Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology of Cervical Cancer: High Risk HPV (16, 18, 31)
Pathophysiology of Cervical Cancer: High Risk HPV (16, 18, 31)
Uploaded by
Moses Gabriel Valledor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
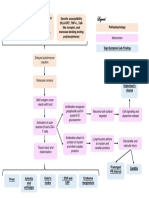
138 views2 pages1. High risk HPV (types 16 and 18) infects and integrates into the basal cells of the cervical squamous epithelium, blocking tumor suppressor genes p53 and pRB and causing abnormal cell growth.
2. This leads to cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and squamous intraepithelial lesions (SIL) as mutated cells proliferate.
3. Without treatment, CIN/SIL can progress to invasive cervical cancer where the tumor fills the cervix and spreads to distant organs via lymphatic or blood vessels.
Original Description:
Original Title
patho cervical
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
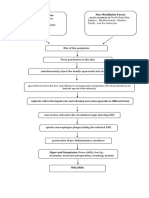
Report this Document1. High risk HPV (types 16 and 18) infects and integrates into the basal cells of the cervical squamous epithelium, blocking tumor suppressor genes p53 and pRB and causing abnormal cell growth.
2. This leads to cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and squamous intraepithelial lesions (SIL) as mutated cells proliferate.
3. Without treatment, CIN/SIL can progress to invasive cervical cancer where the tumor fills the cervix and spreads to distant organs via lymphatic or blood vessels.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
138 views2 pagesPathophysiology of Cervical Cancer: High Risk HPV (16, 18, 31)
Pathophysiology of Cervical Cancer: High Risk HPV (16, 18, 31)
Uploaded by
Moses Gabriel Valledor1. High risk HPV (types 16 and 18) infects and integrates into the basal cells of the cervical squamous epithelium, blocking tumor suppressor genes p53 and pRB and causing abnormal cell growth.
2. This leads to cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and squamous intraepithelial lesions (SIL) as mutated cells proliferate.
3. Without treatment, CIN/SIL can progress to invasive cervical cancer where the tumor fills the cervix and spreads to distant organs via lymphatic or blood vessels.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
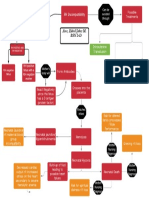
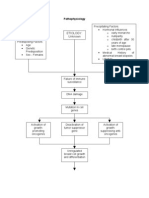
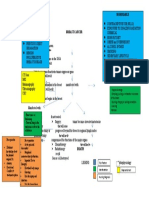
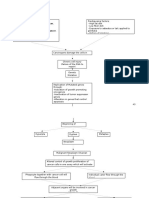
Pathophysiology of Cervical Cancer
High risk HPV (16, 18, 31) Risk factors:
Early age of coitus
Invasion of the basal cell of the Multiple sexual partners
squamous epithelium of the Unsafe sexual practices
cervix
Integration of viral DNA
p53 and pRB tumor suppressor
genes are blocked/deactivated Barrel-shaped
cervix
Mutation and cell proliferation
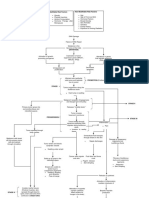
CIN/SIL Tumor fills the entire
Co-carcinogens
Carcinoma in situ cervix
Metastasis to distant body parts
Invasive cancer Tissue necrosis and
sloughing
Increased tumor growth
Lymph invasion
Hypermetabolic Increased
activitypressure to the surrounding tissues, nerves and bladder Fistula formation Hemorrhage Infection
of cell proliferation and Enlargement of lymph
increased tumor growth nodes
needs Leakage of
Metrorrhagia Foul-
urine and
Pelvic and back pain Venous and Ureteral Bleeding smelling
Dysuria feces into the
obstruction after coitus vaginal
vagina
Anorexia anemia discharge
Weight
Hydronephrosi Leg edema
loss
s
You might also like
- Instruction: Do The Following Activities That Will Serve As Your Formative Assessment. Activity 1: CompletionDocument10 pagesInstruction: Do The Following Activities That Will Serve As Your Formative Assessment. Activity 1: CompletionMoses Gabriel Valledor50% (2)
- Social Media and Eating Disorders Power Point 1Document20 pagesSocial Media and Eating Disorders Power Point 1dludwig127100% (1)
- Basic Concept Map - RH IncompatibilityDocument1 pageBasic Concept Map - RH IncompatibilityTechnoShindoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Prostate CancerDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Prostate Cancermkho100% (1)
- Cervical Cancer PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCervical Cancer PathophysiologyBea Dela Cena100% (2)
- TAHBSO PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesTAHBSO Pathophysiologybregette50% (2)
