Professional Documents
Culture Documents
15: Lewis Structures & VSEPR Theory
15: Lewis Structures & VSEPR Theory
Uploaded by
Icathiu CardosoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
15: Lewis Structures & VSEPR Theory
15: Lewis Structures & VSEPR Theory
Uploaded by
Icathiu CardosoCopyright:
Available Formats
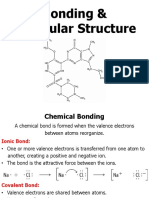
Key Chemistry Terms Arranging Atoms in Lewis Structures
• Valence Shell: Electrons in the outermost shell that are 1. For molecules with only 2 elements, arrange the atoms
involved in bonding. symmetrically.
• Valence Bond Theory: Overlap of atomic orbitals form a 2. “COOH” is a carboxylic acid (both O’s bond to the C and
bond. the H goes on one of the O’s).
• Covalent Bond: A bond formed between two nonmetals 3. Hydrogen and halogens cannot go in the middle.
that involves shared electrons. 4. Write the remaining atoms in the order they appear in the
• Octet Rule: Atoms are most stable with a full valence shell formula.
(with in most cases is “8”). 5. Write the hydrogen and halogen atoms around the
• Lewis Structure: A 2D representation of a molecule and element they are written next to in the formula.
its bonds.
• Lone Pair: Pair of electrons not being shared in a bond.
Drawing Covalent Lewis Structures
• Bonding Pair: Pair of electrons that are a bond. Both 1. Arrange the atoms as above.
atoms sharing the electrons can “count” them in their 2. Determine the # of valence electrons for each atom.
valence shell. 3. Draw the valence electrons—do not double up where a
• Single bond: One pair of shared electrons. bond is going to form between two atoms.
• Double bond: Two pairs of shared electrons. Shorter and 4. Count to see if all atoms have full valences (noting
stronger than a single bond. exceptions above).
• Triple bond: Three pairs of shared electrons. Shorter and 5. If two atoms adjacent to each other do not have full
stronger than a double bond. valences, move in an electron from each to form a double
• Polyatomic Ion: Group of atoms covalently bonded bond. Repeat for triple bond if necessary.
together that have a net charge. 6. If two atoms that are not adjacent to each other need to
• Ionic Compound: Electrons are transferred from one double bond, try moving a hydrogen to one of them to
atom to another. Transfer of electrons results in net cause two atoms adjacent to each other to need the
charges, which bond with electrostatic attraction. double bond.
• Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
(VSEPR): Is used to predict the 3D shape of a molecule
that is based on electron-pair electrostatic repulsion.
Electrons considered include: bonding pairs, nonbonding Single bonds: Double bonds:
pairs and single electron.
• Electron Geometry: 3D structure of a molecule
determined by counting the electron regions around a Polyatomic anion:
central atom.
Drawing Ionic Lewis Structures
• Electron Region: Each bond (single, double or triple) and
lone pair count as “1” electron region. Transfer the electrons from the metal to the nonmetals until
• Molecular Geometry: 3D structure determined by the all have full valences and the net charge = 0.
atoms bonded to the central atom.
• Ligand: Atoms bonded to the central atom. Ionic compound:
Determining # of Valence Electrons Another Approach to Lewis Structures
Determining valence electrons from the periodic table: 1. Arrange the atoms as above.
2. Determine the total # of valence electrons for the whole
molecule.
3. Put 1 bonding pair between a set of atoms to be bonded.
4. Place remaining electrons in lone pairs, starting with the
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 most electronegative element.
5. If atoms do not have full valence shells, move a lone pair
from an adjacent atom in to double, or triple, bond.
VSEPR Theory and Geometry
A = central atom; X = ligands; E = lone pairs
Drawing Lewis Structures for an Element
Electron Molecular Name
1. Use the element symbol to represent the nucleus and
regions Formula
core electrons.
