Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Know How To Read A Codon Chart - Be Able To Identify A Mutation in A DNA Sequence
Know How To Read A Codon Chart - Be Able To Identify A Mutation in A DNA Sequence
Uploaded by
Emiliano Arvizu Franco Jr0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageNucleotides are made up of a sugar, phosphate group, and one of four nitrogen bases. DNA contains adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine as its nitrogen bases while RNA contains adenine, uracil, cytosine, and guanine. Transcription produces RNA from DNA, and translation uses RNA to produce proteins according to codons, which are mRNA triplets that code for amino acids. There are different types of mutations that can occur at the gene or chromosome level, with chromosomal mutations typically affecting multiple genes and sometimes the number of chromosomes. Gene mutations are usually point mutations or frameshifts while chromosomal mutations can involve translocations of DNA between chromosomes.
Original Description:
Original Title
Things to know Unit 10
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNucleotides are made up of a sugar, phosphate group, and one of four nitrogen bases. DNA contains adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine as its nitrogen bases while RNA contains adenine, uracil, cytosine, and guanine. Transcription produces RNA from DNA, and translation uses RNA to produce proteins according to codons, which are mRNA triplets that code for amino acids. There are different types of mutations that can occur at the gene or chromosome level, with chromosomal mutations typically affecting multiple genes and sometimes the number of chromosomes. Gene mutations are usually point mutations or frameshifts while chromosomal mutations can involve translocations of DNA between chromosomes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageKnow How To Read A Codon Chart - Be Able To Identify A Mutation in A DNA Sequence
Know How To Read A Codon Chart - Be Able To Identify A Mutation in A DNA Sequence
Uploaded by
Emiliano Arvizu Franco JrNucleotides are made up of a sugar, phosphate group, and one of four nitrogen bases. DNA contains adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine as its nitrogen bases while RNA contains adenine, uracil, cytosine, and guanine. Transcription produces RNA from DNA, and translation uses RNA to produce proteins according to codons, which are mRNA triplets that code for amino acids. There are different types of mutations that can occur at the gene or chromosome level, with chromosomal mutations typically affecting multiple genes and sometimes the number of chromosomes. Gene mutations are usually point mutations or frameshifts while chromosomal mutations can involve translocations of DNA between chromosomes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
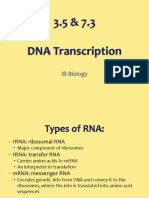
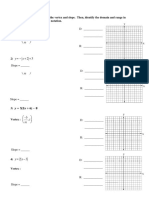
- Nucleotide: sugar, nitrogen base phosphate group
- DNA nitrogen bases: Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
- RNS nitrogen bases: Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine, Guanine
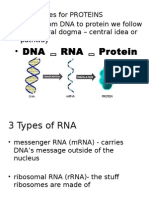
- Transcription= RNA produced
- Translation= RNA made into protein
- Codon= mRNA triplet that codes for an amino acid
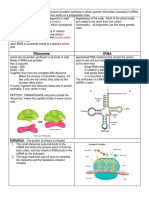
- rRNA= form ribosomes
- mRNA= give message for translation
- tRNA= transfer the amino acids to the ribosome during translation
- Translocation= mutation caused by DNA breaking from its chromosome and attaching to
a nonhomologous chromosome
- Molecules involved in protein synthesis= mRNA, rRNA, tRNA
- Gene mutations vs. chromosomal mutations:
- Gene- only affect one gene
- Chromosome- affect multiple genes, can change # of chromosomes
- Gene mutations:
- Point: substitution
- Frameshift: insertion/deletion
- Chromosomal mutations:
- Translocation: DNA from one chromosome attaching to nonhomologous
chromosome
- Know how to read a codon chart
- Anticodon= opposite of mRNA (STILL WITH U INSTEAD OF T BECAUSE ITS RNA)
- Know how to transcribe mRNA back to DNA (now you will have T)
- Most mutations HAVE NO EFFECT ON THE ORGANISM
- RNA:
- Ribose sugar
- Single stranded
- Uracil instead of Thymine
