIEWER FinalAzi MendozaNo ratings yet
- Heat, Light, SoundDocument32 pagesHeat, Light, SoundJoey Orencia Rimando100% (1)
- Heat Transfer in The AtmosphereDocument21 pagesHeat Transfer in The Atmosphereesthy angeliaNo ratings yet
- p6 Heat TransferDocument3 pagesp6 Heat TransferLeslie MasiyandimaNo ratings yet
- Heat, Light, SoundDocument31 pagesHeat, Light, SoundLen B RoxasNo ratings yet
- S4 Physics Notes 10TH Februry, 2022Document2 pagesS4 Physics Notes 10TH Februry, 2022keosotepyNo ratings yet
- PhysicssDocument5 pagesPhysicsschionumaraliaNo ratings yet
- How Heat Is Produced: 4 Grade ScienceDocument20 pagesHow Heat Is Produced: 4 Grade Sciencenoman turkNo ratings yet
- (Physics)Document18 pages(Physics)ved.kulkarniNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Thermal ProcessesDocument6 pages2.3 Thermal ProcesseshaiderNo ratings yet
- Heating and CoolingsDocument13 pagesHeating and CoolingsMegan CollinsNo ratings yet
- Physci ReviewerDocument18 pagesPhysci ReviewerGrobotan LuchiNo ratings yet
- Physci ReviewerDocument18 pagesPhysci ReviewerGrobotan LuchiNo ratings yet
- (2.3) C - Transfer of Thermal Energy - RadiationDocument2 pages(2.3) C - Transfer of Thermal Energy - Radiationzahra1No ratings yet
- Waves PPDocument21 pagesWaves PPMacha LaraNo ratings yet
- Ch-13 (Limit and Derivatives FINAL 02.01.06)Document9 pagesCh-13 (Limit and Derivatives FINAL 02.01.06)AnnNo ratings yet
- AnotherDocument6 pagesAnotherIrram RanaNo ratings yet
- HE BackDocument2 pagesHE BackJoshua BrightNo ratings yet
- Energy TransferDocument1 pageEnergy TransferCecilia Carrizo SosaNo ratings yet
- Heat Energy Transfer BookletDocument4 pagesHeat Energy Transfer BookletLaurenNo ratings yet
- Physics Reviewer MotionDocument9 pagesPhysics Reviewer MotionCamaddu GelaicaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7Document10 pagesLesson 7Stephen Maina NjorogeNo ratings yet
- Science Notes Term 2Document19 pagesScience Notes Term 2Suha QaisarNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 4 W AnswersDocument2 pagesSCIENCE 4 W AnswersGirlie BacaocoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument8 pagesSCIENCEdive iveNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 3RD QTRDocument6 pagesScience Reviewer 3RD QTRElise Emmry R. OchoaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Lecture Introduction To Passive SolarDocument26 pages2nd Lecture Introduction To Passive SolarmokhtarNo ratings yet
- Thermal EnergyDocument11 pagesThermal Energyyoungboss49gamerNo ratings yet
- Physics Checkpoint Topics Part 1Document23 pagesPhysics Checkpoint Topics Part 1esteban ferrada silvaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Transmission of HeatDocument18 pagesLecture 4 Transmission of Heatdinesh11rNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves and Material InteractionsDocument27 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and Material InteractionsAmy OliverNo ratings yet
- Thermal EnergyDocument11 pagesThermal Energyyoungboss49gamerNo ratings yet
- Modes of Heat TransferDocument6 pagesModes of Heat TransferfaisalNo ratings yet
- Fuels & Energy: Checkpoint PhysicsDocument18 pagesFuels & Energy: Checkpoint PhysicslplkwvNo ratings yet
- Methods of Heat TransferDocument29 pagesMethods of Heat TransferRodriguez ArthursNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer by RadiationDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer by Radiationyesuplus20% (1)
- NsokwjkkkDocument2 pagesNsokwjkkkCitruss TvNo ratings yet
- 1 Heat TransferDocument3 pages1 Heat TransferAdam HartmannNo ratings yet
- Physics RevisionDocument7 pagesPhysics RevisionKhalid IssaNo ratings yet
- HEATDocument16 pagesHEATHoney Mae CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Science Heat Energy Study Guide-32Document6 pagesScience Heat Energy Study Guide-32CarlosCD17100% (1)
- Interface Mass TraDocument26 pagesInterface Mass TraWahid AliNo ratings yet
- PhysicsrevisionnotesDocument12 pagesPhysicsrevisionnotesapi-253698991No ratings yet
