Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LAN Security Concepts PDF
LAN Security Concepts PDF
Uploaded by
Alonso Maurico Bolaños Guillen0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
195 views3 pagesThis document discusses various network security concepts and threats at the LAN layer. It covers endpoint security using devices like VPNs, NGFWs, and ESAs to protect against malware, DDoS attacks, and data breaches. It also discusses access control measures like 802.1x authentication and AAA components for authorization and accounting. Various layer 2 attacks are described such as MAC table flooding, VLAN hopping, DHCP attacks, and steps to mitigate them including port security, DHCP snooping, and BPDU guard. CDP and LLDP are also mentioned as protocols that can reveal device information to attackers.
Original Description:
Original Title
LAN Security Concepts.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses various network security concepts and threats at the LAN layer. It covers endpoint security using devices like VPNs, NGFWs, and ESAs to protect against malware, DDoS attacks, and data breaches. It also discusses access control measures like 802.1x authentication and AAA components for authorization and accounting. Various layer 2 attacks are described such as MAC table flooding, VLAN hopping, DHCP attacks, and steps to mitigate them including port security, DHCP snooping, and BPDU guard. CDP and LLDP are also mentioned as protocols that can reveal device information to attackers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
195 views3 pagesLAN Security Concepts PDF
LAN Security Concepts PDF
Uploaded by
Alonso Maurico Bolaños GuillenThis document discusses various network security concepts and threats at the LAN layer. It covers endpoint security using devices like VPNs, NGFWs, and ESAs to protect against malware, DDoS attacks, and data breaches. It also discusses access control measures like 802.1x authentication and AAA components for authorization and accounting. Various layer 2 attacks are described such as MAC table flooding, VLAN hopping, DHCP attacks, and steps to mitigate them including port security, DHCP snooping, and BPDU guard. CDP and LLDP are also mentioned as protocols that can reveal device information to attackers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Lan Security Concepts
10.1. Endpoint Security.
10.1.1. Network Attacks Today.
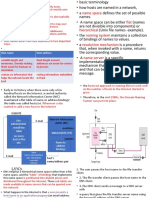
• Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS): • Discard emails with bad links (as shown in the
coordinated attack from many devices, figure).
intention of degrading or halting public access • Block access to newly infected sites.
to an organization website. • Encrypt content in outgoing email to prevent
• Data Breach: Data servers of host are data loss.
compromised to steal confidential information.
10.1.5. Cisco Web Security Appliance.
• Malware: malicious software (WannaCry),
WSA is a mitigation Technology for web-based
encrypts all the data until is paid.
threats.
10.1.2. Network Security Devices
Features and applications:
• Virtual Private Network (VPN)
• Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW): provides • Chat Messaging
Lower bandwidth
stateful inspection, application visibility and • Video
/ limited
control. advanced malware protection (AMP), • Audio
and URL filtering.
• Network Access Control (NAC): Includes Can perform blacklisted URLs, malware scan.
AAA, services may be incorporate, for 10.2. Access Control.
example; The Cisco Identity Services Engine
(ISE). 10.2.1. Authentication with a local password.
Limitations of the data base (SSH):
10.1.3. Endpoint Protection
Traditional host-based security: • Must be configured locally on each device.
• Local database configuration provides no
• Antivirus/Antimalware. fallback authentication method.
• Host-Based Firewalls.
• Host-Based Intrusion Prevention Systems 10.2.2. AAA components.
(HIPSs). • Authentication: who are you?
o Local: Stores usernames and passwords
Endpoints are protected by a combination of locally in a network device
NAC: o Server
▪ Remote Authentication Dial-In User
• Host-Based AMP Software.
Service (RADIUS)
• Email Security Appliance (ESA).
▪ Terminal Access Controller Access
• Web Security Appliance (WSA).
Control System (TACACS+)
10.1.4. Cisco Email Security Appliance. • Authorization: How much can you spend? /
ESA is designed to monitor SMTP what can you do
• Accounting: What did you spend it on?
Functions:
10.2.6. 802.1X
• Block known threats. Port-based access control and authentication
• Remediate against stealth malware that evaded protocol, restricts unauthorized workstations.
initial detection.
Have specific roles:
• Client (Supplicant): device runs 802.1X- IP Source Prevents MAC and IP address spoofing
compliant client software, which is available for Guard attacks.