- PathoPhysiology of Cervical CancerDocument2 pagesPathoPhysiology of Cervical CancerJie BandelariaNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer Patho.2Document2 pagesCervical Cancer Patho.2Verni Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Patho Physiology Ovarian CystDocument3 pagesPatho Physiology Ovarian CystSig Deliso100% (1)
- Pathophysiology (Cervical Cancer) Case StudyDocument7 pagesPathophysiology (Cervical Cancer) Case StudyRosalie Valdez Espiritu100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Breast CancerDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Breast CancerDemocrito Louierick Plaza VINo ratings yet
- SP CSDocument4 pagesSP CSKhan HansNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Book Based Myoma UteriDocument1 pagePathophysiology Book Based Myoma UteriChristina Barroga0% (1)
- Reiki IIDocument39 pagesReiki IIAnonymous DqeRRe100% (2)
- Bruno Breitmeyer-Blindspots - The Many Ways We Cannot See-Oxford University Press, USA (2010) PDFDocument281 pagesBruno Breitmeyer-Blindspots - The Many Ways We Cannot See-Oxford University Press, USA (2010) PDFFrancisco Villar100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Colon Cancer Predisposing Factors: Etiology: Precipitating Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Colon Cancer Predisposing Factors: Etiology: Precipitating Factors: Precipitating FactorstatiNo ratings yet
- Modifiedpatho ToyodaDocument4 pagesModifiedpatho ToyodaCaneEscabarteNo ratings yet
- MYOMA PathoDocument1 pageMYOMA Pathobsn2011100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Breast Cancer: If Not TreatedDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Breast Cancer: If Not TreatedsteffiNo ratings yet
- Patho MyomaDocument1 pagePatho MyomaJurilyne Rose TundagNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Pathophysiology-of-BREAST-CANCERDocument1 pageGroup 3 Pathophysiology-of-BREAST-CANCERArisa VijungcoNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPathophysiologyapi-19762967100% (1)
- Myoma PathoDocument3 pagesMyoma PathoJan Michael Artiaga100% (1)
- Patho of CA & Breast CaDocument3 pagesPatho of CA & Breast CaAngeline EspinasNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Cholelithiasis 2Document2 pagesPathophysiology Cholelithiasis 2Jamie HaravataNo ratings yet
- Super Final NCPDocument16 pagesSuper Final NCPNessaly Jane PrestoNo ratings yet
- CPD Concept MapDocument1 pageCPD Concept MapShandle Dynne Baena100% (1)
- 6 PathophysiologyDocument2 pages6 PathophysiologyAJ SnowhiNo ratings yet
- 4 ConceptDocument1 page4 ConceptStacey GarciaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AMLDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AMLjake251996100% (1)
- Albendazole - Drug Information PDFDocument7 pagesAlbendazole - Drug Information PDFjjjkkNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Inflammatory ResponseDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Inflammatory ResponseDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument1 pagePathophysiology Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverShiella Heart Malana100% (1)
- Pa Tho Physiology of Hodgkin'sDocument10 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Hodgkin'sIvica Rae100% (1)
- Measles PathophysiologyDocument1 pageMeasles PathophysiologyAl TheóNo ratings yet
- Pathophy NCADocument1 pagePathophy NCAKaren ValdezNo ratings yet
- Cystic Mass PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCystic Mass PathophysiologyMa Cheryll DueñasNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology-Ng Hirschsprung DiseaseDocument3 pagesPathophysiology-Ng Hirschsprung DiseaseJan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology, Bone CancerDocument7 pagesPathophysiology, Bone CancerMaria Grace Raquel Ormeneta100% (1)
- PathophyDocument2 pagesPathophymharz_astilloNo ratings yet
- Preterm Labor, Hyperemesis Gravidarum - PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPreterm Labor, Hyperemesis Gravidarum - PathophysiologyreyneldanNo ratings yet
- Acute Rheumatic Fever PathophysiologyDocument1 pageAcute Rheumatic Fever PathophysiologyMoonyeen Jann Casera BalicNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CholelithiasisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of CholelithiasisSherilNo ratings yet
- NCP Hydatidiform Mole PDFDocument2 pagesNCP Hydatidiform Mole PDFKimNo ratings yet
- Problem # 3: Threat of Cross Infection From A Communicable Disease CaseDocument3 pagesProblem # 3: Threat of Cross Infection From A Communicable Disease CaseRolandNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan: Group A3 - ObDocument4 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plan: Group A3 - ObErika CadawanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology PRINTDocument1 pagePathophysiology PRINTNichole Audrey SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Malaria: Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifesta6ons and TreatmentDocument14 pagesMalaria: Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifesta6ons and TreatmentGuilhermeNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The AmericasDocument2 pagesNon-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The Americaschristian quiaoitNo ratings yet
- Acute PyelonephritisDocument53 pagesAcute Pyelonephritiseeymee100% (1)
- Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesPathophysiology PDFJenievieve MerzaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Uterine MyomaDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Uterine Myomaghettodawg187100% (7)
- MannitolDocument3 pagesMannitolAlexandra AntondyNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Community Health NursingDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching Community Health NursingKyla Castro100% (1)
- Patho Cervical CADocument1 pagePatho Cervical CAJanice MǾntañǾ100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Gouty ArthritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Gouty Arthritiskyaw100% (1)
- Action Plan - Inadequate IncomeDocument2 pagesAction Plan - Inadequate IncomeBenedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Concept MapDocument1 pageBreast Cancer Concept MapKeepItSecret100% (1)
- Diagram Myoma IDocument1 pageDiagram Myoma IJoann100% (12)
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- BAUTISTA, DYANNE G. - Oncology Nursing Colorectal Cancer Case StudyDocument16 pagesBAUTISTA, DYANNE G. - Oncology Nursing Colorectal Cancer Case StudyDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Modifiable Risk Factors Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Iv. Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesModifiable Risk Factors Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Iv. Schematic DiagramAIMNo ratings yet
- ObstetricsDocument8 pagesObstetricsmohamed abd elsalamNo ratings yet
- Malignant Neoplasm (Ovarian Cancer)Document4 pagesMalignant Neoplasm (Ovarian Cancer)nursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Greatness Is Not About Power But About How You Change The World and Make A DifferenceDocument2 pagesGreatness Is Not About Power But About How You Change The World and Make A DifferenceMoses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- CFE - Religious Involvement (April 18, 2021)Document1 pageCFE - Religious Involvement (April 18, 2021)Moses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- VALLEDOR - GECOS-Module 2 SAQDocument6 pagesVALLEDOR - GECOS-Module 2 SAQMoses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- Religious Involvement 7Document2 pagesReligious Involvement 7Moses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- Religious Involvement 8Document1 pageReligious Involvement 8Moses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 08-05-2020 06.19.56Document22 pagesCamScanner 08-05-2020 06.19.56Moses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology-Threatened MiscarriageDocument1 pagePathophysiology-Threatened MiscarriageMoses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- MOSES GABRIEL G. VALLEDOR - GECOS - Module 5 SAQ - FinalDocument2 pagesMOSES GABRIEL G. VALLEDOR - GECOS - Module 5 SAQ - FinalMoses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- Journal NSTPDocument1 pageJournal NSTPMoses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- Moses Gabriel Valledor - Journal - July 14Document1 pageMoses Gabriel Valledor - Journal - July 14Moses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- CFE - Religious Involvement Week 3Document1 pageCFE - Religious Involvement Week 3Moses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- MOSES GABRIEL VALLEDOR - ACTIVITY - NSTP-2-Module-3-Short-Term-2020Document3 pagesMOSES GABRIEL VALLEDOR - ACTIVITY - NSTP-2-Module-3-Short-Term-2020Moses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- MOSES GABRIEL VALLEDOR - Evaluation-Unit 3Document2 pagesMOSES GABRIEL VALLEDOR - Evaluation-Unit 3Moses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- Module 1: You and The World You Live inDocument5 pagesModule 1: You and The World You Live inMoses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- Module 1: You and The World You Live inDocument2 pagesModule 1: You and The World You Live inMoses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- NSTP Journal June 15-20Document7 pagesNSTP Journal June 15-20Moses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- Module 1: You and The World You Live inDocument2 pagesModule 1: You and The World You Live inMoses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal Pts Bahasa Inggris Kelas X Semester GenapDocument8 pagesLatihan Soal Pts Bahasa Inggris Kelas X Semester GenapAllisa MasithaNo ratings yet
- Renal Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument21 pagesRenal Anatomy and PhysiologyAbisegan ZeuSNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Diagnosis of PregDocument58 pagesAntenatal Diagnosis of Pregpriyanka33% (3)
- Music POINTERS TO REVIEWDocument2 pagesMusic POINTERS TO REVIEWRacielle Dame RamiloNo ratings yet
- Left Anterior Fascicular Block (LAFB) ECG Review - Criteria and ExamplesDocument1 pageLeft Anterior Fascicular Block (LAFB) ECG Review - Criteria and ExamplesWiwik Puji LestariNo ratings yet
- Total Parenteral NutritionDocument59 pagesTotal Parenteral NutritionMARIAH ALEXIE GASALNo ratings yet
- Mcqs On Excretory SystemDocument3 pagesMcqs On Excretory SystemIshfaq Lone100% (1)
- (Progress in Epileptic Disorders, Vol. 13) Solomon L. Moshé, J. Helen Cross, Linda de Vries, Douglas Nordli, Federico Vigevano-Seizures and Syndromes of PDFDocument283 pages(Progress in Epileptic Disorders, Vol. 13) Solomon L. Moshé, J. Helen Cross, Linda de Vries, Douglas Nordli, Federico Vigevano-Seizures and Syndromes of PDFWalter Huacani HuamaniNo ratings yet
- DS160 ApplicationDocument6 pagesDS160 ApplicationMujjuatharNo ratings yet
- BrahmiDocument3 pagesBrahmiamaroluisNo ratings yet
- Airway Clearance Techniques and Hyperinflation Therapy Walsh Chapter 12Document25 pagesAirway Clearance Techniques and Hyperinflation Therapy Walsh Chapter 12Dennis Páez Torres100% (2)
- Bioactive Compounds in Bamboo Shoots: Health Benefits and Prospects For Developing Functional FoodsDocument7 pagesBioactive Compounds in Bamboo Shoots: Health Benefits and Prospects For Developing Functional FoodsBernardo ErcoliNo ratings yet
- Parenteral NutritionDocument78 pagesParenteral NutritionHazelNo ratings yet
- Long Essay On World Health Day in EnglishDocument2 pagesLong Essay On World Health Day in EnglishHii Ing ChungNo ratings yet
- Iowa Woodlands Vital Habitat For Native PollinatorsDocument8 pagesIowa Woodlands Vital Habitat For Native PollinatorsJNo ratings yet
- Abraham Tenaw 4 Power Point ProposalDocument32 pagesAbraham Tenaw 4 Power Point Proposalnahom fikaduNo ratings yet
- January 2020 (R) MSDocument24 pagesJanuary 2020 (R) MSShaheer KhanNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@978 3 030 37317 7Document99 pages10.1007@978 3 030 37317 7Jason OrangeNo ratings yet
- Learning Disabilities in The ClassroomDocument5 pagesLearning Disabilities in The ClassroomekielaszekNo ratings yet
- Gluteal RegionDocument34 pagesGluteal Regionlion2chNo ratings yet
- b10 GE6674 English Lab Record PDFDocument45 pagesb10 GE6674 English Lab Record PDFbrightenNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi Penyebab KomaDocument19 pagesKlasifikasi Penyebab KomaNoni JacksonNo ratings yet
- Toluse Peace's Seminar Paper.Document23 pagesToluse Peace's Seminar Paper.kaeNo ratings yet
- Position Paper ECOFINDocument3 pagesPosition Paper ECOFINGhina N. TashaNo ratings yet
- Womens OrgasmsDocument30 pagesWomens OrgasmsMarkWoodxxxNo ratings yet
- School of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Document3 pagesSchool of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Duchess Juliane Jose MirambelNo ratings yet
- Words & SentencesDocument152 pagesWords & Sentencessamar abbasNo ratings yet