Professional Documents
Culture Documents
About Omega369 and Benefits
About Omega369 and Benefits
Uploaded by
Ismail Nathar DabapuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
About Omega369 and Benefits
About Omega369 and Benefits
Uploaded by
Ismail Nathar DabapuCopyright:
Available Formats
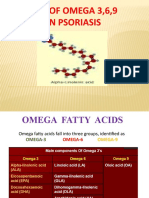
EFA 1300 mg Omega 3-6-9 Softgels
About Omega3 and benefits
Omega-3 fatty acids are a form of polyunsaturated fats that are not made by the body and must
be obtained from a person’s food.
According to the American Heart Association (AHA), the ways in which omega-3 fatty acids
may reduce cardiovascular disease are still being studied. However, the AHA indicates that
research as shown that omega-3 fatty acids:
- decrease the risk of arrhythmias, which can lead to sudden cardiac death,
- decrease triglyceride levels,
- decrease the growth rate of atherosclerotic plaque, and
- lower blood pressure slightly.
In fact, numerous studies show that a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids not only lowers bad
cholesterol (or LDL) , but also lowers triglycerides (the fatty material that circulates in the
blood).
Interestingly, researchers have found that the cholesterol levels of Inuit Eskimos tend to be quite
good, despite the fact that they have a high fat diet.
The researchers found for this reasons is that their diet is high in fatty fish, which is loaded with
omega-3 fatty acids. The same has often been said about the typical Mediterranean-style diet.
About Omega 6 and benefits
Omega-6 fatty acids are one of two groups of essential fatty acids (EFAs) that are required in
human nutrition. This is include linoleic acid and its derivatives.
Essential means that these fatty acids must be consumed in the diet because humans cannot
produce them from other dietary fats or nutrients, nor can they be stored in the body.
They must be consumed daily to meet the body’s requirements.
They are macronutrients, required in amounts of grams per day (compared to micronutrients such
as vitamins, which are required in milligrams per day).
EFAs provide energy and are also components of nerve cells, cellular membranes, and are
converted to hormone-like substances known as prostaglandins.
In the body, prostaglandins and EFAs are necessary for normal physiology, including:
- producing steroids and synthesizing hormones,
- regulates pressure in the eye, joints, and blood vessels,
- mediating immune response,
- regulates bodily secretions and their viscosity,
- dilating or constricting blood vessels,
- regulating collateral circulation,
- directing endocrine hormones to their target cells,
- regulating smooth muscles and autonomic reflexes,
- being primary constituents of cell membranes,
- regulating the rate of cell division,
- maintaining the fluidity and rigidity of cellular membranes,
- regulating the inflow and out-flux of substances into and out of cells,
- transporting oxygen from red blood cells to the tissues,
- maintaining proper kidney function and fluid balance,
- keeping saturated fats mobile in the blood stream,
- preventing blood cells from clumping together (conglomeration, which is the cause of
atherosclerotic plaque, and blood clots, can be a cause of stroke),
- mediating the release of inflammatory substances from cells that may trigger allergic
conditions,
- regulating nerve transmission and communication, and
- being the primary energy source for the heart muscle.
About Omega 9 and benefits
Omega-9 is a family of fatty acids which includes two major fatty acids called stearic acid and
oleic acid.
Stearic acid is a saturated fat which can be converted to oleic acid, which is monounsaturated.
Oleic acid is the most abundant fatty acid found in nature and the primary oil produced by skin
glands.
Omega-9 is a nonessential fatty acid, since it is produced naturally by the body. It does not need
to be supplemented.
Omega-9 is mainly used when there is an insufficiency of either omega-3, omega-6 or both.
When the body doesn’t have enough omega-3 or omega-6, it tries to compensate by producing
omega-9 fatty acids to take their place. Omega-9 derivatives aren’t as effective as omega-3 or
omega-6 though and our health will eventually suffer.
