Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 viewsOperating: A Cleanroom Which Is Complete and Operating: Terminology 283
Operating: A Cleanroom Which Is Complete and Operating: Terminology 283
Uploaded by
rohit1. An operating cleanroom is a cleanroom that is complete, connected, and functioning with production equipment and personnel.
2. A clean zone is a defined space where airborne particle concentration is controlled to meet cleanliness standards, and is constructed to minimize particle introduction.
3. Coils are heat transfer devices used for heating, cooling, or dehumidifying air in hydronic applications, often made of copper and aluminum materials.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- D. Angle of ArticulationDocument10 pagesD. Angle of ArticulationDave Vendivil SambranoNo ratings yet
- SIMEONDocument7 pagesSIMEONVincent Martinez100% (1)
- Prestressed Concrete - 7 Estimation of Prestress LossesDocument29 pagesPrestressed Concrete - 7 Estimation of Prestress Losses4493464100% (1)
- Operating: A Cleanroom Which Is Complete and Operating: Terminology 283Document2 pagesOperating: A Cleanroom Which Is Complete and Operating: Terminology 283Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Class-1-HVAC GLOSSARYDocument7 pagesClass-1-HVAC GLOSSARYAmrit BaniyaNo ratings yet
- Terminology 287Document2 pagesTerminology 287rohitNo ratings yet
- Terminology 285Document2 pagesTerminology 285rohitNo ratings yet
- Air ConditioningDocument13 pagesAir ConditioningSumedha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Acu GlossaryDocument7 pagesAcu GlossaryErika RafaelNo ratings yet
- Notes For Unit Test-1Document7 pagesNotes For Unit Test-1priya dharshiniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document12 pagesChapter 2Mohammad Muawya Nouri HijaziNo ratings yet
- Hvac Def of TermsDocument3 pagesHvac Def of Terms88ncd4y4r7No ratings yet
- Selection Tips For Air-Conditioning Cooling Systems PDFDocument10 pagesSelection Tips For Air-Conditioning Cooling Systems PDFlkakeanNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning SystemsDocument3 pagesAir Conditioning SystemsArman Ul NasarNo ratings yet
- 11 AirconditioningDocument19 pages11 AirconditioningRohit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Two MarksDocument21 pages1.1 Two MarksSubhadharani SNo ratings yet
- 101Document59 pages101Vj AdityaNo ratings yet
- HavcDocument14 pagesHavcSharique AliNo ratings yet
- Air Handling UnitDocument27 pagesAir Handling Unitobaidur_rehman_3100% (1)
- HVAC - Cooling SysDocument14 pagesHVAC - Cooling Sysknotship.comNo ratings yet
- Types of HVAC SystemsDocument6 pagesTypes of HVAC Systemsm2110100% (1)
- Siez Assignment2 ME413Document5 pagesSiez Assignment2 ME413Yehosuah RanoaNo ratings yet
- Heating Ventilation and Air ConditioningDocument14 pagesHeating Ventilation and Air ConditioningMiahsaheb Rafeeq100% (1)
- Istilah Istilah Yang Sering Di Temukan Dalam Kamus PendinginDocument9 pagesIstilah Istilah Yang Sering Di Temukan Dalam Kamus PendinginFriget RusiantoNo ratings yet
- Hvac NotesDocument129 pagesHvac Notesshahinkhan52535No ratings yet
- Air Handling Units: Report by Vaishnavi Chandrakant Kamble B (Voc) - Int Sem IIIDocument7 pagesAir Handling Units: Report by Vaishnavi Chandrakant Kamble B (Voc) - Int Sem IIIVaishnavi KambleNo ratings yet
- HVAC SystemDocument66 pagesHVAC Systemmrccahmed100% (1)
- Hvac HvacDocument11 pagesHvac HvacMuhammadYounusNo ratings yet
- Air Handling Unit (AHU)Document6 pagesAir Handling Unit (AHU)bibombioNo ratings yet
- Selection Tips For HVAC SystemsDocument41 pagesSelection Tips For HVAC SystemsImtiaz Ahmed100% (1)
- Hvac (H V & A C) : Eating Entilation IR OnditioningDocument50 pagesHvac (H V & A C) : Eating Entilation IR OnditioningTushal100No ratings yet
- Hvac Notes: Vapor-Compression Absorption Refrigeration Cycle Heat ExchangerDocument36 pagesHvac Notes: Vapor-Compression Absorption Refrigeration Cycle Heat ExchangerMohd Tarique AnwarNo ratings yet
- AirconDocument142 pagesAirconJervin Ocampo0% (2)