2 AX2 Linear
2. Determine # of valence electrons.
3 AX3 Trigonal Planar
3. Draw valence electrons—placing one on each side before
doubling up. 3 AX2E Bent
4 AX4 Tetrahedron
Exceptions to the Octet Rule 4 AX3E Trigonal pyramidal
1. Hydrogen and Helium can only hold 2 electrons (they 4 AX2E2 Bent
only have a 1s orbital). 5 AX5 Trigonal bipyramidal
2. Boron and Beryllium can be full with 6 electrons. 5 AX4E See-saw
3. Any element in period 3 or below can have more than 8 5 AX3 E2 T-shaped
electrons (they have empty d orbitals that can hold 5 AX2E3 Linear
them). 6 AX6 Octahedron
6 AX5E Square pyramidal
6 AX4 E2 Square planar
15: Lewis Structures & VSEPR Theory
You might also like
- Problems and Solutions in Medical Physics DiagnosticDocument157 pagesProblems and Solutions in Medical Physics DiagnosticSubhrojitBagchiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 7 Slides - General Chemistry - Open StaxDocument96 pagesChapter - 7 Slides - General Chemistry - Open Staxonline purchaseNo ratings yet
- Bili Total RandoxDocument2 pagesBili Total RandoxJesus Guillermo Caceres Fernandez100% (6)
- Ur620c To252 Mosfet SMDDocument4 pagesUr620c To252 Mosfet SMDBRUNONo ratings yet
- Key Chemistry Terms Arranging Atoms in Lewis StructuresDocument1 pageKey Chemistry Terms Arranging Atoms in Lewis StructuresIcathiu CardosoNo ratings yet
- 16: Drawing Molecules - Lewis Structures: High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat SheetDocument1 page16: Drawing Molecules - Lewis Structures: High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat Sheetbooty holeNo ratings yet
- Lewis Atructures and ShapesDocument38 pagesLewis Atructures and ShapesPatrick AbidraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Molecular Geometry & Bonding TheoryDocument139 pagesChapter 3 - Molecular Geometry & Bonding Theoryndhp25011999No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1-VB Theory-SbH-L1Document42 pagesCHAPTER 1-VB Theory-SbH-L1ezanaNo ratings yet
- CHM 121 Chapter 8 LectureDocument21 pagesCHM 121 Chapter 8 Lecturecd aNo ratings yet
- Bonding and StructureDocument72 pagesBonding and StructureHannah Jean EstebanNo ratings yet
- Lewis Atructures and VSEPRDocument50 pagesLewis Atructures and VSEPRPatrick AbidraNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 Chemical BondingDocument53 pagesGen Chem 2 Chemical BondingNoella may de MesaNo ratings yet
- L3 Polar and Nonpolar Covalent MoleculesDocument33 pagesL3 Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Molecules1256- FRONDA, RHOVIC D.No ratings yet
- Chap 1 Valence Bond TheoryDocument86 pagesChap 1 Valence Bond TheoryAre lipNo ratings yet
- P1B Additional Structure and BondingDocument52 pagesP1B Additional Structure and BondingHazell SangalangNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Chemical Bonding NotesDocument89 pagesTopic 3 Chemical Bonding NotesSiti NuraqidahNo ratings yet
- Carbon Compounds and Chemical BondsDocument50 pagesCarbon Compounds and Chemical BondsZafrel ZaffNo ratings yet
- Lewis Structure Spring 2014Document7 pagesLewis Structure Spring 2014Mohamed DahmaneNo ratings yet
- Chem Test RevisionDocument10 pagesChem Test RevisionmaddieNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument29 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesbitangyarahNo ratings yet
- IkatanDocument41 pagesIkatanMuhammad RizkyNo ratings yet
- U5 Properties and Structures of Chemical CompoundsDocument131 pagesU5 Properties and Structures of Chemical CompoundsJack SaxonNo ratings yet
- 14 Lewis Structures and Molecuar Models S19Document14 pages14 Lewis Structures and Molecuar Models S19victorNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Covalent SubstancesDocument53 pagesCH 3 Covalent SubstancesHeidi VagueNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Ionic Bonding Characteristics of Ionic CompoundsDocument2 pagesChemical Bonding Ionic Bonding Characteristics of Ionic CompoundsBittu100% (1)
