Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stroke Week 11: Disease/ Disorder Signs/Symptoms Treatment How Diagnosed Prognosis
Stroke Week 11: Disease/ Disorder Signs/Symptoms Treatment How Diagnosed Prognosis
Uploaded by
shahzaibOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stroke Week 11: Disease/ Disorder Signs/Symptoms Treatment How Diagnosed Prognosis
Stroke Week 11: Disease/ Disorder Signs/Symptoms Treatment How Diagnosed Prognosis
Uploaded by
shahzaibCopyright:
Available Formats
Disease/ Disorder Signs/Symptoms Treatment How diagnosed Prognosis
Stroke Medications:
Blood tests:
Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA):
Your doctor might draw blood for several blood tests. Blood tests can determine:
This emergency medication can be provided during a stroke
your blood sugar levels
to breakup a blood clot causing the stroke. it's the only
if you have an infection
medication currently available that can do this, but it must be
your platelet levels
given within 3 to 4.5 hours after symptoms of a stroke begin.
how fast your blood clots
This drug is injected into a blood vessel so the medication
can start to work as quickly as possible, which reduces the
MRI and ST SCAN:
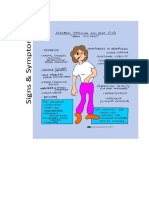
1. Sudden numbness and weakness in the face, risk of complications from the stroke.
Magnetic resonance Imaging (MRI)
arm or legs especially on one side of the body.
Computerized tomography (CT) scan
2. Sudden confusion, trouble speaking, or Anticoaglant:
The MRI will help see if any brain tissue or brain cells have been damaged. A CT scan
difficulty understanding speech. These drugs reduce your blood’s ability to clot. The most
will provide a detailed and clear picture of your brain that shows any bleeding or
3. Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes. common anticoagulant is warfarin (Jantoven, Coumadin).
damage in the brain. It may also show other brain conditions that could be causing People can get better
4. Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of These drugs can also prevent existing blood clots from
your symptoms. after stroke. However, for
balance, or lack of coordination. growing larger, which is why they may be prescribed to
the reasons mentioned,
5. Brain damage. prevent a stroke, or after an ischemic stroke or TIA has
EKG: predicting the degree and
6. Long term disability occurred.
Your doctor may order an electrocardiogram (EKG) too,This simple test records the pace of recovery is very
7. severe, sudden headache without any cause.
Stroke week 8. paralysis Blood pressure drugs:
electrical activity in the heart, measuring its rhythm and recording how fast it beats. It
can determine if you have any heart conditions that may have led to stroke, such as a
difficult. Much of the
recovery after
11 9. nausea High blood pressure can cause pieces of plaque buildup in
prior heart attack or atrial fibrillation. a stroke occurs early,
10. hallucination your arteries to break off. These pieces can block arteries,
usually within the first six
11. shortness of breath or trouble breathing causing a stroke. As a result, controlling high blood pressure
Cerebral angiogram: months. Most experts
12. Sudden behavioural changes can help prevent a stroke.
Another test your doctor may order to determine if you’ve had a stroke is a cerebral agree that the brain can
angiogram. This offers a detailed look at the arteries in your neck and brain. The test continue to heal for up to
Antiplatelet drugs:
can show blockages or clots that may have caused symptoms. two years afterward.
These medications prevent blood clots by making it more
difficult for the blood’s platelets to stick together. The most
Carotid ultrasound:
common antiplatelet drugs include aspirin
A carotid ultrasound, also called a carotid duplex scan, can show fatty deposits
and clopidogrel (Plavix). They can be used to prevent
(plaque) in your carotid arteries, which supply the blood to your face, neck, and brain. It
ischemic strokes and are especially important in preventing
can also show whether your carotid arteries have been narrowed or blocked.
secondary stroke. If you’ve never had a stroke before, you
should only use aspirin as a preventive medication if you
Echocardiogram:
have a high risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
An echocardiogram can find sources of clots in your heart. These clots may have
(e.g., heart attack and stroke) and a low risk of bleeding.
traveled to your brain and caused a stroke.