You might also like
- 10 Super Foods For Super JointsDocument38 pages10 Super Foods For Super JointsNISAR_786100% (2)
- Nutrition For SkinDocument15 pagesNutrition For SkinMuhammad KaleemNo ratings yet
- Know Your FatsDocument348 pagesKnow Your Fatstamy_001100% (3)
- The Healthy BodybuilderDocument60 pagesThe Healthy Bodybuildermoez aryan100% (2)
- Aj Business Plan (Lactation Cookies)Document7 pagesAj Business Plan (Lactation Cookies)Dashiell Robert ParrNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Roles and Requirements of LipidsDocument40 pagesNutrition Roles and Requirements of LipidsLan Phuong PhamNo ratings yet
- Omega-3 & Omega-6 Fatty AcidDocument6 pagesOmega-3 & Omega-6 Fatty Acidمحمود الموسويNo ratings yet
- Nutri Lab: The Importance of Essential Fatty AcidsDocument3 pagesNutri Lab: The Importance of Essential Fatty AcidsChristine Bell Serrano BautistaNo ratings yet
- BiochemisteryDocument12 pagesBiochemistery202302723No ratings yet
- 7 Benefits Daily Omega3Document19 pages7 Benefits Daily Omega3WilberellisNo ratings yet
- BiochemisteryDocument13 pagesBiochemistery202302723No ratings yet
- Omega 3 Fatty Acids 1Document16 pagesOmega 3 Fatty Acids 1sarav dhanuNo ratings yet
- USANA Biomega Fish Oil PDFDocument4 pagesUSANA Biomega Fish Oil PDFHannah Alexander100% (1)
- Omega 3-6-9Document4 pagesOmega 3-6-9Normana ZureikatNo ratings yet
- Fatty AcidsDocument13 pagesFatty AcidsRaviraj MalaniNo ratings yet
- The Benefits of Omega 3 and Where To Find It in Your DietDocument13 pagesThe Benefits of Omega 3 and Where To Find It in Your DietGaurav DhiranNo ratings yet
- OmegaDocument1 pageOmegaaashi27No ratings yet
- OmegaDocument3 pagesOmegadeyaNo ratings yet
- Mancinelli Omega Balance Table CourseDocument19 pagesMancinelli Omega Balance Table Coursemorasaki003No ratings yet
- Omega-3 6 and 9 Fats PDFDocument4 pagesOmega-3 6 and 9 Fats PDFMohd TaufiqNo ratings yet
- About Omega 3 Fish OilsDocument1 pageAbout Omega 3 Fish OilsandyribeirotjNo ratings yet
- Flax SeedsDocument4 pagesFlax Seedsguitarman4224No ratings yet
- Pib Phytomega EnusDocument0 pagesPib Phytomega Enusapi-20476727No ratings yet
- OmegaDocument11 pagesOmegaHaninii Suhaila HKNo ratings yet
- Riya SugandhiDocument7 pagesRiya SugandhiRiya SugandhiNo ratings yet
- Omega-3-6-9 Fatty Acids - A Complete Overview PDFDocument1 pageOmega-3-6-9 Fatty Acids - A Complete Overview PDFMunachande KanondoNo ratings yet
- Essential Fatty Acids v2Document8 pagesEssential Fatty Acids v2SyamsulNo ratings yet
- Omega 3-6-9 60 Capsules Uses: Omega-3 Fatty Acids Can Help Prevent The Buildup of Cholesterol That Can Clog TheDocument1 pageOmega 3-6-9 60 Capsules Uses: Omega-3 Fatty Acids Can Help Prevent The Buildup of Cholesterol That Can Clog TheKnt Nallasamy GounderNo ratings yet
- Omega3 EbfDocument3 pagesOmega3 Ebfapi-306571286No ratings yet
- Essential Fatty Acids Makalah FinalDocument77 pagesEssential Fatty Acids Makalah FinalKeerthy VenthenNo ratings yet
- Role of OmegaDocument12 pagesRole of OmegaparidhisinghalNo ratings yet
- FatsDocument11 pagesFatsBilal ArifNo ratings yet
- Omega-3 Fish OilDocument2 pagesOmega-3 Fish OilAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- MAY 08-23-Linoleic-Acid PDFDocument22 pagesMAY 08-23-Linoleic-Acid PDFJONATHAN KAPLANNo ratings yet
- Pe 1 Lesson 3 NutritionDocument95 pagesPe 1 Lesson 3 Nutritiondario serranoNo ratings yet
- 1.omega XL Approved Product Info PDFDocument15 pages1.omega XL Approved Product Info PDFSharon BonillaNo ratings yet
- How Do Saturated Fats Affect My Health?: Examples AreDocument5 pagesHow Do Saturated Fats Affect My Health?: Examples AreJAY B. MACALINTALNo ratings yet
- ND Week 2 Online - Lipids - W21Document6 pagesND Week 2 Online - Lipids - W21lee00845No ratings yet
- BioefaDocument2 pagesBioefaapi-239680473No ratings yet
- 6 Ways To Ensure Your Omega-3 Supplement Benefits CustomersDocument8 pages6 Ways To Ensure Your Omega-3 Supplement Benefits CustomersBaba SingNo ratings yet
- Omega Fatty Acids and Their Role in Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument13 pagesOmega Fatty Acids and Their Role in Cardiovascular DiseasesSana IqbalNo ratings yet
- Fatty AcidDocument14 pagesFatty AcidFadell MuhammadNo ratings yet
- What Are Essential Fatty Acids?: Shorter Telomeres Are Associated With Bad Diet, Diseases and Early DeathDocument25 pagesWhat Are Essential Fatty Acids?: Shorter Telomeres Are Associated With Bad Diet, Diseases and Early DeathDavid James PNo ratings yet
- Essential Fatty AcidsDocument3 pagesEssential Fatty AcidsMa.Ysabelle TaclaNo ratings yet
- Nih Omega FactsDocument37 pagesNih Omega FactsRavi RayanadeNo ratings yet
- Omega Fatty AcidsDocument3 pagesOmega Fatty AcidsImaan KhanNo ratings yet
- Classification of FatsDocument8 pagesClassification of Fatsvovietphi123456No ratings yet
- High PlateletsDocument9 pagesHigh PlateletsHemal VyasNo ratings yet
- MAY 05-23-Omega-3-Omega-6-Ratio PDFDocument10 pagesMAY 05-23-Omega-3-Omega-6-Ratio PDFJONATHAN KAPLANNo ratings yet
- LipidssssDocument5 pagesLipidssssRaghad AlNo ratings yet
- Omega 3 PresentationDocument12 pagesOmega 3 PresentationAyaaitnaceur3No ratings yet
- THE FOOD GROUPS-WPS OfficeDocument8 pagesTHE FOOD GROUPS-WPS Officepash blessingsNo ratings yet
- RDA of CPF-1 PDFDocument13 pagesRDA of CPF-1 PDFsandeep kaurNo ratings yet
- NUTRITIONDocument12 pagesNUTRITIONJamuna PatelNo ratings yet
- Omega-3 Supplementation GuideDocument12 pagesOmega-3 Supplementation Guidewahyudi.anugrahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Enzymes Practical Handout For 2nd Year MBBSDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Enzymes Practical Handout For 2nd Year MBBSIMDCBiochemNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Semi ActivityDocument2 pagesNutrition Semi ActivitymgracebagulbagulNo ratings yet
- Omega 3 & Omega 6 Fattyacids For TheDocument23 pagesOmega 3 & Omega 6 Fattyacids For TheKrishnareddy DvNo ratings yet
- Acidos Grasos EsencialesDocument5 pagesAcidos Grasos EsencialesEstefanyOrdoñezNo ratings yet
- Lipide: Saturated FatsDocument3 pagesLipide: Saturated FatsMonica CreangaNo ratings yet
- Benefit of Omega 3Document2 pagesBenefit of Omega 3vinayNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For Sports - Quick Sports Nutrition Training TipsDocument5 pagesNutrition For Sports - Quick Sports Nutrition Training Tipsvishal pundirNo ratings yet
- Nutrigenetics & Fatty Acid Metabolism: Genes Analysed in ThisDocument21 pagesNutrigenetics & Fatty Acid Metabolism: Genes Analysed in ThisPetra JobovaNo ratings yet
- Marine Omega Us PipDocument3 pagesMarine Omega Us PipThanh VoNo ratings yet
- New Insights Towards Implications of Sea Buckthorn Oil in Human Health: A ReviewDocument7 pagesNew Insights Towards Implications of Sea Buckthorn Oil in Human Health: A ReviewMaria-Madalina BodescuNo ratings yet
- Lisa Mori OffseasonDocument2 pagesLisa Mori OffseasonDavePalumboSnakeNo ratings yet
