Professional Documents
Culture Documents
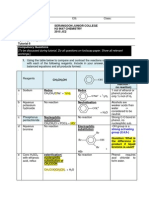
Assignment 1 BKF1323
Assignment 1 BKF1323
Uploaded by
Dharshini DeepaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 1 BKF1323
Assignment 1 BKF1323
Uploaded by
Dharshini DeepaCopyright:
Available Formats
ASSIGNMENT 1 BKF1323
Topic: Introduction, Stereoisomers and Chirality
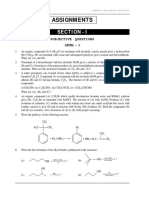
A. Classify and name all the compounds based on their given formulae:
1. CH2(OH)2 2. C3H6 (cyclic, saturate) 3. (CH3)3N 4. CH3COOH
5. CH3CHOHCH3 6. C5H9OH (cyclic) 7. C6H6 (cyclic, unsaturate) 8. CH2(COOH)2
9. (C3H7)2O 10. (C3H7)2CO 11. C3H7COOC3H7 12. CH2O
13. C10H20 (unsaturate) 14. C3H5(OH)3 15. CH2F2 16. C2H3Cl (unsaturate)
17. C2H2 18. C4H4Br4 (cyclic, saturate) 19. CH3COOK 20. C6H5NH2 (aromatic)
B. Categorize these compounds:
1. Methylene glycol
2. 3-hexene
3. Fluoromethanol
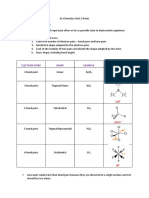
C. Draw a structural formula using an example for each term as follows: chiral, achiral, enantiomers
and diastereomers.
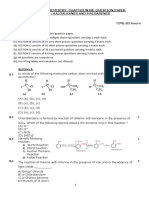
Topic: Alkanes @ Paraffins
A. List the alkanes contained in crude black gold:
1. LPG 2. Gasoline 3. Kerosene 4. Diesel 5. Cokes
B. Explain through mechanism diagram how:
1. Formylene chloride is formed from mixture of liquefied methane and chlorine?
2. Methylene fluoride is formed from mixture of liquefied methane and fluorine?
3. 2-butylene is synthesized from butane?
C. Describe using an example for each alkane synthesis through these ways:
1. Alkylation of terminal alkynes.
2. Reduction of alkyl halides.
3. Corey-House-Posner-Whitesides synthesis from alkyl halides
Topic: Alkenes @ Olefins
A. Draw the skeletal formulae of the following olefins and assign either it is E or Z isomer:
1. 1-fluoro-3-bromo-2-pentene
2. 4,4,4-trichloro-2-methyl-2-buten-1-ol
3. 3-bromo-3-hexen-1,4-diol
4. 3-amino-2-butene
5. 3-amino-5,5-dichloro-4-difluoromethyl-3-octene
B. Explain through mechanism diagram:
1. The preferred product formed if propylene is mixed with steam.
2. The confirmed product formed if 2,3-pentadiene is mixed with excessive hydroiodic acid.
3. The stable product formed from dehydrogenation at 2 nd and 3rd C atom in butane.
C. Describe:
1. Propylene synthesis through tosylation of propyl tosylate (p-propyl toluene sulphonate).
2. An example for ozonolysis of alkenes to produce carbonyls.
3. An example for oxidative cleave of alkenes to produce carbonyls.
Topic: Alkynes
Explain through mechanism diagram:
1. How 2-pentyne becomes diethyl ketone when hydrated, not pentene glycol?
2. How 2-butyne does not directly become 2,2,3,3-tetrafluorobutane when excessively
fluorinated?
3. The confirmed product formed if propyne is mixed first with limited pure hydrofluoric acid
followed with limited steam.
Topic: Mix of all above
You are supposed to produce several products using linear saturated compound (total carbon atoms
= 8) as starting material.
a. Draw its skeletal formula.
b. Name these following compounds based on 8 total carbon atoms for each compound:
i. 6 carbon atoms form a ring, the rest attach at 1st and 4th carbon atoms in the ring
ii. 6 carbon atoms form a line, the rest attach at 2nd and 5th carbon atoms in the line
iii. 5 carbon atoms form a line, the rest attach at 2nd and 4th carbon atoms in the line
iv. 4 carbon atoms form a ring, the rest attach at all carbon atoms in the ring
c. What are the products when the starting material is once dehydrogenated at 4th carbon
atom?
d. List all three (3) products obtained if the products from part c is mixed with aqueous
chlorine.
e. What is the product when the starting material is twice dehydrogenated at:
i. 3rd carbon atom?
ii. 4th carbon atom?
f. Draw the structural formulae of all four (4) products obtained when the product from part e
is once hydrohalogenated with hydrofluoric acid. Predict E and Z isomers for each product.
g. State the main application of
i. Major product obtained from part d.
ii. Products obtained from parts c and e.
You might also like
- Infrared Characterization of Linkage IsomersDocument4 pagesInfrared Characterization of Linkage IsomersCarolyn Charles50% (2)
- Guide To Writing A Laboratory Report & Harvard Referencing SystemDocument2 pagesGuide To Writing A Laboratory Report & Harvard Referencing SystemYap Jun HongNo ratings yet
- Mini Mock Unit 4 4 To 4 11 A2 Organic Chemistry and Structure DeterminationDocument15 pagesMini Mock Unit 4 4 To 4 11 A2 Organic Chemistry and Structure DeterminationSahanNivanthaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Help! Practice Exam Window For Xula-O1e2Document7 pagesOrganic Chemistry Help! Practice Exam Window For Xula-O1e2Kristia Stephanie BejeranoNo ratings yet
- Final Exam 2012Document12 pagesFinal Exam 2012Mat MorashNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 6Document2 pagesLab Report 6bjddjkNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry Exam Questions PDFDocument513 pagesA Level Chemistry Exam Questions PDFClive Doyce100% (2)
- Answers To ROH Tutorial PDFDocument12 pagesAnswers To ROH Tutorial PDFCorvo Haosen Al-Han0% (1)
- Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument4 pagesAldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsAnindya AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Vakev Chemistry-Examination-Of-The-Third-Term-2021-For-S6Document15 pagesVakev Chemistry-Examination-Of-The-Third-Term-2021-For-S6vigiraneza0No ratings yet
- Naming Alkanes - Worksheet #1 Name - #Document4 pagesNaming Alkanes - Worksheet #1 Name - #cheryl retioNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 & 4 - Equilibria & Application of Rates and EquilibriumDocument5 pagesTutorial 3 & 4 - Equilibria & Application of Rates and EquilibriumAhmad Taufiq Mohd ZaidNo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 7 - Answer SchemeDocument7 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 7 - Answer SchemeNicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Ketones and AldehydesDocument31 pagesChapter 18 Ketones and AldehydesRahma AshrafNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chemistry 12Document5 pagesWorksheet Chemistry 12mohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry-1-1Document23 pagesChapter 3 Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry-1-1eas111No ratings yet
- Chapter - 10 (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes) Exercise QuestionsDocument23 pagesChapter - 10 (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes) Exercise QuestionsNabin JoshiNo ratings yet
- 28 Petrucci10e CSMDocument35 pages28 Petrucci10e CSMAlexNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Alkyl Halides Nucleophilic Substitution: You May Have Drawn The Other Enantiomer. Either Is CorrectDocument23 pagesChapter 6-Alkyl Halides Nucleophilic Substitution: You May Have Drawn The Other Enantiomer. Either Is Correct張湧浩No ratings yet
- Alkyl Halide-Jeemain - Guru PDFDocument37 pagesAlkyl Halide-Jeemain - Guru PDFUma JadounNo ratings yet
- Percent Yield: Chemfile Mini-Guide To Problem SolvingDocument11 pagesPercent Yield: Chemfile Mini-Guide To Problem SolvingdhavaleshNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document9 pagesDocument 1Nishi tomarNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry & Numerical MCQ Test 1 - Makox MCQsDocument5 pagesAnalytical Chemistry & Numerical MCQ Test 1 - Makox MCQsنونه الحنونة100% (2)
- Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers PDFDocument37 pagesChemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers PDFMohammed RafiuddinNo ratings yet
- Alcohol (Theory) Module-4Document18 pagesAlcohol (Theory) Module-4Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry s6 AllDocument213 pagesChemistry s6 AllAKAYEZU Body santiveNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11. Organic ChemistryDocument22 pagesChapter 11. Organic ChemistryAnanya SamantaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry: Period 3 ElementsDocument5 pagesInorganic Chemistry: Period 3 ElementsUng Hie HuongNo ratings yet
- Hypervalent Iodine: Dess-Martin Periodane: Selective Oxidation of Prim. Alcohols To Aldehydes, Sec. Alcohols To KetonesDocument15 pagesHypervalent Iodine: Dess-Martin Periodane: Selective Oxidation of Prim. Alcohols To Aldehydes, Sec. Alcohols To Ketonesevsgoud_goudNo ratings yet
- CH CH CCH C CHDocument15 pagesCH CH CCH C CHVirgilio Ebajo Jr.No ratings yet
- Solution-Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument5 pagesSolution-Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsAnindya AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alkenes: CC HX C HX C Markovnikov's OrientationDocument8 pagesReactions of Alkenes: CC HX C HX C Markovnikov's OrientationMarc RitzNo ratings yet
- Practice Question For Second Term 111 1Document18 pagesPractice Question For Second Term 111 1Ramina TamangNo ratings yet
- Sample Test Exam One CH201Document7 pagesSample Test Exam One CH201Ashly PhilipNo ratings yet
- Che 176 AlkanolsDocument42 pagesChe 176 Alkanolsodunowo usmanNo ratings yet
- SCH3U Exam Review QUESTIONSDocument3 pagesSCH3U Exam Review QUESTIONSChen Dingna100% (1)
- Common Foundation Organic Q in A LevelDocument21 pagesCommon Foundation Organic Q in A Level黄维燕No ratings yet
- Ass. 5Document14 pagesAss. 5Saumya SelvarajiNo ratings yet
- Inter Ipe Isomerism & Bond PolarizationDocument9 pagesInter Ipe Isomerism & Bond PolarizationNalla Umapathi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Alcohols TestDocument2 pagesAlcohols TestAboahmed AliNo ratings yet
- Alkenes PDFDocument22 pagesAlkenes PDFIsuri VidyarathneNo ratings yet
- 06 Petrucci10e CSMDocument54 pages06 Petrucci10e CSMAlexNo ratings yet
- RMN ProblemsDocument7 pagesRMN ProblemsAnonymous llSDP0tNo ratings yet
- Schm312 NotesDocument97 pagesSchm312 NotesSandile SynthaxError Mabika100% (1)
- Instructions:: Part-A I. Answer ALL The Questions (Each Question Carries One Mark) 10x1 10Document3 pagesInstructions:: Part-A I. Answer ALL The Questions (Each Question Carries One Mark) 10x1 10anon_850201470No ratings yet
- 2012 Redox Tutorial-TutorDocument11 pages2012 Redox Tutorial-TutorKarunya NarayanamurthyNo ratings yet
- 2015 JC 2 H2 Hydroxyl Tutorial (Teachers)Document21 pages2015 JC 2 H2 Hydroxyl Tutorial (Teachers)JohnNo ratings yet
- CH 07Document96 pagesCH 07Jacquot AbendrothNo ratings yet
- Ap Chemistry Acid-Base Exam Part I Multiple Choice: K (Hco) (Co) (H O) K (Co) (Co) (OH)Document8 pagesAp Chemistry Acid-Base Exam Part I Multiple Choice: K (Hco) (Co) (H O) K (Co) (Co) (OH)Max SaubermanNo ratings yet
- 25 Petrucci10e CSMDocument25 pages25 Petrucci10e CSMAlexNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Question Bank Class: Xii, Chemistry Unit 4: Haloalknaes & HaloarenesDocument27 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Question Bank Class: Xii, Chemistry Unit 4: Haloalknaes & HaloarenesAkshita BoroNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Examples of Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure: Examples of Multiple Choice Questionsngah lidwineNo ratings yet
- Assignment IDocument21 pagesAssignment IChocolaMeilleurNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and Ketones McMurryDocument43 pagesAldehyde and Ketones McMurryShamira100% (1)
- Alkyl Halides & Aryl Halides-03 - Assignments (New)Document21 pagesAlkyl Halides & Aryl Halides-03 - Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- 07 Petrucci10e CSMDocument43 pages07 Petrucci10e CSMPhương Ngân HồNo ratings yet
- Alkenes TutorialDocument8 pagesAlkenes TutorialVarshLokNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2Document5 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2ibdpNo ratings yet
