Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Immune System Flashcards
Immune System Flashcards
Uploaded by
Lej0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views28 pagesThe immune system distinguishes between self and nonself antigens. There are two types of B-lymphocytes: memory cells which remember antigens and speed up secondary responses, and plasma cells which produce and release antibodies. The immune system can develop active immunity through antibody production during a response, or passive immunity through transfer of antibodies between organisms. There are three main types of T-lymphocytes: cytotoxic T-cells which destroy infected cells, helper T-cells which activate other immune cells, and suppressor T-cells which decrease immune responses. The nonspecific immune response includes skin barriers and inflammation. Lymph vessels drain into veins while lacteals absorb fats in the small intestine. Lymph nodes along vessels contain cells that
Original Description:
2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe immune system distinguishes between self and nonself antigens. There are two types of B-lymphocytes: memory cells which remember antigens and speed up secondary responses, and plasma cells which produce and release antibodies. The immune system can develop active immunity through antibody production during a response, or passive immunity through transfer of antibodies between organisms. There are three main types of T-lymphocytes: cytotoxic T-cells which destroy infected cells, helper T-cells which activate other immune cells, and suppressor T-cells which decrease immune responses. The nonspecific immune response includes skin barriers and inflammation. Lymph vessels drain into veins while lacteals absorb fats in the small intestine. Lymph nodes along vessels contain cells that
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views28 pagesImmune System Flashcards
Immune System Flashcards
Uploaded by
LejThe immune system distinguishes between self and nonself antigens. There are two types of B-lymphocytes: memory cells which remember antigens and speed up secondary responses, and plasma cells which produce and release antibodies. The immune system can develop active immunity through antibody production during a response, or passive immunity through transfer of antibodies between organisms. There are three main types of T-lymphocytes: cytotoxic T-cells which destroy infected cells, helper T-cells which activate other immune cells, and suppressor T-cells which decrease immune responses. The nonspecific immune response includes skin barriers and inflammation. Lymph vessels drain into veins while lacteals absorb fats in the small intestine. Lymph nodes along vessels contain cells that
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 28
Biology – Immune System
What does the immune system distinguish between?
The body distinguishes between “self” and “nonself”
(antigens)
Biology – Immune System
What are the types of B-lymphocytes?
Memory cells and plasma cells
Biology – Immune System
Memory cells
Remember antigen, speed up secondary response
Biology – Immune System
Plasma cells
Plasma cells make and release antibodies (IgG, IgA, IgM,
IgD, IgE) which induce antigen phagocytosis
Biology – Immune System
Active Immunity
Antibodies are produced during an immune response
Biology – Immune System
Passive Immunity
Antibodies produced by one organism are transferred to
another organism
Biology – Immune System
What are the types of T-lymphocytes?
Cytotoxic T-Cell
Helper T-Cells
Suppressor T-Cells
Memory Cells
Biology – Immune System
Cytotoxic T-Cell
Destroy cells directly
Biology – Immune System
Helper T-Cells
Activate B- and T-cells and macrophages by secreting
lymphokines
Biology – Immune System
Suppressor T-Cells
Regulate B- and T-cells to decrease anti-antigen activity
Biology – Immune System
Nonspecific Immune Response
Includes skin, passages lined with cilia, macrophages,
inflammatory response, and interferons (proteins that help
prevent the spread of a virus)
Biology – Immune System
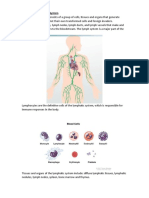
Where do Lymph vessels meet in the Lymphatic
System?
Lymph vessels meet at the thoracic duct in the upper chest
and neck, draining into the left subclavian vein of the
cardiovascular system
Biology – Immune System
What are the functions of vessels and lacteals?
Vessels carry lymph (excess interstitial fluid), and lacteals
collect fats by absorbing chylomicrons in the small
intestine
Biology – Immune System
What occurs with lymph nodes in the Lymphatic
System?