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument79 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryellieNo ratings yet
- Bonding Ionic CovalentDocument30 pagesBonding Ionic CovalentRaul MejiaNo ratings yet
- Structure and BondingDocument100 pagesStructure and BondingJannah AntoninoNo ratings yet
- 4 - Molecular GeometryDocument25 pages4 - Molecular GeometryNam KhansNo ratings yet
- Bonding RefresherDocument28 pagesBonding RefresherPierce TaylorNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - Lewis Sturcture 7th Ed PDFDocument90 pagesCH 3 - Lewis Sturcture 7th Ed PDFNora AounNo ratings yet
- A Lewis StructureDocument9 pagesA Lewis StructureSetch PalmaNo ratings yet
- CHEM 205 Chapter 8 Section 12.3Document30 pagesCHEM 205 Chapter 8 Section 12.3phikjaeNo ratings yet
- CH2 Molecular Bonding & StructureDocument7 pagesCH2 Molecular Bonding & Structuredanny olulanaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 2016Document75 pagesChemical Bonding 2016MBOTAKE LawsonNo ratings yet
- 2020 2.4 Chemistry GZDocument187 pages2020 2.4 Chemistry GZgeetub1No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chemistry RemedialDocument69 pagesUnit 2 Chemistry Remedialabdimoh7522100% (1)
- Lecture 1 Molecular Structure and BondingDocument31 pagesLecture 1 Molecular Structure and Bondingthuy36030No ratings yet
- Lewis Theory Valence Electrons Are The Electrons Involved in BondingDocument15 pagesLewis Theory Valence Electrons Are The Electrons Involved in BondingmaryNo ratings yet
- Concept of Chemical BondingDocument69 pagesConcept of Chemical Bondingsuka11blyatNo ratings yet
- CHM101 - Unit 3 - Chemical Bonding - Lecture Notes Edited 20240508Document153 pagesCHM101 - Unit 3 - Chemical Bonding - Lecture Notes Edited 20240508mercyybandaNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument17 pagesBondingShahd ElfkiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Asst. Prof. Jean Theresa O. GoDocument51 pagesChemical Bonding: Asst. Prof. Jean Theresa O. GoOsannah Irish InsongNo ratings yet
- VSEPR TheoryDocument7 pagesVSEPR TheoryAnnrhea Oleen ArancesNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 1Document18 pagesGen Chem 1JEAN MONSANTONo ratings yet
- CHEM 10a Unit 4Document3 pagesCHEM 10a Unit 4McHaley HalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 2020Document73 pagesChemical Bonding 2020HANNAH JULIA CAPUNGCONo ratings yet
- Bonding: General ConceptsDocument41 pagesBonding: General ConceptsOlufifehanmi OsikoyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingDocument46 pagesBasic Concepts of Chemical BondingHendri KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Molecular Structure and Bonding: 3.1 The Octet RuleDocument89 pagesChapter 2. Molecular Structure and Bonding: 3.1 The Octet RuleAnn BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document35 pagesPart 1Ola100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry,: Structure & BondingDocument74 pagesOrganic Chemistry,: Structure & BondingilhamfaturachmanagusNo ratings yet
- Lewis Structures: Molecular Structure and BondingDocument83 pagesLewis Structures: Molecular Structure and Bondingحني اسفيانيNo ratings yet
- Mariano Marcos State University: PCHM 121: Pharmaceutical Inorganic Chemistry With Qualitative AnalysisDocument14 pagesMariano Marcos State University: PCHM 121: Pharmaceutical Inorganic Chemistry With Qualitative AnalysisKaizenNo ratings yet
- Bonding - Shapes of MoleculesDocument24 pagesBonding - Shapes of Moleculesamarali11420222No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Review of General Chemistry ConceptsDocument32 pagesLesson 1 Review of General Chemistry Conceptsnorlene narita macedaNo ratings yet
- Compiled Lecture in General Chemistry (Organic Chemistry) (Midterm) CcjeDocument21 pagesCompiled Lecture in General Chemistry (Organic Chemistry) (Midterm) CcjeEmil Vince T. CumilangNo ratings yet