- Only mutations in sex (germ) cells will be passed on to your offspring
- Be able to identify a mutation in a DNA sequence
- Nucleotide bases are responsible for the direct coding of traits
- Trisomy= having an extra chromosome (tri=3 instead of the normal 2
You might also like
- RNA PowerPointDocument20 pagesRNA PowerPointAnki0391100% (1)
- Unit C Chap 18 Cell DivisionDocument9 pagesUnit C Chap 18 Cell DivisionJane XuNo ratings yet
- 3 57 3dnatranscription 090907150155 Phpapp02Document12 pages3 57 3dnatranscription 090907150155 Phpapp02Dev AshwaniNo ratings yet
- DNA, RNA, and Protein SynthesisDocument19 pagesDNA, RNA, and Protein SynthesisAnonymous qMToncNo ratings yet
- IB BiologyDocument12 pagesIB BiologyMaria Corazon Leonor OtawaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Bio AssgnmntDocument6 pages2nd Bio AssgnmntNitinmanubanshNo ratings yet
- Genetics 2Document52 pagesGenetics 2Le Phuong LyNo ratings yet
- Molecular Structure of DNA, RNA, and Proteins DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis (Cenabre, Fortun, Ibal)Document2 pagesMolecular Structure of DNA, RNA, and Proteins DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis (Cenabre, Fortun, Ibal)Jessa Mae IbalNo ratings yet
- Transcription Kezia Joice BautistaDocument43 pagesTranscription Kezia Joice BautistaKeziajoicee Bautista0% (1)
- Central Dogma of Biology: DNA RNA ProteinDocument20 pagesCentral Dogma of Biology: DNA RNA Proteinjohn paul.jaisonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document27 pagesLecture 5Animikh RayNo ratings yet
- 14 Rna TranscriptionDocument10 pages14 Rna Transcriptionfirst name last nameNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument6 pagesProtein SynthesisRashFlygon ZNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument93 pagesNucleic AcidbianqueeNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDocument29 pagesProtein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaHritik KumarNo ratings yet
- Bio Eya Cheat Sheet Angelica Yeo1Document2 pagesBio Eya Cheat Sheet Angelica Yeo1joleneNo ratings yet
- BIO G12 Unit 3 Short NotesDocument12 pagesBIO G12 Unit 3 Short NotesAmanuel AyalewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Chromosomes, Genes and DNADocument47 pagesChapter 16 Chromosomes, Genes and DNAZin Min KhantNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument42 pagesTranscription and TranslationConnor EnglandNo ratings yet
- DNA Overview Central DogmaDocument56 pagesDNA Overview Central DogmaBukhari DiangkaNo ratings yet
- Rotein Ynthesis: Big PictureDocument3 pagesRotein Ynthesis: Big PicturehomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Genetic Code, DNA, RNA, Protein SynthesisDocument46 pagesGenetic Code, DNA, RNA, Protein SynthesisdeepakNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument53 pagesDNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDeborah Chloe EnriquezNo ratings yet
- DNA TranslationDocument2 pagesDNA TranslationVanesa Monterroso CruzNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis (Gene Expression)Document63 pagesProtein Synthesis (Gene Expression)jaybeeclaireNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis NotesDocument6 pagesProtein Synthesis NotesRokunuz Jahan RudroNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Day 1Document3 pagesLesson Plan Day 1Stephanie Ngooi Ming MingNo ratings yet
- Notes On DNADocument1 pageNotes On DNAChristina VlietNo ratings yet
- Grade - 12 Biology: Oromia Education Bureau in Collaboration WithDocument79 pagesGrade - 12 Biology: Oromia Education Bureau in Collaboration Withmmree yyttNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience Reviewerkarljosefdelacruz1017No ratings yet
- Bio 1110 Lecture On Protein SynthesisDocument30 pagesBio 1110 Lecture On Protein SynthesisNokutenda KamtsetaNo ratings yet
- Genetics: Eckert Minerva Deland Flip Part 1Document34 pagesGenetics: Eckert Minerva Deland Flip Part 1Carl Agape DavisNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Biology: DNA RNA ProteinDocument16 pagesCentral Dogma of Biology: DNA RNA Proteinmungil_alifNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Biology: DNA RNA ProteinDocument16 pagesCentral Dogma of Biology: DNA RNA ProteinJessa Lynn E. AcalaNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument33 pagesTranscription and TranslationAyesha JamilNo ratings yet
