Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Yearly Plan Y6
Science Yearly Plan Y6
Uploaded by
Mazni BaliCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Grade 6 Weekly Spelling WordsDocument6 pagesGrade 6 Weekly Spelling WordsJessie Ocado100% (1)
- Scheme of Work BiologyDocument7 pagesScheme of Work BiologyDevi RambaranNo ratings yet
- DLP in Science 3 - 4 Q2 WK 3 ValidatedDocument12 pagesDLP in Science 3 - 4 Q2 WK 3 ValidatedSalve Serrano100% (1)
- Yearly Scheme of Work Year 6 2010Document12 pagesYearly Scheme of Work Year 6 2010Khairiza0% (1)
- Yearly Plan SC Year 6Document23 pagesYearly Plan SC Year 6xplore75No ratings yet
- Scienceyearlyplanyear6 PDFDocument12 pagesScienceyearlyplanyear6 PDFnaliniNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Science Yr 6Document10 pagesYearly Plan Science Yr 6jm1718sc100% (5)
- Yearly Plan Science Year 6Document13 pagesYearly Plan Science Year 6mohamad nizam bin mahbob0% (1)
- Yearly Scheme of Week - Science Year 6Document12 pagesYearly Scheme of Week - Science Year 6Din AbNo ratings yet
- DLL Sci G8 Feb. 26-March 2Document2 pagesDLL Sci G8 Feb. 26-March 2Ma'am Mercado100% (1)
- Co TeachingDocument8 pagesCo Teachingapi-508424314No ratings yet
- Y9 Ecology SKC Science Notes 2022Document11 pagesY9 Ecology SKC Science Notes 2022Jem JemNo ratings yet
- DLL in Science Mam CrisjeeDocument3 pagesDLL in Science Mam CrisjeeLyza RodriguezNo ratings yet
- DLL Science Math Filipino Mapeh4 q2 w5Document16 pagesDLL Science Math Filipino Mapeh4 q2 w5Jess Amiel D. TapangNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 4.1Document3 pagesScience Grade 4.1EARL MARCIAL CAINGCOY0% (1)
- 1st Cot Sc3444Document7 pages1st Cot Sc3444Lynn LynnNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Feb 5-9 Content PlansDocument3 pagesWeek 3 Feb 5-9 Content Plansapi-340834297No ratings yet
- Science 7Document3 pagesScience 7LorefelNo ratings yet
- DLL Q2 WK5 Science 6Document4 pagesDLL Q2 WK5 Science 6ARMELA V. MANONGSONGNo ratings yet
- Science 4 Q2 Week 4 DLLDocument10 pagesScience 4 Q2 Week 4 DLLMarie Claire Raneses-Yala TablacNo ratings yet
- Science DLL EditedDocument3 pagesScience DLL EditedJory Aromas AgapayNo ratings yet
- Living Things: Cooperation Competition Live in Group Live in Solitary Factors & ReasonsDocument25 pagesLiving Things: Cooperation Competition Live in Group Live in Solitary Factors & ReasonsFT Geeyah TahirNo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofDocument3 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofJeffrey Selpo BondadNo ratings yet
- Science Rubrics 4-5 T2 Y2 (2016-2017) - 13 Sept 2016Document2 pagesScience Rubrics 4-5 T2 Y2 (2016-2017) - 13 Sept 2016Yuris PradnyaniNo ratings yet
- Science 4-1Document4 pagesScience 4-1Sara A. GloriosoNo ratings yet
- DLP 5 Biodiversity and StabilityDocument11 pagesDLP 5 Biodiversity and StabilityprincessspbsedscicsuandrewsNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Document4 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5arcelie gatbontonNo ratings yet
- DLL Q2 WK9 Science 6Document12 pagesDLL Q2 WK9 Science 6Kjane CgoromNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument5 pagesEcosystemSidra ShahabNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesSample Lesson PlanMANIMALA A/P SOMAKANDAN MoeNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Document4 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Eloyd UngadNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Guide: R U A A E CDocument6 pagesCurriculum Guide: R U A A E CMerce Tojino ManigosNo ratings yet
- Science Year 5 With MindmapDocument25 pagesScience Year 5 With MindmapNanthakumar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Karen Isabel LP-1Document4 pagesKaren Isabel LP-1Karen Isabel Baldera FaminianoNo ratings yet
- Final Demo 2023 2024Document6 pagesFinal Demo 2023 2024Daniela Marie BunoNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Document3 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5mialyn mae legaspi100% (1)
- GEN BIO July 10-14Document5 pagesGEN BIO July 10-14Yay SandovalNo ratings yet
- DLL Science 2q Wk8Document5 pagesDLL Science 2q Wk8MalynNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Document3 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5josefadrilanNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W8NDocument3 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W8NChristian Catherine GonzaloNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Document3 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5mikee vicmudoNo ratings yet
- DLL - SCI 6 2nd Qtr. Week 6Document12 pagesDLL - SCI 6 2nd Qtr. Week 6goeb72No ratings yet
- Q2 DLL Science Sep 2-6Document4 pagesQ2 DLL Science Sep 2-6Florecita CabañogNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument3 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogAbba DagaleaNo ratings yet
- reflection-FEB - VIII BDocument2 pagesreflection-FEB - VIII BelizabethNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Document4 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Maricel Garcia JunioNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Lesson 28 COT1Document3 pagesScience 6 Lesson 28 COT1Rachelle Bernabe100% (2)
