Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Primitive Reflexes/ Stereotypies: Infant Motor Behaviors - Completed Checklist Tables
Primitive Reflexes/ Stereotypies: Infant Motor Behaviors - Completed Checklist Tables
Uploaded by
Amy Emyla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
151 views4 pagesThis document provides a checklist of infant motor behaviors including primitive reflexes, stereotypies, non-developmental reflexes, and postural reactions. It describes how each behavior is elicited, the stimulus and sensory receptors involved, the infant's physical response, and notes many of the behaviors' unknown apparent functions. Over 40 infant motor behaviors are listed and explained concisely.
Original Description:
Original Title
InfantMBCompleteChklst
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a checklist of infant motor behaviors including primitive reflexes, stereotypies, non-developmental reflexes, and postural reactions. It describes how each behavior is elicited, the stimulus and sensory receptors involved, the infant's physical response, and notes many of the behaviors' unknown apparent functions. Over 40 infant motor behaviors are listed and explained concisely.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
151 views4 pagesPrimitive Reflexes/ Stereotypies: Infant Motor Behaviors - Completed Checklist Tables
Primitive Reflexes/ Stereotypies: Infant Motor Behaviors - Completed Checklist Tables
Uploaded by
Amy EmylaThis document provides a checklist of infant motor behaviors including primitive reflexes, stereotypies, non-developmental reflexes, and postural reactions. It describes how each behavior is elicited, the stimulus and sensory receptors involved, the infant's physical response, and notes many of the behaviors' unknown apparent functions. Over 40 infant motor behaviors are listed and explained concisely.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
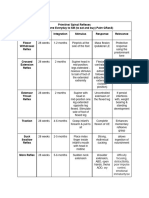
Infant Motor Behaviors – Completed Checklist Tables
Primitive Reflexes/ Stereotypies
Reflex Name How to elicit the reflex Stimulus/ energy Sensory receptor Response Apparent function
Apply pressure to palm of physical pressure - tactile/ cutaneous flexion of digits (fingers) unknown: atavistic?
Palmar grasp hand at base of digits mechanical energy receptors of hand 2-5, but not the thumb aid clinging/ no fall
Apply pressure to sole of foot tactile/ cutaneous flexion of digits (toes) unknown: vestigial?
Plantar grasp at base of digits (toes) receptors of foot 2-5, but not the pollux aid clinging/ no fall
Stroke sole of foot from heel receptors entire sole extension and fanning of toes unknown: used to
Babinski to toes of foot, tactile screen SCI/ CNS
Lower baby’s head rapidly head acceleration - vestibular - semi- Extension of 4 limbs, unknown: atavistic?
Moro while cradling in arms kinetic energy circular canals followed by flexion prenatal PMP posit?
Lightly stroke the cheek near light pressure and tactile/cutaneous mouth opens, tongue moves unknown: PMP for
Rooting one side of mouth mechanical energy receptors of cheek and head turns toward survival after birth?
Place clean object on tongue physical pressure - cutaneous receptor rhythmic action of tongue
Sucking or in mouth mechanical energy of tongue &mouth pressing against soft palate
Hold upright & alternately let cutaneous receptor Alternate hip/ knee flexion, + unknown: integrate to
Stepping feet touch table surface of plantar foot often external rotation vol. locomotion?
Touch dorsal foot surface cutaneous receptor Hip/knee flexion, followed by
Placing with table edge of dorsal foot skin “placing” on tabletop
Place prone in water, w/ or CNS arousal? unclear - inner ear?Alternate + cross lateral limb unknown: integrate in
Swimming w/out face in water vestibular/ cutaneous skin? or PNS motor flexion/extension w/ lateral aquatic loco.?
neurons? trunk flexion
Place prone on flat surface Alternate flexion/ extension unknown: integrate in
Crawling of limbs, lat. trunk flexion crawling?