- SCIENCE 3rd Quarter PhysicsDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 3rd Quarter PhysicsAlzon Joseph SamboNo ratings yet
- Conduction, Convection and Radiation-1Document19 pagesConduction, Convection and Radiation-1Alvin JacobNo ratings yet
- Forms of EnergyDocument37 pagesForms of Energygren5269No ratings yet
- Science 2Document37 pagesScience 2Hannah Leigh CoronelNo ratings yet
- Cape Phy Mod 3 - Heat Transfer 2Document3 pagesCape Phy Mod 3 - Heat Transfer 2kerriemarsNo ratings yet
- Science VocabularyDocument6 pagesScience Vocabularysamed brionesNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Understanding Conduction Convection RadiationDocument29 pagesModule 2 Understanding Conduction Convection RadiationVishnupriya B.No ratings yet
- MatterDocument2 pagesMatterMICHELLE LOREN A. ABRENILLANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Thermal Imaging: Joseph E. Osowski, PEDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Thermal Imaging: Joseph E. Osowski, PEashokmmmNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument17 pagesSCIENCENIÑA JANE BARREDONo ratings yet
- Physics GlossaryDocument5 pagesPhysics GlossaryShania AlertNo ratings yet
- Physics AssignDocument4 pagesPhysics Assignsparkle-A TenchNo ratings yet
- Conduction, Convection, RadiationDocument4 pagesConduction, Convection, RadiationChloe LiewNo ratings yet
- IB Physics Notes On Thermal Energy TransferDocument7 pagesIB Physics Notes On Thermal Energy TransferTheodore KimNo ratings yet
- What Is Conduction?Document9 pagesWhat Is Conduction?Ali Usman AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Philippine History: Spaces For Conflict and ControversiesDocument74 pagesPhilippine History: Spaces For Conflict and ControversiesGuki SuzukiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3.1.1 DebateDocument4 pagesExercise 3.1.1 DebateGuki SuzukiNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: C. The Evidence of LimasawaDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: C. The Evidence of LimasawaGuki SuzukiNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Primary Source: Pigafetta's Testimony On The Route of Magellan's ExpeditionDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Primary Source: Pigafetta's Testimony On The Route of Magellan's ExpeditionGuki SuzukiNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Pigafetta's Testimny On The Route of Magellan's ExpeditionDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Pigafetta's Testimny On The Route of Magellan's ExpeditionGuki SuzukiNo ratings yet
- Pigafetta's: Testimony On The Route of Magellan"s ExpeditionDocument11 pagesPigafetta's: Testimony On The Route of Magellan"s ExpeditionGuki SuzukiNo ratings yet
- Rizal RetractionDocument1 pageRizal RetractionGuki SuzukiNo ratings yet
Long Wavelength: Low Frequency & Low Energy
Long Wavelength: Low Frequency & Low Energy
Uploaded by
Guki SuzukiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Long Wavelength: Low Frequency & Low Energy
Long Wavelength: Low Frequency & Low Energy
Uploaded by
Guki SuzukiCopyright:
Available Formats
Elasticity– the ability of an object to bounce back to its original shape.
Lenses– a curved piece of material used to bend light
Insulator – a material that does not transfer heat well: air, carpet, wood
Intensity– the amount of energy the wave carries per second per meter squared
Long wavelength : Low Frequency & Low Energy
Transparent: The material transmits light – allows light to pass through it– glass
Density– generally speaking, in material of the same state of matter (solid, liquid or gas) the denser the
medium the slower the sound travels. Sound travels slower in lead than it does in steel
Wavelength– the distance between two corresponding parts of a wave.
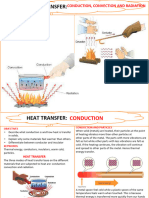
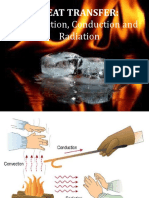
Convection – movement that transfers heat by movement of currents within the particles.
