Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 2 (DC Meter)
Tutorial 2 (DC Meter)
Uploaded by
Anson NaiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Ball ScrewDocument3 pagesBall ScrewAngel Moran PachecoNo ratings yet
- Nidhi EM Numerical - Examples - For - TestsDocument10 pagesNidhi EM Numerical - Examples - For - Testsapi-26910047No ratings yet
- Practice Problem 2 (s2 - 3)Document1 pagePractice Problem 2 (s2 - 3)de_stanszaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 - Fluid KinematicsDocument3 pagesTutorial 4 - Fluid KinematicsAnson Nai0% (1)
- Daniel H Nichols - Physics For Technology, Second Edition-CRC Press (2019) PDFDocument431 pagesDaniel H Nichols - Physics For Technology, Second Edition-CRC Press (2019) PDFWidusha PrabashwaraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2SYAFIQAH ISMAILNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Past Year QuestionDocument8 pagesFinal Exam Past Year Questionmuhdarshad645No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 2015 AnswerDocument14 pagesTutorial 2 2015 AnswerPaul YuNo ratings yet
- Chap2 - AcDcmeter1 Ver2Document14 pagesChap2 - AcDcmeter1 Ver2NR_LocusNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On Principles On Measurement and InstrumentationsDocument4 pagesTutorial On Principles On Measurement and InstrumentationsElaine YosoresNo ratings yet
- Measurement (Ques - Ch2 - Electromechanical Instruments) PDFDocument56 pagesMeasurement (Ques - Ch2 - Electromechanical Instruments) PDFmadivala nagarajaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Compilation - Update 16 Oct 2015Document9 pagesTutorial Compilation - Update 16 Oct 2015Sarah HarunNo ratings yet
- Part2 PDFDocument33 pagesPart2 PDFSYAFIQAH ISMAILNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document9 pagesExperiment 3Abel CarlosNo ratings yet
- Nov 2011 SupDocument8 pagesNov 2011 SupViswa ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Measurements JNTUK OldDocument8 pagesMeasurements JNTUK OldRama raoNo ratings yet
- Roll NoDocument2 pagesRoll Noimman46920No ratings yet
- Me I 18 TutorialDocument7 pagesMe I 18 TutorialArkadebSenguptaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - Ammeter and VoltmeterDocument43 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Ammeter and VoltmeterMuhammad Anaz'sNo ratings yet
- Electrical Meas May 2012Document8 pagesElectrical Meas May 2012Rama raoNo ratings yet
- Lab1-Week 3aDocument4 pagesLab1-Week 3apropigismeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 PsDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 PsAmin RafidNo ratings yet
- Set No.1: Code No.V3109/R07Document8 pagesSet No.1: Code No.V3109/R07Ashish AtriNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 2A (Measurement)Document6 pagesEXPERIMENT 2A (Measurement)Lim sui phing Lim sui phingNo ratings yet
- Ee307 2017 06Document4 pagesEe307 2017 06Simbarashe UsaiNo ratings yet
- R 11 KeyDocument12 pagesR 11 KeyKiran Kumar NallamekalaNo ratings yet
- EMI Previous Question Papers Topic Wise PDFDocument24 pagesEMI Previous Question Papers Topic Wise PDFjaganmohanrsNo ratings yet
- Swinburne'S Test ON D.C. Shunt Machine. (Predetermination of Efficiency of Given D.C.Shunt Machine Working As Motor and Generator)Document24 pagesSwinburne'S Test ON D.C. Shunt Machine. (Predetermination of Efficiency of Given D.C.Shunt Machine Working As Motor and Generator)pragatinareshNo ratings yet