(IPSG)
wired or wireless devices.
• Switch (Authenticator): switch acts as an This solution will not be effective if protocols are
not secured
intermediary between the client and the
authentication server. It requests identifying Strategies:
information from the client, verifies that
information with the authentication server, and • Always use secure variants of these protocols
relays a response to the client. Another device such as SSH, Secure Copy Protocol (SCP),
that could act as authenticator is a wireless Secure FTP (SFTP), and Secure Socket
access point. Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS).
• Authentication server: The server validates the • Consider using out-of-band management
identity of the client and notifies the switch or network to manage devices.
wireless access point that the client is or is not • Use a dedicated management VLAN where
authorized to access the LAN and switch nothing but management traffic resides.
services. • Use ACLs to filter unwanted access.
10.3. Layer 2 Security Threats 10.4. MAC Address Table Attack
10.3.2. Switch Attack Categories. • Tools: Macof.
Layer 2 attacks: • MAC Address Table Flooding: MAC Table is
full.
Category Examples • MAC Address Table Attack Mitigation: To
MAC Includes MAC address flooding attacks. mitigate MAC address table overflow attacks,
Table
Attacks
must implement port security.
VLAN Includes VLAN hopping and VLAN 10.5. LAN Attacks
Attacks double-tagging attacks. It also includes
attacks between devices on a common 10.5.2. Vlan Hopping Attacks
VLAN.
Enables traffic from one Vlan to be seen by
DHCP Includes DHCP starvation and DHCP
Attacks spoofing attacks. another VLAN. The threat actor configures the
ARP Includes ARP spoofing and ARP host to spoof 802.1Q signaling DTP to trunk with
Attacks poisoning attacks. the connecting switch and can access to the vlans
Address Includes MAC address and IP address and can receive the traffic.
Spoofing spoofing attacks.
Attacks 10.5.3. VLAN Double-Tagging Attack
STP Includes Spanning Tree Protocol A VLAN double-tagging is unidirectional and
Attacks manipulation attacks. works only when the attacker is connected to a
10.3.3. Switch Attack Mitigation Techniques. port residing in the same VLAN as the native
Solution Description VLAN of the trunk port.
Port Prevents many types of attacks including
Security MAC address flooding attacks and DHCP Vlan Attack Prevention:
starvation attacks.
DHCP Prevents DHCP starvation and DHCP
• Disable trunking on all access ports.
Snooping spoofing attacks. • Disable auto trunking on trunk links so that
Dynamic Prevents ARP spoofing and ARP trunks must be manually enabled.
ARP poisoning attacks. • Be sure that the native VLAN is only used for
Inspection
(DAI) trunk links.
10.5.5. DHCP Attacks • native VLAN
DHCP Starvation Attack
Disable
Creates a DoS for connecting clients (globbler
app) On a port: no cdp enable
DHCP Spoofing Attack On a device: no cdp run
Occurs when a rogue DHCP server is connected Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is also vulnerable to
reconnaissance attacks. Configure no lldp run to disable
to the network and provides false IP
LLDP globally. To disable LLDP on the interface, configure
configuration. Misleading information: no lldp transmit and no lldp receive.
• Wrong default gateway.
• Wrong DNS server.
• Wrong IP address.
10.5.7. ARP Attacks
An attacker can send a gratuitous ARP message
containing a spoofed MAC address to a switch,
and the switch would update its MAC table
accordingly.
10.5.8. Address Spoofing Attacks.
MAC address spoofing attacks occur when the
threat actors alter the MAC address of their host
to match another known MAC address of a target
host.
IP and MAC address spoofing can be mitigated
by implementing IPSG.
10.5.9. STP Attack
the attacking host broadcasts STP bridge protocol
data units (BPDUs) containing configuration and
topology changes that will force spanning-tree
recalculations. This announcing a lower bridge
priority.
This STP attack is mitigated by implementing
BPDU Guard on all access ports. BPDU Guard is
discussed in more detail later in the course.
10.5.10. CDP Reconnaissance
Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is useful for
troubleshooting.
Information:
• IP address of the device,
• IOS software version
• Platform
• Capabilities
You might also like
- MA5801S-GP16 Product Datasheet 01Document8 pagesMA5801S-GP16 Product Datasheet 01Samuel NesibuNo ratings yet
- HackLikePro v3Document72 pagesHackLikePro v3Shams HassanNo ratings yet
- Eric Coomer: Pawn, Plant or Perp?Document118 pagesEric Coomer: Pawn, Plant or Perp?Chris BentelNo ratings yet
- Packet Sniffing and Spoofing LabDocument12 pagesPacket Sniffing and Spoofing LabZihao MiaoNo ratings yet
- Presentation On TCP-IP VulnerabilitiesDocument34 pagesPresentation On TCP-IP Vulnerabilitiesmohit_kohli6739100% (1)
- IMSI-Catch Me If You Can: IMSI-Catcher-CatchersDocument10 pagesIMSI-Catch Me If You Can: IMSI-Catcher-CatchersAdvanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - L Notes - Introduction To MicrocontrollerDocument53 pagesUnit 4 - L Notes - Introduction To MicrocontrollerAKSHANSH MATHUR100% (1)
- Configuration and Evaluation of Some Microsoft and Linux Proxy Servers, Security, Intrusion Detection, AntiVirus and AntiSpam ToolsFrom EverandConfiguration and Evaluation of Some Microsoft and Linux Proxy Servers, Security, Intrusion Detection, AntiVirus and AntiSpam ToolsNo ratings yet
- Domain Name Server (DNS)Document28 pagesDomain Name Server (DNS)sweatha NNo ratings yet
- Address Resolution ProtocolDocument8 pagesAddress Resolution Protocolksuresh0055599No ratings yet
- Determining IP Routes: © 2000, Cisco Systems, IncDocument40 pagesDetermining IP Routes: © 2000, Cisco Systems, Incmadagoneraju100% (1)
- VPN Rce's PDFDocument122 pagesVPN Rce's PDFAman MahendraNo ratings yet
- Ui For Mobile DevicesDocument10 pagesUi For Mobile Devicespadmavathy2kNo ratings yet
- Arp SpoofingDocument2 pagesArp SpoofingArun SangwanNo ratings yet
- GPS World - July 2019Document52 pagesGPS World - July 2019Diego FrancoNo ratings yet
- 3.2.2.3 Lab - Discover Your Own Risky Online Behavior PDFDocument3 pages3.2.2.3 Lab - Discover Your Own Risky Online Behavior PDFOmyjayd KeNo ratings yet
- Config Basica Router SwitchDocument4 pagesConfig Basica Router SwitchRogelio Tello100% (1)
- Static MAC Address Table EntryDocument2 pagesStatic MAC Address Table EntryphamvanhaNo ratings yet
- GSMA - Report On Overaly SIM CardsDocument2 pagesGSMA - Report On Overaly SIM CardsWalu JohnNo ratings yet
- How To Connect Internet From PC or Laptop To Android Mobile PhoneDocument15 pagesHow To Connect Internet From PC or Laptop To Android Mobile PhoneSakthhi LakshmiNo ratings yet
- C) 256 Bits AESDocument4 pagesC) 256 Bits AESsyafiq rossleyNo ratings yet
- Mobile Phone EvaluationDocument6 pagesMobile Phone EvaluationKishor MahmudNo ratings yet
- A Step-By-Step Guide To Setting Up A Home NetworkDocument3 pagesA Step-By-Step Guide To Setting Up A Home NetworkBilal Salam100% (1)
- SMAC MAC Address Changer For Windows 10, 8, 7, 2008, 2003, VISTA, XP, 2000Document4 pagesSMAC MAC Address Changer For Windows 10, 8, 7, 2008, 2003, VISTA, XP, 2000Salvatore BonaffinoNo ratings yet
- Networking DevicesDocument66 pagesNetworking DevicesMichael John GregorioNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Techniques: - Chapter 1Document37 pagesConcepts and Techniques: - Chapter 1indiraNo ratings yet
- A New Model For Forensic Data Extraction From Encrypted Mobile DevicesDocument11 pagesA New Model For Forensic Data Extraction From Encrypted Mobile DevicesRémi GilliotNo ratings yet
- What You See Is Not What You SeeDocument29 pagesWhat You See Is Not What You SeeDebarghya KunduNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To Mobile ComputingDocument178 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Mobile Computinggoraniya reenaNo ratings yet
- Jftut1 4 5Document276 pagesJftut1 4 5Philip HerrNo ratings yet
- PROXMARKDocument4 pagesPROXMARKfher76No ratings yet
- Commands For VLAN and MAC Address ConfigurationDocument39 pagesCommands For VLAN and MAC Address ConfigurationPhạm Văn ThuânNo ratings yet
- Installing Software With FreeBSDDocument66 pagesInstalling Software With FreeBSDMaisiba BravoNo ratings yet
- Ip Multi-Site Connect Application Notes r2.0 163Document52 pagesIp Multi-Site Connect Application Notes r2.0 163JohnNo ratings yet
- Cable Modem Modification How-ToDocument15 pagesCable Modem Modification How-ToKalyan KantiNo ratings yet
- BlackhatDocument1 pageBlackhatjiveso3482No ratings yet
- DEF CON Safe Mode - Cooper Quintin - Detecting Fake 4G Base Stations in Real TimeDocument48 pagesDEF CON Safe Mode - Cooper Quintin - Detecting Fake 4G Base Stations in Real TimeasdfNo ratings yet
- Activist Information SecurityDocument19 pagesActivist Information SecurityDante IrreraNo ratings yet
- GSM - Addresses and Identifiers (Imei, Imsi, Tmsi, Lmsi, Msisdn, MSRN)Document2 pagesGSM - Addresses and Identifiers (Imei, Imsi, Tmsi, Lmsi, Msisdn, MSRN)Avanti Mukhopadhaya100% (1)
- Research Paper On DNS SpoofingDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On DNS Spoofingmwjhkmrif100% (1)
- Mobile TechnoloiesDocument30 pagesMobile TechnoloiesВиктори ЈаNo ratings yet
- RAT RemoteAdministrativeTrojanDocument5 pagesRAT RemoteAdministrativeTrojanAkyll TutorNo ratings yet
- Kali Linux - A Comprehensive Step by Step Beginner's Guide to Learn the Basics of Cybersecurity and Ethical Computer Hacking, Including Wireless Penetration Testing Tools to Secure Your Network by Jason KnoDocument104 pagesKali Linux - A Comprehensive Step by Step Beginner's Guide to Learn the Basics of Cybersecurity and Ethical Computer Hacking, Including Wireless Penetration Testing Tools to Secure Your Network by Jason KnoSecurity Cyber100% (2)
- 3 Network ArchitectureDocument6 pages3 Network ArchitectureDiwakar Mishra100% (1)
- IP Address Spoofing - Wikipedia PDFDocument14 pagesIP Address Spoofing - Wikipedia PDFAnju VijayanNo ratings yet
- eMMC To SD Hack Rescues Data From A Waterlogged Phone - HackadayDocument10 pageseMMC To SD Hack Rescues Data From A Waterlogged Phone - HackadayAlainN2200No ratings yet
- SS7 Software 1008Document4 pagesSS7 Software 1008Edwin MontesNo ratings yet
- Network Security Lab Manual DraftDocument29 pagesNetwork Security Lab Manual DraftShraddha PatilNo ratings yet
- Basics of Computer NetworksDocument10 pagesBasics of Computer NetworkskunalNo ratings yet
- Computer Security Questions and Answers:: 1:: What Is A Firewall?Document9 pagesComputer Security Questions and Answers:: 1:: What Is A Firewall?NagarajuRaginaboyinaNo ratings yet
- Virtual MachinesDocument35 pagesVirtual MachinesArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Unbound DNS TutorialDocument14 pagesUnbound DNS TutorialSetiawanNo ratings yet
- SIM Card StrongDocument243 pagesSIM Card StrongFaqihNo ratings yet
- Tutorial: How To Crack WPA/WPA2Document10 pagesTutorial: How To Crack WPA/WPA2GerardoCuevasHNo ratings yet
- Computer Security: Hackers and Viruses: Theory of Computation Mesfer Alrizq Naif AlrashidiDocument83 pagesComputer Security: Hackers and Viruses: Theory of Computation Mesfer Alrizq Naif AlrashidiGhanshyam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Browser & System Configuration - Charles Web Debugging ProxyDocument3 pagesBrowser & System Configuration - Charles Web Debugging ProxyDavhec363No ratings yet
