Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aerobic Processes English
Aerobic Processes English
Uploaded by
plennyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Aerobic Processes EnglishDocument1 pageAerobic Processes EnglishIR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- IHG Engineering Design Guidelines RevisiDocument5 pagesIHG Engineering Design Guidelines RevisiMohammad Abd Alrahim ShaarNo ratings yet
- Secondry Unit Operation and Process of Wastewater TreatmentDocument11 pagesSecondry Unit Operation and Process of Wastewater Treatmentshivam randiveNo ratings yet
- ESTII 22 23 TP Lecture 03Document53 pagesESTII 22 23 TP Lecture 03YaraNo ratings yet
- AS-process-control-pdfDocument52 pagesAS-process-control-pdfEco PlusNo ratings yet
- Trickling Filter InpDocument4 pagesTrickling Filter InpAnirudh GuptaNo ratings yet
- PL SP03 PDFDocument8 pagesPL SP03 PDFdinar restiNo ratings yet
- Cleansewage-Bio Biological Sewage TreatmentDocument3 pagesCleansewage-Bio Biological Sewage Treatmentirshad sonde100% (1)
- ChE 3202 - Conventional and Non Conventional MethodsDocument8 pagesChE 3202 - Conventional and Non Conventional MethodsWingel LullabyNo ratings yet
- 3479-Article Text-9641-2-10-20190731Document6 pages3479-Article Text-9641-2-10-20190731Valencia ClaraNo ratings yet
- Tinjauan Aspek Teknis Pemilihan Media Biofilter Untuk Pengolahan Air LimbahDocument10 pagesTinjauan Aspek Teknis Pemilihan Media Biofilter Untuk Pengolahan Air LimbahHasnanurfajriahNo ratings yet
- Oil Adsorbtion MaterialDocument17 pagesOil Adsorbtion MaterialFaris Mat100% (1)
- Activated Sludge ProcessDocument13 pagesActivated Sludge Processzubair k peerzadeNo ratings yet
- 7-Trickling Filter - F11Document31 pages7-Trickling Filter - F11farajelmabroukNo ratings yet
- Suspended VS Attached Growth IJEE - Volume 7 - Issue 2 - Pages 114-123Document10 pagesSuspended VS Attached Growth IJEE - Volume 7 - Issue 2 - Pages 114-123Priyatno JuniantoNo ratings yet
- Rotating Biological ContactorDocument6 pagesRotating Biological ContactorDebasish NayakNo ratings yet
- Brochure CE 705 - Activated Sludge Process ENDocument9 pagesBrochure CE 705 - Activated Sludge Process ENedimaprwNo ratings yet
- Bioreactor Wastewater TreatmentDocument17 pagesBioreactor Wastewater TreatmentSadhana loharNo ratings yet
- Waste TreatmentDocument6 pagesWaste TreatmentAnindya GuhaNo ratings yet
- W13 Trickling Filter Rotating Biological Contactor BiofilterDocument52 pagesW13 Trickling Filter Rotating Biological Contactor BiofilterQamara DaffaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Wastewater TreatmentDocument54 pagesMethods of Wastewater TreatmentPamela MendozaNo ratings yet
- 1.fixed Films/ Attached GrowthDocument3 pages1.fixed Films/ Attached GrowthkuekNo ratings yet
- STP Comparision of ProcessDocument11 pagesSTP Comparision of Processwd100% (1)
- Smart TechnologyDocument7 pagesSmart Technologyhimelhimel34No ratings yet
- 14 EcologyDocument4 pages14 EcologyPHANI KUMAR A.V.SNo ratings yet
- Rotating Biological ContactorDocument6 pagesRotating Biological Contactorvignesh9489No ratings yet
- Submitted By: Jusay, Rabin U. Sumain, Angela Rochelle Balahim, Charwina Arconada, Joymarie A. Tani, Sherhana UDocument5 pagesSubmitted By: Jusay, Rabin U. Sumain, Angela Rochelle Balahim, Charwina Arconada, Joymarie A. Tani, Sherhana URenel RenelNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment OperationsDocument10 pagesWastewater Treatment OperationsAnne TayongNo ratings yet
- Final Term ReviewerDocument3 pagesFinal Term ReviewerJalan Mei EstebanNo ratings yet
- 7 - D21WW - Wastewater Treatment BDocument48 pages7 - D21WW - Wastewater Treatment BDominic WaldronNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 3 - Wastewater Treatment - Aerobic and Anaerobic-1Document11 pagesLecture - 3 - Wastewater Treatment - Aerobic and Anaerobic-1negaathanipalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Sludge Treatment and DisposalDocument16 pagesSludge Treatment and Disposalsandhya bhattiNo ratings yet
- LEC 5 Use of Microorganisms in Effluent TreatmentDocument5 pagesLEC 5 Use of Microorganisms in Effluent TreatmentDysmas100% (1)
- Actvated Sludge Process SSWMDocument28 pagesActvated Sludge Process SSWMGREENLAB ECL TECHNo ratings yet
- Bioremediation NotesDocument10 pagesBioremediation Notesbushra farmanNo ratings yet
- Classification of Water PollutantsDocument11 pagesClassification of Water PollutantsNaveenNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment From Municipal Waste Using Biological MethodDocument20 pagesWastewater Treatment From Municipal Waste Using Biological Methodnoorain zulkapliNo ratings yet
- L6 Activated Sludge SystemDocument38 pagesL6 Activated Sludge SystemNurul Aliza100% (2)
- Effluent Treatment PlantDocument67 pagesEffluent Treatment PlantSWATHI ACHARNo ratings yet
- Waste Treatment & ManagementDocument1 pageWaste Treatment & ManagementSonali SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Industrial Wastewater Treatment ProcessDocument63 pagesChapter 4-Industrial Wastewater Treatment ProcessFadhli JapryNo ratings yet
- 311 222003WSTComettGonzlezWildererDocument8 pages311 222003WSTComettGonzlezWildererujjval chauhanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Technology Activity #3Document9 pagesEnvironmental Technology Activity #3Ray Siemon MatalogNo ratings yet
- Effluent Treatment3Document14 pagesEffluent Treatment3Mirza Md. Nazmus SakibNo ratings yet
- 09 Chapter 1Document22 pages09 Chapter 1BALASUBRAMANIAN SMNo ratings yet
- WWT7 - Physical TreatmentDocument17 pagesWWT7 - Physical TreatmentHelder MbidiNo ratings yet
- Sludge Mngment, Anaerobic Treatment and Aquatic Plant SystemsDocument33 pagesSludge Mngment, Anaerobic Treatment and Aquatic Plant SystemsAndrew Marquez DonaireNo ratings yet
- TechnologiesDocument12 pagesTechnologiesHamed MehriNo ratings yet
- School of Civil Engineering & Architecture: Adama Science and Technology UniversityDocument112 pagesSchool of Civil Engineering & Architecture: Adama Science and Technology UniversityHusen DugoNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Biofilteration of VOCDocument35 pagesUnit - 4 Biofilteration of VOCWALLELGNNo ratings yet
- Waste WaterDocument6 pagesWaste WaterManish KR AryanNo ratings yet
- 2017-CH-738 Environmental AssignmentDocument9 pages2017-CH-738 Environmental AssignmentMuHaMMaD BiLaLNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment AssignmentDocument14 pagesWastewater Treatment AssignmentKanishka JayalathNo ratings yet
- Blue Barrel System Manual EnglishDocument12 pagesBlue Barrel System Manual EnglishKennedy NgoseyweNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument16 pages1 PBTamara BravoNo ratings yet
- Biofilter: Biofiltration Is A Pollution Control Technique Using A BioreactorDocument6 pagesBiofilter: Biofiltration Is A Pollution Control Technique Using A BioreactorNirmal BhowmickNo ratings yet
- Corresponding Author:: A, B A C D, eDocument9 pagesCorresponding Author:: A, B A C D, ePutry1No ratings yet
- Secondary Treatment - SEWAGEDocument32 pagesSecondary Treatment - SEWAGEMONINDRA NATH PATRANo ratings yet
- Engenvi Presentation - Group 2 PDFDocument17 pagesEngenvi Presentation - Group 2 PDFAngela LimNo ratings yet
- NmunhizuDocument1 pageNmunhizuplennyNo ratings yet
- 17 en Produktbereich Niederspannungsschaltanlagen Neu EnglischDocument1 page17 en Produktbereich Niederspannungsschaltanlagen Neu EnglischplennyNo ratings yet
- Circuit 12 YDocument1 pageCircuit 12 YplennyNo ratings yet
- Draulic System4Document1 pageDraulic System4plennyNo ratings yet
- WayniconDocument1 pageWayniconplennyNo ratings yet
- HBJKDocument1 pageHBJKplennyNo ratings yet
- Ed Engineers AppendixDocument28 pagesEd Engineers AppendixplennyNo ratings yet
- Lighting TechnologyDocument12 pagesLighting TechnologyplennyNo ratings yet
- MeopoDocument1 pageMeopoplennyNo ratings yet
- 947 E EGT 2 Wiring Installation For Lighting and Appliance Circuits ShortDocument8 pages947 E EGT 2 Wiring Installation For Lighting and Appliance Circuits ShortplennyNo ratings yet
- Insulation SystemDocument8 pagesInsulation SystemplennyNo ratings yet
- 9039 E AC-motor With Starting Operating Capacitor 0 3kWDocument1 page9039 E AC-motor With Starting Operating Capacitor 0 3kWplennyNo ratings yet
- Generator Type Hco38 2L26 A: Electrical CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesGenerator Type Hco38 2L26 A: Electrical CharacteristicsplennyNo ratings yet
- WP Focus On Miniature Pumps Selecting The Right Motor TechnologyDocument4 pagesWP Focus On Miniature Pumps Selecting The Right Motor TechnologyplennyNo ratings yet
- 8498 E EPD Busbar Systems ShortDocument7 pages8498 E EPD Busbar Systems ShortplennyNo ratings yet
- Ed Brushless DC Motors Timing RelattionshipDocument2 pagesEd Brushless DC Motors Timing RelattionshipplennyNo ratings yet
- Shaft Stiffness Rev3Document9 pagesShaft Stiffness Rev3plennyNo ratings yet
- En Engineering Definitions and FormulasDocument1 pageEn Engineering Definitions and FormulasplennyNo ratings yet
- MeccalteDocument13 pagesMeccalteplennyNo ratings yet
- WP Brush DC Motor Basics 0Document4 pagesWP Brush DC Motor Basics 0plennyNo ratings yet
- MAU2673 European Grid CodesDocument8 pagesMAU2673 European Grid CodesplennyNo ratings yet
- Ecp34 1l4Document5 pagesEcp34 1l4plennyNo ratings yet
- Ecp3 1s4Document5 pagesEcp3 1s4plennyNo ratings yet
- tkf13 Insobs v1 5 AngDocument9 pagestkf13 Insobs v1 5 AngplennyNo ratings yet
- Ecp28 1VS4 ADocument5 pagesEcp28 1VS4 AplennyNo ratings yet
- tdr-410 en 1.02 Druk KPLDocument24 pagestdr-410 en 1.02 Druk KPLplennyNo ratings yet
- vt-2 Ins Obs v10 GBDocument1 pagevt-2 Ins Obs v10 GBplennyNo ratings yet
- Mining Excavator Hoist en 93Document1 pageMining Excavator Hoist en 93plennyNo ratings yet
- tkf12 Insobs v1 4 AngDocument6 pagestkf12 Insobs v1 4 AngplennyNo ratings yet
- p-1 Insobs v17 Harmonijka AngDocument2 pagesp-1 Insobs v17 Harmonijka AngplennyNo ratings yet
- Global Issues Data Response Questions AdviceDocument9 pagesGlobal Issues Data Response Questions Adviceapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Song Review Ysabelle CuevasDocument4 pagesSong Review Ysabelle Cuevasnurul amaliaNo ratings yet
- The Present Perfect and The Present Perfect Continuous: Finished and Unfinished ActionsDocument26 pagesThe Present Perfect and The Present Perfect Continuous: Finished and Unfinished ActionsyahiaouimalekNo ratings yet
- Ent530 - Case Study - Guidelines & Template For Ba Prog OnlyDocument5 pagesEnt530 - Case Study - Guidelines & Template For Ba Prog Onlynurul hashimaNo ratings yet
- RBLDocument19 pagesRBLD J GamingNo ratings yet
- Procemin 2015 Sizing Stages of Weir High Pressure Grinding Rolls Mills, Based On Pilot TestsDocument25 pagesProcemin 2015 Sizing Stages of Weir High Pressure Grinding Rolls Mills, Based On Pilot TestsNereo SpenglerNo ratings yet
- SB19 Water-KomprimiertDocument101 pagesSB19 Water-KomprimiertNatasa KakesNo ratings yet
- Skylab 3 PAO Mission Commentary 3 of 6Document851 pagesSkylab 3 PAO Mission Commentary 3 of 6Bob AndrepontNo ratings yet
- FG Riskadjustmentmethodology Module1Document12 pagesFG Riskadjustmentmethodology Module1J CHANGNo ratings yet
- The Coat of ArmsDocument3 pagesThe Coat of Armsnaseeb100% (1)
- File System - Node - Js v12.10.0 DocumentationDocument82 pagesFile System - Node - Js v12.10.0 DocumentationMarcos GarciaNo ratings yet
- Bennett 2003Document8 pagesBennett 2003Emir OkucuNo ratings yet
- Fpso - LNG ProcessDocument15 pagesFpso - LNG ProcessYeshWaNth100% (1)
- BL M22 1011 PDFDocument46 pagesBL M22 1011 PDFDmitryNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Promia 50 Application - Material HandlingDocument110 pagesUser Manual: Promia 50 Application - Material Handlingred_shobo_85100% (2)
- Call CardsDocument1 pageCall CardsFarmers CooperativeNo ratings yet
- SvlogDocument7 pagesSvlogmekhanaikopiNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Market Europe - June 2020Document50 pagesPharmaceutical Market Europe - June 2020Areg GhazaryanNo ratings yet
- MYY&MZZ Manual Transmission (Ver4)Document32 pagesMYY&MZZ Manual Transmission (Ver4)Vahid Reza MohammadiNo ratings yet
- 10 Known Issues: Tusbaudio Driver For WindowsDocument4 pages10 Known Issues: Tusbaudio Driver For WindowsWillian LimaNo ratings yet
- Oliveto - Ala Carte MenuDocument8 pagesOliveto - Ala Carte Menuk.alhusain23No ratings yet
- WPC Aco PDFDocument16 pagesWPC Aco PDFpetar spalevicNo ratings yet
- Barton Floco Fra Automatic Sampler User ManualDocument40 pagesBarton Floco Fra Automatic Sampler User ManualedwinmenaNo ratings yet
- The Real EveDocument2 pagesThe Real EveKangMaru_025No ratings yet
- Travel Management - User ManualDocument24 pagesTravel Management - User ManualAlok Samataray100% (2)
- Wget - Curl Large File From Google Drive - Stack OverflowDocument29 pagesWget - Curl Large File From Google Drive - Stack OverflowManoj KamisettiNo ratings yet
- Perbandingan Algoritma Naïve Bayes Dan KNN Dalam Analisis Sentimen Masyarakat Terhadap Pelaksanaan PPPK GuruDocument7 pagesPerbandingan Algoritma Naïve Bayes Dan KNN Dalam Analisis Sentimen Masyarakat Terhadap Pelaksanaan PPPK GuruNur Fajar SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Strategic Human Resource Management Canadian 2Nd Edition Noe Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument58 pagesStrategic Human Resource Management Canadian 2Nd Edition Noe Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFrowanariel26r2100% (9)
- Laya Marxlenin - CE152P-2 - E02 - Experiment2 - Module1Document5 pagesLaya Marxlenin - CE152P-2 - E02 - Experiment2 - Module1Marxlenin LayaNo ratings yet
Aerobic Processes English
Aerobic Processes English
Uploaded by
plennyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aerobic Processes English
Aerobic Processes English
Uploaded by
plennyCopyright:
Available Formats
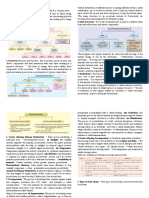
WATER TREATMENT BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES
BASIC KNOWLEDGE
AEROBIC PROCESSES
Biological processes enable dissolved biodegrad- organisms convert ammonium initially into Biofilm processes
able substances (organic matter) to be removed from nitrate (nitrification). Another group of micro-
Biofilm processes are based on microorganisms settling on
wastewater. The organic matter provides a nutrient organisms then reduces the nitrate to nitrogen gas
the surfaces of solids. The resulting layer of microorgan-
for microorganisms, and is converted under aerobic which escapes to the atmosphere (denitrification).
isms is called a biofilm. The solids used in this process are
conditions into biomass, carbon dioxide and water.
A distinction is made between biofilm and activated called carrier material. This means the wastewater must be
Aerobic microorganisms need oxygen for respiration.
sludge processes. brought into contact with the biofilm affixed to the carrier
As well as organic matter, nitrogenous compounds material.
such as ammonium and nitrate must usually also
The most important version are trickling filters. Here
be removed from wastewater. Specific micro-
the wastewater is trickled over a layer of carrier material
(fixed bed) using a rotating distributor. Whilst the waste-
water passes through the carrier material it is biologically
cleaned by the microorganisms. Aeration of the trickling 1 2
filter is normally via natural convection. This is based on
Activated sludge process Carrier materials for biofilms:
the temperature difference between the outside air and the
In this process, the microorganisms are suspended in the inside of the trickling filter. 1 artificial carrier material (plastic),
2 natural carrier material (e. g. extrusive rocks)
wastewater. Aeration of the wastewater in the aeration tank
Carrier materials have high specific surface areas
provides the aerobic microorganisms with oxygen. The
(approx. 200 m²/m³). Carrier materials can be of natural
metabolic process causes them to form into flocs – the so
origin (e.g. extrusive rocks) or be artificially produced.
called activated sludge. This is separated from the waste-
water by means of sedimentation (secondary clarification).
More biomass is removed from the aeration tank than is
produced in the same period of time. In order to balance
out this loss of biomass in the aeration tank, part of the 6
activated sludge is returned to the aeration tank (return
sludge). The portion of the activated sludge which is not
returned is termed surplus sludge and is a waste product 5
of the process.
Activated sludge
7 6
1
2 5
1 4
2 2
4
3
3
Fundamental principle of the activated sludge process: How a trickling filter works:
1 air, 2 wastewater, 3 return sludge, 4 surplus sludge, 5 treated water, 6 secondary clarifier (sedimentation) 1 wastewater, 2 aeration by natural convection, 3 treated water, 4 carrier material, 5 biofilm, 6 distributor
7 aeration tank
21
You might also like
- Aerobic Processes EnglishDocument1 pageAerobic Processes EnglishIR Ika EtyEtyka DoraNo ratings yet
- IHG Engineering Design Guidelines RevisiDocument5 pagesIHG Engineering Design Guidelines RevisiMohammad Abd Alrahim ShaarNo ratings yet
- Secondry Unit Operation and Process of Wastewater TreatmentDocument11 pagesSecondry Unit Operation and Process of Wastewater Treatmentshivam randiveNo ratings yet
- ESTII 22 23 TP Lecture 03Document53 pagesESTII 22 23 TP Lecture 03YaraNo ratings yet
- AS-process-control-pdfDocument52 pagesAS-process-control-pdfEco PlusNo ratings yet
- Trickling Filter InpDocument4 pagesTrickling Filter InpAnirudh GuptaNo ratings yet
- PL SP03 PDFDocument8 pagesPL SP03 PDFdinar restiNo ratings yet
- Cleansewage-Bio Biological Sewage TreatmentDocument3 pagesCleansewage-Bio Biological Sewage Treatmentirshad sonde100% (1)
- ChE 3202 - Conventional and Non Conventional MethodsDocument8 pagesChE 3202 - Conventional and Non Conventional MethodsWingel LullabyNo ratings yet
- 3479-Article Text-9641-2-10-20190731Document6 pages3479-Article Text-9641-2-10-20190731Valencia ClaraNo ratings yet
- Tinjauan Aspek Teknis Pemilihan Media Biofilter Untuk Pengolahan Air LimbahDocument10 pagesTinjauan Aspek Teknis Pemilihan Media Biofilter Untuk Pengolahan Air LimbahHasnanurfajriahNo ratings yet
- Oil Adsorbtion MaterialDocument17 pagesOil Adsorbtion MaterialFaris Mat100% (1)
- Activated Sludge ProcessDocument13 pagesActivated Sludge Processzubair k peerzadeNo ratings yet
- 7-Trickling Filter - F11Document31 pages7-Trickling Filter - F11farajelmabroukNo ratings yet