- Demonstrate Understanding of Parts and Functions of Animals and Importance To HumansDocument3 pagesDemonstrate Understanding of Parts and Functions of Animals and Importance To HumansAngel AndersonNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument3 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Logthoraxe slasherNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Document3 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Lendel Mariz O. CepilloNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 3 - Q2 - W5Document3 pagesDLL - Science 3 - Q2 - W5Keenlys MagsaysayNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W9Document13 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W9CARLOS FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Quarter 4Document51 pagesGrade 8 Quarter 4DhangManongas-LlaboreVeteNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Environmental ScienceDocument2 pagesDaily Lesson Log Environmental ScienceDiane Marr N. DencioNo ratings yet
- SDLP-DAY - Eco-Bio 1Document7 pagesSDLP-DAY - Eco-Bio 1Jessica SudioNo ratings yet
- Science 8 4th Quarter 1Document55 pagesScience 8 4th Quarter 1James Russell AbellarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document2 pagesAssignment 4waranya kasemchittNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument8 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LognylNo ratings yet
- AGURO 5E LESSON PLAN Interactions Among Living Things in Coral Reefs and Tropical RainforestDocument3 pagesAGURO 5E LESSON PLAN Interactions Among Living Things in Coral Reefs and Tropical RainforestRecxs Baludio Atcha80% (5)
- Guidelines For BTP ReportDocument15 pagesGuidelines For BTP Reportmayan yadavNo ratings yet
- Textbook Safety at Work and Emergency Control A Holistic Approach Benedito Cardella Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Safety at Work and Emergency Control A Holistic Approach Benedito Cardella Ebook All Chapter PDFtimothy.caldwell636100% (5)
- Earth Pressure and Retaining StructuresDocument46 pagesEarth Pressure and Retaining Structures2K18/CE/006 ABHISHEK SINGH100% (1)
- Assignment 3 ArkhangelskiiDocument4 pagesAssignment 3 ArkhangelskiiEvgeniiNo ratings yet
- 2021 Winter FinalDocument3 pages2021 Winter FinalHAITOF BADR-EDDINENo ratings yet
- Loch Ness Monster Research PaperDocument5 pagesLoch Ness Monster Research Paperegabnlrhf100% (1)
- Pioneer English Delhi 11 Sep 2023Document12 pagesPioneer English Delhi 11 Sep 2023Vishal DhimanNo ratings yet
- HCMUT Internship Report DoanTienThongDocument21 pagesHCMUT Internship Report DoanTienThongThông Đoàn TiếnNo ratings yet
- Hysicsaholics: Video Solution On Website:-Video Solution On YoutubeDocument2 pagesHysicsaholics: Video Solution On Website:-Video Solution On YoutubeAbhishek jainNo ratings yet
- ARC1043 2023 Assignment 9 BriefDocument2 pagesARC1043 2023 Assignment 9 BriefRocky ShiNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Form 1Document2 pagesEvaluation Form 1Cherissa Abay OmegaNo ratings yet
- Dogs BreedsDocument20 pagesDogs BreedsdonovanwickNo ratings yet
- How Weather Has Changed World HistoryDocument2 pagesHow Weather Has Changed World HistoryalzachNo ratings yet
- Predictive ZVS Control With Improved ZVS Time Margin and Limited Variable Frequency Range For A 99 Efficient 130-W In3 MHZ GaN Totem-Pole PFC RectifierDocument13 pagesPredictive ZVS Control With Improved ZVS Time Margin and Limited Variable Frequency Range For A 99 Efficient 130-W In3 MHZ GaN Totem-Pole PFC RectifierMuhammad Arsalan FarooqNo ratings yet
- Science 6-4TH Periodical TestDocument8 pagesScience 6-4TH Periodical TestIRENE DE LOS REYESNo ratings yet
- From: Roth, L., Understanding Architecture: Its Elements, History and MeaningDocument19 pagesFrom: Roth, L., Understanding Architecture: Its Elements, History and Meaningjoseph arao-araoNo ratings yet
- Roles of Statistics in ResearchDocument18 pagesRoles of Statistics in ResearchJevan A. Calaque100% (2)
- (English) Building The World's Most Powerful Gearbox For Wind Turbines - The Winergy 8 MW Gearbox (DownSub - Com)Document5 pages(English) Building The World's Most Powerful Gearbox For Wind Turbines - The Winergy 8 MW Gearbox (DownSub - Com)Joe JiNo ratings yet
- 20% UtilizationDocument13 pages20% Utilizationnilo biaNo ratings yet
- The Midnight WorldDocument224 pagesThe Midnight WorldRebecca EleyNo ratings yet
- كيمياء المعادن - تعريفاتDocument2 pagesكيمياء المعادن - تعريفاتmohamed ElsayedNo ratings yet
- Nano AllDocument183 pagesNano AllvenuNo ratings yet
- October 10, 2022 1 / 100Document105 pagesOctober 10, 2022 1 / 100Girik KhullarNo ratings yet
- Geneva UseDocument135 pagesGeneva UseMohit Sahu60% (5)
- Lab Spot SpeedDocument11 pagesLab Spot SpeedshazwanNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Lesson 5.1 - Nano-WorldDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was: Lesson 5.1 - Nano-WorldLee SuarezNo ratings yet
- CE21M112 Gopalji L11Document2 pagesCE21M112 Gopalji L11Gopalji Sudamaji Kalojiya ce21m112No ratings yet
- Script of Today's ProgrammeDocument3 pagesScript of Today's ProgrammeP ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Half Bridge Converter PaperDocument6 pagesHalf Bridge Converter PaperAryaNo ratings yet
Science Yearly Plan Y6
Science Yearly Plan Y6
Uploaded by
Mazni BaliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Yearly Plan Y6
Science Yearly Plan Y6
Uploaded by
Mazni BaliCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Yearly Lesson Plan
Year 6
SCIENCE YEARLY LESSON PLAN (YEAR 6) 2008
SK KEBAWANG, SIPITANG SABAH
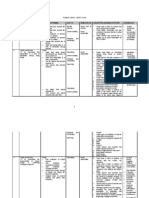
WE LEARNING LEARNING LEARNING SUGGESTED LEARNING SKILLS VOCABULARY
EK AREA OBJECTIVE OUTCOMES ACTIVITIES
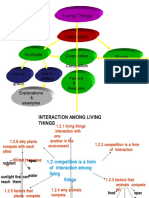
2 1. Interaction 1.1 a) state that some Pupils view a video on animals SPS : solitary .
among Understanding animals live in that live in groups and in solitary. Observing menyendiri
living that some groups. Communicating safety-
Pupils gather information and give
things animals live in b) state that some Making keselamatan
examples of
groups and animals live in Inference cooperation -
animals that live in group and in
others live in solitary. Relating bekerjasama
solitary.
solitary Classifying competition-
c) give examples
Pupils discuss why animals live in persaingan
of animals that
groups, e.g. Scientific
live in groups.
a) for safety, Attitude/
d) give examples b) for food. Noble Value
of animals that Being Thankful
live in solitary. Pupils observe how ants live
Appreciating the
e) explain why together in a vivarium.
balance of
animals live in Pupils discuss why animals live in nature
groups. solitary, e.g. Being
f) explain why a) to avoid competition for food, cooperative
animals live in b) to avoid competition for space.
solitary.
g) state that
cooperation is a
form of
interaction
among animals.
3 1. Interaction 1.2 a) state that living Pupils view video on interaction SPS : interaction-
among Understanding things interact among living Observing interaksi
living that with one things in various habitats. Communicating competition-
things competition another in the Making persaingan
Pupils discuss and give examples
is a form of environment Inference limited
of interaction
interaction b) state that resources-
among living things.
among living competition is a Scientific sumber terhad
things form of Pupils discuss that competition is Attitude/ territory-wilayah
interaction. a form of Noble Value breeding-
interaction. Having an pembiakan
c) list the factors
interest and mate-pasangan
Prepared By : Mazni Binti Bali, SK Kebawang Sipitang, Sabah 1/11
Science Yearly Lesson Plan
Year 6
that animals Pupils view video or computer curiosity the defend-
compete for. simulation of environment mempertahanka
d) give reasons competition among animals. Appreciating the n
why animals balance of space-ruang
Pupils discuss and list the factors
compete. nature shelter-tempat
that animals
perlindungan
compete for:
a) food,
b) water,
c) mate,
d) shelter,
e) territory/space.
Pupils carry out activities to
observe animals competing for
food, e.g. fish or bird.
Pupils discuss that animals
compete because of:
a) limited food resources,
b) limited water resources,
c) trying to get a mate for
breeding,
d) defending or looking for
territory,
e) defending or looking for
shelter.
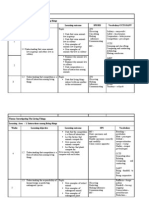
4 1. Interaction 1.2 a) list factors that Pupils view a video or pictures of SPS :
among Understanding plants compete plants in the Observing
living that for forest. Based on the video or Making
things competition is b) give reasons pictures pupils discuss why plants Inference
a form of why plants in the forest have different Interpreting
interaction compete with heights. data
among living each other. Making
Pupils carry out activities to
things conclusion
observe competition among
Relating
plants.
Pupils discuss that plants compete Scientific
for: Attitude/
a) sunlight, Noble Value
b) water, Having an
Prepared By : Mazni Binti Bali, SK Kebawang Sipitang, Sabah 2/11
Science Yearly Lesson Plan
Year 6
c) space, interest and
d) nutrient. curiosity the
environment
Pupils discuss and conclude that
Appreciating the
plants
balance of
compete because of:
nature
a) limited sunlight that can reach
them,
b) limited water resources,
c) limited space,
d) limited nutrient.
5 1. Interaction 1.3 a) give examples Pupils view a video or pictures of SPS : rafflesia- bunga
among Understanding of extinct animals that are extinct, e.g. Observing pakma
living the animal. dinosaurs. Making hornbill-burung
things responsibility b) give examples Inference enggang
Pupils view a video or pictures of
of human in of endangered Generating idea conservation-
endangered
protecting animal. Relating pemuliharaan
animals and plants, e.g. tiger,
endangered protection-
species
c) give examples turtle, orang utan,
Scientific pelindungan
of endangered panda, rhinoceros and rafflesia
Attitude/ endangered -
plant. and pitcher plant.
Noble Value terancam
Pupils discuss and conclude that Having an extinct-pupus
d) explain why certain animals and plants are interest and excessive-
certain animals facing the threat curiosity the berleluasa
or plants are of extinction because of human environment threat- ancaman
facing the activities such as illegal or Appreciating the logging-
threat of excessive: balance of pembalakan
extinction. a) logging, nature consume-
b) hunting, Being menggunakan
c) development. responsible enforcement-
penguatkuasaan
Discuss ways to prevent animals
e) suggest ways to and plants from extinction, e.g.
prevent animals a) campaign against excessive
and plants from logging
extinction. b) educating the public about the
importance Of protecting and
conserving animals and plants,
c) avoid consuming or buying
products made from
Prepared By : Mazni Binti Bali, SK Kebawang Sipitang, Sabah 3/11
Science Yearly Lesson Plan
Year 6
endangered species,
d) enforcing the law.
6 1. Interaction 1.4 a) give examples Pupils view video or see pictures SPS : balance of
among Knowing the of of environmental destructions Observing nature-
living impact of environmental caused by human activities, e.g. Making keseimbangan
things human destruction a) erosion, Inference alam
activities on caused by b) landslide, Predicting illegal logging-
environment human. c) flash-flood, Generating idea pembalakan
d) water pollution, Relating haram
e) air pollution. illegal hunting-
Scientific pemburuan
Pupils view a video and discuss
Attitude/ haram
human activities that cause
Noble Value landslide-tanah
b) explain how destruction to the
Having an runtuh
human environment, e.g.
interest and flash-flood-
activities cause a) illegal and excessive logging,
curiosity the banjir kilat
environmental b) illegal and excessive hunting,
environment pollution-
destruction. c) improper management of
Appreciating the pencemaran
development.
balance of erosion-hakisan
Pupils discuss what will happen to nature disaster-bencana
the Earth if Being destruction -
c) predict what human activities that caused responsible kemusnahan
will happen to
environmental destructions are
the Earth if
not controlled.
human
activities are Pupils prepare a scrap book on
not controlled. environmental
destruction caused by human
activities and steps taken to
reduce its effects.
7 1. Force 1.1 a) state that push Pupils push and pull each other.s SPS : pull-tarikan
Understanding and pull are palms to feel the effect of forces. Observing push-tolakan
that push and forces. Inferring force-daya
Pupils discuss and conclude that
pull b) state that force Classifying palm-tapak
push and pull
are forces cannot be seen Making tangan
are forces.
but its effects conclusion
can be Based on the above activity pupils
Scientific
observed. discuss and
Attitude/
conclude that a force cannot be
Prepared By : Mazni Binti Bali, SK Kebawang Sipitang, Sabah 4/11
Science Yearly Lesson Plan
Year 6
seen but its Noble Value
effects can be observed. Having an
interest and
curiosity the
environment
8 1. Force 1.2 a) state that a Pupils carry out activities and SPS : speed . kelajuan
Understanding force can move discuss the effects of pushing Inferring stationary.pegun
the effects of a a stationary a) a stationary ball, Generating idea moving .
force object. b) a moving ball. Attributing bergerak
b) state that a twist-pulas
Pupils press, twist or squeeze
force can Scientific press- tekan
objects such as
change the Attitude/
plasticine, sponge and spring.
motion of an Noble Value
object. Pupils observe and discuss the Being
effects of forces. systematic
c) state that a
Being flexible
force can Pupils discuss and conclude that a
and open
change the force can:
minded
shape of an a) move the stationary object,
object. b) stop a moving object,
c) change the direction of a
moving object,
d) make an object move faster or
slower,
e) change the shape of an object.
9 1. Force 1.3 a) state that Pupils observe an object such as a SPS : Friction -
Analysing friction is a type book or a coin sliding on a Observing geseran
friction of force. surface. Making aerodynamic-
Inference aerodinamik
Pupils discuss that friction slows
Predicting oppose . -
down a moving object and
Communicating bertentangan
conclude that friction is
Comparing and effect - kesan
a force.
contrasting reduce -
Pupils carry out activities that kurangkan
involve friction, e.g. Scientific increase-
a) open the lid of a jar with dry Attitude/ menambahkan
hands, Noble Value surfaces in
b) open the lid of a jar with oily Being honest contact
hands. Being - permukaan
Prepared By : Mazni Binti Bali, SK Kebawang Sipitang, Sabah 5/11
Science Yearly Lesson Plan
Year 6
Pupils discuss and conclude that it cooperative yang
is easier to open the lid of a jar Being bersentuhan
with dry hands responsible
because of greater friction
10 1. Force 1.3 a) describe the Pupils carry out activities that SPS : friction . geseran
Analysing effects of involve friction, e.g. Predicting aerodynamic-
friction friction a) rubbing their palms, Communicating aerodinamik
b) pulling a heavy object, Making oppose -
c) rubbing an eraser against a conclusion bertentangan
surface. effect - kesan
Scientific reduce -
Based on the above activities Attitude/ kurangkan
pupils explain the Noble Value increase .
effects of friction: Being menambahkan
a) their palms become warmer systematic surfaces in
because friction produces heat, Being contact
b) it is difficult to move the object cooperative - permukaan
because friction opposes Being thankful yang
motion, to God bersentuhan
c) the eraser becomes smaller
because friction causes wear
and tear.
Pupils list and discuss the effects
of friction in everyday life.
Pupils compare the effects of
b) describe friction by rubbing their palms:
ways to reduce a) without oil,
friction. b) with oil.
c) describe Pupils discuss and conclude that
ways to oil reduces friction.
increase
Pupils suggest various ways to
friction.
reduce friction.
.
Pupils carry out activities to test
their suggestions.
11 1. Force 1.3 a) state the Pupils gather information the SPS :
Analysing advantages of advantages and Predicting
Prepared By : Mazni Binti Bali, SK Kebawang Sipitang, Sabah 6/11
Science Yearly Lesson Plan
Year 6
friction friction. disadvantages of friction in Communicating
b) state the everyday life. Making
disadvantages conclusion
of friction. Pupils discuss various situations
c) conclude that where friction Scientific
friction occurs occurs and conclude that friction Attitude/
when two is produced when surfaces are in Noble Value
surfaces are in contact with one another. Being
contact. systematic
Pupils plan and carry out an Being
d) design a fair
experiment to investigate how cooperative
test to find out
different types of surfaces affects Being thankful
how different
the distance a trolley moves. to God
types of
surfaces affect
the distance a
trolley moves
by deciding
what to change,
what to keep
the same and
what to
measure.
12 2. Movement 2.1 a) state that an Pupils carry out activities to: SPS :
Understanding object which a) compare the distances Measuring and
speed moves faster travelled in a given time by using numbers
travels a longer two moving objects, Relating
distance in a b) compare the time taken by two Conclusion
given time. moving objects to travel a
given distance. Scientific
b) state that an Attitude/
object which Pupils discuss and conclude that: Noble Value
moves faster a) an object which moves faster Appericiate
takes a shorter travels a longer distance in a Being
time to travel a given time, systematic
given distance. b) an object which moves faster Being honest
c) state what takes a shorter time to travel a
speed is given distance.
Pupils conclude that:
a) speed is a measurement of
Prepared By : Mazni Binti Bali, SK Kebawang Sipitang, Sabah 7/11
Science Yearly Lesson Plan
Year 6
how fast an object moves,
d) solve problems b) speed can be calculated by
using the using the formula speed =
formula. distance/time.
Pupils solve problems using
the formula.
13 1. Food 1.1 a) describe what Pupils observe samples of spoilt SPS : medium -
preservation Understanding spoilt food is. food. Observing keadaan
food spoilag b) identify Communicating
characteristics Pupils discuss and conclude that Using space-
of spoilt food. spoilt food is unsafe to eat. time relationship
c) state that Controlling
microorganisms Pupils conclude that spoilt food variable
can spoil food. has one or more of the following Handle
characteristics: specimen
d) state the a) unpleasant smell, correctly and
conditions for b) unpleasant taste, carefully
microorganisms c) changed colour, Attributing
to grow d) changed texture, Making
• air, e) mouldy. conclusions
• water,
• nutrient, Pupils carry out an activity to Scientific
• suitable observe that food turns bad by Attitude/
temperature, leaving a slice of bread in the Noble Value
open for a few days. Being
• suitable
systematic
acidity.
Pupils discuss and conclude that Being
microorganisms can spoil food. cooperative
Being Honest
Pupils gather information and Having an
conclude that interest an
microorganisms need certain curiosity
conditions to grow: towards the
environment
14 1. Food 1.2 a) describe ways Pupils find information about SPS : drying-
preservation Synthesisng to preserve ways to preserve Classifying pengeringan
the food. food and examples of food for Making pickling-
concept of food each type of inferences penjerukan
Prepared By : Mazni Binti Bali, SK Kebawang Sipitang, Sabah 8/11
Science Yearly Lesson Plan
Year 6
preservation b) give examples preservation, i.e. Using space- heating -
of food for each a) drying, time relationship pemanasan
type of food b) boiling, Handle vacuum packing-
preservation. c) cooling, specimen pembungkusan
c) give reasons d) vacuum packing, correctly and vakum
why each way e) pickling, carefully cooling-
of food f) freezing, Comparing and pendinginan
preservation is g) bottling/canning, contrasting freezing-
used. h) pasteurising, Attributing penyejuk
i) salting, Making bekuan
d) state what food
j) smoking, generalizations bottling-
preservation is.
k) waxing. Relating pembotolan
e) design and canning-
carry out a Pupils discuss and explain why Scientific pengetinan
project to the above ways are used to Attitude/ smoking- salai
preserve a preserve food. Noble Value salting-
given food. Being pengasina
Pupils view a video or visit food
systematic
factory to observe how food is
Being thankful
processed and
to God
preserved.
Being Honest
Having an
Pupils discuss that food
interest an
preservation is a process of
curiosity
slowing down the food from
towards the
becoming bad.
environment
Pupils carry out a project on food
preservation to preserve a given
food
15 1. Food 1.3 a) give reasons Pupils discuss and give SPS :
preservation Realising the why we need reasons why we need to Classifying
importance of to preserve preserve food, e.g. Making
preserving foo food a) the food will last longer, inferences
b) the food is easy to store, Using space-
c) to reduce wastage of food time relationship
16 2. Waste 2.1 a) identify types Pupils observe various waste in a SPS : harmful effects-
management Understanding of waste in the rubbish bin, e.g. plastic, glass, Classifying kesan buruk
the effects of environment. chemical waste, organic waste Measuring and waste disposal -
Prepared By : Mazni Binti Bali, SK Kebawang Sipitang, Sabah 9/11
Science Yearly Lesson Plan
Year 6
improper b) identify and metal. using numbers pembuangan
disposal of sources of Communication bahan buangan
waste on the waste. Pupils view a video on various Making
environment waste from factories, food stalls conclusion
c) state the and market. Attributing
improper ways Pupils gather information on: Visualizing
of waste a) sources of waste,
disposal. b) various ways of waste disposal.
d) state the Scientific
proper ways of Pupils discuss and classify the Attitude/
waste disposal. proper and improper ways of Noble Value
e) describe the waste disposal. Being
harmful effects cooperative
of improper Pupils discuss the harmful effects Being Honest
waste disposal. of improper waste disposal, e.g. and accurate
a) air pollution, Having an
b) water pollution, interest an
c) sickness and diseases, curiosity
d) acid rain, towards the
e) flash-flood environment
f) describe how Appreciating
waste is Pupils gather information on how
clean and
disposed in a waste in a local area is disposed.
healthy living
local area.
g) suggest ways Pupils discuss and suggest ways
to improve to improve waste disposal in a
waste disposal. local area.
Pupils visit a waste management
centre or listen to a talk to gather
information on how waste is
treated
17 2. Waste 2.2 a) state that Pupils view videos and time-lapse SPS : decay-reput
management Understanding certain waste clippings about waste that decay Making harmful-
that some can decay. and waste that inferences merbahaya
waste b) give examples do not decay. Communicating separate-
can decay of waste that Visualizing asingkan
can decay. Pupils separate waste in a rubbish Generating
c) give examples bin according to the categories ideas
of waste that do such as
Prepared By : Mazni Binti Bali, SK Kebawang Sipitang, Sabah 10/11
Science Yearly Lesson Plan
Year 6
not decay. vegetables, paper, glass, plastics Scientific
d) state that and wood. Attitude/
microorganisms Noble Value
can cause Put each type into separate thick Being
waste materials plastic bags. Place these bags in cooperative
to decay the open and observe the Having an
changes over a period of time. interest an
curiosity
Pupils discuss and give examples
towards the
of waste that:
environment
a) decay,
b) do not decay.
Pupils discuss and conclude
a) some microorganisms caused
waste to decay,
e) state the b) during the decaying process
advantages of nutrients are returned to the
waste decaying. soil, in this way they can be
f) state the used again.
disadvantages
of waste Pupils gather information and
decaying. discuss the advantages and
disadvantages of decay
g) predict what
of waste.
will happen to
human and the
Pupils discuss and predict what
environment if
will happen to human and the
waste do not
environment if waste do not
decay
decay.
18 1. Eclipses 1.1 a) state Pupils use models to simulate the SPS : eclipse-gerhana
Understanding what eclipse of movement of Making position-
the eclipse of the moon is. the Earth, the Moon and the Sun. inferences kedudukan
the moon b) state Communicating partial eclipse-
the position of Pupils view a video or computer Visualizing gerhana separa
the Moon, the simulation about partial and total Generating total eclipse-
Earth and the eclipse ofthe moon. ideas gerhana penuh
Sun during the
eclipse of the Pupils discuss and conclude that Scientific
eclipse of the moon occurs Attitude/
Prepared By : Mazni Binti Bali, SK Kebawang Sipitang, Sabah 11/11
Science Yearly Lesson Plan
Year 6
moon. because: Noble Value
c) explain a) the Earth is between the Moon Being
why eclipse of and the Sun, and cooperative
the moon b) the Earth, the Moon and the Having an
occurs Sun are positioned in a straight interest an
line. curiosity
towards the
Pupils draw diagrams to show the environment
position of the Moon, the Earth
and the Sun during the eclipse of
the moon.
19 1. Eclipses 1.2 a) state what Pupils use models to simulate the SPS :
Understanding eclipse of the movement of Observing
the eclipse of sun is the Earth, the Moon and the Sun Making
the sun b) state the inferences
position of the Pupils discuss that the eclipse of Using space-
Moon, the Earth the sun occurs during daytime. time relationship
and the Sun Communicating
during the Pupils view videos or computer
eclipse of the simulations about partial and total Scientific
sun. eclipse of the sun. Attitude/
Noble Value
Pupils discuss and conclude that Being
eclipse of the sun occurs because: cooperative
c) explain why a) the Moon is between the Earth Having an
eclipse of the and the Sun, interest an
sun occurs b) the Earth, the Moon and the curiosity
Sun are positioned in a straight towards the
line. environment
Thinking
Pupils draw diagrams to show the rationally
position of the Moon, the Earth
and the Sun during the eclipse of
the sun.
Pupils discuss and predict the
d) predict the scenario on the Earth during the
scenario on the eclipse of the sun.
Earth during the
eclipse of the
sun.
Prepared By : Mazni Binti Bali, SK Kebawang Sipitang, Sabah 12/11
Science Yearly Lesson Plan
Year 6
20 1. Machine 1.1 a) explain what Pupils try to remove the lid of a SPS : id- penutup
Understanding simple machine tin using Observing wheel and axle-
simple is. a) bare hands, Communicating roda dan gandar
machine b) spoon. lever-tuas
Scientific wedge-baji
Pupils compare the difficulty to Attitude/ pulley-takal
complete the Noble Value gear-gear
b) state types of task and discuss the function of Being inclined plane-
simple the tool. cooperative satah condong
machines Appreciating the screw-skru
Pupils discuss that a simple contribution of
machine is a device that allows us science and
c) give an to use less force technology
example for to make work easier or faster.
each type of
simple machine. Pupils examine and manipulate
the following
simple machines:
a) wheel and axle,
b) lever,
c) wedge,
d) pulley,
e) gear,
f) inclined plane,
g) screw.
Pupils discuss types and examples
of simple
machines.
Pupils walk around the school
compound and
identify various types of simple
machines.
21 1. Machine 1.2 a) identify simple Pupils identify the simple SPS : wheel barrow-
Analysing a machines in a machines in a bicycle or a wheel Observing kereta sorong
complex complex barrow. Communicating
machine machine.
Pupils discuss and conclude that a
b) conclude that a Scientific
complex machine is a machine
Prepared By : Mazni Binti Bali, SK Kebawang Sipitang, Sabah 13/11
Science Yearly Lesson Plan
Year 6
complex made up of more Attitude/
machine is than one simple machine. Noble Value
made up of Appreciating the
more than one Pupils prepare scrap books on contribution of
simple machine. examples of complex machines. science and
c) give examples technolog
of complex
machines.