- May 2010 SupDocument8 pagesMay 2010 SupViswa ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Beni Suief 3rd TH Year Electrical Sheet 2 MeasuremntsDocument5 pagesBeni Suief 3rd TH Year Electrical Sheet 2 MeasuremntsengshimaaNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument9 pagesLab ReportAhmed HasanNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies MT3-Electrical TechnologyDocument5 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies MT3-Electrical TechnologySrikanth AllamsettyNo ratings yet
- R09 Set No. 2Document8 pagesR09 Set No. 2Samiullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- RT 31021112017Document8 pagesRT 31021112017JohnNo ratings yet
- Eee111 Experiment 2Document9 pagesEee111 Experiment 2Amirul 0205100% (1)
- Assignment 2: Indicating Instruments (Analog and Digital Meter) (CO2)Document1 pageAssignment 2: Indicating Instruments (Analog and Digital Meter) (CO2)SebastianNo ratings yet
- Full Marks: 50 Duration: 3 HoursDocument2 pagesFull Marks: 50 Duration: 3 HoursK JaiswalNo ratings yet
- SheetsDocument9 pagesSheetsnassim.197950% (2)
- Eec 115 Practical - Electrical EngineeringDocument35 pagesEec 115 Practical - Electrical EngineeringVietHungCao90% (10)
- Rr210303-Electrical-Engineering Feb 2007Document8 pagesRr210303-Electrical-Engineering Feb 2007devineni100% (1)
- EG 232 Assignment 2 PDFDocument4 pagesEG 232 Assignment 2 PDFNalucha MukumbutaNo ratings yet
- Rr310202 Electrical MeasurementsDocument8 pagesRr310202 Electrical MeasurementsSrinivasa Rao G100% (2)
- EE Lab ManualDocument23 pagesEE Lab ManualMoordhan SongadeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Q 2023Document3 pagesTutorial 1 Q 2023j2yshjzzsxNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 NTKDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 NTKtsegay100% (1)
- F Chapter2 3 PDFDocument22 pagesF Chapter2 3 PDFwong NXNo ratings yet
- Fow Seng Joe (B1757) - Lab 2 IEEDocument12 pagesFow Seng Joe (B1757) - Lab 2 IEERobert Fow JOENo ratings yet
- R059210302 Electrical EngineeringDocument8 pagesR059210302 Electrical EngineeringJhonloyd Rosete LittauaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3,4 and 5Document10 pagesExperiment 3,4 and 5airaNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits ODL Manual 1-1Document6 pagesElectric Circuits ODL Manual 1-1Idk Maybe AwaisNo ratings yet
- V1-Final Exam Question Sem2!18!19Document8 pagesV1-Final Exam Question Sem2!18!19Mohammed AlshatriNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1AemalkhanNo ratings yet
- GATE Syllabus: Sr. Chapter PagesDocument41 pagesGATE Syllabus: Sr. Chapter PagesNARENDRA KUMAR DHAKARNo ratings yet
- rr310202 Electrical MeasurementsDocument8 pagesrr310202 Electrical MeasurementsSRINIVASA RAO GANTA100% (1)
- Experiment 2 Circuit Simplification A. Series and Parallel Circuit. B. Star and Delta TransformationDocument12 pagesExperiment 2 Circuit Simplification A. Series and Parallel Circuit. B. Star and Delta TransformationronakNo ratings yet
- Winsem2023-24 Beee215p Lo Ch2023240502403 Reference Material I Lab Manual Beee215pDocument25 pagesWinsem2023-24 Beee215p Lo Ch2023240502403 Reference Material I Lab Manual Beee215pshrinidhi.rm2022No ratings yet
- GATE-2014 Electrical MeasurementsDocument42 pagesGATE-2014 Electrical MeasurementsRamaDinakaran100% (1)
- Ee324 - Electrical Machines and DrivesDocument6 pagesEe324 - Electrical Machines and DrivesDavid Jnr PeraNo ratings yet
- Mutah University The Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument32 pagesMutah University The Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Departmentgangstarvegas919No ratings yet
- Electricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandElectricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Resistivity Modeling: Propagation, Laterolog and Micro-Pad AnalysisFrom EverandResistivity Modeling: Propagation, Laterolog and Micro-Pad AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 (Pressure and Fluid Static) PDFDocument3 pagesTutorial 3 (Pressure and Fluid Static) PDFAnson NaiNo ratings yet
- Ch01-Intro PT 2 PDFDocument47 pagesCh01-Intro PT 2 PDFAnson NaiNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Mechatronic Engineering: - WWW - Polipd.edu - MyDocument1 pageDiploma in Mechatronic Engineering: - WWW - Polipd.edu - MyAnson NaiNo ratings yet
- Concept Quiz Mars at UmhbDocument58 pagesConcept Quiz Mars at UmhbzazoNo ratings yet
- Steam and Rankine Cycle OtDocument5 pagesSteam and Rankine Cycle OtRegineil JavierNo ratings yet
- Practice With Kinematic Equations (ws#2)Document2 pagesPractice With Kinematic Equations (ws#2)Kimberly OlivaresNo ratings yet
- Polar Relay For Legacy Teletype ApplicationsDocument4 pagesPolar Relay For Legacy Teletype ApplicationsRandom73No ratings yet
- 200d New AmplifileDocument6 pages200d New AmplifilePunky Hero100% (1)
- Electric Flux and GaussDocument8 pagesElectric Flux and GaussArlynKaren VargasNo ratings yet
- (Template) 9702 Student Learner Guide (Revision Checklist)Document36 pages(Template) 9702 Student Learner Guide (Revision Checklist)shahzodbekaliyev07No ratings yet
- Physics MCQS For CSS PMS: AdminDocument3 pagesPhysics MCQS For CSS PMS: AdminMuhamamd Asfand YarNo ratings yet
- Source/Grid Data: 0 % CalcDocument6 pagesSource/Grid Data: 0 % CalcAlla Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- 4 - Current & ResistanceDocument13 pages4 - Current & ResistanceRichie BobbyNo ratings yet
- Physics IMU CET Sample Questions 05Document10 pagesPhysics IMU CET Sample Questions 05Bhupendra singh chouhanNo ratings yet
- A Practical Approach For Determining The Grounding Grid PDFDocument6 pagesA Practical Approach For Determining The Grounding Grid PDFOscar ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Rotameter Equations and DerivationsDocument2 pagesRotameter Equations and DerivationsMariam flittyNo ratings yet
- Class 10th CH 10 PhysicsDocument3 pagesClass 10th CH 10 PhysicsIrteza khan50% (2)
- Excercise 1 - 2022 - SolutionDocument6 pagesExcercise 1 - 2022 - SolutionDũng VũNo ratings yet
- Phys101l Report No.Document11 pagesPhys101l Report No.Nathan MasilunganNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: JEE (Advanced), 2014Document22 pagesFiitjee: JEE (Advanced), 2014Gaurav BansalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Work, Energy and PowerDocument13 pagesChapter 3 - Work, Energy and PowerJackhyBSyNo ratings yet
- Rev. 0 - PhysPropBenzeneDocument11 pagesRev. 0 - PhysPropBenzenePhượng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- NSW Mathematics-Es1-Scope-And-SequenceDocument26 pagesNSW Mathematics-Es1-Scope-And-SequenceSylvia WEINo ratings yet
- CPI3011 2021 NotesDocument250 pagesCPI3011 2021 NotesSiphoNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To Forces Lesson Plan Student Book, Pages 8-9 ObjectivesDocument1 page1.1 Introduction To Forces Lesson Plan Student Book, Pages 8-9 ObjectivesLeisuread 2No ratings yet
- Revised Maintenance Manual For LHB AC and Non AC CoachesDocument261 pagesRevised Maintenance Manual For LHB AC and Non AC CoachesAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- PXIe-4080 4082Document28 pagesPXIe-4080 4082lauguicoNo ratings yet
- Mec203 Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesMec203 Engineering ThermodynamicsDeedar SinghNo ratings yet
- 17S2 EE3010 PPT Lecture1-ACMachinesDocument34 pages17S2 EE3010 PPT Lecture1-ACMachinesming yangNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Velocity and Speed: - (Guided Notes)Document4 pages1.3 Velocity and Speed: - (Guided Notes)Alexandre CabrelNo ratings yet
- محاضرة 3. ـ موقع الفريد في الفيزياءDocument3 pagesمحاضرة 3. ـ موقع الفريد في الفيزياءMahdiTahar BrahimiNo ratings yet
Tutorial 2 (DC Meter)
Tutorial 2 (DC Meter)
Uploaded by
Anson NaiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 2 (DC Meter)
Tutorial 2 (DC Meter)
Uploaded by
Anson NaiCopyright:
Available Formats
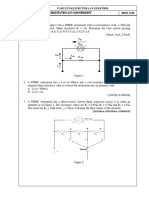
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRIK
SUBJECT: PRINCIPLES OF INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT BEKG 1233
TUTORIAL 2
1. An ammeter as in Figure 1 has a PMMC instrument with a coil resistance of Rm = 99Ω and
f.s.d current of 0.1mA. Shunt resistance Rs = 1Ω. Determine the total current passing through
the ammeter at a) f.s.d, b) 0.5 f.s.d, c) 0.25 f.s.d
[10mA, 5mA, 2.5mA]
Figure 1
2. A PMMC instrument has a f.s.d of 100µA and a coil resistance of 1kΩ. Calculate the required
shunt resistance value to convert the instrument into an ammeter with:
a) f.s.d = 100mA
b) f.s.d = 1A
[1.001Ω, 0.10001Ω]
3. A PMMC instrument has a three-resistor Ayrton shunt connected across it to make an ammeter
as in Figure 2. The resistance values are R1 = 4.5Ω, R2 = 0.45Ω and R3 = 0.05Ω. The meter has
Rm = 1kΩ and If.s.d = 50µA. Calculate the three ranges of the ammeter.
[10.05mA, 100.05mA, 1.005A]
Rm=1k
+ -
C B A
R3 R2 R1
I3 I2 I1
Selector
+
Figure 2
TUTORIAL TUTORIAL 2: DC METER
GROUP: DATE: PAGE: 1
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRIK
SUBJECT: PRINCIPLES OF INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT BEKG 1233
4. An ammeter is connected to measure the current in a 10Ω load supplied from a 10V source as
in Figure 3. Calculate the circuit current if the ammeter resistance Rs is :
a) 0.1Ω
b) 1.0Ω
Also in each case, calculate the effect of the ammeter on the current level.
[0.99A, 1.0%, 0.909A, 9.1%]
Figure 3
5. A PMMC instrument with a f.s.d of 100µA and a coil resistance of 1kΩ in Figure 4 to be
converted into a voltmeter. Determine the required multiplier resistance if the voltmeter is to
measure 100V at full scale. Also calculate the applied voltage when the instrument indicates
0.75, 0.5 and 0.25 f.s.d.
[999kΩ, 75V, 25V]
Figure 4
6. A PMMC instrument with a f.s.d of 50µA and Rm = 1700Ω to be employed as a voltmeter
with range of 10V, 50V and 100V. Calculate the required values of multiplier resistors for the
circuits of Figure 5(a) and Figure 5(b).
[a)198.3kΩ, 998.3kΩ, 1.9983MΩ, b)198.3kΩ, 800kΩ, 1MΩ]
TUTORIAL TUTORIAL 2: DC METER
GROUP: DATE: PAGE: 2
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRIK
SUBJECT: PRINCIPLES OF INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT BEKG 1233
Figure 5(a) Figure 5(b)
7. A voltmeter on a 5V range is connected to measure the voltage across R2 = 50kΩ in the circuit
shown in Figure 6 given R1 = 70kΩ. Calculate VR2
a) without the meter connected
b) with a voltmeter having a sensitivity of 20kΩ/V
c) with a voltmeter having a sensitivity of 200kΩ/V
[5V, 3.87V, 4.86V]
Figure 6
8. Referring to the Figure 7 the reading of voltmeter A is 3.53V when it is connected across point
X and Y. When the voltmeter B is connected at the same terminal, the output voltage produced
will be 4.9V. What is the sensitivity value for voltmeter B if the sensitivity of voltmeter A is
1kΩ/V and both voltmeters A and B are set on its 10V range.