Lymph nodes are swellings along the vessels with
phagocytic cells (leukocytes); they remove foreign particles
from lymph
You might also like
- What Does The Immune System Distinguish Between?Document2 pagesWhat Does The Immune System Distinguish Between?LejNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Immune System: Zoran Galic PH.DDocument18 pagesOverview of The Immune System: Zoran Galic PH.DAniruddha RoyNo ratings yet
- IMMUNITYDocument23 pagesIMMUNITYFlorence Lynn BaisacNo ratings yet
- Immunity: by Ashok K TiwariDocument42 pagesImmunity: by Ashok K TiwariXEDGER09No ratings yet
- MODULE 21 HANDOUTS The Lymphatic SystemDocument6 pagesMODULE 21 HANDOUTS The Lymphatic SystemMichaela PoNo ratings yet
- 4 Sistem Raspuns Imun 2011 PDFDocument63 pages4 Sistem Raspuns Imun 2011 PDFGigiEnergieNo ratings yet
- Immune System Docs 2019Document13 pagesImmune System Docs 2019David DavidNo ratings yet
- Sistem Limfatik Dan ImunitasDocument78 pagesSistem Limfatik Dan ImunitasMasna Arisah NasutionNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Study of How The Body Limits Invasion by Non-Self and Recognises and Eliminates Altered SelfDocument28 pagesImmunology: Study of How The Body Limits Invasion by Non-Self and Recognises and Eliminates Altered SelfDuodu StevenNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument7 pagesBio ProjectJanki KarwaNo ratings yet
- Functions of Immune SystemDocument6 pagesFunctions of Immune Systemanna jean oliquianoNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument82 pagesImmune SystemMa Divina Kristi Discar100% (1)
- Immune SystemDocument6 pagesImmune SystemSanNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System: Jeezreel M. Orquina, RN, LPTDocument18 pagesLymphatic System: Jeezreel M. Orquina, RN, LPTJezreel OrquinaNo ratings yet
- ANATOMYDocument3 pagesANATOMYKara Faith DeocadesNo ratings yet
- 2ND Quarter - General Biology 2Document34 pages2ND Quarter - General Biology 2Nicole KhazelNo ratings yet
- 02 ImmunityDocument49 pages02 Immunityglenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- BIOL25441 Class 5 and 6 Winter 2013Document58 pagesBIOL25441 Class 5 and 6 Winter 2013raunak .comNo ratings yet
- Immunology and SerologyDocument225 pagesImmunology and SerologyialegnaNo ratings yet
- The Immune System: A Tutorial: Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta'asanDocument33 pagesThe Immune System: A Tutorial: Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta'asanManendra PatwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Lymphatic SystemDocument4 pagesChapter 14 Lymphatic SystemDivinefavourNo ratings yet
- Inbound 5512190204664159847Document12 pagesInbound 5512190204664159847Barzan A MahmudNo ratings yet
- Iv. Review of Anatomy and Physiology Figure 1. The Immune SystemDocument7 pagesIv. Review of Anatomy and Physiology Figure 1. The Immune SystemNejie Zarrah Diaz100% (1)
- Concept On Immune Response and Inflammation REVISEDDocument163 pagesConcept On Immune Response and Inflammation REVISEDKirk08100% (1)
- S6 Blood & ImmunityDocument41 pagesS6 Blood & ImmunityZoltan FodorNo ratings yet
- Lymphocytes - 12Document19 pagesLymphocytes - 12Nikhil BijuNo ratings yet
- 1 ImmunityDocument12 pages1 Immunitydebasmitabera5947No ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunityDocument54 pagesIntroduction To ImmunityHadi Adam100% (1)
- Immune Response and The Role of Lymphatic SystemDocument6 pagesImmune Response and The Role of Lymphatic SystemchiomasingsNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic SystemDocument10 pagesThe Lymphatic SystemChloe MercadoNo ratings yet
- B 11 LymphaticDocument31 pagesB 11 Lymphaticชนิตพล กาญจนวนิชกุลNo ratings yet
- Immunity STPMDocument2 pagesImmunity STPMjennie0% (1)
- Immune System by Asif PresentationDocument35 pagesImmune System by Asif PresentationHassan AsifNo ratings yet
- Immunology OverviewDocument83 pagesImmunology OverviewHARIS KKNo ratings yet
- Hematology & Immune SystemDocument81 pagesHematology & Immune SystemAmanuel Maru100% (1)
- Anatomy Physiology DengueDocument8 pagesAnatomy Physiology DengueArms PrielaNo ratings yet
- Immune System Overview - Understanding The Immune SystemDocument60 pagesImmune System Overview - Understanding The Immune Systemlourdesbr100% (2)
- Basic Concepts in ImmunologyDocument56 pagesBasic Concepts in ImmunologyDedy SambahtraNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Lymphatic SystemDocument35 pagesGroup 3 - Lymphatic SystemGLTSyed MiqueNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues of The Lymphoid SystemDocument27 pagesCells and Tissues of The Lymphoid SystemAlbaraa Arbab MohammedNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 BioDocument14 pagesUnit 5 Bioiam SaveMeNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic and Immune SystemsDocument4 pagesThe Lymphatic and Immune SystemsHua YueNo ratings yet
- CBS Imm1Document31 pagesCBS Imm1tyhbbhhNo ratings yet
- Immune Response: Cell Biology and Its Application BI-1202Document35 pagesImmune Response: Cell Biology and Its Application BI-1202Eriani Wulandari100% (1)
- Cell and Tissue of Immune SystemDocument15 pagesCell and Tissue of Immune SystemFatmaAnnisaNo ratings yet
- Immunity: Innate Defenses Specific Immunity Cell Mediated Immunity Self RecognitionDocument56 pagesImmunity: Innate Defenses Specific Immunity Cell Mediated Immunity Self RecognitionMiranda sekar arumNo ratings yet
- Cell and Tissue of Immune SystemDocument15 pagesCell and Tissue of Immune SystemfatmawatiNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System Notes StudentDocument7 pagesThe Lymphatic System Notes Studentapi-655732711No ratings yet