- 13 - Translation, Transcription and Processing of RnaDocument13 pages13 - Translation, Transcription and Processing of Rnawhether913No ratings yet
- Dna, Replikasi, Transkripsi Dan Translasi DR - Ruswana Anwar, Spog Pembimbing DR - Herman Wibisono MS, SpandDocument41 pagesDna, Replikasi, Transkripsi Dan Translasi DR - Ruswana Anwar, Spog Pembimbing DR - Herman Wibisono MS, Spandyuyu tuptupNo ratings yet
- Protien SynthesisDocument20 pagesProtien Synthesisapi-277471896No ratings yet
- 8 Protein SynthesisDocument42 pages8 Protein SynthesisAuryn Astrawita HendroSaputriNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument43 pagesTranscription and TranslationSaqlain Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Central Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiDocument27 pagesCentral Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiPuja KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesProtein SynthesisEverly Joy JingcoNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 6 GuideDocument7 pagesAP Biology Unit 6 Guidelolo2212008No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis With Video LinksDocument31 pagesProtein Synthesis With Video LinksSmilingNo ratings yet
- Rna Protein Synthesis VocabDocument1 pageRna Protein Synthesis VocabChastity MiddlebrooksNo ratings yet
- Heredity: 10 - AmaziahDocument33 pagesHeredity: 10 - AmaziahAlice KrodeNo ratings yet
- Biology Cheat Sheet For EllaDocument3 pagesBiology Cheat Sheet For EllaJay EdwardsNo ratings yet
- CHapter 14Document10 pagesCHapter 14alaskamofoNo ratings yet
- DNA Notes - Grade 10Document1 pageDNA Notes - Grade 10Foxy WaxyNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: It Is Expected That Students WillDocument32 pagesProtein Synthesis: It Is Expected That Students WillIMY PAMEROYANNo ratings yet
- Ribonucleic Acid: DescriptionDocument3 pagesRibonucleic Acid: DescriptionMira LutfianaNo ratings yet
- 6.2 D Protein Synthesis: ContosoDocument13 pages6.2 D Protein Synthesis: Contosoruva gundaNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiDocument27 pagesCentral Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Yarsiinez100% (1)
- 5th Part Nucleic AcidDocument3 pages5th Part Nucleic AcidAichal HmjNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Biosynthesis of Protein & Protein ChemistryDocument113 pagesBiochemistry - Biosynthesis of Protein & Protein ChemistryAdella AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- 5 11transcription-2013Document30 pages5 11transcription-2013jernsssNo ratings yet
- Dna and Rna: Molecule of HeredityDocument74 pagesDna and Rna: Molecule of Heredityalfani wahyuNo ratings yet
- Great Depress Notes pt2Document5 pagesGreat Depress Notes pt2Emiliano Arvizu Franco JrNo ratings yet
- Gene Action and MutationsDocument2 pagesGene Action and MutationsEmiliano Arvizu Franco JrNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Industrialization The Gilded AgeDocument20 pagesCH 5 Industrialization The Gilded AgeEmiliano Arvizu Franco JrNo ratings yet
- How To - Live TV ProductionDocument3 pagesHow To - Live TV ProductionEmiliano Arvizu Franco JrNo ratings yet
- Content Filter Login InstructionsDocument1 pageContent Filter Login InstructionsEmiliano Arvizu Franco JrNo ratings yet
- School Calendar: September October July AugustDocument2 pagesSchool Calendar: September October July AugustEmiliano Arvizu Franco JrNo ratings yet
- 2-5 Assignment PDFDocument2 pages2-5 Assignment PDFEmiliano Arvizu Franco JrNo ratings yet
- Cells of The Immune System-Student WorksheetDocument3 pagesCells of The Immune System-Student WorksheetEmiliano Arvizu Franco Jr100% (2)
- Test Over 2-6 (V1-Online) (20-21)Document1 pageTest Over 2-6 (V1-Online) (20-21)Emiliano Arvizu Franco JrNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 VocabDocument1 pageUnit 4 VocabEmiliano Arvizu Franco JrNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Study GuideDocument8 pagesCH 2 Study GuideEmiliano Arvizu Franco JrNo ratings yet
- The Crucible and Mccarthyism: Reading For InformationDocument6 pagesThe Crucible and Mccarthyism: Reading For InformationEmiliano Arvizu Franco JrNo ratings yet