You might also like
- CPR ChecklistDocument2 pagesCPR Checklistlemuel88% (8)
- Epilepsy Management Plan TemplateDocument2 pagesEpilepsy Management Plan TemplateIPNo ratings yet
- COURSE TASK 2 Mrs. Clot's and Alexa's Case - POLICIOS, SHARMAINE ANNE M. BSN 3Y2 - 3ADocument10 pagesCOURSE TASK 2 Mrs. Clot's and Alexa's Case - POLICIOS, SHARMAINE ANNE M. BSN 3Y2 - 3ASHARMAINE ANNE POLICIOSNo ratings yet
- Stroke NCPDocument5 pagesStroke NCPChantal Caragan100% (1)
- Reflective Essay-Rexson A. DalanginDocument3 pagesReflective Essay-Rexson A. DalanginRexson Alcantara DalanginNo ratings yet
- Improve Your Breathing With The Alexander TechniqueDocument3 pagesImprove Your Breathing With The Alexander TechniqueLeland Vall86% (14)
- Bida2 Stroke DiagDocument6 pagesBida2 Stroke DiagKatniss Dawn Martinez DruecoNo ratings yet
- Left Ventricular Aneurysm Is14Document2 pagesLeft Ventricular Aneurysm Is14iqbalNo ratings yet
- WWW - Stroke.nih - Gov: Stroke Strikes Fast. You Should TooDocument4 pagesWWW - Stroke.nih - Gov: Stroke Strikes Fast. You Should Toosatyagraha84No ratings yet
- Ataxia Week 13: Signs/Symptoms Treatment How Diagnosed Disease/ DisorderDocument2 pagesAtaxia Week 13: Signs/Symptoms Treatment How Diagnosed Disease/ DisordershahzaibNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument15 pagesCerebrovascular AccidentBeeshma BirjasinghNo ratings yet
- Life After Stroke Guide - 7819Document36 pagesLife After Stroke Guide - 7819Dr. Victor A. RochaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis. OCENA AUBREYDocument26 pagesMultiple Sclerosis. OCENA AUBREYCHRISTIAN RAY ALPAS PASILIAONo ratings yet
- Stability Indicating RP-HPLC Method Development and Validation For Estimation of Tiagabine Hydrochloride in TabletDocument26 pagesStability Indicating RP-HPLC Method Development and Validation For Estimation of Tiagabine Hydrochloride in TabletBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAnesthesia Drug Studyczeremar chanNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident: Reporter: John Marlo R. OlaybarDocument18 pagesCerebrovascular Accident: Reporter: John Marlo R. Olaybarkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Insights StrokesDocument2 pagesInsights StrokesRoxana SurliuNo ratings yet
- Brain Stroke 2.0Document17 pagesBrain Stroke 2.0krutarthgohil21No ratings yet
- Multiple SclerosisDocument15 pagesMultiple Sclerosiscloud kumoishNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument11 pagesStrokemakioedesemiNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident: Types Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Outlook PreventionDocument6 pagesCerebrovascular Accident: Types Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Outlook PreventionAlfrien Ivanovich LarchsonNo ratings yet
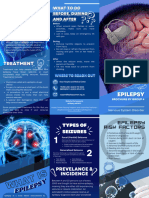
- EpilepsyDocument2 pagesEpilepsyMay DalinasNo ratings yet
- NCP StrokeDocument6 pagesNCP StrokeAnna PalimaNo ratings yet
- Motor Neuron Disease Week 14: Signs/Symptoms Treatment How Diagnosed Prognosis Disease/ DisorderDocument1 pageMotor Neuron Disease Week 14: Signs/Symptoms Treatment How Diagnosed Prognosis Disease/ DisordershahzaibNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCardiac Arrest, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer's Disease Is An Irreversible, Progressive Brain Disorder That Slowly Destroys MemoryDocument3 pagesAlzheimer's Disease Is An Irreversible, Progressive Brain Disorder That Slowly Destroys Memorywalid hassanNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument21 pagesCerebrovascular AccidentCJNo ratings yet
- About StrokeDocument1 pageAbout StrokeZarida ArabainNo ratings yet
- Salud ComunitariaDocument7 pagesSalud ComunitariaPablo IgnacioNo ratings yet
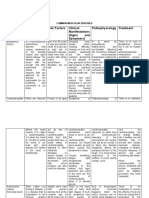
- Diseases Condition Risk Factors Clinical Manifestations (Signs and Symptoms) Pathophysiology TreatmentDocument8 pagesDiseases Condition Risk Factors Clinical Manifestations (Signs and Symptoms) Pathophysiology TreatmentZheriz Vhien L. SendicoNo ratings yet
- What To Expect During A Myocardial Perfusion ScanDocument2 pagesWhat To Expect During A Myocardial Perfusion ScanR K PathamNo ratings yet
- Stroke Handout..Document12 pagesStroke Handout..Ghadeer AlomariNo ratings yet
- Do Your Part, Care For Your HeartDocument2 pagesDo Your Part, Care For Your HeartHannah BangkilingNo ratings yet
- Pet Scan: IndicationDocument1 pagePet Scan: IndicationTavaneethan MoganNo ratings yet
- Biopsych Reviewer For FinalsDocument6 pagesBiopsych Reviewer For Finalsnicole.recedeNo ratings yet
- What Is StrokeDocument6 pagesWhat Is StrokeY. Beatrice AbigailNo ratings yet