- An Ultimate Guide To DDos Attack: Detection, Prevention and MitigationDocument41 pagesAn Ultimate Guide To DDos Attack: Detection, Prevention and MitigationTechAppriseNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WP Email Tools: Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WP Email Tools: Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsNo ratings yet
- Methods to Increase the Internal Storage Space of Android DevicesFrom EverandMethods to Increase the Internal Storage Space of Android DevicesNo ratings yet
- Common Windows, Linux and Web Server Systems Hacking TechniquesFrom EverandCommon Windows, Linux and Web Server Systems Hacking TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Mind-blowing Signal 101 Guide for Beginners and Experts: Unravel the Best Signal Private Messenger Tips for Secured Calls and ChatsFrom EverandMind-blowing Signal 101 Guide for Beginners and Experts: Unravel the Best Signal Private Messenger Tips for Secured Calls and ChatsNo ratings yet
- Model Name: GA-H61-S3: Vcore Cpu - VTTDocument34 pagesModel Name: GA-H61-S3: Vcore Cpu - VTTsỹ QuốcNo ratings yet
- Programming With PythonDocument26 pagesProgramming With Pythonartibhardwaj8419No ratings yet
- Lecture 01 - IntroductionDocument54 pagesLecture 01 - IntroductionAhmed HamdyNo ratings yet
- A Secure and Verifiable Color Visual Cryptography Scheme With LSB Based Image SteganographyDocument9 pagesA Secure and Verifiable Color Visual Cryptography Scheme With LSB Based Image SteganographyWARSE JournalsNo ratings yet
- MSMP ConfigDocument4 pagesMSMP ConfighkodaliNo ratings yet
- Cast Bolted Brackets: W Series: Nominal Connector DimensionsDocument2 pagesCast Bolted Brackets: W Series: Nominal Connector Dimensionsaams_sNo ratings yet
- Thinkpad Tablet 2Document3 pagesThinkpad Tablet 2depalakNo ratings yet
- Calculation SheetDocument30 pagesCalculation SheetMAB AliNo ratings yet
- OpenScape Desk Phone CP110 SIP User GuideDocument168 pagesOpenScape Desk Phone CP110 SIP User Guidetranhongquan96hiieNo ratings yet
- Apollo Case Study - 0 PDFDocument18 pagesApollo Case Study - 0 PDFVisweswar AnimelaNo ratings yet
- Cse115-Lab-Manual-4-If - Else Part1Document2 pagesCse115-Lab-Manual-4-If - Else Part1AbidNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument164 pagesIntroPerubus SoyuzNo ratings yet
- MCS 011Document4 pagesMCS 011kk2760057No ratings yet
- ControlLogix - Redundancy Firmware Bundle Revision HistoryDocument45 pagesControlLogix - Redundancy Firmware Bundle Revision Historyyoquins22No ratings yet
- Magnito Digital - Agency CredentialsDocument46 pagesMagnito Digital - Agency CredentialsBiprajit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Normal Approximation of The Poisson DistributionDocument1 pageNormal Approximation of The Poisson DistributionChooi Jia YueNo ratings yet
- Standard Template LibraryDocument24 pagesStandard Template LibraryHIMANSHU DHARNo ratings yet
- Huawei Ce6880 24S4Q2CQ DatasheetDocument22 pagesHuawei Ce6880 24S4Q2CQ DatasheetSameel MaharNo ratings yet
- Use of English Worksheets-Unit-12Document2 pagesUse of English Worksheets-Unit-129k2cwnnk8tNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Mapping of AKTU - 3Document6 pagesSyllabus Mapping of AKTU - 3Naman SharmaNo ratings yet
- LogDocument12 pagesLogAyesha AbbasNo ratings yet
- Graphics Kernel SystemDocument8 pagesGraphics Kernel SystemASHIJ KRISHNAN SURESHNo ratings yet
- Telecom TransformersDocument6 pagesTelecom TransformersUmithiNo ratings yet
- Ai & ML - ModuleDocument35 pagesAi & ML - ModulePrem PatilNo ratings yet
- Iot Based Intelligent TrolleyDocument10 pagesIot Based Intelligent TrolleyHithesh GowdaNo ratings yet
- Mon-53 p4 Milestone1Document15 pagesMon-53 p4 Milestone1api-529470340No ratings yet
- Service ManualDocument60 pagesService Manual강형근No ratings yet