- Gcms-Fish OilDocument9 pagesGcms-Fish OilSyifa KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Get Ripped Eating Fast Food: Nate Palmer Precision Nutrition Coach, Certified Personal Trainer Nasm CPT, Ces, TRXDocument22 pagesGet Ripped Eating Fast Food: Nate Palmer Precision Nutrition Coach, Certified Personal Trainer Nasm CPT, Ces, TRXsantiago_vNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Power of The ParentsDocument57 pagesChapter 6 Power of The ParentsSkyalesNo ratings yet
- Fit in 40 EbookDocument102 pagesFit in 40 EbookJames CooperNo ratings yet
- Smoothies For Weight Loss Health and Beauty by Holly JohnsonDocument151 pagesSmoothies For Weight Loss Health and Beauty by Holly JohnsonEnrique ArocaNo ratings yet
- Combined Anti-Inflammatory and Elimination Diet For Adults Living With Endometriosis BookletDocument28 pagesCombined Anti-Inflammatory and Elimination Diet For Adults Living With Endometriosis Bookletpoptot000100% (1)
- KFC Grilled ChickenDocument10 pagesKFC Grilled ChickenNurul Safura RosliNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Psychiatry - Towards Improving Mental Health by What You EatDocument12 pagesNutritional Psychiatry - Towards Improving Mental Health by What You EatYox FloresNo ratings yet
- AAK Product - Catalogue - 2011 PDFDocument8 pagesAAK Product - Catalogue - 2011 PDFMónica AguilarNo ratings yet
- (ACS Symposium Volume 788) Fereidoon Shahidi and John W. Finley (Eds.) - Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Chemistry, Nutrition, and Health Effects-American Chemical Society (2001)Document328 pages(ACS Symposium Volume 788) Fereidoon Shahidi and John W. Finley (Eds.) - Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Chemistry, Nutrition, and Health Effects-American Chemical Society (2001)Carl OSNo ratings yet
- 00 The Story of MannatechDocument25 pages00 The Story of MannatechChristoff777No ratings yet
- Without Grain 100 Delicious Recipes For Eating A Grain-Free - Gluten-Free - Wheat-Free Diet PDFDocument211 pagesWithout Grain 100 Delicious Recipes For Eating A Grain-Free - Gluten-Free - Wheat-Free Diet PDFChuôngGió100% (1)
- Hempseed As A Nutritional Resource: An Overview: J.C. CallawayDocument8 pagesHempseed As A Nutritional Resource: An Overview: J.C. CallawayCarmen Yuliana GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Stranger ProjectDocument177 pagesStranger Projectabhi maneNo ratings yet
- The Hidden Story of CancerDocument74 pagesThe Hidden Story of CancerNasir Khan88% (8)
- Sesame Oil Refined-Tx008267 PdsDocument3 pagesSesame Oil Refined-Tx008267 PdsAbdul Rahman ChoudhryNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy I Final RevisionDocument38 pagesPharmacognosy I Final RevisionMohamed mokhtarNo ratings yet
- Peskin PrimerDocument26 pagesPeskin PrimerDavid Alan SmithNo ratings yet
- Chia Seed1541-4337.12423Document20 pagesChia Seed1541-4337.12423MARÍA CRISTINA CHICA MARULANDANo ratings yet
- Fats and Lipids in Nutrition: Dr. David L. Gee FCSN 245 - Basic NutritionDocument91 pagesFats and Lipids in Nutrition: Dr. David L. Gee FCSN 245 - Basic NutritionYuni Nur AzizahNo ratings yet
- The Brain Needs Animal FatDocument6 pagesThe Brain Needs Animal FatMihai SinzianaNo ratings yet
- Business Presentation PDF en INDDocument57 pagesBusiness Presentation PDF en INDMohammed NizamNo ratings yet
- Anti Inflammatory Diets 2015Document9 pagesAnti Inflammatory Diets 2015twice againNo ratings yet