Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gallium Arsenide Laser
Gallium Arsenide Laser
Uploaded by
bhatchinmay70 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
718 views4 pagesThe semiconductor laser is constructed from a single crystal of gallium-arsenide with a p-n junction. The n-section is heavily doped with tellurium and the p-section is heavily doped with zinc. When a forward bias is applied, electrons and holes recombine at the junction, emitting photons. At high current, the population inverts and stimulated emission produces coherent laser light in the infrared region. The resonant cavity is formed by cleaving the crystal ends to partially reflect light and provide feedback for lasing.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe semiconductor laser is constructed from a single crystal of gallium-arsenide with a p-n junction. The n-section is heavily doped with tellurium and the p-section is heavily doped with zinc. When a forward bias is applied, electrons and holes recombine at the junction, emitting photons. At high current, the population inverts and stimulated emission produces coherent laser light in the infrared region. The resonant cavity is formed by cleaving the crystal ends to partially reflect light and provide feedback for lasing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
718 views4 pagesGallium Arsenide Laser
Gallium Arsenide Laser
Uploaded by
bhatchinmay7The semiconductor laser is constructed from a single crystal of gallium-arsenide with a p-n junction. The n-section is heavily doped with tellurium and the p-section is heavily doped with zinc. When a forward bias is applied, electrons and holes recombine at the junction, emitting photons. At high current, the population inverts and stimulated emission produces coherent laser light in the infrared region. The resonant cavity is formed by cleaving the crystal ends to partially reflect light and provide feedback for lasing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Construction and working of Semiconductor laser (Ga As)
Semi conductor laser is a device whose active medium is a
semiconductor. It has a p-n junction doped in a single crystal of
semiconductor such as gallium-arsenide (Ga As).
Construction:
It is a single crystal of Ga-As and consisting heavily doped n and p-
sections.
n-section is doped with tellurium and the p-section is doped with
zinc.
The doping concentration is very high and is of the order of 1017 to
1019 dopant atoms/cm3.
The p- n junction is connected to a dc power supply in a forward bias
condition.
The resonant cavity is obtained by cleaving (polishing) the end faces
of the junction diode.
Other sides of the p-n junction device are made as rough surfaces to
prevent the leakage of light Smitha M G, Asst Professor, D.O.Physics, RNSIT
Active region
+ p- type
Laser
n- type
Cleaved face-partially reflecting
Cleaved face-Fully reflecting
Smitha M G, Asst Professor, D.O.Physics, RNSIT
Working:
The Ga-As laser diode is subjected to a forward bias current.
Under the influence of the applied voltage, electrons from the n –
section and holes from p –section flow across the junction.
The width of depletion region decreases due to injection of
electrons and holes.
When a hole meets an electron, recombination takes place
resulting in the emission of a photon.
At low forward currents the diode act as an LED.
As the current is increased (applied voltage nearly equal to band
gap voltage), a threshold for lasing will be attained at which time an
active region is formulated very near the junction (depletion layer),
where the population gets inverted.
At this stage, a photon originally released by spontaneous emission
may trigger stimulated emission over a large number of
recombination, leading to the build up of laser radiation of high
power Smitha M G, Asst Professor, D.O.Physics, RNSIT
In case of gallium-arsenide, we get a light radiation in the
infrared region. 8874 Å at room temperature.
