Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 viewsSpectroscopy Flashcards
Spectroscopy Flashcards
Uploaded by
LejThis document provides an overview of various spectroscopy techniques used in organic chemistry, including infrared spectroscopy (IR), ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV), and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR). It lists the characteristic functional groups observed in IR spectroscopy and their typical absorption ranges. It also outlines the general chemical shift ranges seen for common proton environments in 1H NMR spectroscopy and how the number of adjacent protons affects peak splitting.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- (Organo) Part BDocument9 pages(Organo) Part BAmirul Amin Bin ShukriNo ratings yet
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Asymmetric SynthesisDocument55 pagesAsymmetric Synthesisevsgoud_goud0% (1)
- Lab Report Sds-Page WB - PT 1 (1-5)Document5 pagesLab Report Sds-Page WB - PT 1 (1-5)Ezad juferiNo ratings yet
- 2d NMRDocument32 pages2d NMRDelicz TanNo ratings yet
- 39 SpectrosDocument9 pages39 SpectrosDinel JosephNo ratings yet
- Measures Molecular Vibrations of Characteristic Functional GroupsDocument4 pagesMeasures Molecular Vibrations of Characteristic Functional GroupsLejNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy and ChromatographyDocument7 pagesSpectroscopy and ChromatographyPa GesNo ratings yet
- 6spectroscopy and ChromatographyDocument15 pages6spectroscopy and ChromatographyThinaya JayarathneNo ratings yet
- Ilcpa 202 2014 219 233Document15 pagesIlcpa 202 2014 219 233KassimNo ratings yet
- Mass SpectrometryDocument111 pagesMass SpectrometryRajesh Kadavath100% (2)
- Topic 5Document30 pagesTopic 5Shehnaz KamarNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectroscopy & NMR Spectroscopy: Big PictureDocument13 pagesMass Spectroscopy & NMR Spectroscopy: Big PictureluyawinNo ratings yet
- IR and NMR SpectrosDocument13 pagesIR and NMR SpectrosAnand BarapatreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document8 pagesChapter 14nelaojNo ratings yet
- Analytical TechniquesDocument6 pagesAnalytical TechniquesahumanbeinginearthNo ratings yet
- NMR Hly09Document44 pagesNMR Hly09Giang NguyenNo ratings yet
- 5.Nmr Class LatestDocument81 pages5.Nmr Class Latestdimitra shenoyNo ratings yet
- 1455877785CHE P12 M35 EtextDocument8 pages1455877785CHE P12 M35 EtextSaurav PaulNo ratings yet
- Spectrochim-Acta-2012-Single Crystal Structure, Spectroscopic Studies, Physico-Chemical Properties and Theoretical Calculations of TriazeneDocument9 pagesSpectrochim-Acta-2012-Single Crystal Structure, Spectroscopic Studies, Physico-Chemical Properties and Theoretical Calculations of TriazeneELKIN ALFONSO RODRIGUEZ AGUALIMPIANo ratings yet
- Problem of Spectroscopy: Teacher: Nguyen Thien ThaoDocument49 pagesProblem of Spectroscopy: Teacher: Nguyen Thien Thaogianghha50% (2)
- Experiment 1Document16 pagesExperiment 1Izhharuddin100% (2)
- Coii Niii Cuii and Criii Complexes of Heterocyclic Schiff Base Ligand Synthesis Spectroscopic and Thermal StudyDocument5 pagesCoii Niii Cuii and Criii Complexes of Heterocyclic Schiff Base Ligand Synthesis Spectroscopic and Thermal StudyIJARP Publications100% (1)
- ChemistryDocument70 pagesChemistryKieran SangheraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Proton NMR SpectroscopyNJTDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Proton NMR SpectroscopyNJTNicoleNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectra and IRDocument7 pagesMass Spectra and IRSyed FahimNo ratings yet
- Structure Determination: Mass SpectrometryDocument3 pagesStructure Determination: Mass SpectrometrySharmeen HelalNo ratings yet
- Mo JAEDocument4 pagesMo JAEThanhThao TranNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Results in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) SpectrosDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Results in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) SpectrostypodleeNo ratings yet
- NMR SpectrosDocument29 pagesNMR Spectroshareesh13h100% (1)
- Applications of UV IRDocument32 pagesApplications of UV IRShaikh SalmanNo ratings yet
- Biophysics: Nuclear Magnetic ResonanceDocument28 pagesBiophysics: Nuclear Magnetic Resonancejosito2003No ratings yet
- Spectroscopic Techniques & Application: Unit VIIDocument20 pagesSpectroscopic Techniques & Application: Unit VIIshubh mehtaNo ratings yet