- The Lymphatic and Immune SystemDocument12 pagesThe Lymphatic and Immune SystemAthena Huynh100% (1)
- B) Acquired Immunity ( Adaptive or Specific Immunity)Document32 pagesB) Acquired Immunity ( Adaptive or Specific Immunity)punamsingh2k0% (1)
- An Overview of The Immune SystemDocument7 pagesAn Overview of The Immune SystemChandan AhireNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34 Guyton and HallDocument5 pagesChapter 34 Guyton and Hallg_komolafeNo ratings yet
- Hiv & AdisDocument60 pagesHiv & Adisomarism1960No ratings yet
- It 4 - Sel Dan Jaringan Sistim ImunDocument90 pagesIt 4 - Sel Dan Jaringan Sistim Imunezra soNo ratings yet
- Immunology NotesDocument4 pagesImmunology NotesDavinci LegaspiNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument41 pagesImmunityBonzowoNo ratings yet
- Immune System: Phagocytic LeukocyteDocument23 pagesImmune System: Phagocytic LeukocyteikaNo ratings yet
- Women and Autoimmune Disease: The Mysterious Ways Your Body Betrays ItselfFrom EverandWomen and Autoimmune Disease: The Mysterious Ways Your Body Betrays ItselfRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- A Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisNo ratings yet
- The Slim Book of Health Pearls: Man the Barricades - The Story of the Immune SystemFrom EverandThe Slim Book of Health Pearls: Man the Barricades - The Story of the Immune SystemNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Waves FlaschardsDocument39 pagesFluids and Waves FlaschardsLejNo ratings yet
- Kinematics, Motion, Force, and Torque FlashcardsDocument73 pagesKinematics, Motion, Force, and Torque FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- What Is The Functional Group Displayed Below?Document3 pagesWhat Is The Functional Group Displayed Below?LejNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics and Magnetism FlashcardsDocument29 pagesElectrostatics and Magnetism FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Energy, Momentum, and Work FlashcardsDocument82 pagesEnergy, Momentum, and Work FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- The Average of The Data Points: Negatively SkewedDocument3 pagesThe Average of The Data Points: Negatively SkewedLejNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature, Bonding, and Isomers FlashcardsDocument106 pagesNomenclature, Bonding, and Isomers FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Measures Molecular Vibrations of Characteristic Functional GroupsDocument4 pagesMeasures Molecular Vibrations of Characteristic Functional GroupsLejNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy FlashcardsDocument66 pagesSpectroscopy FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Extraction: R Distance of Substance Solvent L IneDocument2 pagesExtraction: R Distance of Substance Solvent L IneLejNo ratings yet
- Label The Parts of The Neuron:: Biology - Nervous SystemDocument25 pagesLabel The Parts of The Neuron:: Biology - Nervous SystemLejNo ratings yet
- Purification Methods FlashcardsDocument35 pagesPurification Methods FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- What Are The Stages of Cell Division? Describe Them:: Biology - ReproductionDocument29 pagesWhat Are The Stages of Cell Division? Describe Them:: Biology - ReproductionLejNo ratings yet
- When Is The Population in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?: Biology - EvolutionDocument6 pagesWhen Is The Population in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?: Biology - EvolutionLejNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System FlashcardsDocument23 pagesMusculoskeletal System FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis FlashcardsDocument46 pagesHomeostasis FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Where Does Gas Exchange Occur?: Biology - RespirationDocument14 pagesWhere Does Gas Exchange Occur?: Biology - RespirationLejNo ratings yet
- Label The Parts of The NeuronDocument3 pagesLabel The Parts of The NeuronLejNo ratings yet
- What Is The Base Unit of The Nucleic Acids?Document2 pagesWhat Is The Base Unit of The Nucleic Acids?LejNo ratings yet
- What Does The Immune System Distinguish Between?Document2 pagesWhat Does The Immune System Distinguish Between?LejNo ratings yet
- When Frequencies Are Stable: When Is The Population in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?Document1 pageWhen Frequencies Are Stable: When Is The Population in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?LejNo ratings yet
- What Is The Liver's Role in Homeostasis?Document4 pagesWhat Is The Liver's Role in Homeostasis?LejNo ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics FlashcardsDocument34 pagesMolecular Genetics FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Genetics of Prokaryotic Cells FlashcardsDocument12 pagesGenetics of Prokaryotic Cells FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Classical GeneticsDocument1 pageClassical GeneticsLejNo ratings yet
- What Do Direct Hormones Stimulate?: Biology - EndocrineDocument66 pagesWhat Do Direct Hormones Stimulate?: Biology - EndocrineLejNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Pathway Through The Heart: Biology - CirculationDocument34 pagesCirculatory Pathway Through The Heart: Biology - CirculationLejNo ratings yet
- Digestion FlaschardsDocument76 pagesDigestion FlaschardsLejNo ratings yet
- Classical Genetics FlashcardsDocument14 pagesClassical Genetics FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet