Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Uploaded by
Adriana AfiqahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Uploaded by
Adriana AfiqahCopyright:
Available Formats
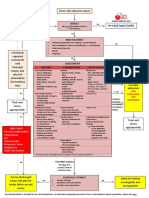
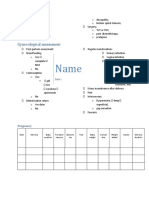
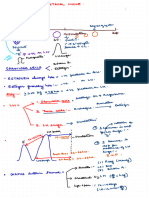
❑ Menstrual History- cycle, when menarche, when menopause.
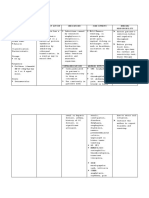
Laboratory Investigation
Polyp
❑ The nature of bleeding; amount, type of pads, either soaked, frequency changing pads, flooding Full Blood Count
❑ Related symptoms • Hb Anemia
Adenomyosis
❑ intermenstrual bleeding • Urinary pregnancy test In pre-menopausal woman to rule out
Leiomyoma pregnancy
❑ Vaginal discharge
Coagulation Profile Considered in woman who have had HMB since
❑ Weight changes, skin changes, fatigue, mood dso (hypothyroid) Malignancy menarche/family history coagulation dso
❑ Dysmenorrhea and/or pressure symptoms TFT Considered in woman who have sign &
Coagulopathy
symptoms of thyroid disease
❑ Dyspareunia
Differential diagnosis
❑ Anemic symptoms Ovulatory dysfunction Imaging
❑ Subfertility Hysteroscopy or ultrasound as the first-line investigation
Endometrial • Hysteroscopy is diagnostic and therapeutic.
❑ Blood disorders (easy bruising/mucosal bleeding) • Endometrial biopsy during hysteroscopy
❑ Urinary and bowel symptoms History Iatrogenic Others: MRI if indicated
❑ Constitutional symptoms Not-yet classified
❑ Medication History
❑ COCP/HRT use
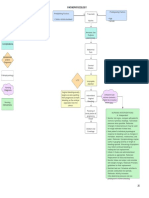
❑ Anti-coagulants Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (menorrhagia)
Defined as bleeding in excess of 80ml per menstrual cycle when measure Treatment
❑ Past Surgical History
objectively Pharmacological Non-hormonal
❑ Previous uterine surgery
❑ Family History • NSAIDS
Hormonal • Tranexamic Acid
❑ Family History of blood disorder Non-
pharmacological • LNG-IUS
❑ Social/Psychosocial History Complications • COCP
❑ Affect of symptoms towards quality of life • Norethisterone
Surgical • Injectables
❑ Other factors that may affect treatment options • GnRH agonist (pre-op)
Due to bleeding Due to treatment
❑ If she wants to get pregnant afterwards.
Hysterectomy Endometrial ablation
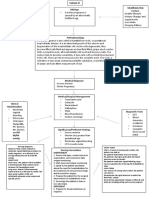
General Examination:
• Severe anemia • Dilatation& curettage :
• Obese/cahexic Uterine perforation,
• Hypotension
• Signs of anemia, thyroid mass, signs of Physical examination Asherman Syndrome Myomectomy
PCOS/ hyperandrogenism Dilatation &
• Vital signs; tachycardia/bradycardia/normal • Endoemterial ablation: Risk curettage
Ovarian mass Pelvic mass
Located at peripheral and pouch of Located at central of abnormal placentation in Urine artery
douglas subsequent preganancy embolisation
Move horizontal and vertical Move horizontal
Abdominal examination Consistency – soft (cyst form) Consistenscy – firm • Others: hemorrhages,
I: Scar, Distension # if hard/solid = malignancy infections
P: Tenderness, Mass
On bimanual examination; On bimanual examination;
P: Dullness - presence of adnexal mass - If move the mass towards xiphersternum,
A: Bruit the mass move. Thus, mass originate from
uterus.