- 13C NMR Spectroscopy Power Point PresentationDocument34 pages13C NMR Spectroscopy Power Point PresentationSagarChedeNo ratings yet
- CHMBD 449 - Organic Spectral: AnalysisDocument43 pagesCHMBD 449 - Organic Spectral: AnalysisIleana ManciuleaNo ratings yet
- IR, Raman and Ab-Initio Calcualtions of Glycolic AcidDocument6 pagesIR, Raman and Ab-Initio Calcualtions of Glycolic AcidGerald See TohNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document28 pagesLecture 1Sebastián Castro FragueiroNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosDocument18 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosAMAN JATNo ratings yet
- NMR Multiple Choice Questions PDFDocument71 pagesNMR Multiple Choice Questions PDFDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- C-13 NMR and DEPTDocument41 pagesC-13 NMR and DEPTV G Viju Kumar100% (1)
- NMR 7.Document36 pagesNMR 7.Imran KhanNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument78 pagesChemistryShabnam Fatima SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- FTIR1Document5 pagesFTIR1Romajun Villamor MaputiNo ratings yet
- IR and Raman Spectroscopy of Organometallic Compounds-HCDocument38 pagesIR and Raman Spectroscopy of Organometallic Compounds-HCrakesh1521100% (2)
- UltravioletDocument76 pagesUltravioletRadius JuliusNo ratings yet
- Structure Determination of Organic Compounds - ChemvoiceDocument37 pagesStructure Determination of Organic Compounds - ChemvoiceJubin Kumar0% (1)
- SCHB032 NMR Part2redoDocument29 pagesSCHB032 NMR Part2redoemjayNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Modern Analytical Techniques IDocument2 pagesTopic 7 - Modern Analytical Techniques Ijulian maltoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Compatibility Mode)Document76 pagesChapter 2 (Compatibility Mode)HaiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - EasyDocument12 pagesOrganic Chemistry - EasyNaevisweloveuNo ratings yet
- Mcmurry 12Document62 pagesMcmurry 12Ngurah MahasviraNo ratings yet
- Tructural Hemistry Ommunications: DFT Based Characterization of Some Heterocyclic Compounds and Their Biological StudiesDocument10 pagesTructural Hemistry Ommunications: DFT Based Characterization of Some Heterocyclic Compounds and Their Biological StudiesAlex-Mihai CiubaraNo ratings yet
- 3 - Carbon-13-NMRDocument21 pages3 - Carbon-13-NMRahmed mohamedNo ratings yet
- NMR Spectropscopy HkaurDocument42 pagesNMR Spectropscopy Hkaurakshatgoyal643No ratings yet
- Simulation - ": Gas-Phase Inorganic Chemlstry: Laser Spectroscopy of Calcium and Strontium Monopyrrolate MoleculesDocument4 pagesSimulation - ": Gas-Phase Inorganic Chemlstry: Laser Spectroscopy of Calcium and Strontium Monopyrrolate MoleculesDamxz5No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NMR NotesDocument160 pagesOrganic Chemistry NMR NotesMaximilian Müller100% (1)
- CHM 233 Gould Complete Outlines F10Document19 pagesCHM 233 Gould Complete Outlines F10Christian PridayNo ratings yet
- Electron Paramagnetic Resonance in Modern Carbon-Based NanomaterialsFrom EverandElectron Paramagnetic Resonance in Modern Carbon-Based NanomaterialsNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Waves FlaschardsDocument39 pagesFluids and Waves FlaschardsLejNo ratings yet
- Kinematics, Motion, Force, and Torque FlashcardsDocument73 pagesKinematics, Motion, Force, and Torque FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- What Are The Stages of Cell Division? Describe Them:: Biology - ReproductionDocument29 pagesWhat Are The Stages of Cell Division? Describe Them:: Biology - ReproductionLejNo ratings yet
- The Average of The Data Points: Negatively SkewedDocument3 pagesThe Average of The Data Points: Negatively SkewedLejNo ratings yet
- Energy, Momentum, and Work FlashcardsDocument82 pagesEnergy, Momentum, and Work FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics and Magnetism FlashcardsDocument29 pagesElectrostatics and Magnetism FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- What Is The Functional Group Displayed Below?Document3 pagesWhat Is The Functional Group Displayed Below?LejNo ratings yet
- What Is The Liver's Role in Homeostasis?Document4 pagesWhat Is The Liver's Role in Homeostasis?LejNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature, Bonding, and Isomers FlashcardsDocument106 pagesNomenclature, Bonding, and Isomers FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Measures Molecular Vibrations of Characteristic Functional GroupsDocument4 pagesMeasures Molecular Vibrations of Characteristic Functional GroupsLejNo ratings yet
- Label The Parts of The NeuronDocument3 pagesLabel The Parts of The NeuronLejNo ratings yet
- Extraction: R Distance of Substance Solvent L IneDocument2 pagesExtraction: R Distance of Substance Solvent L IneLejNo ratings yet
- Purification Methods FlashcardsDocument35 pagesPurification Methods FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Where Does Gas Exchange Occur?: Biology - RespirationDocument14 pagesWhere Does Gas Exchange Occur?: Biology - RespirationLejNo ratings yet
- What Does The Immune System Distinguish Between?Document2 pagesWhat Does The Immune System Distinguish Between?LejNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System FlashcardsDocument23 pagesMusculoskeletal System FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- What Do Direct Hormones Stimulate?: Biology - EndocrineDocument66 pagesWhat Do Direct Hormones Stimulate?: Biology - EndocrineLejNo ratings yet
- Label The Parts of The Neuron:: Biology - Nervous SystemDocument25 pagesLabel The Parts of The Neuron:: Biology - Nervous SystemLejNo ratings yet
- What Is The Base Unit of The Nucleic Acids?Document2 pagesWhat Is The Base Unit of The Nucleic Acids?LejNo ratings yet
- Immune System FlashcardsDocument28 pagesImmune System FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics FlashcardsDocument34 pagesMolecular Genetics FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Classical GeneticsDocument1 pageClassical GeneticsLejNo ratings yet
- Genetics of Prokaryotic Cells FlashcardsDocument12 pagesGenetics of Prokaryotic Cells FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- When Frequencies Are Stable: When Is The Population in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?Document1 pageWhen Frequencies Are Stable: When Is The Population in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?LejNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis FlashcardsDocument46 pagesHomeostasis FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Pathway Through The Heart: Biology - CirculationDocument34 pagesCirculatory Pathway Through The Heart: Biology - CirculationLejNo ratings yet
- When Is The Population in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?: Biology - EvolutionDocument6 pagesWhen Is The Population in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?: Biology - EvolutionLejNo ratings yet
- Digestion FlaschardsDocument76 pagesDigestion FlaschardsLejNo ratings yet
- Classical Genetics FlashcardsDocument14 pagesClassical Genetics FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Simple Distillation and Gas Chromatography: ContributionsDocument4 pagesSimple Distillation and Gas Chromatography: ContributionsyectepNo ratings yet
- Sample Pfund Scale Grade LH1 LH2 LH3 LH4: Figure. Pfund Scale For Honey (Source: WWW - Oxfordhoney.uk)Document3 pagesSample Pfund Scale Grade LH1 LH2 LH3 LH4: Figure. Pfund Scale For Honey (Source: WWW - Oxfordhoney.uk)Nindya SulistyaniNo ratings yet
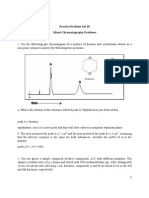
- Practice Problem Set Mixed Chromatography QuestionsDocument14 pagesPractice Problem Set Mixed Chromatography QuestionsMelinda AndersonNo ratings yet
- IR QualitativeDocument4 pagesIR QualitativeredaelwanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Experiment 2Document12 pagesChemistry Experiment 2Malak MahmoudNo ratings yet
- 6 - Gas - Chromatography Principle and ApplicationDocument27 pages6 - Gas - Chromatography Principle and ApplicationMridul JainNo ratings yet
- Central Instrument Facility, Iit Guwahati: Type of Analysis Sample Charge (In INR)Document4 pagesCentral Instrument Facility, Iit Guwahati: Type of Analysis Sample Charge (In INR)tasadukNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Lesson 3 - Microscope 2021Document9 pagesUnit 1. Lesson 3 - Microscope 2021Angeline VerboNo ratings yet
- AKTA Systems Selection GuideDocument1 pageAKTA Systems Selection GuidekenratihprobosariNo ratings yet
- AN LS 001 DNA MeasurementDocument3 pagesAN LS 001 DNA MeasurementLufia CeruleanNo ratings yet
- Sour Rude DeerDocument1 pageSour Rude Deercproczz002No ratings yet
- Comparative Forensic Analysis of Lipsticks Using Thin Layer Chromatography and Gas ChromatographyDocument5 pagesComparative Forensic Analysis of Lipsticks Using Thin Layer Chromatography and Gas ChromatographyvickyNo ratings yet
- Downstream Processing-2-SolutionsDocument7 pagesDownstream Processing-2-SolutionsannaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument11 pagesAssignmentjapjot singhNo ratings yet