- Air ConditioningDocument22 pagesAir ConditioningEmmanuel BuhwaNo ratings yet
- HVAC PresentationDocument54 pagesHVAC PresentationShiv Kumar Verma100% (3)
- CFD SimulationDocument39 pagesCFD SimulationSambhav JainNo ratings yet
- Construction: Air FilterDocument10 pagesConstruction: Air FilterSreekanth MadakaNo ratings yet
- Architectural Science (HVAC) Lecture 6 & 7Document32 pagesArchitectural Science (HVAC) Lecture 6 & 7ezakbelachewNo ratings yet
- Tips-Selection of Cooling SysDocument0 pagesTips-Selection of Cooling SysmohdnazirNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument2 pages1 PDFrohitNo ratings yet
- Air HandlerDocument7 pagesAir Handlercreate foxesNo ratings yet
- Central AcDocument39 pagesCentral Acmonica singh100% (1)
- Heating And/or Cooling Elements: Heat Exchanger HVAC Air CoilsDocument3 pagesHeating And/or Cooling Elements: Heat Exchanger HVAC Air CoilsAshiqNo ratings yet
- Air Handler: Blower Filter Dampers Ductwork Ventilation SystemDocument16 pagesAir Handler: Blower Filter Dampers Ductwork Ventilation SystemKanika MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Hvac 4Document6 pagesHvac 4emumerr69No ratings yet
- Unit 1 FilesDocument5 pagesUnit 1 FilesAsma Parveen .ANo ratings yet
- 1334337428180-Electr - QUESTION - BANK - TL - AC - AND - EM - Final PDFDocument116 pages1334337428180-Electr - QUESTION - BANK - TL - AC - AND - EM - Final PDFPankaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Air Handler: Navigation SearchDocument5 pagesAir Handler: Navigation SearchNikhil KallaNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Basics: Air-Source, Split SystemsDocument4 pagesAir Conditioning Basics: Air-Source, Split SystemsAhmad MujahidNo ratings yet
- Week 6maint MGMT BIE2016 MechanicalDocument90 pagesWeek 6maint MGMT BIE2016 MechanicalaimanfznnnNo ratings yet
- Script:-.Air Condition ScriptDocument11 pagesScript:-.Air Condition Scriptaimri_cochinNo ratings yet
- Hvac 5Document3 pagesHvac 5emumerr69No ratings yet
- Refrigeration ME 201Document13 pagesRefrigeration ME 201pathan_440No ratings yet
- Air Handling UnitDocument8 pagesAir Handling UnitSN Shuhada ZakariaNo ratings yet
- 1 HVAC IntroductionDocument41 pages1 HVAC IntroductionAbdullah SendiNo ratings yet
- HVAC Case Study PPT ChanduDocument72 pagesHVAC Case Study PPT Chanduprasahnthrk0775% (4)
- Architectural Building Services: Vedita Bhat Roll No-03Document8 pagesArchitectural Building Services: Vedita Bhat Roll No-03Vedita Bhat100% (1)
- Heating Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC)Document12 pagesHeating Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC)Atia Khursheed50% (2)
- Temperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemFrom EverandTemperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemNo ratings yet
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseFrom EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 33Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 33rohitNo ratings yet
- Figure 3-3. Btu Change in One Pound of Ice To Water To Steam To Superheated SteamDocument2 pagesFigure 3-3. Btu Change in One Pound of Ice To Water To Steam To Superheated SteamrohitNo ratings yet
- Figure 4-.2 Air Conditioning System ExampleDocument2 pagesFigure 4-.2 Air Conditioning System ExamplerohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 57Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 57rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 37: Figure 3-6. Combustion Chamber and Fire Tubes. Two-Pass BoilerDocument2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 37: Figure 3-6. Combustion Chamber and Fire Tubes. Two-Pass BoilerrohitNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument2 pages1 PDFrohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 29: Figure 3-2. Steam BoilerDocument2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 29: Figure 3-2. Steam BoilerrohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 63: Evaporators (Heat Picked Up From The Conditioned Space)Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 63: Evaporators (Heat Picked Up From The Conditioned Space)rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 27Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 27rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 25Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 25rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 35Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 35rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 55Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 55rohitNo ratings yet