Image: a copy of an object formed by reflected or refracted light
resonance– when the frequency of sound matches the natural frequency of an object
Translucent: allows some light to pass through – can’t see image clearly – wax paper, frosted glass.
Chuck Yeager– first man to fly faster than the speed of sound
Transverse Waves: waves that move the medium at right angles to the direction in which the waves are
traveling.
Conduction – heat is transferred from one particle to the next Radiation particle w/out the particles
actually moving or changing place. – Examples include: a metal spoon in hot water gets hot or a pot gets
hot as it sits on an electric stove.
Opaque: a material that reflects or absorbs the light – can’t see through it. -wood
Radiation Zone – transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves. – Examples include: the Sun’s energy
traveling thru space and heating up the Earth w/out heating space itself, Heat lamps used at fast food
restaurants, and the radiator of a car dissipating the heat of an engine
standing waves– the combining of the incoming and reflected wave so that the resultant appears to be standing
still
Thermal energy – TOTAL energy of all of the particles
Law of Reflection: Angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection
Wave– a disturbance that transfers energy from place to place
You might also like
- Philippine History: Spaces For Conflict and ControversiesDocument74 pagesPhilippine History: Spaces For Conflict and ControversiesGuki Suzuki80% (10)
- SCIENCE REVIEWER FinalDocument8 pagesSCIENCE REVIEWER FinalAzi MendozaNo ratings yet
- Heat, Light, SoundDocument32 pagesHeat, Light, SoundJoey Orencia Rimando100% (1)
- Heat Transfer in The AtmosphereDocument21 pagesHeat Transfer in The Atmosphereesthy angeliaNo ratings yet
- p6 Heat TransferDocument3 pagesp6 Heat TransferLeslie MasiyandimaNo ratings yet
- Heat, Light, SoundDocument31 pagesHeat, Light, SoundLen B RoxasNo ratings yet
- S4 Physics Notes 10TH Februry, 2022Document2 pagesS4 Physics Notes 10TH Februry, 2022keosotepyNo ratings yet
- PhysicssDocument5 pagesPhysicsschionumaraliaNo ratings yet
- How Heat Is Produced: 4 Grade ScienceDocument20 pagesHow Heat Is Produced: 4 Grade Sciencenoman turkNo ratings yet
- (Physics)Document18 pages(Physics)ved.kulkarniNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Thermal ProcessesDocument6 pages2.3 Thermal ProcesseshaiderNo ratings yet
- Heating and CoolingsDocument13 pagesHeating and CoolingsMegan CollinsNo ratings yet
- Physci ReviewerDocument18 pagesPhysci ReviewerGrobotan LuchiNo ratings yet
- Physci ReviewerDocument18 pagesPhysci ReviewerGrobotan LuchiNo ratings yet
- (2.3) C - Transfer of Thermal Energy - RadiationDocument2 pages(2.3) C - Transfer of Thermal Energy - Radiationzahra1No ratings yet
- Waves PPDocument21 pagesWaves PPMacha LaraNo ratings yet
- Ch-13 (Limit and Derivatives FINAL 02.01.06)Document9 pagesCh-13 (Limit and Derivatives FINAL 02.01.06)AnnNo ratings yet
- AnotherDocument6 pagesAnotherIrram RanaNo ratings yet
- HE BackDocument2 pagesHE BackJoshua BrightNo ratings yet
- Energy TransferDocument1 pageEnergy TransferCecilia Carrizo SosaNo ratings yet
- Heat Energy Transfer BookletDocument4 pagesHeat Energy Transfer BookletLaurenNo ratings yet
- Physics Reviewer MotionDocument9 pagesPhysics Reviewer MotionCamaddu GelaicaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7Document10 pagesLesson 7Stephen Maina NjorogeNo ratings yet
- Science Notes Term 2Document19 pagesScience Notes Term 2Suha QaisarNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 4 W AnswersDocument2 pagesSCIENCE 4 W AnswersGirlie BacaocoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument8 pagesSCIENCEdive iveNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 3RD QTRDocument6 pagesScience Reviewer 3RD QTRElise Emmry R. OchoaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Lecture Introduction To Passive SolarDocument26 pages2nd Lecture Introduction To Passive SolarmokhtarNo ratings yet
- Thermal EnergyDocument11 pagesThermal Energyyoungboss49gamerNo ratings yet
- Physics Checkpoint Topics Part 1Document23 pagesPhysics Checkpoint Topics Part 1esteban ferrada silvaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Transmission of HeatDocument18 pagesLecture 4 Transmission of Heatdinesh11rNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves and Material InteractionsDocument27 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and Material InteractionsAmy OliverNo ratings yet
- Thermal EnergyDocument11 pagesThermal Energyyoungboss49gamerNo ratings yet
- Modes of Heat TransferDocument6 pagesModes of Heat TransferfaisalNo ratings yet
- Fuels & Energy: Checkpoint PhysicsDocument18 pagesFuels & Energy: Checkpoint PhysicslplkwvNo ratings yet
- Methods of Heat TransferDocument29 pagesMethods of Heat TransferRodriguez ArthursNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer by RadiationDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer by Radiationyesuplus20% (1)
- NsokwjkkkDocument2 pagesNsokwjkkkCitruss TvNo ratings yet
- 1 Heat TransferDocument3 pages1 Heat TransferAdam HartmannNo ratings yet
- Physics RevisionDocument7 pagesPhysics RevisionKhalid IssaNo ratings yet
- HEATDocument16 pagesHEATHoney Mae CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Science Heat Energy Study Guide-32Document6 pagesScience Heat Energy Study Guide-32CarlosCD17100% (1)
- Interface Mass TraDocument26 pagesInterface Mass TraWahid AliNo ratings yet
- PhysicsrevisionnotesDocument12 pagesPhysicsrevisionnotesapi-253698991No ratings yet
- SCIENCE 3rd Quarter PhysicsDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 3rd Quarter PhysicsAlzon Joseph SamboNo ratings yet
- Conduction, Convection and Radiation-1Document19 pagesConduction, Convection and Radiation-1Alvin JacobNo ratings yet
- Forms of EnergyDocument37 pagesForms of Energygren5269No ratings yet
- Science 2Document37 pagesScience 2Hannah Leigh CoronelNo ratings yet
- Cape Phy Mod 3 - Heat Transfer 2Document3 pagesCape Phy Mod 3 - Heat Transfer 2kerriemarsNo ratings yet
- Science VocabularyDocument6 pagesScience Vocabularysamed brionesNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Understanding Conduction Convection RadiationDocument29 pagesModule 2 Understanding Conduction Convection RadiationVishnupriya B.No ratings yet
- MatterDocument2 pagesMatterMICHELLE LOREN A. ABRENILLANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Thermal Imaging: Joseph E. Osowski, PEDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Thermal Imaging: Joseph E. Osowski, PEashokmmmNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument17 pagesSCIENCENIÑA JANE BARREDONo ratings yet
- Physics GlossaryDocument5 pagesPhysics GlossaryShania AlertNo ratings yet
- Physics AssignDocument4 pagesPhysics Assignsparkle-A TenchNo ratings yet
- Conduction, Convection, RadiationDocument4 pagesConduction, Convection, RadiationChloe LiewNo ratings yet
- IB Physics Notes On Thermal Energy TransferDocument7 pagesIB Physics Notes On Thermal Energy TransferTheodore KimNo ratings yet
- What Is Conduction?Document9 pagesWhat Is Conduction?Ali Usman AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Philippine History: Spaces For Conflict and ControversiesDocument74 pagesPhilippine History: Spaces For Conflict and ControversiesGuki SuzukiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3.1.1 DebateDocument4 pagesExercise 3.1.1 DebateGuki SuzukiNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: C. The Evidence of LimasawaDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: C. The Evidence of LimasawaGuki SuzukiNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Primary Source: Pigafetta's Testimony On The Route of Magellan's ExpeditionDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Primary Source: Pigafetta's Testimony On The Route of Magellan's ExpeditionGuki SuzukiNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Pigafetta's Testimny On The Route of Magellan's ExpeditionDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Pigafetta's Testimny On The Route of Magellan's ExpeditionGuki SuzukiNo ratings yet
- Pigafetta's: Testimony On The Route of Magellan"s ExpeditionDocument11 pagesPigafetta's: Testimony On The Route of Magellan"s ExpeditionGuki SuzukiNo ratings yet
- Rizal RetractionDocument1 pageRizal RetractionGuki SuzukiNo ratings yet