Bimanual : have to know diff uterine and
Presence of ascites
ovary origin
and Speculum examination
You might also like
- IsoxsuprineDocument2 pagesIsoxsuprineAnreezahy Gnoihc63% (8)
- Laparascopic Uterine ElevatorDocument4 pagesLaparascopic Uterine Elevatorgeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- CASE Study Deepika3Document25 pagesCASE Study Deepika3Kavi rajput100% (5)
- L6 7 - REPRO RESPI DisordersDocument16 pagesL6 7 - REPRO RESPI DisordersRose Anne AbivaNo ratings yet
- CH 41 Drugs Affecting The Male Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesCH 41 Drugs Affecting The Male Reproductive Systemericka abasNo ratings yet
- Abdominal PDFDocument1 pageAbdominal PDFChakra BaktiNo ratings yet
- Algoritmo Fiebre de Origen DesconocidoDocument1 pageAlgoritmo Fiebre de Origen Desconocidoluisa gonzálezNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk Factors: EtiologyDocument1 pageNon-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk Factors: EtiologyDenise FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Fibroids HX TemplateDocument6 pagesFibroids HX TemplateJessica Kimmie RampaulNo ratings yet
- Gangguan Haid - PPT YudisDocument34 pagesGangguan Haid - PPT YudisIde Yudis TiyoNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding-Dr DagalaDocument51 pagesAbnormal Uterine Bleeding-Dr DagalaAnonymous yoa7t0No ratings yet
- Drug Study BevacizumabDocument1 pageDrug Study BevacizumabBARRISTERFLOWERSEAURCHIN6No ratings yet
- Menorrhagia (Heavy Menstrual Bleeding)Document55 pagesMenorrhagia (Heavy Menstrual Bleeding)Aizi DwimeilaNo ratings yet
- Atenolol 1Document4 pagesAtenolol 1Nicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Placenta Praevia and AbruptioDocument1 pageDifferential Diagnosis of Placenta Praevia and Abruptiojalan_zNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis Care Pathway MenorrhagiaDocument1 pageDiagnosis Care Pathway MenorrhagianadiyadieNo ratings yet
- Pulmo Oral - 240511 - 003625Document84 pagesPulmo Oral - 240511 - 003625sastirahulNo ratings yet
- AUBDocument26 pagesAUByayaslaras96No ratings yet
- ObsNGyn - Abnormal Uterine Bleeding AtfDocument9 pagesObsNGyn - Abnormal Uterine Bleeding AtfarongeremewNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 - Renal DisordersDocument4 pagesNCM 112 - Renal DisordersCailah Sofia SelausoNo ratings yet
- Sample Pathogenesis Pathophysiology.2Document4 pagesSample Pathogenesis Pathophysiology.2gladysfaye.reyes.osioNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding - FinalDocument2 pagesAbnormal Uterine Bleeding - FinalJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding - 407550 - 51433 - v1Document6 pagesAbnormal Uterine Bleeding - 407550 - 51433 - v1lord676No ratings yet
- Anorectal Disease and Common Anorectal DisordersDocument2 pagesAnorectal Disease and Common Anorectal DisordersIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Patient With Adenomyosis FINALDocument56 pagesApproach To A Patient With Adenomyosis FINALapi-3700579No ratings yet
- Amenorrhoea: 8 Semester ROLL NO: 90, 91, 92, 93, 94Document69 pagesAmenorrhoea: 8 Semester ROLL NO: 90, 91, 92, 93, 94Sharoon KumarNo ratings yet
- Urogynecology AssessmentDocument7 pagesUrogynecology Assessmentanne laureNo ratings yet
- Patient's Name: Alindajao, Filoteo Diagnosis: CAD Date of Admission: Sex: 58yo Age: Male Height/WeightDocument1 pagePatient's Name: Alindajao, Filoteo Diagnosis: CAD Date of Admission: Sex: 58yo Age: Male Height/WeightButts McgeeNo ratings yet
- Nephrology A (Mattheus) : HematuriaDocument10 pagesNephrology A (Mattheus) : HematuriaShekinah MalimbanNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing Endometriosis MO 18aug15 PDFDocument1 pageDiagnosing Endometriosis MO 18aug15 PDFRifki Hilman FauziNo ratings yet
- Pre Anesthetic EvaluationDocument1 pagePre Anesthetic EvaluationАндрій ДанильцівNo ratings yet
- CNS: Dizziness, Assessment History: Allergy ToDocument7 pagesCNS: Dizziness, Assessment History: Allergy To6teen_gurlNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument44 pagesAbnormal Uterine BleedingBezza Mae Roche CruzNo ratings yet
- O&G LO SlidesDocument60 pagesO&G LO Slideskatherine nunnNo ratings yet
- Endo Handouts (Prof. Perpetua)Document88 pagesEndo Handouts (Prof. Perpetua)Jayson Mherl GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Breast MassesDocument12 pagesBreast MassesTrivedi NisargNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Concept MapDocument1 pageBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia Concept MapSarah RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Uterine Atony: Group 3Document23 pagesUterine Atony: Group 3Trisha Mae MarquezNo ratings yet
- Tumors of The Head and NeckDocument5 pagesTumors of The Head and NeckMiguel CuevasNo ratings yet
- Hormone Replacement TherapyDocument24 pagesHormone Replacement TherapyFatima JamshaidNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Jenna JureckyDocument24 pagesAbnormal Uterine Bleeding: Jenna JureckyGeneNo ratings yet
- Management Menopause ToolkitDocument8 pagesManagement Menopause ToolkitJeffreyWengNo ratings yet
- 53 Year Old Woman Wanting To Start Hormone Replacement Therapy (Gy 5.3)Document24 pages53 Year Old Woman Wanting To Start Hormone Replacement Therapy (Gy 5.3)Fatima JamshaidNo ratings yet
- Menstrual DisordersDocument29 pagesMenstrual DisorderstuhinsinghNo ratings yet
- Algoritmo Peritoneal EffusionDocument2 pagesAlgoritmo Peritoneal EffusionJuliana Torres GarciaNo ratings yet
- Isolated Hematuria - Genitourinary Disorders - MSD Manual Professional EditionDocument3 pagesIsolated Hematuria - Genitourinary Disorders - MSD Manual Professional EditionleozdmNo ratings yet
- 7 Dengue FeverDocument6 pages7 Dengue FeverNicole HipolNo ratings yet
- Gynecological Assessment: DateDocument4 pagesGynecological Assessment: Dateanne laureNo ratings yet
- 3 HX Upper GI BleedingDocument1 page3 HX Upper GI Bleedingمحمد حسنNo ratings yet
- PATHOLOGY MAIN HANDOUT - ExtractDocument15 pagesPATHOLOGY MAIN HANDOUT - ExtractAshley Chloé UyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyJeraldine GumpalNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Ectopic PregnancyDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Ectopic PregnancyRaya cademaNo ratings yet
- Paediatric CardiologyDocument15 pagesPaediatric CardiologyAaron Nameer Abrar RahmanNo ratings yet
- P.O.C Endometriosis Externa Endometriosis Interna (Adenomyosis)Document1 pageP.O.C Endometriosis Externa Endometriosis Interna (Adenomyosis)kukadiyaNo ratings yet
- Endometrial PolyPDocument6 pagesEndometrial PolyPAnthony JosephNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- PATHOGYNEDocument1 pagePATHOGYNEaprilkate banagodosNo ratings yet
- اسسمنت ١Document7 pagesاسسمنت ١almayasa2002No ratings yet
- Ob WARDDocument7 pagesOb WARDNursingNooBNo ratings yet
- Gyne: Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Structural Abnormalities (PALM)Document6 pagesGyne: Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Structural Abnormalities (PALM)M MNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta. Final OutputDocument15 pagesAbruptio Placenta. Final OutputCharles Loriaga Cruz IINo ratings yet
- Feminism in India: at DefiningDocument6 pagesFeminism in India: at DefiningBhoomejaa SKNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System ReviewerDocument167 pagesReproductive System ReviewerRhyza Marie Lopez100% (1)
- Placenta Previa PhatoDocument2 pagesPlacenta Previa PhatoMarl Jarl E BayanesNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Humans: Chapter - I Reproduction SystemsDocument18 pagesSexual Reproduction in Humans: Chapter - I Reproduction Systemsrajendra110778No ratings yet
- Donna Shoupe: EditorDocument1,112 pagesDonna Shoupe: Editordr Farah Imad AliNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Endometriosis in Women Desiring FertilityDocument23 pagesTreatment of Endometriosis in Women Desiring FertilityVaisnavi Muthoovaloo67% (3)
- Jadwal Kegiatan Blok-18 Sistem ReproduksiDocument7 pagesJadwal Kegiatan Blok-18 Sistem Reproduksiicha chanNo ratings yet
- Gas Module 1 PDFDocument58 pagesGas Module 1 PDFHIEZEL BAYUGNo ratings yet
- Maternal Notes 1Document34 pagesMaternal Notes 1Mica Campoy CabinongNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2Document12 pagesLesson Plan 2Leonidah jeronoNo ratings yet
- Gynecology - Anatomy: Dr. Fidia MumtahanaDocument125 pagesGynecology - Anatomy: Dr. Fidia MumtahanaSonny JhaNo ratings yet
- Endometrial Cytology OriginalDocument37 pagesEndometrial Cytology Originalreuben kwotaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive AnatomyDocument28 pagesFemale Reproductive AnatomySuho Leexokleader KimNo ratings yet
- Vbac - YurDocument20 pagesVbac - YurkikiNo ratings yet
- Case Study 120Document2 pagesCase Study 120jhan jhanNo ratings yet
- Postnatal PalpationDocument21 pagesPostnatal PalpationAnonymous 4txA8N8etNo ratings yet
- Vera Nazarian, The Perpetual Calendar of InspirationDocument1 pageVera Nazarian, The Perpetual Calendar of InspirationMyoui HyeonNo ratings yet
- 1a. Reproductive OrgansDocument60 pages1a. Reproductive OrgansJerrald Meyer L. BayaniNo ratings yet
- Adorio Partograph ScenarioDocument2 pagesAdorio Partograph Scenariojonathan liboonNo ratings yet
- WhyWhy Feminism Is ObsoleteDocument2 pagesWhyWhy Feminism Is ObsoleteLukas E Koube0% (1)
- CH 19Document5 pagesCH 19Ryan Carlo IbayanNo ratings yet
- Science 10-Q3 M-EDocument2 pagesScience 10-Q3 M-Enelson dante jr.No ratings yet
- Supports of UterusDocument16 pagesSupports of UterusinnyNo ratings yet
- Cumulative RecordDocument4 pagesCumulative Recordtanmai nooluNo ratings yet
- Gynae T and D Expl - 1Document44 pagesGynae T and D Expl - 1vivekanurag97No ratings yet
- Vaginal Birth After Caesarean Section: Aternity UidelinesDocument12 pagesVaginal Birth After Caesarean Section: Aternity UidelinesNeeta AnandaNo ratings yet
- DysmenorrheaDocument2 pagesDysmenorrheacristin ungabNo ratings yet
- Prolaps UteriDocument7 pagesProlaps Uteridr.raziNo ratings yet