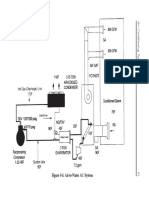
- Figure 4-4. Air-to-Water AC SystemDocument2 pagesFigure 4-4. Air-to-Water AC SystemrohitNo ratings yet
- Btuh GPM ×: Heat Flow 23Document2 pagesBtuh GPM ×: Heat Flow 23rohitNo ratings yet
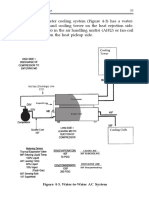
- Air Conditioning Systems 59: Figure 4-3. Water-to-Water AC SystemDocument2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 59: Figure 4-3. Water-to-Water AC SystemrohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 47Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 47rohitNo ratings yet
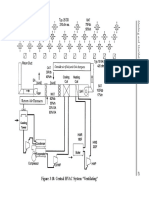
- Figure 3-10. Central HVAC System "Ventilating"Document2 pagesFigure 3-10. Central HVAC System "Ventilating"rohitNo ratings yet
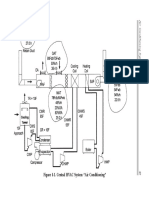
- Figure 4-1. Central HVAC System "Air Conditioning"Document2 pagesFigure 4-1. Central HVAC System "Air Conditioning"rohitNo ratings yet
- HVAC Systems 1Document2 pagesHVAC Systems 1rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 51Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 51rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 43: MAT (%OA ×Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 43: MAT (%OA ×rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 41: Figure 3-8. Oil BurnerDocument2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 41: Figure 3-8. Oil BurnerrohitNo ratings yet
- Latent HeatDocument2 pagesLatent HeatrohitNo ratings yet
- This Page Intentionally Left BlankDocument2 pagesThis Page Intentionally Left BlankrohitNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow 17: ConductionDocument2 pagesHeat Flow 17: ConductionrohitNo ratings yet
- This Page Intentionally Left BlankDocument2 pagesThis Page Intentionally Left BlankrohitNo ratings yet
- HVAC Systems 13: VentilatingDocument2 pagesHVAC Systems 13: VentilatingrohitNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow 19Document2 pagesHeat Flow 19rohitNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow 15Document2 pagesHeat Flow 15rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Volume: HVAC Systems 11Document2 pagesAir Volume: HVAC Systems 11rohitNo ratings yet
- Renk Slide Bearings Type HGDocument4 pagesRenk Slide Bearings Type HGgrupa2904No ratings yet
- Almeida 2018Document12 pagesAlmeida 2018بلال بن عميرهNo ratings yet
- English For ChemistryDocument17 pagesEnglish For ChemistryMelvina theodora simanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Design Considerations DMEDocument59 pagesModule 1 - Design Considerations DMEsreeramhariharanNo ratings yet
- HP40 NBDocument13 pagesHP40 NBTarun ChandraNo ratings yet
- Structural Report - Type 4 Health PostDocument29 pagesStructural Report - Type 4 Health PostSaurav ShahNo ratings yet
- Steam Distribution & End Users - Efficiency Improvements PDFDocument22 pagesSteam Distribution & End Users - Efficiency Improvements PDFcarlosleonardiniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lesson 2Document9 pagesChapter 3 Lesson 2karinaderalonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 8 SolutionsDocument7 pagesAssignment 8 SolutionsCarlos Israel Esparza AndradeNo ratings yet
- Sec. VIII Div 1 Apen 1Document16 pagesSec. VIII Div 1 Apen 1ADRIANNo ratings yet
- BSCPH 202Document4 pagesBSCPH 202pp1560078No ratings yet
- Batch Distillation W 10Document6 pagesBatch Distillation W 10Junaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- 22-23 - SemB L9 Condensed MatterDocument84 pages22-23 - SemB L9 Condensed MatterChloe ChongNo ratings yet