- Answer Key For Organic ChemDocument10 pagesAnswer Key For Organic Chemanusha pradhanNo ratings yet
- 4.carbon and Its CompoundsDocument8 pages4.carbon and Its CompoundsBhai JaanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Worksheet - Carbon and Its CompoundDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 10 Chemistry Worksheet - Carbon and Its CompoundRaghav GuptaNo ratings yet
- B) From Hydrocarbon:-: A) by Free Radical Halogenation ReactionDocument2 pagesB) From Hydrocarbon:-: A) by Free Radical Halogenation ReactionRaju kumarNo ratings yet
- Halo Alkanes Sample PaperDocument6 pagesHalo Alkanes Sample PapervasuNo ratings yet
- B.SC Life Sciences SyllabusDocument122 pagesB.SC Life Sciences SyllabusRonit ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- CHM 222, Organic Chemistry II Chapter 15 Organometallic Compunds PDFDocument34 pagesCHM 222, Organic Chemistry II Chapter 15 Organometallic Compunds PDFMelissa ChehwaneNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2 NotesDocument101 pagesChemistry 2 NotesAnna Conigrave100% (2)
- 12 Chemistry FinalDocument24 pages12 Chemistry Finalvenkat gantaNo ratings yet
- Halogen Derivatives PDFDocument32 pagesHalogen Derivatives PDFRaju Singh100% (1)
- Set 11 HaloalkanesDocument2 pagesSet 11 HaloalkanesNurul FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 12 Homework Assignment 3-1Document7 pagesChemistry 12 Homework Assignment 3-1erstz00g100% (1)
- Chemistry SyllabusDocument42 pagesChemistry SyllabusKartikey JainNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument1 pageHaloalkanes and HaloarenesPES 21No ratings yet
- Heterocyclic Chemistry: Dr. Mohamed El-NaggarDocument124 pagesHeterocyclic Chemistry: Dr. Mohamed El-NaggarDeepshika WahengbamNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Organic Synthesis (Reaction Pathways) : Pupil Notes Learning Outcomes Questions & AnswersDocument58 pages3.2 Organic Synthesis (Reaction Pathways) : Pupil Notes Learning Outcomes Questions & AnswersJennifer Carolina Rosales NoriegaNo ratings yet
- CHSE Science Revised Syllabus 20-21 PDFDocument106 pagesCHSE Science Revised Syllabus 20-21 PDFKiLLER OPNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry,: AlkynesDocument19 pagesOrganic Chemistry,: AlkynesDesra wellyNo ratings yet
- B.SC 1st Year Organic1Document57 pagesB.SC 1st Year Organic1levana dhea lumi100% (1)
- Organic-Chemistry (As Level)Document8 pagesOrganic-Chemistry (As Level)Pirate HunterNo ratings yet
- Halo Alkanes and ArenesDocument8 pagesHalo Alkanes and ArenesRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Organic Preparations and Procedures International: The New Journal For Organic SynthesisDocument7 pagesOrganic Preparations and Procedures International: The New Journal For Organic SynthesisYudistiro SubektiNo ratings yet
- CAIE Chemistry A-Level: 21: Organic SynthesisDocument4 pagesCAIE Chemistry A-Level: 21: Organic SynthesisahumanbeinginearthNo ratings yet
- What Are Hydrocarbon DerivativesDocument9 pagesWhat Are Hydrocarbon DerivativesJohn Michael BagandoNo ratings yet
- H2 Chemistry (9729) Lecture Notes 13 - Organic Chemistry Halogen DerivativesDocument27 pagesH2 Chemistry (9729) Lecture Notes 13 - Organic Chemistry Halogen DerivativesArvin LiangdyNo ratings yet
- Free Radical Substitution and Electrophilic AdditionDocument17 pagesFree Radical Substitution and Electrophilic Additionchicko33No ratings yet
- Alcohols 1630993189Document56 pagesAlcohols 1630993189Sahisa MahatNo ratings yet
- IChO 2009 Prep Prob PracticalDocument15 pagesIChO 2009 Prep Prob PracticalRSLNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NotesDocument26 pagesUnit 2 NotesRameez Mazhar Siddiqi100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Organic Chemistry SL WorksheetDocument25 pagesChapter 10 Organic Chemistry SL Worksheetfei shenNo ratings yet
- FR 1 (E6)Document5 pagesFR 1 (E6)JR CastorNo ratings yet