Turn head either to left or Asymmetric neck muscle propriocept- Fencer pose: arm extension unknown: prenatal
ATNR right (or get baby to turn it) muscle stretch - ors of neck on face side, arm flexion PMP for position?
proprioceptors
Flex or extend head while sym neck muscle Arms = head action; feet
STNR suspend/supporting body stretch - proprioceptor opposite
Place head in prone or supine vestibular - head otolith organ of Prone = limb flexion
TLR position position re gravity inner ear Supine = limb extension
Supine leg kicking Place infant on back (supine) Internal arousal N.A. Flexion-extension of 1-2 legs Hardwired neural
occur spontaneously circuits
Infant Motor Behaviors – Completed Checklist Tables
Lifespan, Nondevelopmental Reflexes/ Stereotypies
Reflex Name How to elicit the reflex Stimulus/ energy Sensory receptor Response Apparent function
shine bright light in eye intensity of light - retinal cells Pupil constricts with adjust light intensity to
Pupillary after being in the dark electromagnetic especially cones increased light intensity; retinal image; protect
spectrum dilates with low intensity cones
Vestibulo-ocular Quickly spin person acceleration of head - semicircular canals “ramp movement”of eye unknown - link head
(nystagmus) around longitudinal axis mechanical energy of inner ear with slow, tracking mvt -eye motion; maintain
opposite rotation followed by balance; track objects?
saccade in rot. direction
Quickly move object visual and/or cutaneous receptors Rapid closing of eyelid over protect corneal surface
Eye blink toward eye or puff of air mechanical of eyeball eyeball; stimulation of tear of eye
or foreign object (dust) duct to lub. cornea
Change emotional state; varies, but involves Thalamus/ cardiac muscle contractions circulate sufficient O2
Heart rate exercise; fright-fight increased excitatory hypothalamus and increase rate with exercise or to tissues/organs
nervous stimulation node of heart CNS activation
Change emotional or CO2 levels in arterial intracirculatory increased ventilatory rate/ provide adequate O2
Breathing exercise state of body blood supply cells of CNS contractions of diaphragm or exchange in lungs for
costal muscles circulation
Swallow liquid or solid physical pressure - laryngeal epiglottis contracts and protect bronchia from
Epiglottal food mechanical energy swallowing covers the bronchial opening foreign obj.
contractions
Firmly tap a relaxed, muscles spindles/ rapid contraction of protect muscles from
Tendon stretch stretched tendon (eg GTOs of muscle stimulated muscle overstretch
patellar, Achilles)
Flexor Noxious, painful, or tickle cutaneous receptor flexion of entire limb of remove limb from
withdrawl stimulus to extremity including free nerve stimulated extremity noxious stimulus
ending
Crossed Elicit flexor withdrawl extension of entire limb support body during
extension reflex in opposite limb opposite stimulated withdrawl
extremity
Sudden, unexpected, any type of energy visual, auditory, sudden, rapid limb extension “flight or fight”
Startle and/or intense light, that is unexpected, gustatory,vestibular or “startle” reaction preparation - CNS
sound, touch, etc. intense, sudden , proprioception activation
Supine leg kick See previous sheet of
primitive reflexes
Infant Motor Behaviors – Completed Checklist Tables
Postural, Equilibrium Reactions
Reaction How reaction is elicited Stimulus/ energy Sensory receptor Response Apparent function
Righting Body out of alignment w/ grav. gravitational force vestibular apparatus generically to align w/ gravity
maintain upright posture
Head Place infant in prone position on head position in otolith organ - inner Head hyperextends at neck, Get head upright in space,
flat surface relation to gravity ear raising face from surface aligned with gravity
Sagittal trunk Place infant in prone position on Trunk hyperextends, arching Get trunk upright/ aligned and
flat surface head and legs off surface minimize energy use
pivot prone/Landau Place infant in prone position on Get trunk upright/ aligned to
flat surface maintain vertical
Derotative Place infant supine and twist legs physical energy - muscle receptors, esp Opposite segment “untwists” in To reduce muscle stretch/
and/or shoulder girdle muscle stretch muscle spindles direction of twisted segment keep segments aligned
Parachute/propping Body position changed quickly Acceleration - kinetic vestibular apparatus extension in direction of mvt reduce pot. impact forces
Downward - arms In vertical position, displace downward semicircular canals of Arms extend and abduct up Anticipate impact from
acceleration/
Downward - legs body downward quickly kinetic energy vestibular apparatus Legs extend and abduct + down falling downward
Sideward/ Displace infant laterally in a lateral acceleration hair cells of semi- Arms extend laterally in Anticipate and cushion impact
lateral quick motion kinetic energy circular canals direction of the fall from sideward fall
Forward/ Quickly displace infant in the anterior acceleration/ hair cells of semi- Arms extend anteriorly in Anticipate and cushion impact
anterior anterior direction/plane kinetic energy circular canals direction of the fall from forward fall
Backward/ Quickly displace infant in the posterior acceleration/ hair cells of semi- Arms extend posteriorly in Anticipate and cushion impact
posterior posterior direction/plane kinetic energy circular canals direction of the fall from backward fall
Tilting displacing support surface vestibular/propriocept inner ear + muscle adjustment of head/torso Keep alignment w/ grav.