- Vapour Permeability of Porous Materials Using Payne Diffusion CellDocument7 pagesVapour Permeability of Porous Materials Using Payne Diffusion CellarnetaNo ratings yet
- Cinetica Oxido de Etileno y AguaDocument16 pagesCinetica Oxido de Etileno y AguaJuan Felipe Cortes FernandezNo ratings yet
- Airborne Weather RadarDocument42 pagesAirborne Weather RadarAndreNo ratings yet
- Nylon: Roger Kho R&D PenfabricDocument10 pagesNylon: Roger Kho R&D PenfabricKhoRogerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document14 pagesChapter 2Bùi Hữu ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Plastic HingeDocument12 pagesPlastic HingeJakov OrebNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Short Tricks & Advanced TheoryDocument11 pagesGas Laws Short Tricks & Advanced TheoryRutesh JavalkarNo ratings yet
- Fracture and Fracture Toughness of Cast Irons: W. L. Bradley and M. N. SrinivasanDocument33 pagesFracture and Fracture Toughness of Cast Irons: W. L. Bradley and M. N. SrinivasanNarasimha Murthy InampudiNo ratings yet
- Rock PhysicsDocument9 pagesRock PhysicsKurniasari FitriaNo ratings yet
- 1) Size Dependent Analysis of Wave Propagation in Functionally Graded CompositeDocument24 pages1) Size Dependent Analysis of Wave Propagation in Functionally Graded CompositeHamid M SedighiNo ratings yet
- Chem M5 ColloidsDocument19 pagesChem M5 ColloidsEstrie Niku Sanes JaleerNo ratings yet
- Sylvania Guide To Energy Saving Lamps Brochure 1986Document12 pagesSylvania Guide To Energy Saving Lamps Brochure 1986Alan Masters100% (1)
- SIREG - Waterstop JointsDocument8 pagesSIREG - Waterstop JointsMario RuggieroNo ratings yet
- Plasma Cleaning Treatment For Flourine, Oxides and ContaminationDocument4 pagesPlasma Cleaning Treatment For Flourine, Oxides and ContaminationGilbert Bonilla100% (1)
- Ir 3 5 DN 32 100Document9 pagesIr 3 5 DN 32 100henddikNo ratings yet
Operating: A Cleanroom Which Is Complete and Operating: Terminology 283
Operating: A Cleanroom Which Is Complete and Operating: Terminology 283
Uploaded by
rohit0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pages1. An operating cleanroom is a cleanroom that is complete, connected, and functioning with production equipment and personnel.
2. A clean zone is a defined space where airborne particle concentration is controlled to meet cleanliness standards, and is constructed to minimize particle introduction.
3. Coils are heat transfer devices used for heating, cooling, or dehumidifying air in hydronic applications, often made of copper and aluminum materials.
Original Description:
rohit
Original Title
1 (14)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. An operating cleanroom is a cleanroom that is complete, connected, and functioning with production equipment and personnel.
2. A clean zone is a defined space where airborne particle concentration is controlled to meet cleanliness standards, and is constructed to minimize particle introduction.
3. Coils are heat transfer devices used for heating, cooling, or dehumidifying air in hydronic applications, often made of copper and aluminum materials.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesOperating: A Cleanroom Which Is Complete and Operating: Terminology 283
Operating: A Cleanroom Which Is Complete and Operating: Terminology 283
Uploaded by
rohit1. An operating cleanroom is a cleanroom that is complete, connected, and functioning with production equipment and personnel.
2. A clean zone is a defined space where airborne particle concentration is controlled to meet cleanliness standards, and is constructed to minimize particle introduction.
3. Coils are heat transfer devices used for heating, cooling, or dehumidifying air in hydronic applications, often made of copper and aluminum materials.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Terminology 283
Operating: A cleanroom which is complete and operating
with all services connected and functioning. It has produc-
tion equipment and personnel.