- Soal Kasus HipertensiDocument3 pagesSoal Kasus HipertensiAlya NamiraNo ratings yet
- What Is A StrokeDocument10 pagesWhat Is A StrokeRatnaPrasadNalamNo ratings yet
- 5 CS and 5 RSDocument54 pages5 CS and 5 RSKristine CatariningNo ratings yet
- Cva RevalidaDocument25 pagesCva Revalidarica avendañoNo ratings yet
- What Is StrokeDocument14 pagesWhat Is StrokedindaNo ratings yet
- 98-Article Text-302-1-10-20170315Document2 pages98-Article Text-302-1-10-20170315mamhandy28No ratings yet
- Heart Attack and StrokeDocument4 pagesHeart Attack and StrokeJO HN Scuba-rNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome: Mechanisms, Manifestations, and ManagementDocument13 pagesAlcohol Withdrawal Syndrome: Mechanisms, Manifestations, and ManagementValentina QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Stroke: Let's Talk AboutDocument2 pagesIschemic Stroke: Let's Talk AboutAlexandra OpreaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac BiomarkersDocument7 pagesCardiac BiomarkersJethro Floyd QuintoNo ratings yet
- Stress Echocardiography and Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument1 pageStress Echocardiography and Coronary Artery DiseaseAudrius BNo ratings yet
- Stroke 1Document7 pagesStroke 1mildred alidonNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading - Ayana Saberina Aprillia - 201810401011083Document12 pagesJournal Reading - Ayana Saberina Aprillia - 201810401011083ayanaprilliaNo ratings yet
- Types of StrokeDocument12 pagesTypes of Strokefakher adnanNo ratings yet
- Drugs and Acupuncture: The Energetic Impact of Antidepressant MedicationsDocument7 pagesDrugs and Acupuncture: The Energetic Impact of Antidepressant Medicationspeter911x2134No ratings yet
- Multiple SclerosisDocument4 pagesMultiple Sclerosisapi-3801039100% (1)
- " An Attempt To Shorten Hospitalization ": Code StrokeDocument56 pages" An Attempt To Shorten Hospitalization ": Code Stroketricia isabella100% (1)
- Myasthenia Gravis: Prepared by Under Supervision of DRDocument13 pagesMyasthenia Gravis: Prepared by Under Supervision of DRAhoood ,No ratings yet
- Lacunar Stroke Guide - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment OptionsDocument6 pagesLacunar Stroke Guide - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment OptionsRismanto TorsioNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Depressed Mood Loss of Interest and Pleasure in ActivitiesDocument4 pagesPathophysiology: Depressed Mood Loss of Interest and Pleasure in ActivitiesBrittany VandermeulenNo ratings yet
- Amlo, Simvastatin, TamsulosinDocument7 pagesAmlo, Simvastatin, TamsulosinGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- NCMB 316 Lecture & RleDocument34 pagesNCMB 316 Lecture & RleVenansius GanggusNo ratings yet
- Research Assignment - FinalDocument5 pagesResearch Assignment - Finalapi-301796386No ratings yet
- Readings About Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis (CVST) (ER-RMPH)Document8 pagesReadings About Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis (CVST) (ER-RMPH)Raquel Beldia FuentesNo ratings yet
- Stroke Case Study 3-Wendte 1Document18 pagesStroke Case Study 3-Wendte 1api-371766376No ratings yet
- Transient Ischemic AttackDocument3 pagesTransient Ischemic AttackJevisco LauNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (Drug Study)Document3 pagesAcute Myeloid Leukemia (Drug Study)Krisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Risk Management Script - EditedDocument2 pagesSupply Chain Risk Management Script - EditedshahzaibNo ratings yet
- Security Policy - Week 04Document8 pagesSecurity Policy - Week 04shahzaibNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 3 Fall 2020Document5 pagesProblem Set 3 Fall 2020shahzaibNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Deadline: 17/10/2020 at 23:59: College of Administrative and Financial SciencesDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 Deadline: 17/10/2020 at 23:59: College of Administrative and Financial SciencesshahzaibNo ratings yet
- Ataxia Week 13: Signs/Symptoms Treatment How Diagnosed Disease/ DisorderDocument2 pagesAtaxia Week 13: Signs/Symptoms Treatment How Diagnosed Disease/ DisordershahzaibNo ratings yet
- Bell's Palsy Week 9: Disease/ Disorder Signs/Symptoms Treatment How DiagnosedDocument2 pagesBell's Palsy Week 9: Disease/ Disorder Signs/Symptoms Treatment How DiagnosedshahzaibNo ratings yet
- Disease/ Disorder Signs/Symptoms TreatmentDocument2 pagesDisease/ Disorder Signs/Symptoms TreatmentshahzaibNo ratings yet