spindles
Prone In prone position, tilt support head position in space otolith organ of inner Head and trunk move away Minimize energy use and
surface forward or backward + muscle stretch ear + proprioceptors from direction of tilt maintain prone posture
Supine In supine position, tilt support Head and trunk move away Minimize energy use and
surface forward or backward from direction of tilt maintain supine posture
Sitting In sitting position, tilt support Trunk and spine move in Minimize energy use and
surface to front/back/side direction away from tilt maintain sitting posture
All-fours On “all-fours,” tilt support Limb adjustment away from Minimize energy use and
surface to front/back/side direction of downward tilt maintain all-four balance
Standing In upright/stand, tilt support Trunk and legs lean away from Minimize energy use and
surface to front/back/side direction of downward tilt maintain upright posture
Infant Motor Behaviors – Completed Checklist Tables
Voluntary Motor Skills (a.k.a. Motor Milestones)
Motor skill Goal/ function of skill Critical features/ components Changing movement characteristics Task factors movement
characteristics
allow person to change rotation of head, trunk, pelvis, leg from inability to roll over to turn over surface characteristics, speed
Rolling over prone to supine or vs. action, arm action to twisting during turn over demands, original position, ATNR
position trunk in upright trunk posture, head posture, leg from inability to sit up independently sitting surface, presence of back or
Sitting up posture w/ pelvis-leg base position, arm action to partial sit to upright sit sit support, strength, CNS
locomotion while in prone head position, trunk in contact with from no crawling to initial attempts to head position, trunk action, arm and
Crawling position – trunk contact surface, arm/leg actions advanced crawling with progress leg actions
Locomotion in prone head position, quadripedal surface from crawling action w/trunk touching distance to cover, height of mvt
Creeping position with quadripedal contact, arm/ leg actions to rapid, all-4s creeping movement space, type of surface, strength
contact
maintaining upright posture head posture, trunk posture, leg inability to stand to standing with assist surface char., arm support, trunk
Standing with feet as base of support action/posture; arm position/action to standing independently support, leg strength, balance
Independent upright locomotion on feet trunk/pelvic action, leg action, arm no walking to cruising to independent surface characteristics, arm/trunk
Walking w/alternating leg action action walking to heel-toe action/alt. arms support, leg strength, balance
Fundamental Motor Skills
Jumping upright locomotion on feet trunk action, leg action, arm action; from no jump to step down to surface char., distance, height, time,
from 2 feet to 2 feet different phases of mvt momentary flight to bounce jump etc. leg strength
Galloping/ Sliding Step + backward leap/ side Leg action, arm action From no leap and same lead leg to Speed, direction, lead leg, obstacles
facing leaping with either leg leading
Running/ Leaping upright locomotion alt. leg trunk/pelvis action, leg action, arm from no run to momentary run to surface, speed, distance, leg
action w/ flight phase action, stance vs swing phase advanced run with different speeds strength
Hopping upright locomotion - w/ leg action, arm action movement from pre-hop through 4 steps of leg distance to hop, speed, obstacles,
weight shift on 1 leg only components and 5 steps of arm actions leg strength, balance
Skipping Step and hop on alternate Leg action, arm action From single side skip to 2-side skip on Distance to skip, speed, obstacles,
feet with uneven rhythm ball of foot landing; bilateral to oppos. leg strength, balance
Throwing /Striking Projecting/sending away a foot/leg, trunk, forearm, humerus 4 steps in leg, 3 trunk, 3 forearm, 3 force/distance, ball-hand ratio,