22 1. Machine 1.3 a) predict how life Pupils carry out simulation to find SPS :
Appreciating is without out how life would be without Observing
the machines. machines. Communicating
invention of explain how Making
machines that machines can Pupils discuss and predict how life conclusions
make life make our lives would be without machines.
easier easier. Scientific
Pupils discuss and explain how
b) design a Attitude/
machines make our lives easier.
machine to Noble Value
solve a Being
Pupils identify a problem and
problem. cooperative
design a machine to solve the
Appreciating the
problem.
contribution of
science and
technology
23- Revision Science Year 4, 5 & 6
38
Prepared By : Mazni Binti Bali, SK Kebawang Sipitang, Sabah 14/11
You might also like
- Grade 6 Weekly Spelling WordsDocument6 pagesGrade 6 Weekly Spelling WordsJessie Ocado100% (1)
- Scheme of Work BiologyDocument7 pagesScheme of Work BiologyDevi RambaranNo ratings yet
- DLP in Science 3 - 4 Q2 WK 3 ValidatedDocument12 pagesDLP in Science 3 - 4 Q2 WK 3 ValidatedSalve Serrano100% (1)
- Yearly Scheme of Work Year 6 2010Document12 pagesYearly Scheme of Work Year 6 2010Khairiza0% (1)
- Yearly Plan SC Year 6Document23 pagesYearly Plan SC Year 6xplore75No ratings yet
- Scienceyearlyplanyear6 PDFDocument12 pagesScienceyearlyplanyear6 PDFnaliniNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan Science Yr 6Document10 pagesYearly Plan Science Yr 6jm1718sc100% (5)
- Yearly Plan Science Year 6Document13 pagesYearly Plan Science Year 6mohamad nizam bin mahbob0% (1)
- Yearly Scheme of Week - Science Year 6Document12 pagesYearly Scheme of Week - Science Year 6Din AbNo ratings yet
- DLL Sci G8 Feb. 26-March 2Document2 pagesDLL Sci G8 Feb. 26-March 2Ma'am Mercado100% (1)
- Co TeachingDocument8 pagesCo Teachingapi-508424314No ratings yet
- Y9 Ecology SKC Science Notes 2022Document11 pagesY9 Ecology SKC Science Notes 2022Jem JemNo ratings yet
- DLL in Science Mam CrisjeeDocument3 pagesDLL in Science Mam CrisjeeLyza RodriguezNo ratings yet
- DLL Science Math Filipino Mapeh4 q2 w5Document16 pagesDLL Science Math Filipino Mapeh4 q2 w5Jess Amiel D. TapangNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 4.1Document3 pagesScience Grade 4.1EARL MARCIAL CAINGCOY0% (1)
- 1st Cot Sc3444Document7 pages1st Cot Sc3444Lynn LynnNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Feb 5-9 Content PlansDocument3 pagesWeek 3 Feb 5-9 Content Plansapi-340834297No ratings yet
- Science 7Document3 pagesScience 7LorefelNo ratings yet
- DLL Q2 WK5 Science 6Document4 pagesDLL Q2 WK5 Science 6ARMELA V. MANONGSONGNo ratings yet
- Science 4 Q2 Week 4 DLLDocument10 pagesScience 4 Q2 Week 4 DLLMarie Claire Raneses-Yala TablacNo ratings yet
- Science DLL EditedDocument3 pagesScience DLL EditedJory Aromas AgapayNo ratings yet
- Living Things: Cooperation Competition Live in Group Live in Solitary Factors & ReasonsDocument25 pagesLiving Things: Cooperation Competition Live in Group Live in Solitary Factors & ReasonsFT Geeyah TahirNo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofDocument3 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofJeffrey Selpo BondadNo ratings yet
- Science Rubrics 4-5 T2 Y2 (2016-2017) - 13 Sept 2016Document2 pagesScience Rubrics 4-5 T2 Y2 (2016-2017) - 13 Sept 2016Yuris PradnyaniNo ratings yet
- Science 4-1Document4 pagesScience 4-1Sara A. GloriosoNo ratings yet
- DLP 5 Biodiversity and StabilityDocument11 pagesDLP 5 Biodiversity and StabilityprincessspbsedscicsuandrewsNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Document4 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5arcelie gatbontonNo ratings yet
- DLL Q2 WK9 Science 6Document12 pagesDLL Q2 WK9 Science 6Kjane CgoromNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument5 pagesEcosystemSidra ShahabNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesSample Lesson PlanMANIMALA A/P SOMAKANDAN MoeNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Document4 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Eloyd UngadNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Guide: R U A A E CDocument6 pagesCurriculum Guide: R U A A E CMerce Tojino ManigosNo ratings yet
- Science Year 5 With MindmapDocument25 pagesScience Year 5 With MindmapNanthakumar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Karen Isabel LP-1Document4 pagesKaren Isabel LP-1Karen Isabel Baldera FaminianoNo ratings yet
- Final Demo 2023 2024Document6 pagesFinal Demo 2023 2024Daniela Marie BunoNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Document3 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5mialyn mae legaspi100% (1)
- GEN BIO July 10-14Document5 pagesGEN BIO July 10-14Yay SandovalNo ratings yet
- DLL Science 2q Wk8Document5 pagesDLL Science 2q Wk8MalynNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Document3 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5josefadrilanNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W8NDocument3 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W8NChristian Catherine GonzaloNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Document3 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5mikee vicmudoNo ratings yet
- DLL - SCI 6 2nd Qtr. Week 6Document12 pagesDLL - SCI 6 2nd Qtr. Week 6goeb72No ratings yet
- Q2 DLL Science Sep 2-6Document4 pagesQ2 DLL Science Sep 2-6Florecita CabañogNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument3 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogAbba DagaleaNo ratings yet