- Affinity ChromatographyDocument9 pagesAffinity ChromatographyRatish SinghNo ratings yet
- Atomic Emission Spectroscopy AsaDocument16 pagesAtomic Emission Spectroscopy AsaMark Cliffton Badlon100% (1)
- Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) : Anders Werner Bredvei Skilbred Harald FjeldDocument44 pagesScanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) : Anders Werner Bredvei Skilbred Harald FjeldPiranha TourniquetNo ratings yet
- Chem 155 Quiz 3 Review Topics and Questions With AnswersDocument6 pagesChem 155 Quiz 3 Review Topics and Questions With Answersuvir iitmNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption SpectrometerDocument24 pagesAtomic Absorption SpectrometerDrVikas50% (2)
- Bragg'S Law, and Diffractometer: by Ayesha SiddiqaDocument11 pagesBragg'S Law, and Diffractometer: by Ayesha SiddiqaAyesha SiddiqaNo ratings yet
- Cuidado de ColumnasDocument8 pagesCuidado de ColumnasjbfNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lect-P2 Exam A4 4Document7 pagesHistopath Lect-P2 Exam A4 4RuchieNo ratings yet
- Questions Molecular CloningDocument4 pagesQuestions Molecular CloningMariz MartinezNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulphide NanoparticlesDocument17 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulphide NanoparticlesHoneylyn IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Column Chromatography - Principle, Procedure, ApplicationsDocument1 pageColumn Chromatography - Principle, Procedure, ApplicationsSahiba ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document38 pagesChapter 18NewtinhooNo ratings yet
- Application of Electrophoresis Techniques in Forensic ScienceDocument2 pagesApplication of Electrophoresis Techniques in Forensic ScienceNaeem MalikNo ratings yet
- Acquity UPLC H-ClassDocument6 pagesAcquity UPLC H-Classchaerul.anwar554No ratings yet
- (Updated 7/20, Listed by Date Certified) : List of NGSP Certified MethodsDocument21 pages(Updated 7/20, Listed by Date Certified) : List of NGSP Certified Methodsmichel samanta chaparro saineaNo ratings yet
Spectroscopy Flashcards
Spectroscopy Flashcards
Uploaded by
Lej0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views66 pagesThis document provides an overview of various spectroscopy techniques used in organic chemistry, including infrared spectroscopy (IR), ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV), and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR). It lists the characteristic functional groups observed in IR spectroscopy and their typical absorption ranges. It also outlines the general chemical shift ranges seen for common proton environments in 1H NMR spectroscopy and how the number of adjacent protons affects peak splitting.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of various spectroscopy techniques used in organic chemistry, including infrared spectroscopy (IR), ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV), and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR). It lists the characteristic functional groups observed in IR spectroscopy and their typical absorption ranges. It also outlines the general chemical shift ranges seen for common proton environments in 1H NMR spectroscopy and how the number of adjacent protons affects peak splitting.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views66 pagesSpectroscopy Flashcards
Spectroscopy Flashcards
Uploaded by
LejThis document provides an overview of various spectroscopy techniques used in organic chemistry, including infrared spectroscopy (IR), ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV), and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR). It lists the characteristic functional groups observed in IR spectroscopy and their typical absorption ranges. It also outlines the general chemical shift ranges seen for common proton environments in 1H NMR spectroscopy and how the number of adjacent protons affects peak splitting.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 66
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
Infrared Spectroscopy (IR)
Measures molecular vibrations of characteristic functional
groups
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
IR Alkanes
C-H 2800-3000
C-C 1200
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
IR Alkenes
=C-H 3080-3140
C=C 1645
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
IR Alkynes
C≡C 2200
≡C-H 3300
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
IR Aromatic
C-H 2900-3100
C-C 1475-1625
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
IR Alcohols
O-H 3100-3500 (broad)
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
IR Ethers
C-O 1050-1150
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
IR Aldehydes
(O)C-H 2700-2900
C=O 1700-1750
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
IR Ketones
C=O 1700-1750
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
IR Carboxylic Acids
C=O 1700-1750
O-H 2800-3200 (broad)
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
IR Amines
N-H (sharp) 3100-3500
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
UV Spectroscopy
Involves passing UV light through a chemical sample and
plotting absorbance vs. wavelength. It is most useful for
studying compounds containing double bonds and
heteroatoms with lone pairs
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
Nucleus Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
H-NMR is a form of NMR, only looking at proton shifts
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
NMR RCH3
Approximate shift: 0.9
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
NMR RCH2
Approximate shift: 1.25
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
NMR R3CH
Approximate shift: 1.5
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
NMR –CH=CH
Approximate shift: 4.6-6
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
NMR –C≡CH
Approximate shift: 2-3
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
NMR Ar–H
Approximate shift: 6-8.5
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
NMR –CHX
Approximate shift: 2-4.5
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
NMR –CHOH/–CHOR
Approximate shift: 3.4-4
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
NMR RCHO
Approximate shift: 9-10
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
NMR RCHCO–
Approximate shift: 2-2.5
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
NMR –CHCOOH/–CHOOR
Approximate shift: 2-.2.6
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
NMR –CHOH–CH2OH
Approximate shift: 1-5.5
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
NMR ArOH
Approximate shift: 4-12
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
NMR –COOH
Approximate shift: 10.5-12
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
NMR –NH2
Approximate shift: 1-5
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
NMR –CHOH–CH2OH
Approximate shift: 1-5.5
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
NMR Types of Protons
Corresponds to the number of peaks seen in the spectrum
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
Position of peaks
The further left-shifted (downfield) the peak, the more
deshielded the proton. Usually this corresponds to more
electron-withdrawing groups
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
Integration of peaks
The larger the integration, the more protons contained
under the peak
Organic Chemistry – Spectroscopy
Splitting
Hydrogens on adjacent carbons will split a peak into a n +
1 subpeaks, where n is the number of hydrogens on the
adjacent carbon
You might also like
- (Organo) Part BDocument9 pages(Organo) Part BAmirul Amin Bin ShukriNo ratings yet
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Asymmetric SynthesisDocument55 pagesAsymmetric Synthesisevsgoud_goud0% (1)
- Lab Report Sds-Page WB - PT 1 (1-5)Document5 pagesLab Report Sds-Page WB - PT 1 (1-5)Ezad juferiNo ratings yet
- 2d NMRDocument32 pages2d NMRDelicz TanNo ratings yet
- 39 SpectrosDocument9 pages39 SpectrosDinel JosephNo ratings yet
- Measures Molecular Vibrations of Characteristic Functional GroupsDocument4 pagesMeasures Molecular Vibrations of Characteristic Functional GroupsLejNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy and ChromatographyDocument7 pagesSpectroscopy and ChromatographyPa GesNo ratings yet
- 6spectroscopy and ChromatographyDocument15 pages6spectroscopy and ChromatographyThinaya JayarathneNo ratings yet
- Ilcpa 202 2014 219 233Document15 pagesIlcpa 202 2014 219 233KassimNo ratings yet
- Mass SpectrometryDocument111 pagesMass SpectrometryRajesh Kadavath100% (2)
- Topic 5Document30 pagesTopic 5Shehnaz KamarNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectroscopy & NMR Spectroscopy: Big PictureDocument13 pagesMass Spectroscopy & NMR Spectroscopy: Big PictureluyawinNo ratings yet
- IR and NMR SpectrosDocument13 pagesIR and NMR SpectrosAnand BarapatreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document8 pagesChapter 14nelaojNo ratings yet