ball from the hand of actions, backswing components humerus, 4 backswing components target size/accuracy/mvt, body size
person or using implement
Kicking Projecting a ball with foot Prep. backswing, step, trunk Segmented action to integrated Size of ball, distance, mvt. ball
Catching Receiving or gathering in Arms, hands, trunk 3 components with different levels Size, weight of ball, trajectory,
object distance, speed, color contrast
Rising to Stand getting up from lying upper extremity, trunk(axial), lower 6 steps in upper extremity, 5 steps in speed, surface type, surface hgt, use
from Supine supine to upright stand extremity components trunk, 5 steps in lower extremity of hands, clothing, body comp
You might also like
- The Basics: A Comprehensive Outline of Nursing School ContentFrom EverandThe Basics: A Comprehensive Outline of Nursing School ContentRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Chapter 1 Psychology of TravelDocument39 pagesChapter 1 Psychology of TravelCha Garcia100% (4)
- Lab Report Group 6 Nerves and ReflexesDocument5 pagesLab Report Group 6 Nerves and ReflexesKristina Esta50% (2)
- New Born ReflexesDocument11 pagesNew Born ReflexesBinal JoshiNo ratings yet
- Perception and Coordination Module ADocument3 pagesPerception and Coordination Module ARosmary100% (1)
- The Mindful Way Through DepressionDocument2 pagesThe Mindful Way Through Depressionjulie77a0% (4)
- Purpose in Life Test CrumbaughDocument8 pagesPurpose in Life Test CrumbaughПламен МинчевNo ratings yet
- How Culture Is LearnedDocument11 pagesHow Culture Is Learnedims offiiceNo ratings yet
- ReflexTesting (OT120 CVI Lecture) PDFDocument15 pagesReflexTesting (OT120 CVI Lecture) PDFAndrea Estaniel100% (1)
- Health Assessment: NeuroDocument34 pagesHealth Assessment: Neuroiamjennykim76No ratings yet
- ReflexDocument6 pagesReflexsiti syafiqahNo ratings yet
- Reflex Testing (Week 11) ReviewerDocument8 pagesReflex Testing (Week 11) ReviewerKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- Spine ExaminationDocument45 pagesSpine ExaminationNadya LiemNo ratings yet
- Postural ReflexesDocument25 pagesPostural ReflexesGksNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument20 pagesBiology ProjectPratyusha SinghNo ratings yet
- OT1029 Module-3 ReflexesDocument4 pagesOT1029 Module-3 ReflexesJica GulaNo ratings yet
- 6 Parts: o Mental Status o Cranial Nerves o Sensory Function o Motor Function o Cerebellar Function o Reflexes 1. Cranial NervesDocument3 pages6 Parts: o Mental Status o Cranial Nerves o Sensory Function o Motor Function o Cerebellar Function o Reflexes 1. Cranial NervesTaraKyleUyNo ratings yet
- Demonstration ReflexDocument40 pagesDemonstration Reflexnikita jainNo ratings yet
- Neuro Part 2Document6 pagesNeuro Part 2vetthamilNo ratings yet
- Understanding Primitive Reflexes and Their Role in Growth and Development: A ReviewDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Primitive Reflexes and Their Role in Growth and Development: A ReviewZuveria LatifNo ratings yet
- ReflexesDocument37 pagesReflexesSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Global Delay DevelopmentDocument2 pagesGlobal Delay DevelopmentRiani DwiastutiNo ratings yet
- Reflexes TableDocument5 pagesReflexes TableElizabeth CarpioNo ratings yet
- Classic Reflex Hierarchy and ReflexesDocument8 pagesClassic Reflex Hierarchy and ReflexesJaclyn ArpinNo ratings yet
- Neonatal HypotoniaDocument7 pagesNeonatal HypotoniaShirley KoehNo ratings yet
- GUILLAIN BARRЀ SYNDROMEDocument9 pagesGUILLAIN BARRЀ SYNDROMEzhapper2002No ratings yet
- Neuro Exam SchemeDocument229 pagesNeuro Exam SchemeRanjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Plantar ReflexDocument5 pagesPlantar ReflexrazakmdpaedNo ratings yet
- Roods ApproachDocument21 pagesRoods ApproachnrusinghNo ratings yet
- Cns Part ExaminationDocument68 pagesCns Part ExaminationHarshita CoolNo ratings yet