- reflection-FEB - VIII BDocument2 pagesreflection-FEB - VIII BelizabethNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Document4 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Maricel Garcia JunioNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Lesson 28 COT1Document3 pagesScience 6 Lesson 28 COT1Rachelle Bernabe100% (2)
- Demonstrate Understanding of Parts and Functions of Animals and Importance To HumansDocument3 pagesDemonstrate Understanding of Parts and Functions of Animals and Importance To HumansAngel AndersonNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument3 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Logthoraxe slasherNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Document3 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W5Lendel Mariz O. CepilloNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 3 - Q2 - W5Document3 pagesDLL - Science 3 - Q2 - W5Keenlys MagsaysayNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W9Document13 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W9CARLOS FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Quarter 4Document51 pagesGrade 8 Quarter 4DhangManongas-LlaboreVeteNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Environmental ScienceDocument2 pagesDaily Lesson Log Environmental ScienceDiane Marr N. DencioNo ratings yet
- SDLP-DAY - Eco-Bio 1Document7 pagesSDLP-DAY - Eco-Bio 1Jessica SudioNo ratings yet
- Science 8 4th Quarter 1Document55 pagesScience 8 4th Quarter 1James Russell AbellarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document2 pagesAssignment 4waranya kasemchittNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument8 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LognylNo ratings yet
- AGURO 5E LESSON PLAN Interactions Among Living Things in Coral Reefs and Tropical RainforestDocument3 pagesAGURO 5E LESSON PLAN Interactions Among Living Things in Coral Reefs and Tropical RainforestRecxs Baludio Atcha80% (5)
- Guidelines For BTP ReportDocument15 pagesGuidelines For BTP Reportmayan yadavNo ratings yet
- Textbook Safety at Work and Emergency Control A Holistic Approach Benedito Cardella Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Safety at Work and Emergency Control A Holistic Approach Benedito Cardella Ebook All Chapter PDFtimothy.caldwell636100% (5)
- Earth Pressure and Retaining StructuresDocument46 pagesEarth Pressure and Retaining Structures2K18/CE/006 ABHISHEK SINGH100% (1)
- Assignment 3 ArkhangelskiiDocument4 pagesAssignment 3 ArkhangelskiiEvgeniiNo ratings yet
- 2021 Winter FinalDocument3 pages2021 Winter FinalHAITOF BADR-EDDINENo ratings yet
- Loch Ness Monster Research PaperDocument5 pagesLoch Ness Monster Research Paperegabnlrhf100% (1)
- Pioneer English Delhi 11 Sep 2023Document12 pagesPioneer English Delhi 11 Sep 2023Vishal DhimanNo ratings yet
- HCMUT Internship Report DoanTienThongDocument21 pagesHCMUT Internship Report DoanTienThongThông Đoàn TiếnNo ratings yet
- Hysicsaholics: Video Solution On Website:-Video Solution On YoutubeDocument2 pagesHysicsaholics: Video Solution On Website:-Video Solution On YoutubeAbhishek jainNo ratings yet
- ARC1043 2023 Assignment 9 BriefDocument2 pagesARC1043 2023 Assignment 9 BriefRocky ShiNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Form 1Document2 pagesEvaluation Form 1Cherissa Abay OmegaNo ratings yet
- Dogs BreedsDocument20 pagesDogs BreedsdonovanwickNo ratings yet
- How Weather Has Changed World HistoryDocument2 pagesHow Weather Has Changed World HistoryalzachNo ratings yet
- Predictive ZVS Control With Improved ZVS Time Margin and Limited Variable Frequency Range For A 99 Efficient 130-W In3 MHZ GaN Totem-Pole PFC RectifierDocument13 pagesPredictive ZVS Control With Improved ZVS Time Margin and Limited Variable Frequency Range For A 99 Efficient 130-W In3 MHZ GaN Totem-Pole PFC RectifierMuhammad Arsalan FarooqNo ratings yet
- Science 6-4TH Periodical TestDocument8 pagesScience 6-4TH Periodical TestIRENE DE LOS REYESNo ratings yet
- From: Roth, L., Understanding Architecture: Its Elements, History and MeaningDocument19 pagesFrom: Roth, L., Understanding Architecture: Its Elements, History and Meaningjoseph arao-araoNo ratings yet
- Roles of Statistics in ResearchDocument18 pagesRoles of Statistics in ResearchJevan A. Calaque100% (2)
- (English) Building The World's Most Powerful Gearbox For Wind Turbines - The Winergy 8 MW Gearbox (DownSub - Com)Document5 pages(English) Building The World's Most Powerful Gearbox For Wind Turbines - The Winergy 8 MW Gearbox (DownSub - Com)Joe JiNo ratings yet
- 20% UtilizationDocument13 pages20% Utilizationnilo biaNo ratings yet
- The Midnight WorldDocument224 pagesThe Midnight WorldRebecca EleyNo ratings yet
- كيمياء المعادن - تعريفاتDocument2 pagesكيمياء المعادن - تعريفاتmohamed ElsayedNo ratings yet
- Nano AllDocument183 pagesNano AllvenuNo ratings yet
- October 10, 2022 1 / 100Document105 pagesOctober 10, 2022 1 / 100Girik KhullarNo ratings yet
- Geneva UseDocument135 pagesGeneva UseMohit Sahu60% (5)
- Lab Spot SpeedDocument11 pagesLab Spot SpeedshazwanNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Lesson 5.1 - Nano-WorldDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was: Lesson 5.1 - Nano-WorldLee SuarezNo ratings yet
- CE21M112 Gopalji L11Document2 pagesCE21M112 Gopalji L11Gopalji Sudamaji Kalojiya ce21m112No ratings yet
- Script of Today's ProgrammeDocument3 pagesScript of Today's ProgrammeP ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Half Bridge Converter PaperDocument6 pagesHalf Bridge Converter PaperAryaNo ratings yet