- Batten Week 12: Signs/Symptoms Treatment How Diagnosed Disease/ DisorderDocument2 pagesBatten Week 12: Signs/Symptoms Treatment How Diagnosed Disease/ DisordershahzaibNo ratings yet
- Motor Neuron Disease Week 14: Signs/Symptoms Treatment How Diagnosed Prognosis Disease/ DisorderDocument1 pageMotor Neuron Disease Week 14: Signs/Symptoms Treatment How Diagnosed Prognosis Disease/ DisordershahzaibNo ratings yet
- Umar HayyatDocument1 pageUmar HayyatshahzaibNo ratings yet
- Assignment Question(s) : (Marks 5) : Inflow of CashDocument3 pagesAssignment Question(s) : (Marks 5) : Inflow of CashshahzaibNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Is A New Type of Virus That Spreads From The Wuhan, The City of China. It CanDocument3 pagesCOVID-19 Is A New Type of Virus That Spreads From The Wuhan, The City of China. It CanshahzaibNo ratings yet
- Monthly Health, Safety & Environment (Hse) Report: MPCL DaharkiDocument2 pagesMonthly Health, Safety & Environment (Hse) Report: MPCL DaharkishahzaibNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Electronic MediaDocument3 pagesAssignment of Electronic Mediashahzaib100% (1)
- Loa LoaDocument22 pagesLoa LoaphilmonNo ratings yet
- Lesson - 01colour TherapyDocument7 pagesLesson - 01colour TherapyprasadmvkNo ratings yet
- Sophy Mini Monopressure Valve: Instructions For UseDocument64 pagesSophy Mini Monopressure Valve: Instructions For UseKenneth SaganNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis: Kartika Farahdilla Lubna Qatrunada M Ananta WinartoDocument46 pagesViral Hepatitis: Kartika Farahdilla Lubna Qatrunada M Ananta WinartolubnaNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer Disease Including Focal Presentations PDFDocument14 pagesAlzheimer Disease Including Focal Presentations PDFpiedrahitasaNo ratings yet
- Activity Intolerance CholecystectomyDocument2 pagesActivity Intolerance CholecystectomyPrincess Danica Purcia100% (3)
- Renzo Colombo, Richard Naspro PDFDocument9 pagesRenzo Colombo, Richard Naspro PDFHidayah Mararotua HarahapNo ratings yet
- Approach To Abdominal PainDocument44 pagesApproach To Abdominal PainEleanorNo ratings yet
- DR - Elamaran.E Senior Resident Dept. of CTVS, JIPMERDocument43 pagesDR - Elamaran.E Senior Resident Dept. of CTVS, JIPMEREla MaranNo ratings yet
- Nursing ProcessDocument12 pagesNursing ProcessKyla RamosNo ratings yet
- PulseoximetryDocument2 pagesPulseoximetryRakshith NagarajaiahNo ratings yet
- Atypical MycobacteriumDocument57 pagesAtypical Mycobacteriumtummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (1)
- Bicon Short Implant 2Document6 pagesBicon Short Implant 2Bicon Implant InaNo ratings yet
- Chronic OsteomyelitisDocument18 pagesChronic OsteomyelitisMar OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- OCDDocument10 pagesOCDkiran mahalNo ratings yet
- H.E - Care of New BronDocument12 pagesH.E - Care of New BronPãtël Âñjãlï100% (3)
- Calculus CholecystitisDocument48 pagesCalculus CholecystitisEdderlyn LamarcaNo ratings yet
- Balido, John Emmanuel A. BSN223/Grp89 Drug Study: 8 G/dayDocument1 pageBalido, John Emmanuel A. BSN223/Grp89 Drug Study: 8 G/dayEmman BalidoNo ratings yet
- Anesthetic Concerns For Difficult Airway in A Child With Congenital Hydrocephalus For Ventriculoperitoneal ShuntDocument2 pagesAnesthetic Concerns For Difficult Airway in A Child With Congenital Hydrocephalus For Ventriculoperitoneal ShuntasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Cipla Generic Products ListDocument55 pagesCipla Generic Products ListJeninNo ratings yet
- PDIS Assignment 1Document2 pagesPDIS Assignment 1Michelle Elisha CartanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanTrisNo ratings yet
- Assistant PharmacistDocument3 pagesAssistant PharmacistAashish BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Dissolution Specifications For Oral Drug Products (IR, DR, ER) in The USA - A Regulatory PerspectiveDocument6 pagesDissolution Specifications For Oral Drug Products (IR, DR, ER) in The USA - A Regulatory PerspectiveFaisal AbbasNo ratings yet
- Pain Nursing Care Plan and Bactrobran Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPain Nursing Care Plan and Bactrobran Drug StudyAnni BarbaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Drawing Classification Dosage/Time/ Route Indication Mechanism of Action Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument4 pagesName of Drug Drawing Classification Dosage/Time/ Route Indication Mechanism of Action Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameJanella Kyle ParejaNo ratings yet
- Rwanda Medicaments EssentielsDocument85 pagesRwanda Medicaments EssentielsportosinNo ratings yet