Smitha M G, Asst Professor, D.O.Physics, RNSIT
You might also like
- Muhurtha ChinthamaniDocument322 pagesMuhurtha Chinthamanibhatchinmay7100% (11)
- R.G.rao - Transit of Planets On Thy BirthchartDocument142 pagesR.G.rao - Transit of Planets On Thy Birthchartbhatchinmay782% (11)
- Scientech 2266Document33 pagesScientech 2266sarikapravinNo ratings yet
- Conductivity Modulation PDFDocument55 pagesConductivity Modulation PDFAkhilesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Indus Lab Exp 1Document12 pagesIndus Lab Exp 1plokplokplokNo ratings yet
- Satya JatakamDocument140 pagesSatya Jatakambhatchinmay7100% (2)
- MUHURTA by BV - RAMANDocument109 pagesMUHURTA by BV - RAMANattikka100% (8)
- Shree Mahalakshmi MantrahaDocument1 pageShree Mahalakshmi Mantrahabhatchinmay7No ratings yet
- Properties of A P - N JunctionDocument6 pagesProperties of A P - N JunctionSharmistha JuiNo ratings yet
- Tunnel DiodeDocument5 pagesTunnel DiodeKhanpurKing1No ratings yet
- Mems Switches Seminar ReportDocument29 pagesMems Switches Seminar ReportNidhi SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Tunnel Diode PDFDocument9 pagesTunnel Diode PDFSONIKA R R 18BEC152No ratings yet
- Fermi Level and Fermi EnergyDocument36 pagesFermi Level and Fermi Energygirishkumardarisi254No ratings yet
- 7 Extrinsic Semiconductor-1Document11 pages7 Extrinsic Semiconductor-1api-462620165No ratings yet
- Ect401 M2Document15 pagesEct401 M2hrithikNo ratings yet
- Diode Tutorial Sheet-1 PDFDocument4 pagesDiode Tutorial Sheet-1 PDFjeetesh raghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- 12th Imp Topics Chapter WiseDocument4 pages12th Imp Topics Chapter WiserampriyachinNo ratings yet
- Elements of Communication SystemDocument31 pagesElements of Communication SystemsujithNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Plane-Wave Propagation PDFDocument47 pagesChapter 2 Plane-Wave Propagation PDFTran Nguyen KhangNo ratings yet
- Plasma Antenna 1Document21 pagesPlasma Antenna 1Jaseel KylmNo ratings yet
- DC&RF SputteringDocument14 pagesDC&RF SputteringSamdar Singh JhalaNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of PhotodiodeDocument2 pagesWorking Principle of PhotodiodeAta Ur Rahman KhalidNo ratings yet
- Triangular Wave Generator Using Op Amp - EEEGUIDE PDFDocument6 pagesTriangular Wave Generator Using Op Amp - EEEGUIDE PDFDeepanshi RuhelaNo ratings yet
- PUT Experiment EditedDocument9 pagesPUT Experiment EditedReineirDuranNo ratings yet
- Week 12 - Chapter 17 - RLC CircuitDocument27 pagesWeek 12 - Chapter 17 - RLC CircuitPHẠM ĐỖ ĐỨC KHẢINo ratings yet
- Extrinsic SemiconductorsDocument28 pagesExtrinsic SemiconductorsSahil AhujaNo ratings yet
- Drift and Diffusion CurrentsDocument6 pagesDrift and Diffusion Currentsprabhat_prem50% (4)
- Transistor Current ComponentsDocument3 pagesTransistor Current ComponentsDiptendu MitraNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Semiconductors and Rectifiers: TopicsDocument21 pagesUnit-1 Semiconductors and Rectifiers: TopicsMuthuvel MNo ratings yet
- On PN Junction DiodeDocument12 pagesOn PN Junction DiodeSATHEESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics 1 Notes by Rajiv Gandhi CollegeDocument144 pagesEngineering Physics 1 Notes by Rajiv Gandhi Collegesanjit singhNo ratings yet
- A Laboratory Manual Of: Antenna & Wave PropagationDocument29 pagesA Laboratory Manual Of: Antenna & Wave PropagationRommy PasvanNo ratings yet
- Tunnel Diode DefinitionDocument12 pagesTunnel Diode Definitionshwet_vNo ratings yet
- Effective ApertureDocument10 pagesEffective ApertureLeo HambirepiNo ratings yet
- Fermi EnergyDocument7 pagesFermi EnergyBobNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT ElectronicDocument9 pagesASSIGNMENT ElectronicShaukat KhanNo ratings yet
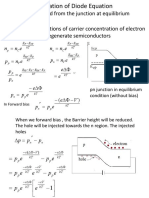
- Derivation of Diode EquationDocument7 pagesDerivation of Diode EquationSatyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document13 pagesChapter 6aregawi weleabezgiNo ratings yet
- London EquationsDocument5 pagesLondon Equationsyehtt0212No ratings yet
- CHAP 1 Part 2Document36 pagesCHAP 1 Part 2ksreddy2002No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Theory (EMT)Document7 pagesElectromagnetic Theory (EMT)Sudalai MadanNo ratings yet
- 5.AC Phase Control Using SCRDocument8 pages5.AC Phase Control Using SCRabcdefgNo ratings yet
- Energy MeterDocument7 pagesEnergy MeterEd J. SaguinNo ratings yet
- Docuyan Properties of NanomaterialsDocument5 pagesDocuyan Properties of NanomaterialsShane Patrick PanilagNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11: NPN BJT Common Emitter CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesExperiment 11: NPN BJT Common Emitter CharacteristicsMalikAlrahabiNo ratings yet
- AI Techniques in Electrical EngineeringDocument1 pageAI Techniques in Electrical EngineeringNarasimha Prasad TulasiNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 2: To Study The Characteristics of Photo-Transistor To Measure The Intensity of Light ApparatusDocument3 pagesExperiment No 2: To Study The Characteristics of Photo-Transistor To Measure The Intensity of Light ApparatusMuhammudAliNo ratings yet
- Gunn Diode Working Principle and Its Applications PDFDocument5 pagesGunn Diode Working Principle and Its Applications PDFAzim WarNo ratings yet
- PNPN and Other Devices: Robert BoylestadDocument53 pagesPNPN and Other Devices: Robert BoylestadTe Ng0% (1)
- Band To Band Radiative RecombinationDocument19 pagesBand To Band Radiative RecombinationnikithaNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor ElectronicsDocument20 pagesSemiconductor Electronicskatti1084154No ratings yet
- Asynchronous Sequential NetworkDocument20 pagesAsynchronous Sequential NetworkGulzar Ahamd100% (1)
- FET BiasingDocument3 pagesFET BiasingAnj HernandezNo ratings yet
- SCR Firing CircuitsDocument4 pagesSCR Firing CircuitsShubham BagalNo ratings yet
- Transistor at Low FrequenciesDocument40 pagesTransistor at Low Frequenciesjoydeep12100% (1)
- Research Project Room Temperature Superconductors PDFDocument120 pagesResearch Project Room Temperature Superconductors PDFVladimir VoloshinNo ratings yet
- VaractorDocument8 pagesVaractorshwet_vNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics NotesDocument4 pagesWave Optics NotesDharamvir SinghNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic Semiconductor: Free Electrons HolesDocument7 pagesIntrinsic Semiconductor: Free Electrons HolesSyed Zubair ZahidNo ratings yet
- Analysis On Conversion Efficiency of Homojunction and Heterojunction Solar Cell Using Semiconductor MaterialsDocument4 pagesAnalysis On Conversion Efficiency of Homojunction and Heterojunction Solar Cell Using Semiconductor MaterialsAnonymous izrFWiQNo ratings yet
- EMI Chapter7 PDFDocument50 pagesEMI Chapter7 PDFGADIGE SWATHI100% (1)
- An LED With A Spectral Width of 17 NM Is Used As An Optical SourceDocument1 pageAn LED With A Spectral Width of 17 NM Is Used As An Optical Sourceddemo17demoNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Power Quality Issues of Grid Connected Renewable Energy Sources IDocument7 pages5.1 Power Quality Issues of Grid Connected Renewable Energy Sources IABHIRAM K REJIKUMAR EE19-23No ratings yet
- Opticalfibercommunicationsourcesanddetectors 160426061235 PDFDocument144 pagesOpticalfibercommunicationsourcesanddetectors 160426061235 PDFJayakumar ThangavelNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 01: SVKM'S Nmims Mpstme Shirpur CampusDocument7 pagesExperiment - 01: SVKM'S Nmims Mpstme Shirpur CampusSachin PatilNo ratings yet
- Sukar Naadi - 3Document12 pagesSukar Naadi - 3bhatchinmay7No ratings yet
- De Broglie Wavelength and Uncertainity Principle PDFDocument7 pagesDe Broglie Wavelength and Uncertainity Principle PDFbhatchinmay7No ratings yet
- Sambhu Hora Prakasha-R SanthanamDocument341 pagesSambhu Hora Prakasha-R Santhanambhatchinmay7100% (2)
- Cseelements of Mechanical Engg. L2Document13 pagesCseelements of Mechanical Engg. L2bhatchinmay7No ratings yet
- Essence of or Research Made On Nadi Astrology Part 3-NegandhiDocument124 pagesEssence of or Research Made On Nadi Astrology Part 3-Negandhibhatchinmay775% (4)
- KSK Trib PDFDocument3 pagesKSK Trib PDFbhatchinmay7No ratings yet
- Æã Àä ƺàätå Àäæwðgà Àgàä: Àäzàä É Àavàgà Fã À ÀDocument16 pagesÆã Àä ƺàätå Àäæwðgà Àgàä: Àäzàä É Àavàgà Fã À Àbhatchinmay7No ratings yet
- Kannada Pustaka Naadi PDFDocument162 pagesKannada Pustaka Naadi PDFbhatchinmay7No ratings yet
- DM English - Sury PDFDocument177 pagesDM English - Sury PDFbhatchinmay7No ratings yet
- RG RAO Kashyapa Hora 1 PDFDocument93 pagesRG RAO Kashyapa Hora 1 PDFbhatchinmay7No ratings yet
- 7th CPC Order CftisDocument2 pages7th CPC Order Cftisknighthood4allNo ratings yet
- Horoscope in Your Hand PDFDocument14 pagesHoroscope in Your Hand PDFbhatchinmay7No ratings yet
- Jyotish Anga Vidya Varahamihira PDFDocument53 pagesJyotish Anga Vidya Varahamihira PDFjyothi100% (2)