- Analytical TechniquesDocument6 pagesAnalytical TechniquesahumanbeinginearthNo ratings yet
- NMR Hly09Document44 pagesNMR Hly09Giang NguyenNo ratings yet
- 5.Nmr Class LatestDocument81 pages5.Nmr Class Latestdimitra shenoyNo ratings yet
- 1455877785CHE P12 M35 EtextDocument8 pages1455877785CHE P12 M35 EtextSaurav PaulNo ratings yet
- Spectrochim-Acta-2012-Single Crystal Structure, Spectroscopic Studies, Physico-Chemical Properties and Theoretical Calculations of TriazeneDocument9 pagesSpectrochim-Acta-2012-Single Crystal Structure, Spectroscopic Studies, Physico-Chemical Properties and Theoretical Calculations of TriazeneELKIN ALFONSO RODRIGUEZ AGUALIMPIANo ratings yet
- Problem of Spectroscopy: Teacher: Nguyen Thien ThaoDocument49 pagesProblem of Spectroscopy: Teacher: Nguyen Thien Thaogianghha50% (2)
- Experiment 1Document16 pagesExperiment 1Izhharuddin100% (2)
- Coii Niii Cuii and Criii Complexes of Heterocyclic Schiff Base Ligand Synthesis Spectroscopic and Thermal StudyDocument5 pagesCoii Niii Cuii and Criii Complexes of Heterocyclic Schiff Base Ligand Synthesis Spectroscopic and Thermal StudyIJARP Publications100% (1)
- ChemistryDocument70 pagesChemistryKieran SangheraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Proton NMR SpectroscopyNJTDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Proton NMR SpectroscopyNJTNicoleNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectra and IRDocument7 pagesMass Spectra and IRSyed FahimNo ratings yet
- Structure Determination: Mass SpectrometryDocument3 pagesStructure Determination: Mass SpectrometrySharmeen HelalNo ratings yet
- Mo JAEDocument4 pagesMo JAEThanhThao TranNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Results in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) SpectrosDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Results in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) SpectrostypodleeNo ratings yet
- NMR SpectrosDocument29 pagesNMR Spectroshareesh13h100% (1)
- Applications of UV IRDocument32 pagesApplications of UV IRShaikh SalmanNo ratings yet
- Biophysics: Nuclear Magnetic ResonanceDocument28 pagesBiophysics: Nuclear Magnetic Resonancejosito2003No ratings yet
- Spectroscopic Techniques & Application: Unit VIIDocument20 pagesSpectroscopic Techniques & Application: Unit VIIshubh mehtaNo ratings yet
- 13C NMR Spectroscopy Power Point PresentationDocument34 pages13C NMR Spectroscopy Power Point PresentationSagarChedeNo ratings yet
- CHMBD 449 - Organic Spectral: AnalysisDocument43 pagesCHMBD 449 - Organic Spectral: AnalysisIleana ManciuleaNo ratings yet
- IR, Raman and Ab-Initio Calcualtions of Glycolic AcidDocument6 pagesIR, Raman and Ab-Initio Calcualtions of Glycolic AcidGerald See TohNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document28 pagesLecture 1Sebastián Castro FragueiroNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosDocument18 pagesNuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosAMAN JATNo ratings yet
- NMR Multiple Choice Questions PDFDocument71 pagesNMR Multiple Choice Questions PDFDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- C-13 NMR and DEPTDocument41 pagesC-13 NMR and DEPTV G Viju Kumar100% (1)
- NMR 7.Document36 pagesNMR 7.Imran KhanNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument78 pagesChemistryShabnam Fatima SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- FTIR1Document5 pagesFTIR1Romajun Villamor MaputiNo ratings yet
- IR and Raman Spectroscopy of Organometallic Compounds-HCDocument38 pagesIR and Raman Spectroscopy of Organometallic Compounds-HCrakesh1521100% (2)
- UltravioletDocument76 pagesUltravioletRadius JuliusNo ratings yet
- Structure Determination of Organic Compounds - ChemvoiceDocument37 pagesStructure Determination of Organic Compounds - ChemvoiceJubin Kumar0% (1)
- SCHB032 NMR Part2redoDocument29 pagesSCHB032 NMR Part2redoemjayNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Modern Analytical Techniques IDocument2 pagesTopic 7 - Modern Analytical Techniques Ijulian maltoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Compatibility Mode)Document76 pagesChapter 2 (Compatibility Mode)HaiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - EasyDocument12 pagesOrganic Chemistry - EasyNaevisweloveuNo ratings yet
- Mcmurry 12Document62 pagesMcmurry 12Ngurah MahasviraNo ratings yet