- Suspended VS Attached Growth IJEE - Volume 7 - Issue 2 - Pages 114-123Document10 pagesSuspended VS Attached Growth IJEE - Volume 7 - Issue 2 - Pages 114-123Priyatno JuniantoNo ratings yet
- Rotating Biological ContactorDocument6 pagesRotating Biological ContactorDebasish NayakNo ratings yet
- Brochure CE 705 - Activated Sludge Process ENDocument9 pagesBrochure CE 705 - Activated Sludge Process ENedimaprwNo ratings yet
- Bioreactor Wastewater TreatmentDocument17 pagesBioreactor Wastewater TreatmentSadhana loharNo ratings yet
- Waste TreatmentDocument6 pagesWaste TreatmentAnindya GuhaNo ratings yet
- W13 Trickling Filter Rotating Biological Contactor BiofilterDocument52 pagesW13 Trickling Filter Rotating Biological Contactor BiofilterQamara DaffaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Wastewater TreatmentDocument54 pagesMethods of Wastewater TreatmentPamela MendozaNo ratings yet
- 1.fixed Films/ Attached GrowthDocument3 pages1.fixed Films/ Attached GrowthkuekNo ratings yet
- STP Comparision of ProcessDocument11 pagesSTP Comparision of Processwd100% (1)
- Smart TechnologyDocument7 pagesSmart Technologyhimelhimel34No ratings yet
- 14 EcologyDocument4 pages14 EcologyPHANI KUMAR A.V.SNo ratings yet
- Rotating Biological ContactorDocument6 pagesRotating Biological Contactorvignesh9489No ratings yet
- Submitted By: Jusay, Rabin U. Sumain, Angela Rochelle Balahim, Charwina Arconada, Joymarie A. Tani, Sherhana UDocument5 pagesSubmitted By: Jusay, Rabin U. Sumain, Angela Rochelle Balahim, Charwina Arconada, Joymarie A. Tani, Sherhana URenel RenelNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment OperationsDocument10 pagesWastewater Treatment OperationsAnne TayongNo ratings yet
- Final Term ReviewerDocument3 pagesFinal Term ReviewerJalan Mei EstebanNo ratings yet
- 7 - D21WW - Wastewater Treatment BDocument48 pages7 - D21WW - Wastewater Treatment BDominic WaldronNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 3 - Wastewater Treatment - Aerobic and Anaerobic-1Document11 pagesLecture - 3 - Wastewater Treatment - Aerobic and Anaerobic-1negaathanipalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Sludge Treatment and DisposalDocument16 pagesSludge Treatment and Disposalsandhya bhattiNo ratings yet
- LEC 5 Use of Microorganisms in Effluent TreatmentDocument5 pagesLEC 5 Use of Microorganisms in Effluent TreatmentDysmas100% (1)
- Actvated Sludge Process SSWMDocument28 pagesActvated Sludge Process SSWMGREENLAB ECL TECHNo ratings yet
- Bioremediation NotesDocument10 pagesBioremediation Notesbushra farmanNo ratings yet
- Classification of Water PollutantsDocument11 pagesClassification of Water PollutantsNaveenNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment From Municipal Waste Using Biological MethodDocument20 pagesWastewater Treatment From Municipal Waste Using Biological Methodnoorain zulkapliNo ratings yet
- L6 Activated Sludge SystemDocument38 pagesL6 Activated Sludge SystemNurul Aliza100% (2)
- Effluent Treatment PlantDocument67 pagesEffluent Treatment PlantSWATHI ACHARNo ratings yet
- Waste Treatment & ManagementDocument1 pageWaste Treatment & ManagementSonali SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Industrial Wastewater Treatment ProcessDocument63 pagesChapter 4-Industrial Wastewater Treatment ProcessFadhli JapryNo ratings yet
- 311 222003WSTComettGonzlezWildererDocument8 pages311 222003WSTComettGonzlezWildererujjval chauhanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Technology Activity #3Document9 pagesEnvironmental Technology Activity #3Ray Siemon MatalogNo ratings yet
- Effluent Treatment3Document14 pagesEffluent Treatment3Mirza Md. Nazmus SakibNo ratings yet
- 09 Chapter 1Document22 pages09 Chapter 1BALASUBRAMANIAN SMNo ratings yet
- WWT7 - Physical TreatmentDocument17 pagesWWT7 - Physical TreatmentHelder MbidiNo ratings yet
- Sludge Mngment, Anaerobic Treatment and Aquatic Plant SystemsDocument33 pagesSludge Mngment, Anaerobic Treatment and Aquatic Plant SystemsAndrew Marquez DonaireNo ratings yet
- TechnologiesDocument12 pagesTechnologiesHamed MehriNo ratings yet
- School of Civil Engineering & Architecture: Adama Science and Technology UniversityDocument112 pagesSchool of Civil Engineering & Architecture: Adama Science and Technology UniversityHusen DugoNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Biofilteration of VOCDocument35 pagesUnit - 4 Biofilteration of VOCWALLELGNNo ratings yet
- Waste WaterDocument6 pagesWaste WaterManish KR AryanNo ratings yet
- 2017-CH-738 Environmental AssignmentDocument9 pages2017-CH-738 Environmental AssignmentMuHaMMaD BiLaLNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment AssignmentDocument14 pagesWastewater Treatment AssignmentKanishka JayalathNo ratings yet
- Blue Barrel System Manual EnglishDocument12 pagesBlue Barrel System Manual EnglishKennedy NgoseyweNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument16 pages1 PBTamara BravoNo ratings yet
- Biofilter: Biofiltration Is A Pollution Control Technique Using A BioreactorDocument6 pagesBiofilter: Biofiltration Is A Pollution Control Technique Using A BioreactorNirmal BhowmickNo ratings yet
- Corresponding Author:: A, B A C D, eDocument9 pagesCorresponding Author:: A, B A C D, ePutry1No ratings yet
- Secondary Treatment - SEWAGEDocument32 pagesSecondary Treatment - SEWAGEMONINDRA NATH PATRANo ratings yet
- Engenvi Presentation - Group 2 PDFDocument17 pagesEngenvi Presentation - Group 2 PDFAngela LimNo ratings yet
- NmunhizuDocument1 pageNmunhizuplennyNo ratings yet
- 17 en Produktbereich Niederspannungsschaltanlagen Neu EnglischDocument1 page17 en Produktbereich Niederspannungsschaltanlagen Neu EnglischplennyNo ratings yet
- Circuit 12 YDocument1 pageCircuit 12 YplennyNo ratings yet
- Draulic System4Document1 pageDraulic System4plennyNo ratings yet
- WayniconDocument1 pageWayniconplennyNo ratings yet
- HBJKDocument1 pageHBJKplennyNo ratings yet
- Ed Engineers AppendixDocument28 pagesEd Engineers AppendixplennyNo ratings yet
- Lighting TechnologyDocument12 pagesLighting TechnologyplennyNo ratings yet
- MeopoDocument1 pageMeopoplennyNo ratings yet
- 947 E EGT 2 Wiring Installation For Lighting and Appliance Circuits ShortDocument8 pages947 E EGT 2 Wiring Installation For Lighting and Appliance Circuits ShortplennyNo ratings yet
- Insulation SystemDocument8 pagesInsulation SystemplennyNo ratings yet
- 9039 E AC-motor With Starting Operating Capacitor 0 3kWDocument1 page9039 E AC-motor With Starting Operating Capacitor 0 3kWplennyNo ratings yet
- Generator Type Hco38 2L26 A: Electrical CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesGenerator Type Hco38 2L26 A: Electrical CharacteristicsplennyNo ratings yet
- WP Focus On Miniature Pumps Selecting The Right Motor TechnologyDocument4 pagesWP Focus On Miniature Pumps Selecting The Right Motor TechnologyplennyNo ratings yet
- 8498 E EPD Busbar Systems ShortDocument7 pages8498 E EPD Busbar Systems ShortplennyNo ratings yet
- Ed Brushless DC Motors Timing RelattionshipDocument2 pagesEd Brushless DC Motors Timing RelattionshipplennyNo ratings yet
- Shaft Stiffness Rev3Document9 pagesShaft Stiffness Rev3plennyNo ratings yet
- En Engineering Definitions and FormulasDocument1 pageEn Engineering Definitions and FormulasplennyNo ratings yet
- MeccalteDocument13 pagesMeccalteplennyNo ratings yet
- WP Brush DC Motor Basics 0Document4 pagesWP Brush DC Motor Basics 0plennyNo ratings yet
- MAU2673 European Grid CodesDocument8 pagesMAU2673 European Grid CodesplennyNo ratings yet
- Ecp34 1l4Document5 pagesEcp34 1l4plennyNo ratings yet
- Ecp3 1s4Document5 pagesEcp3 1s4plennyNo ratings yet
- tkf13 Insobs v1 5 AngDocument9 pagestkf13 Insobs v1 5 AngplennyNo ratings yet
- Ecp28 1VS4 ADocument5 pagesEcp28 1VS4 AplennyNo ratings yet
- tdr-410 en 1.02 Druk KPLDocument24 pagestdr-410 en 1.02 Druk KPLplennyNo ratings yet
- vt-2 Ins Obs v10 GBDocument1 pagevt-2 Ins Obs v10 GBplennyNo ratings yet