- ReflexesDocument5 pagesReflexes1204.rubyguptaNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics ReflexesDocument6 pagesPediatrics ReflexesElizabeth CarpioNo ratings yet
- International Journalof Pediatricsand Neonatology Planter ReflexDocument4 pagesInternational Journalof Pediatricsand Neonatology Planter ReflexUmesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Roods ApproachDocument23 pagesRoods ApproachyigoNo ratings yet
- Brain Dance HandoutDocument10 pagesBrain Dance HandoutCSelena MuzikeraNo ratings yet
- Reflexes: Laboratory Practical General ObjectivesDocument4 pagesReflexes: Laboratory Practical General ObjectivesPhysio08No ratings yet
- Manual Muscle Testing: RD TH TH TH TH TH TH TH THDocument6 pagesManual Muscle Testing: RD TH TH TH TH TH TH TH THAljon S. TemploNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Piyush Verma Mds 2 Yr Dept of Paedodontics & Preventive DentistryDocument51 pagesPresented By: Piyush Verma Mds 2 Yr Dept of Paedodontics & Preventive DentistryJodene Rose RojasNo ratings yet
- General Psychology 4: THE Physiological Basis OF Behavior: Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R. Abejo RN, MANDocument4 pagesGeneral Psychology 4: THE Physiological Basis OF Behavior: Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R. Abejo RN, MANMariel EfrenNo ratings yet
- Pengkajian Neurologi - HafnaDocument91 pagesPengkajian Neurologi - HafnaC111 Maysi Puji IsanggrainiNo ratings yet
- Spinal Examination 2: Siti Amalina Binti Awang (112013172)Document30 pagesSpinal Examination 2: Siti Amalina Binti Awang (112013172)Anonymous 5teDt47yNo ratings yet
- Vojta TherapyDocument17 pagesVojta Therapymadhu S MNo ratings yet
- 14.understanding Primitive Reflexes and Their Role in Growth and DevelopmentDocument6 pages14.understanding Primitive Reflexes and Their Role in Growth and DevelopmentGeotamNo ratings yet
- Neurological Examination at 40 Weeks of Gestational AgeDocument11 pagesNeurological Examination at 40 Weeks of Gestational AgeMelina Defita SariNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Nuclei TractsDocument1 pageSpinal Cord Nuclei TractsKarthik TNo ratings yet
- Neurologic Examination of Newborn and InfantsDocument6 pagesNeurologic Examination of Newborn and InfantsRem AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Reflexes:: DefinitionDocument11 pagesReflexes:: DefinitionUMAIR JAMEELNo ratings yet
- Tahapan Perkembangan Motor Skill (0-12 BLN) Fisiopedi Ums: Ridho Budi Rahmad, S.FisDocument46 pagesTahapan Perkembangan Motor Skill (0-12 BLN) Fisiopedi Ums: Ridho Budi Rahmad, S.FisAtikah HanunNo ratings yet
- Cerebellar FunctionDocument49 pagesCerebellar FunctionIris Kate MallariNo ratings yet
- Neuropediatric ExaminationDocument43 pagesNeuropediatric ExaminationShaniaNo ratings yet
- David Butler Neural Tissue Mobilisation-1Document11 pagesDavid Butler Neural Tissue Mobilisation-1Himani BhondgeNo ratings yet
- CNS ExaminationDocument3 pagesCNS ExaminationsekharNo ratings yet
- Remaining NEUROLOGIC SYSTEMDocument67 pagesRemaining NEUROLOGIC SYSTEMtendi AndriansayahNo ratings yet
- Pri ReflexesDocument50 pagesPri ReflexesMv.suravijay Mv.suravijayNo ratings yet
- 14.understanding Primitive Reflexes and Their Role in Growth and DevelopmentDocument6 pages14.understanding Primitive Reflexes and Their Role in Growth and Developmenthadiatullah alifNo ratings yet
- Prospective Follow-Up of Primitive Reflex Profiles in High-Risk Infants: Clues To An Early Diagnosis of Cerebral PalsyDocument5 pagesProspective Follow-Up of Primitive Reflex Profiles in High-Risk Infants: Clues To An Early Diagnosis of Cerebral Palsyanajara44No ratings yet
- Paediatrics - Neurological ExaminationDocument5 pagesPaediatrics - Neurological ExaminationhalesipsumNo ratings yet
- Anatomy L7C PPDocument69 pagesAnatomy L7C PPsiddhi meenaNo ratings yet