- Tructural Hemistry Ommunications: DFT Based Characterization of Some Heterocyclic Compounds and Their Biological StudiesDocument10 pagesTructural Hemistry Ommunications: DFT Based Characterization of Some Heterocyclic Compounds and Their Biological StudiesAlex-Mihai CiubaraNo ratings yet
- 3 - Carbon-13-NMRDocument21 pages3 - Carbon-13-NMRahmed mohamedNo ratings yet
- NMR Spectropscopy HkaurDocument42 pagesNMR Spectropscopy Hkaurakshatgoyal643No ratings yet
- Simulation - ": Gas-Phase Inorganic Chemlstry: Laser Spectroscopy of Calcium and Strontium Monopyrrolate MoleculesDocument4 pagesSimulation - ": Gas-Phase Inorganic Chemlstry: Laser Spectroscopy of Calcium and Strontium Monopyrrolate MoleculesDamxz5No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NMR NotesDocument160 pagesOrganic Chemistry NMR NotesMaximilian Müller100% (1)
- CHM 233 Gould Complete Outlines F10Document19 pagesCHM 233 Gould Complete Outlines F10Christian PridayNo ratings yet
- Electron Paramagnetic Resonance in Modern Carbon-Based NanomaterialsFrom EverandElectron Paramagnetic Resonance in Modern Carbon-Based NanomaterialsNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Waves FlaschardsDocument39 pagesFluids and Waves FlaschardsLejNo ratings yet
- Kinematics, Motion, Force, and Torque FlashcardsDocument73 pagesKinematics, Motion, Force, and Torque FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- What Are The Stages of Cell Division? Describe Them:: Biology - ReproductionDocument29 pagesWhat Are The Stages of Cell Division? Describe Them:: Biology - ReproductionLejNo ratings yet
- The Average of The Data Points: Negatively SkewedDocument3 pagesThe Average of The Data Points: Negatively SkewedLejNo ratings yet
- Energy, Momentum, and Work FlashcardsDocument82 pagesEnergy, Momentum, and Work FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics and Magnetism FlashcardsDocument29 pagesElectrostatics and Magnetism FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- What Is The Functional Group Displayed Below?Document3 pagesWhat Is The Functional Group Displayed Below?LejNo ratings yet
- What Is The Liver's Role in Homeostasis?Document4 pagesWhat Is The Liver's Role in Homeostasis?LejNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature, Bonding, and Isomers FlashcardsDocument106 pagesNomenclature, Bonding, and Isomers FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Measures Molecular Vibrations of Characteristic Functional GroupsDocument4 pagesMeasures Molecular Vibrations of Characteristic Functional GroupsLejNo ratings yet
- Label The Parts of The NeuronDocument3 pagesLabel The Parts of The NeuronLejNo ratings yet
- Extraction: R Distance of Substance Solvent L IneDocument2 pagesExtraction: R Distance of Substance Solvent L IneLejNo ratings yet
- Purification Methods FlashcardsDocument35 pagesPurification Methods FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Where Does Gas Exchange Occur?: Biology - RespirationDocument14 pagesWhere Does Gas Exchange Occur?: Biology - RespirationLejNo ratings yet
- What Does The Immune System Distinguish Between?Document2 pagesWhat Does The Immune System Distinguish Between?LejNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System FlashcardsDocument23 pagesMusculoskeletal System FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- What Do Direct Hormones Stimulate?: Biology - EndocrineDocument66 pagesWhat Do Direct Hormones Stimulate?: Biology - EndocrineLejNo ratings yet
- Label The Parts of The Neuron:: Biology - Nervous SystemDocument25 pagesLabel The Parts of The Neuron:: Biology - Nervous SystemLejNo ratings yet
- What Is The Base Unit of The Nucleic Acids?Document2 pagesWhat Is The Base Unit of The Nucleic Acids?LejNo ratings yet
- Immune System FlashcardsDocument28 pagesImmune System FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics FlashcardsDocument34 pagesMolecular Genetics FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Classical GeneticsDocument1 pageClassical GeneticsLejNo ratings yet
- Genetics of Prokaryotic Cells FlashcardsDocument12 pagesGenetics of Prokaryotic Cells FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- When Frequencies Are Stable: When Is The Population in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?Document1 pageWhen Frequencies Are Stable: When Is The Population in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?LejNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis FlashcardsDocument46 pagesHomeostasis FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Pathway Through The Heart: Biology - CirculationDocument34 pagesCirculatory Pathway Through The Heart: Biology - CirculationLejNo ratings yet
- When Is The Population in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?: Biology - EvolutionDocument6 pagesWhen Is The Population in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?: Biology - EvolutionLejNo ratings yet
- Digestion FlaschardsDocument76 pagesDigestion FlaschardsLejNo ratings yet
- Classical Genetics FlashcardsDocument14 pagesClassical Genetics FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Simple Distillation and Gas Chromatography: ContributionsDocument4 pagesSimple Distillation and Gas Chromatography: ContributionsyectepNo ratings yet
- Sample Pfund Scale Grade LH1 LH2 LH3 LH4: Figure. Pfund Scale For Honey (Source: WWW - Oxfordhoney.uk)Document3 pagesSample Pfund Scale Grade LH1 LH2 LH3 LH4: Figure. Pfund Scale For Honey (Source: WWW - Oxfordhoney.uk)Nindya SulistyaniNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem Set Mixed Chromatography QuestionsDocument14 pagesPractice Problem Set Mixed Chromatography QuestionsMelinda AndersonNo ratings yet
- IR QualitativeDocument4 pagesIR QualitativeredaelwanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Experiment 2Document12 pagesChemistry Experiment 2Malak MahmoudNo ratings yet
- 6 - Gas - Chromatography Principle and ApplicationDocument27 pages6 - Gas - Chromatography Principle and ApplicationMridul JainNo ratings yet
- Central Instrument Facility, Iit Guwahati: Type of Analysis Sample Charge (In INR)Document4 pagesCentral Instrument Facility, Iit Guwahati: Type of Analysis Sample Charge (In INR)tasadukNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Lesson 3 - Microscope 2021Document9 pagesUnit 1. Lesson 3 - Microscope 2021Angeline VerboNo ratings yet
- AKTA Systems Selection GuideDocument1 pageAKTA Systems Selection GuidekenratihprobosariNo ratings yet
- AN LS 001 DNA MeasurementDocument3 pagesAN LS 001 DNA MeasurementLufia CeruleanNo ratings yet
- Sour Rude DeerDocument1 pageSour Rude Deercproczz002No ratings yet
- Comparative Forensic Analysis of Lipsticks Using Thin Layer Chromatography and Gas ChromatographyDocument5 pagesComparative Forensic Analysis of Lipsticks Using Thin Layer Chromatography and Gas ChromatographyvickyNo ratings yet
- Downstream Processing-2-SolutionsDocument7 pagesDownstream Processing-2-SolutionsannaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument11 pagesAssignmentjapjot singhNo ratings yet
- Affinity ChromatographyDocument9 pagesAffinity ChromatographyRatish SinghNo ratings yet
- Atomic Emission Spectroscopy AsaDocument16 pagesAtomic Emission Spectroscopy AsaMark Cliffton Badlon100% (1)
- Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) : Anders Werner Bredvei Skilbred Harald FjeldDocument44 pagesScanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) : Anders Werner Bredvei Skilbred Harald FjeldPiranha TourniquetNo ratings yet
- Chem 155 Quiz 3 Review Topics and Questions With AnswersDocument6 pagesChem 155 Quiz 3 Review Topics and Questions With Answersuvir iitmNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption SpectrometerDocument24 pagesAtomic Absorption SpectrometerDrVikas50% (2)
- Bragg'S Law, and Diffractometer: by Ayesha SiddiqaDocument11 pagesBragg'S Law, and Diffractometer: by Ayesha SiddiqaAyesha SiddiqaNo ratings yet
- Cuidado de ColumnasDocument8 pagesCuidado de ColumnasjbfNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lect-P2 Exam A4 4Document7 pagesHistopath Lect-P2 Exam A4 4RuchieNo ratings yet
- Questions Molecular CloningDocument4 pagesQuestions Molecular CloningMariz MartinezNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulphide NanoparticlesDocument17 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulphide NanoparticlesHoneylyn IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Column Chromatography - Principle, Procedure, ApplicationsDocument1 pageColumn Chromatography - Principle, Procedure, ApplicationsSahiba ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document38 pagesChapter 18NewtinhooNo ratings yet
- Application of Electrophoresis Techniques in Forensic ScienceDocument2 pagesApplication of Electrophoresis Techniques in Forensic ScienceNaeem MalikNo ratings yet
- Acquity UPLC H-ClassDocument6 pagesAcquity UPLC H-Classchaerul.anwar554No ratings yet
- (Updated 7/20, Listed by Date Certified) : List of NGSP Certified MethodsDocument21 pages(Updated 7/20, Listed by Date Certified) : List of NGSP Certified Methodsmichel samanta chaparro saineaNo ratings yet