Clean Zone: A defined or dedicated space in which the concentra-
tion of airborne particles is controlled to meet a specified airborne
particulate cleanliness class. A clean zone is constructed and used
in a manner to minimize the introduction, generation, and reten-
tion of particles inside the zone. Other relevant parameters, e.g.
temperature, humidity, and pressure, are controlled as necessary.
A clean zone may be open or enclosed and may or may not be
located within a cleanroom.
Coil: Coils are heat transfer devices (heat exchangers). They come
in a variety of type and sizes and are designed for various fluid
combinations. In hydronic applications coils are used for heating,
cooling or dehumidifying air. Hydronic coils are most often made
of copper headers and tubes with aluminum or copper fins and
galvanized steel frames.
Cold: Cold is a relative term to describe the temperature of an
object or area compared to a known temperature. For instance,
50°F in the winter might be considered a warm temperature while
in the summer it would be a cool temperature.
Cold Deck: In a multizone, or dual duct, unit, it is the chamber
after the air leaves the cooling coil.
Condensation Stage: Condensation stage is the cooling of a re-
frigerant vapor to convert it to a liquid in this condenser.
Cubic Feet Per Minute: Airflow volume (cfm).
Constant Volume Single Duct Box: A single inlet terminal box
supplied with air at a constant volume and temperature (typically
cool air). Air flowing through the box is controlled by a manually
284 HVAC Fundamentals
operated damper or a mechanical constant volume regulator. The
mechanical volume regulator uses springs and perforated plates
or damper blades, which decrease or increase the available flow
area as the pressure at the inlet to the box, increases or decreases.
A reheat coil or cooling coil may be installed in the box or imme-
diately downstream from it. A room thermostat controls the coil.
Cooling Coil: A chilled water or refrigerant coil.
Damper: A device used to regulate airflow.
Diffuser: A supply air outlet generally found in the ceiling with
various deflectors arranged to promote mixing of primary air
with secondary air. Types of diffusers are: round, square, rectan-
gular, linear and troffers. Some diffusers have a fixed airflow
pattern while others have field adjusted patterns.
Digital Signal: Representation of a numerical quantity by a num-
ber of discrete signals (not continuous) or by the presence or
absence of signals in particular positions. Binary digital signals
have one of two states (0 or 1) defined by voltage or current lev-
els.
Direct-Acting: A direct-acting controller increases its branch out-
put as the condition it is sensing increases (D/A).
Diversity in Constant Air Volume Systems: The total cfm output
of the fan is greater than the maximum required volume through
the cooling coil.
Diversity in Variable Air Volume (VAV) Systems: The total cfm
output of the fan is less than the maximum required volume
through the VAV boxes and outlets.
Draft: A localized feeling of coolness caused by high air velocity,
low ambient temperature, or direction of airflow.
You might also like
- D. Angle of ArticulationDocument10 pagesD. Angle of ArticulationDave Vendivil SambranoNo ratings yet
- SIMEONDocument7 pagesSIMEONVincent Martinez100% (1)
- Prestressed Concrete - 7 Estimation of Prestress LossesDocument29 pagesPrestressed Concrete - 7 Estimation of Prestress Losses4493464100% (1)
- Operating: A Cleanroom Which Is Complete and Operating: Terminology 283Document2 pagesOperating: A Cleanroom Which Is Complete and Operating: Terminology 283Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Class-1-HVAC GLOSSARYDocument7 pagesClass-1-HVAC GLOSSARYAmrit BaniyaNo ratings yet
- Terminology 287Document2 pagesTerminology 287rohitNo ratings yet
- Terminology 285Document2 pagesTerminology 285rohitNo ratings yet
- Air ConditioningDocument13 pagesAir ConditioningSumedha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Acu GlossaryDocument7 pagesAcu GlossaryErika RafaelNo ratings yet
- Notes For Unit Test-1Document7 pagesNotes For Unit Test-1priya dharshiniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document12 pagesChapter 2Mohammad Muawya Nouri HijaziNo ratings yet
- Hvac Def of TermsDocument3 pagesHvac Def of Terms88ncd4y4r7No ratings yet
- Selection Tips For Air-Conditioning Cooling Systems PDFDocument10 pagesSelection Tips For Air-Conditioning Cooling Systems PDFlkakeanNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning SystemsDocument3 pagesAir Conditioning SystemsArman Ul NasarNo ratings yet
- 11 AirconditioningDocument19 pages11 AirconditioningRohit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Two MarksDocument21 pages1.1 Two MarksSubhadharani SNo ratings yet
- 101Document59 pages101Vj AdityaNo ratings yet
- HavcDocument14 pagesHavcSharique AliNo ratings yet
- Air Handling UnitDocument27 pagesAir Handling Unitobaidur_rehman_3100% (1)
- HVAC - Cooling SysDocument14 pagesHVAC - Cooling Sysknotship.comNo ratings yet
- Types of HVAC SystemsDocument6 pagesTypes of HVAC Systemsm2110100% (1)
- Siez Assignment2 ME413Document5 pagesSiez Assignment2 ME413Yehosuah RanoaNo ratings yet
- Heating Ventilation and Air ConditioningDocument14 pagesHeating Ventilation and Air ConditioningMiahsaheb Rafeeq100% (1)
- Istilah Istilah Yang Sering Di Temukan Dalam Kamus PendinginDocument9 pagesIstilah Istilah Yang Sering Di Temukan Dalam Kamus PendinginFriget RusiantoNo ratings yet
- Hvac NotesDocument129 pagesHvac Notesshahinkhan52535No ratings yet
- Air Handling Units: Report by Vaishnavi Chandrakant Kamble B (Voc) - Int Sem IIIDocument7 pagesAir Handling Units: Report by Vaishnavi Chandrakant Kamble B (Voc) - Int Sem IIIVaishnavi KambleNo ratings yet
- HVAC SystemDocument66 pagesHVAC Systemmrccahmed100% (1)
- Hvac HvacDocument11 pagesHvac HvacMuhammadYounusNo ratings yet
- Air Handling Unit (AHU)Document6 pagesAir Handling Unit (AHU)bibombioNo ratings yet
- Selection Tips For HVAC SystemsDocument41 pagesSelection Tips For HVAC SystemsImtiaz Ahmed100% (1)
- Hvac (H V & A C) : Eating Entilation IR OnditioningDocument50 pagesHvac (H V & A C) : Eating Entilation IR OnditioningTushal100No ratings yet
- Hvac Notes: Vapor-Compression Absorption Refrigeration Cycle Heat ExchangerDocument36 pagesHvac Notes: Vapor-Compression Absorption Refrigeration Cycle Heat ExchangerMohd Tarique AnwarNo ratings yet
- AirconDocument142 pagesAirconJervin Ocampo0% (2)
- Air ConditioningDocument22 pagesAir ConditioningEmmanuel BuhwaNo ratings yet
- HVAC PresentationDocument54 pagesHVAC PresentationShiv Kumar Verma100% (3)
- CFD SimulationDocument39 pagesCFD SimulationSambhav JainNo ratings yet
- Construction: Air FilterDocument10 pagesConstruction: Air FilterSreekanth MadakaNo ratings yet
- Architectural Science (HVAC) Lecture 6 & 7Document32 pagesArchitectural Science (HVAC) Lecture 6 & 7ezakbelachewNo ratings yet
- Tips-Selection of Cooling SysDocument0 pagesTips-Selection of Cooling SysmohdnazirNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument2 pages1 PDFrohitNo ratings yet
- Air HandlerDocument7 pagesAir Handlercreate foxesNo ratings yet
- Central AcDocument39 pagesCentral Acmonica singh100% (1)
- Heating And/or Cooling Elements: Heat Exchanger HVAC Air CoilsDocument3 pagesHeating And/or Cooling Elements: Heat Exchanger HVAC Air CoilsAshiqNo ratings yet
- Air Handler: Blower Filter Dampers Ductwork Ventilation SystemDocument16 pagesAir Handler: Blower Filter Dampers Ductwork Ventilation SystemKanika MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Hvac 4Document6 pagesHvac 4emumerr69No ratings yet
- Unit 1 FilesDocument5 pagesUnit 1 FilesAsma Parveen .ANo ratings yet
- 1334337428180-Electr - QUESTION - BANK - TL - AC - AND - EM - Final PDFDocument116 pages1334337428180-Electr - QUESTION - BANK - TL - AC - AND - EM - Final PDFPankaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Air Handler: Navigation SearchDocument5 pagesAir Handler: Navigation SearchNikhil KallaNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Basics: Air-Source, Split SystemsDocument4 pagesAir Conditioning Basics: Air-Source, Split SystemsAhmad MujahidNo ratings yet
- Week 6maint MGMT BIE2016 MechanicalDocument90 pagesWeek 6maint MGMT BIE2016 MechanicalaimanfznnnNo ratings yet
- Script:-.Air Condition ScriptDocument11 pagesScript:-.Air Condition Scriptaimri_cochinNo ratings yet
- Hvac 5Document3 pagesHvac 5emumerr69No ratings yet
- Refrigeration ME 201Document13 pagesRefrigeration ME 201pathan_440No ratings yet
- Air Handling UnitDocument8 pagesAir Handling UnitSN Shuhada ZakariaNo ratings yet
- 1 HVAC IntroductionDocument41 pages1 HVAC IntroductionAbdullah SendiNo ratings yet
- HVAC Case Study PPT ChanduDocument72 pagesHVAC Case Study PPT Chanduprasahnthrk0775% (4)
- Architectural Building Services: Vedita Bhat Roll No-03Document8 pagesArchitectural Building Services: Vedita Bhat Roll No-03Vedita Bhat100% (1)
- Heating Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC)Document12 pagesHeating Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC)Atia Khursheed50% (2)
- Temperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemFrom EverandTemperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemNo ratings yet
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseFrom EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 33Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 33rohitNo ratings yet
- Figure 3-3. Btu Change in One Pound of Ice To Water To Steam To Superheated SteamDocument2 pagesFigure 3-3. Btu Change in One Pound of Ice To Water To Steam To Superheated SteamrohitNo ratings yet
- Figure 4-.2 Air Conditioning System ExampleDocument2 pagesFigure 4-.2 Air Conditioning System ExamplerohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 57Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 57rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 37: Figure 3-6. Combustion Chamber and Fire Tubes. Two-Pass BoilerDocument2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 37: Figure 3-6. Combustion Chamber and Fire Tubes. Two-Pass BoilerrohitNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument2 pages1 PDFrohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 29: Figure 3-2. Steam BoilerDocument2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 29: Figure 3-2. Steam BoilerrohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 63: Evaporators (Heat Picked Up From The Conditioned Space)Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 63: Evaporators (Heat Picked Up From The Conditioned Space)rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 27Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 27rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 25Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 25rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 35Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 35rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 55Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 55rohitNo ratings yet
- Figure 4-4. Air-to-Water AC SystemDocument2 pagesFigure 4-4. Air-to-Water AC SystemrohitNo ratings yet
- Btuh GPM ×: Heat Flow 23Document2 pagesBtuh GPM ×: Heat Flow 23rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 59: Figure 4-3. Water-to-Water AC SystemDocument2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 59: Figure 4-3. Water-to-Water AC SystemrohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 47Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 47rohitNo ratings yet
- Figure 3-10. Central HVAC System "Ventilating"Document2 pagesFigure 3-10. Central HVAC System "Ventilating"rohitNo ratings yet
- Figure 4-1. Central HVAC System "Air Conditioning"Document2 pagesFigure 4-1. Central HVAC System "Air Conditioning"rohitNo ratings yet
- HVAC Systems 1Document2 pagesHVAC Systems 1rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 51Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 51rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 43: MAT (%OA ×Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 43: MAT (%OA ×rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 41: Figure 3-8. Oil BurnerDocument2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 41: Figure 3-8. Oil BurnerrohitNo ratings yet