[20kΩ/V]
Figure 7
TUTORIAL TUTORIAL 2: DC METER
GROUP: DATE: PAGE: 3
You might also like
- Ball ScrewDocument3 pagesBall ScrewAngel Moran PachecoNo ratings yet
- Nidhi EM Numerical - Examples - For - TestsDocument10 pagesNidhi EM Numerical - Examples - For - Testsapi-26910047No ratings yet
- Practice Problem 2 (s2 - 3)Document1 pagePractice Problem 2 (s2 - 3)de_stanszaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 - Fluid KinematicsDocument3 pagesTutorial 4 - Fluid KinematicsAnson Nai0% (1)
- Daniel H Nichols - Physics For Technology, Second Edition-CRC Press (2019) PDFDocument431 pagesDaniel H Nichols - Physics For Technology, Second Edition-CRC Press (2019) PDFWidusha PrabashwaraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2SYAFIQAH ISMAILNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Past Year QuestionDocument8 pagesFinal Exam Past Year Questionmuhdarshad645No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 2015 AnswerDocument14 pagesTutorial 2 2015 AnswerPaul YuNo ratings yet
- Chap2 - AcDcmeter1 Ver2Document14 pagesChap2 - AcDcmeter1 Ver2NR_LocusNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On Principles On Measurement and InstrumentationsDocument4 pagesTutorial On Principles On Measurement and InstrumentationsElaine YosoresNo ratings yet
- Measurement (Ques - Ch2 - Electromechanical Instruments) PDFDocument56 pagesMeasurement (Ques - Ch2 - Electromechanical Instruments) PDFmadivala nagarajaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Compilation - Update 16 Oct 2015Document9 pagesTutorial Compilation - Update 16 Oct 2015Sarah HarunNo ratings yet
- Part2 PDFDocument33 pagesPart2 PDFSYAFIQAH ISMAILNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document9 pagesExperiment 3Abel CarlosNo ratings yet
- Nov 2011 SupDocument8 pagesNov 2011 SupViswa ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Measurements JNTUK OldDocument8 pagesMeasurements JNTUK OldRama raoNo ratings yet
- Roll NoDocument2 pagesRoll Noimman46920No ratings yet
- Me I 18 TutorialDocument7 pagesMe I 18 TutorialArkadebSenguptaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - Ammeter and VoltmeterDocument43 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Ammeter and VoltmeterMuhammad Anaz'sNo ratings yet
- Electrical Meas May 2012Document8 pagesElectrical Meas May 2012Rama raoNo ratings yet
- Lab1-Week 3aDocument4 pagesLab1-Week 3apropigismeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 PsDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 PsAmin RafidNo ratings yet
- Set No.1: Code No.V3109/R07Document8 pagesSet No.1: Code No.V3109/R07Ashish AtriNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 2A (Measurement)Document6 pagesEXPERIMENT 2A (Measurement)Lim sui phing Lim sui phingNo ratings yet
- Ee307 2017 06Document4 pagesEe307 2017 06Simbarashe UsaiNo ratings yet
- R 11 KeyDocument12 pagesR 11 KeyKiran Kumar NallamekalaNo ratings yet
- EMI Previous Question Papers Topic Wise PDFDocument24 pagesEMI Previous Question Papers Topic Wise PDFjaganmohanrsNo ratings yet
- Swinburne'S Test ON D.C. Shunt Machine. (Predetermination of Efficiency of Given D.C.Shunt Machine Working As Motor and Generator)Document24 pagesSwinburne'S Test ON D.C. Shunt Machine. (Predetermination of Efficiency of Given D.C.Shunt Machine Working As Motor and Generator)pragatinareshNo ratings yet
- May 2010 SupDocument8 pagesMay 2010 SupViswa ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Beni Suief 3rd TH Year Electrical Sheet 2 MeasuremntsDocument5 pagesBeni Suief 3rd TH Year Electrical Sheet 2 MeasuremntsengshimaaNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument9 pagesLab ReportAhmed HasanNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies MT3-Electrical TechnologyDocument5 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies MT3-Electrical TechnologySrikanth AllamsettyNo ratings yet
- R09 Set No. 2Document8 pagesR09 Set No. 2Samiullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- RT 31021112017Document8 pagesRT 31021112017JohnNo ratings yet
- Eee111 Experiment 2Document9 pagesEee111 Experiment 2Amirul 0205100% (1)
- Assignment 2: Indicating Instruments (Analog and Digital Meter) (CO2)Document1 pageAssignment 2: Indicating Instruments (Analog and Digital Meter) (CO2)SebastianNo ratings yet
- Full Marks: 50 Duration: 3 HoursDocument2 pagesFull Marks: 50 Duration: 3 HoursK JaiswalNo ratings yet
- SheetsDocument9 pagesSheetsnassim.197950% (2)
- Eec 115 Practical - Electrical EngineeringDocument35 pagesEec 115 Practical - Electrical EngineeringVietHungCao90% (10)
- Rr210303-Electrical-Engineering Feb 2007Document8 pagesRr210303-Electrical-Engineering Feb 2007devineni100% (1)
- EG 232 Assignment 2 PDFDocument4 pagesEG 232 Assignment 2 PDFNalucha MukumbutaNo ratings yet
- Rr310202 Electrical MeasurementsDocument8 pagesRr310202 Electrical MeasurementsSrinivasa Rao G100% (2)
- EE Lab ManualDocument23 pagesEE Lab ManualMoordhan SongadeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Q 2023Document3 pagesTutorial 1 Q 2023j2yshjzzsxNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 NTKDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 NTKtsegay100% (1)
- F Chapter2 3 PDFDocument22 pagesF Chapter2 3 PDFwong NXNo ratings yet
- Fow Seng Joe (B1757) - Lab 2 IEEDocument12 pagesFow Seng Joe (B1757) - Lab 2 IEERobert Fow JOENo ratings yet
- R059210302 Electrical EngineeringDocument8 pagesR059210302 Electrical EngineeringJhonloyd Rosete LittauaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3,4 and 5Document10 pagesExperiment 3,4 and 5airaNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits ODL Manual 1-1Document6 pagesElectric Circuits ODL Manual 1-1Idk Maybe AwaisNo ratings yet
- V1-Final Exam Question Sem2!18!19Document8 pagesV1-Final Exam Question Sem2!18!19Mohammed AlshatriNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1AemalkhanNo ratings yet
- GATE Syllabus: Sr. Chapter PagesDocument41 pagesGATE Syllabus: Sr. Chapter PagesNARENDRA KUMAR DHAKARNo ratings yet
- rr310202 Electrical MeasurementsDocument8 pagesrr310202 Electrical MeasurementsSRINIVASA RAO GANTA100% (1)
- Experiment 2 Circuit Simplification A. Series and Parallel Circuit. B. Star and Delta TransformationDocument12 pagesExperiment 2 Circuit Simplification A. Series and Parallel Circuit. B. Star and Delta TransformationronakNo ratings yet
- Winsem2023-24 Beee215p Lo Ch2023240502403 Reference Material I Lab Manual Beee215pDocument25 pagesWinsem2023-24 Beee215p Lo Ch2023240502403 Reference Material I Lab Manual Beee215pshrinidhi.rm2022No ratings yet
- GATE-2014 Electrical MeasurementsDocument42 pagesGATE-2014 Electrical MeasurementsRamaDinakaran100% (1)
- Ee324 - Electrical Machines and DrivesDocument6 pagesEe324 - Electrical Machines and DrivesDavid Jnr PeraNo ratings yet
- Mutah University The Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument32 pagesMutah University The Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Departmentgangstarvegas919No ratings yet
- Electricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandElectricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Resistivity Modeling: Propagation, Laterolog and Micro-Pad AnalysisFrom EverandResistivity Modeling: Propagation, Laterolog and Micro-Pad AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 (Pressure and Fluid Static) PDFDocument3 pagesTutorial 3 (Pressure and Fluid Static) PDFAnson NaiNo ratings yet
- Ch01-Intro PT 2 PDFDocument47 pagesCh01-Intro PT 2 PDFAnson NaiNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Mechatronic Engineering: - WWW - Polipd.edu - MyDocument1 pageDiploma in Mechatronic Engineering: - WWW - Polipd.edu - MyAnson NaiNo ratings yet
- Concept Quiz Mars at UmhbDocument58 pagesConcept Quiz Mars at UmhbzazoNo ratings yet
- Steam and Rankine Cycle OtDocument5 pagesSteam and Rankine Cycle OtRegineil JavierNo ratings yet
- Practice With Kinematic Equations (ws#2)Document2 pagesPractice With Kinematic Equations (ws#2)Kimberly OlivaresNo ratings yet
- Polar Relay For Legacy Teletype ApplicationsDocument4 pagesPolar Relay For Legacy Teletype ApplicationsRandom73No ratings yet
- 200d New AmplifileDocument6 pages200d New AmplifilePunky Hero100% (1)
- Electric Flux and GaussDocument8 pagesElectric Flux and GaussArlynKaren VargasNo ratings yet
- (Template) 9702 Student Learner Guide (Revision Checklist)Document36 pages(Template) 9702 Student Learner Guide (Revision Checklist)shahzodbekaliyev07No ratings yet
- Physics MCQS For CSS PMS: AdminDocument3 pagesPhysics MCQS For CSS PMS: AdminMuhamamd Asfand YarNo ratings yet
- Source/Grid Data: 0 % CalcDocument6 pagesSource/Grid Data: 0 % CalcAlla Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- 4 - Current & ResistanceDocument13 pages4 - Current & ResistanceRichie BobbyNo ratings yet
- Physics IMU CET Sample Questions 05Document10 pagesPhysics IMU CET Sample Questions 05Bhupendra singh chouhanNo ratings yet
- A Practical Approach For Determining The Grounding Grid PDFDocument6 pagesA Practical Approach For Determining The Grounding Grid PDFOscar ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Rotameter Equations and DerivationsDocument2 pagesRotameter Equations and DerivationsMariam flittyNo ratings yet
- Class 10th CH 10 PhysicsDocument3 pagesClass 10th CH 10 PhysicsIrteza khan50% (2)
- Excercise 1 - 2022 - SolutionDocument6 pagesExcercise 1 - 2022 - SolutionDũng VũNo ratings yet
- Phys101l Report No.Document11 pagesPhys101l Report No.Nathan MasilunganNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: JEE (Advanced), 2014Document22 pagesFiitjee: JEE (Advanced), 2014Gaurav BansalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Work, Energy and PowerDocument13 pagesChapter 3 - Work, Energy and PowerJackhyBSyNo ratings yet
- Rev. 0 - PhysPropBenzeneDocument11 pagesRev. 0 - PhysPropBenzenePhượng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- NSW Mathematics-Es1-Scope-And-SequenceDocument26 pagesNSW Mathematics-Es1-Scope-And-SequenceSylvia WEINo ratings yet
- CPI3011 2021 NotesDocument250 pagesCPI3011 2021 NotesSiphoNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To Forces Lesson Plan Student Book, Pages 8-9 ObjectivesDocument1 page1.1 Introduction To Forces Lesson Plan Student Book, Pages 8-9 ObjectivesLeisuread 2No ratings yet
- Revised Maintenance Manual For LHB AC and Non AC CoachesDocument261 pagesRevised Maintenance Manual For LHB AC and Non AC CoachesAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- PXIe-4080 4082Document28 pagesPXIe-4080 4082lauguicoNo ratings yet
- Mec203 Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesMec203 Engineering ThermodynamicsDeedar SinghNo ratings yet
- 17S2 EE3010 PPT Lecture1-ACMachinesDocument34 pages17S2 EE3010 PPT Lecture1-ACMachinesming yangNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Velocity and Speed: - (Guided Notes)Document4 pages1.3 Velocity and Speed: - (Guided Notes)Alexandre CabrelNo ratings yet
- محاضرة 3. ـ موقع الفريد في الفيزياءDocument3 pagesمحاضرة 3. ـ موقع الفريد في الفيزياءMahdiTahar BrahimiNo ratings yet