- Chm131 Chapter 3 Chemical Bonds1Document68 pagesChm131 Chapter 3 Chemical Bonds1Adibah Qistina QistinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Bonding Powerpoint AP ChemDocument68 pagesChapter 8 Bonding Powerpoint AP ChemAbdul jan sultaniNo ratings yet
- LewisHO PDFDocument12 pagesLewisHO PDFanon_35443243No ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Oracle 10g WaitsDocument55 pagesOracle 10g Waitssunilreddy123No ratings yet
- MWMDocument4 pagesMWMरितेश हरोडेNo ratings yet
- COBOL QuesbankDocument23 pagesCOBOL Quesbankapi-27095622No ratings yet
- Depositiona LenvironmentsDocument17 pagesDepositiona LenvironmentsVikiFintaruNo ratings yet
- Ece V Digital Signal Processing (10ec52) NotesDocument160 pagesEce V Digital Signal Processing (10ec52) NotesVijay SaiNo ratings yet
- LBM FinalDocument7 pagesLBM FinalJohan NicholasNo ratings yet
- Certificate: MSG-SGKM College Arts, Science and CommerceDocument34 pagesCertificate: MSG-SGKM College Arts, Science and CommerceSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- TWJO-1-TCD-ST1-0004-Rev E-A6Document61 pagesTWJO-1-TCD-ST1-0004-Rev E-A6Anang AprizalNo ratings yet
- Brosur T172 BARU Uk A3 (Revised 201212)Document2 pagesBrosur T172 BARU Uk A3 (Revised 201212)Angga VidaryantoNo ratings yet
- Irs Unit 4 CH 1Document58 pagesIrs Unit 4 CH 1ZeenathNo ratings yet
- Basic Steam Pipe Sizing Charts: Technical ManualDocument4 pagesBasic Steam Pipe Sizing Charts: Technical ManualAymen KhlifiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Information & Communication Technology 0417/02 October/November 2021Document17 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Information & Communication Technology 0417/02 October/November 2021EffNo ratings yet
- UM0384Document35 pagesUM0384Pat 14HS1No ratings yet
- Homework 1Document4 pagesHomework 1Itzel A. GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Update UI Components With NavigationUIDocument21 pagesUpdate UI Components With NavigationUISanjay PatelNo ratings yet
- Master Boot Record: Usman Mansoor Junaid Ali Husnain Manzoor Fahad AliDocument10 pagesMaster Boot Record: Usman Mansoor Junaid Ali Husnain Manzoor Fahad AliJunaidAliNo ratings yet
- MpsDocument5 pagesMpssajjad aliNo ratings yet
- Application of Water Quality Model QUAL2K To Model The Dispersion of Pullutants in River Ndarug, KenyaDocument9 pagesApplication of Water Quality Model QUAL2K To Model The Dispersion of Pullutants in River Ndarug, KenyasteveNo ratings yet
- 3.2 - Worksheet 3 - Mark Scheme - Gravitational FieldDocument3 pages3.2 - Worksheet 3 - Mark Scheme - Gravitational FieldTinboyNo ratings yet
- Report On Supermarket Billing SystemDocument23 pagesReport On Supermarket Billing SystemChidgana HegdeNo ratings yet
- School Based Assessment 2022 GRADE 4 (Section-A) MATHEMATICS PART - B (Subjective Type)Document6 pagesSchool Based Assessment 2022 GRADE 4 (Section-A) MATHEMATICS PART - B (Subjective Type)Muhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- HBL632RT2: Construction Electrical Optics Specification FeaturesDocument2 pagesHBL632RT2: Construction Electrical Optics Specification FeaturesVictor HernandezNo ratings yet
- Computer Science - Strings (CBSE Class 11)Document6 pagesComputer Science - Strings (CBSE Class 11)Abhishek BiswalNo ratings yet
- Day 1 - Part 1 Introduction To FEA CAEDocument64 pagesDay 1 - Part 1 Introduction To FEA CAEFaroukh RashidNo ratings yet
- 15-Bertolini Diaphragm PumpDocument41 pages15-Bertolini Diaphragm PumpJohn Robinson100% (2)
- Addendum: Manual Updates Addendum: Manual Updates: 48 Door Type 1 - 8Document13 pagesAddendum: Manual Updates Addendum: Manual Updates: 48 Door Type 1 - 8Zoran Borojević-TeslaNo ratings yet
- Centr Eur J BiolDocument8 pagesCentr Eur J Bioldhafer alhaidaryNo ratings yet