- Latent HeatDocument2 pagesLatent HeatrohitNo ratings yet
- This Page Intentionally Left BlankDocument2 pagesThis Page Intentionally Left BlankrohitNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow 17: ConductionDocument2 pagesHeat Flow 17: ConductionrohitNo ratings yet
- This Page Intentionally Left BlankDocument2 pagesThis Page Intentionally Left BlankrohitNo ratings yet
- HVAC Systems 13: VentilatingDocument2 pagesHVAC Systems 13: VentilatingrohitNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow 19Document2 pagesHeat Flow 19rohitNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow 15Document2 pagesHeat Flow 15rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Volume: HVAC Systems 11Document2 pagesAir Volume: HVAC Systems 11rohitNo ratings yet
- Renk Slide Bearings Type HGDocument4 pagesRenk Slide Bearings Type HGgrupa2904No ratings yet
- Almeida 2018Document12 pagesAlmeida 2018بلال بن عميرهNo ratings yet
- English For ChemistryDocument17 pagesEnglish For ChemistryMelvina theodora simanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Design Considerations DMEDocument59 pagesModule 1 - Design Considerations DMEsreeramhariharanNo ratings yet
- HP40 NBDocument13 pagesHP40 NBTarun ChandraNo ratings yet
- Structural Report - Type 4 Health PostDocument29 pagesStructural Report - Type 4 Health PostSaurav ShahNo ratings yet
- Steam Distribution & End Users - Efficiency Improvements PDFDocument22 pagesSteam Distribution & End Users - Efficiency Improvements PDFcarlosleonardiniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lesson 2Document9 pagesChapter 3 Lesson 2karinaderalonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 8 SolutionsDocument7 pagesAssignment 8 SolutionsCarlos Israel Esparza AndradeNo ratings yet
- Sec. VIII Div 1 Apen 1Document16 pagesSec. VIII Div 1 Apen 1ADRIANNo ratings yet
- BSCPH 202Document4 pagesBSCPH 202pp1560078No ratings yet
- Batch Distillation W 10Document6 pagesBatch Distillation W 10Junaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- 22-23 - SemB L9 Condensed MatterDocument84 pages22-23 - SemB L9 Condensed MatterChloe ChongNo ratings yet
- Vapour Permeability of Porous Materials Using Payne Diffusion CellDocument7 pagesVapour Permeability of Porous Materials Using Payne Diffusion CellarnetaNo ratings yet
- Cinetica Oxido de Etileno y AguaDocument16 pagesCinetica Oxido de Etileno y AguaJuan Felipe Cortes FernandezNo ratings yet
- Airborne Weather RadarDocument42 pagesAirborne Weather RadarAndreNo ratings yet
- Nylon: Roger Kho R&D PenfabricDocument10 pagesNylon: Roger Kho R&D PenfabricKhoRogerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document14 pagesChapter 2Bùi Hữu ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Plastic HingeDocument12 pagesPlastic HingeJakov OrebNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Short Tricks & Advanced TheoryDocument11 pagesGas Laws Short Tricks & Advanced TheoryRutesh JavalkarNo ratings yet
- Fracture and Fracture Toughness of Cast Irons: W. L. Bradley and M. N. SrinivasanDocument33 pagesFracture and Fracture Toughness of Cast Irons: W. L. Bradley and M. N. SrinivasanNarasimha Murthy InampudiNo ratings yet
- Rock PhysicsDocument9 pagesRock PhysicsKurniasari FitriaNo ratings yet
- 1) Size Dependent Analysis of Wave Propagation in Functionally Graded CompositeDocument24 pages1) Size Dependent Analysis of Wave Propagation in Functionally Graded CompositeHamid M SedighiNo ratings yet
- Chem M5 ColloidsDocument19 pagesChem M5 ColloidsEstrie Niku Sanes JaleerNo ratings yet
- Sylvania Guide To Energy Saving Lamps Brochure 1986Document12 pagesSylvania Guide To Energy Saving Lamps Brochure 1986Alan Masters100% (1)
- SIREG - Waterstop JointsDocument8 pagesSIREG - Waterstop JointsMario RuggieroNo ratings yet
- Plasma Cleaning Treatment For Flourine, Oxides and ContaminationDocument4 pagesPlasma Cleaning Treatment For Flourine, Oxides and ContaminationGilbert Bonilla100% (1)
- Ir 3 5 DN 32 100Document9 pagesIr 3 5 DN 32 100henddikNo ratings yet