- Mining Excavator Hoist en 93Document1 pageMining Excavator Hoist en 93plennyNo ratings yet
- tkf12 Insobs v1 4 AngDocument6 pagestkf12 Insobs v1 4 AngplennyNo ratings yet
- p-1 Insobs v17 Harmonijka AngDocument2 pagesp-1 Insobs v17 Harmonijka AngplennyNo ratings yet
- Global Issues Data Response Questions AdviceDocument9 pagesGlobal Issues Data Response Questions Adviceapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Song Review Ysabelle CuevasDocument4 pagesSong Review Ysabelle Cuevasnurul amaliaNo ratings yet
- The Present Perfect and The Present Perfect Continuous: Finished and Unfinished ActionsDocument26 pagesThe Present Perfect and The Present Perfect Continuous: Finished and Unfinished ActionsyahiaouimalekNo ratings yet
- Ent530 - Case Study - Guidelines & Template For Ba Prog OnlyDocument5 pagesEnt530 - Case Study - Guidelines & Template For Ba Prog Onlynurul hashimaNo ratings yet
- RBLDocument19 pagesRBLD J GamingNo ratings yet
- Procemin 2015 Sizing Stages of Weir High Pressure Grinding Rolls Mills, Based On Pilot TestsDocument25 pagesProcemin 2015 Sizing Stages of Weir High Pressure Grinding Rolls Mills, Based On Pilot TestsNereo SpenglerNo ratings yet
- SB19 Water-KomprimiertDocument101 pagesSB19 Water-KomprimiertNatasa KakesNo ratings yet
- Skylab 3 PAO Mission Commentary 3 of 6Document851 pagesSkylab 3 PAO Mission Commentary 3 of 6Bob AndrepontNo ratings yet
- FG Riskadjustmentmethodology Module1Document12 pagesFG Riskadjustmentmethodology Module1J CHANGNo ratings yet
- The Coat of ArmsDocument3 pagesThe Coat of Armsnaseeb100% (1)
- File System - Node - Js v12.10.0 DocumentationDocument82 pagesFile System - Node - Js v12.10.0 DocumentationMarcos GarciaNo ratings yet
- Bennett 2003Document8 pagesBennett 2003Emir OkucuNo ratings yet
- Fpso - LNG ProcessDocument15 pagesFpso - LNG ProcessYeshWaNth100% (1)
- BL M22 1011 PDFDocument46 pagesBL M22 1011 PDFDmitryNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Promia 50 Application - Material HandlingDocument110 pagesUser Manual: Promia 50 Application - Material Handlingred_shobo_85100% (2)
- Call CardsDocument1 pageCall CardsFarmers CooperativeNo ratings yet
- SvlogDocument7 pagesSvlogmekhanaikopiNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Market Europe - June 2020Document50 pagesPharmaceutical Market Europe - June 2020Areg GhazaryanNo ratings yet
- MYY&MZZ Manual Transmission (Ver4)Document32 pagesMYY&MZZ Manual Transmission (Ver4)Vahid Reza MohammadiNo ratings yet
- 10 Known Issues: Tusbaudio Driver For WindowsDocument4 pages10 Known Issues: Tusbaudio Driver For WindowsWillian LimaNo ratings yet
- Oliveto - Ala Carte MenuDocument8 pagesOliveto - Ala Carte Menuk.alhusain23No ratings yet
- WPC Aco PDFDocument16 pagesWPC Aco PDFpetar spalevicNo ratings yet
- Barton Floco Fra Automatic Sampler User ManualDocument40 pagesBarton Floco Fra Automatic Sampler User ManualedwinmenaNo ratings yet
- The Real EveDocument2 pagesThe Real EveKangMaru_025No ratings yet
- Travel Management - User ManualDocument24 pagesTravel Management - User ManualAlok Samataray100% (2)
- Wget - Curl Large File From Google Drive - Stack OverflowDocument29 pagesWget - Curl Large File From Google Drive - Stack OverflowManoj KamisettiNo ratings yet
- Perbandingan Algoritma Naïve Bayes Dan KNN Dalam Analisis Sentimen Masyarakat Terhadap Pelaksanaan PPPK GuruDocument7 pagesPerbandingan Algoritma Naïve Bayes Dan KNN Dalam Analisis Sentimen Masyarakat Terhadap Pelaksanaan PPPK GuruNur Fajar SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Strategic Human Resource Management Canadian 2Nd Edition Noe Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument58 pagesStrategic Human Resource Management Canadian 2Nd Edition Noe Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFrowanariel26r2100% (9)
- Laya Marxlenin - CE152P-2 - E02 - Experiment2 - Module1Document5 pagesLaya Marxlenin - CE152P-2 - E02 - Experiment2 - Module1Marxlenin LayaNo ratings yet