- Examination of The CNS in Children: Professor Low Poh Sim Department of Paediatrics UcmiDocument40 pagesExamination of The CNS in Children: Professor Low Poh Sim Department of Paediatrics UcmiVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- Ears: Nose: EyeDocument1 pageEars: Nose: Eyeapi-72312524No ratings yet
- New Born ReflexesDocument40 pagesNew Born ReflexesKarun Prakash100% (1)
- Reflex NotesDocument2 pagesReflex NotesJade Niña GemiraNo ratings yet
- Primitive Reflex in Preterm BabiesDocument5 pagesPrimitive Reflex in Preterm BabiesAmirul Zakri IsmailNo ratings yet
- Symbiosis & AttachmentDocument8 pagesSymbiosis & Attachmentwonder_full77No ratings yet
- Leadership Academy AnthonyRobbins PDFDocument1 pageLeadership Academy AnthonyRobbins PDFEssexschool Inglés CastellónNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Myths of Aging (Aspuria, Trisha Mae)Document2 pagesActivity 1 - Myths of Aging (Aspuria, Trisha Mae)Trisha Mae AspuriaNo ratings yet
- PERDEVDocument5 pagesPERDEVlennie cotiocoNo ratings yet
- Instructional Strategies Chart 1Document9 pagesInstructional Strategies Chart 1api-421516141No ratings yet
- Short Vowels: Created By: Bethany GardnerDocument15 pagesShort Vowels: Created By: Bethany GardnerSherineNo ratings yet
- PHAR 200 Course Outline 2018Document1 pagePHAR 200 Course Outline 2018yash tayNo ratings yet
- Conclusion On Concepts, Nature, and Purposes of CurriculumDocument4 pagesConclusion On Concepts, Nature, and Purposes of CurriculumMall Concert Challenge/ KAKASA KA BA? /JayrraNo ratings yet
- The 7 Real Mind Power SecretsDocument23 pagesThe 7 Real Mind Power SecretsTibetanDream100% (7)
- Movement DisordersDocument6 pagesMovement Disordersspicychips7No ratings yet
- Adaptation ModelDocument2 pagesAdaptation ModelDenise Allyson MoldezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ESP DAY 2Document2 pagesLesson Plan in ESP DAY 2Krystal Claire Dioso MarimonNo ratings yet
- Architectural Thesis: Aditi GuptaDocument24 pagesArchitectural Thesis: Aditi GuptaAditi gupta100% (1)
- Official Lab 01 SBF3033Document14 pagesOfficial Lab 01 SBF3033Foster Van VossenNo ratings yet
- VASQ Scoring2 With Supp June12 PDFDocument3 pagesVASQ Scoring2 With Supp June12 PDFdinuroxanadanielaNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Question Paper AI Soln v2Document6 pagesMid Term Question Paper AI Soln v2haris razaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Stress On The Academic Performance of Dentistry Students of National UniversityDocument14 pagesEffects of Stress On The Academic Performance of Dentistry Students of National UniversityDufuxwerr Werr100% (1)
- Grief Models and TheoriesDocument5 pagesGrief Models and TheoriesIleana Dafina Chiorean NicolaNo ratings yet
- CBL and Habits of Mindv6Document1 pageCBL and Habits of Mindv6api-342501740No ratings yet
- Invitational Counseling: An Expanded Framework For Comprehensive School Counseling ProgramsDocument36 pagesInvitational Counseling: An Expanded Framework For Comprehensive School Counseling ProgramsAdie CaberteNo ratings yet
- 22 August 2020 Schedule Eac Psych 3Document3 pages22 August 2020 Schedule Eac Psych 3Dhruva PatelNo ratings yet
- A Short Proposal For A Research Using InferenceDocument3 pagesA Short Proposal For A Research Using Inferencemaroua.sayahNo ratings yet
- Attention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder: Russell A. BarkleyDocument69 pagesAttention-Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder: Russell A. BarkleybolbolNo ratings yet
- in Inquiry Based LearningDocument29 pagesin Inquiry Based LearningRonnelNo ratings yet
- Positive and Negative Reinforcement Handout 1Document1 pagePositive and Negative Reinforcement Handout 1Ивона Шујак100% (1)
- Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders DSM - V Ocd and Related DisordersDocument2 pagesObsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders DSM - V Ocd and Related DisordersJaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet