Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 3 Safety Precautions
Lesson 3 Safety Precautions
Uploaded by
ryekeaanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 3 Safety Precautions
Lesson 3 Safety Precautions
Uploaded by
ryekeaanCopyright:
Available Formats
Safety Precautions
Personal Safety Guidelines
These are general guidelines for all types of troubleshooting, installation, and maintenance
tasks. Take them seriously; they may keep you out of a dangerous situation, protect equipment
from damage and protect the environment.
Before repairing any electronic device, it is important to know the hazards and safety
factors. Use extreme care and follow these safety procedures at all times.
1. Remove all jewelry.
2. Always unplug the power cord before removing or re-installing any electrical component or
circuit board, or when performing maintenance on electrical equipment.
3. Do not touch any exposed circuit with power applied.
4. Only have power applied when taking voltage measurements or waveforms.
5. Insert test probes with one hand only. Do not insert probes with both hands. Keeping one
hand behind the student’s back or under the test bench will reduce the chance of fatal
electrocution. This is referred to as the one-hand rule.
6. Do not leave any objects loose on the equipment, such as screws, nuts, or washers. These
items can fall into the equipment.
7. Before handling or replacing IC processors, students should touch the outside metal of the
equipment and use an antistatic wrist strap that is connected to the chassis to be properly
grounded. Make sure that the equipment is grounded prior to removing its case. This
reduces ESD damage.
8. Do not troubleshoot electronic equipment without having appropriate documentation, unless
instructor approval is given.
9. Never solder any connection with the power on.
10. After soldering, look for possible solder splashes, cold solder joints, or damaged insulation.
11. Always maintain a clean and safe work area.
12. The student will not rush through the procedures.
13. The student should be certain about what is to be done. If the student is unsure about a
procedure, ask for help.
14. Do not touch anything if there are any doubts.
15. The instructor covers fire extinguisher locations, fire evacuation procedures, safety and
first-aid kit locations, and emergency phone numbers in class.
16. Shoes, shirt, and long pants are required when soldering and working on equipment.
17. Never work alone
Basic Lab Safety Principles
1. The workspace should be situated away from carpeted areas because carpets can cause the
buildup of electrostatic charges.
2. It should be a nonconductive surface.
PCHS Trainer Marikina Polytechnic College, Marikina City Lesson 3
Danilo S. Ibarrola Personal Computer Hardware Servicing Page 1
Safety Precautions
3. It should be distant from areas of heavy electrical equipment or concentrations of
electronics.
4. It should be free of dust.
5. It should have a filtered air system to reduce dust and contaminants.
6. Lighting should be adequate to see small details.
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
Static electricity is created whenever two materials are rubbed together and electrons are
transferred from one material to the other. This imbalance in electron distribution is equalized
when the charged objected is connected with a ground path, which causes a rapid transference of
electrons.
PCHS Trainer Marikina Polytechnic College, Marikina City Lesson 3
Danilo S. Ibarrola Personal Computer Hardware Servicing Page 2
Safety Precautions
Human senses cannot detect a static electric charge of less than 2500 volts. A static
electric charge of 3000 volts or more will create the familiar spark when you touch a light switch, a
piece of metal, or another person. It is not uncommon to create a static electric charge of up to
30,000 volts, by simply "shushing" across carpet wearing leather-soled shoes. With most
computer electronics running at three to five volts, it is easy to see how this static electric charge
can destroy these devices. In fact, only a 10-volt static discharge through a device rated at five
volts can destroy it.
Workspace Practices that Help Reduces ESD Potential
1. Use antistatic bags to store components
2. Use grounded mats on workbenches
3. Use grounded floor mats in work areas
4. Use antistatic wrist straps when working on computers
ESD Effects
Some microcircuits are more prone to ESD damage than others. Older Transistor-
Transistor Logic (TTL) chips are more robust than the newer Complementary Metal Oxide
Semiconductor (CMOS) chips.
To prevent destruction to components by ESD, static must be equalized between you and
the equipment being serviced.
Power Fluctuation
AC power fluctuations can cause data loss or hardware failure:
Blackouts, brownouts, noise, spikes, power surges
To help shield against power fluctuation issues, use power protection devices to protect the data
and computer equipment:
Surge suppressors
UPS
SPS
CAUTION: Never plug a printer into a UPS device. UPS manufacturers suggest not plugging a
printer into a UPS for fear of burning up the printer motor.
Proper Disposal
Batteries from portable computer systems may contain lead, cadmium, lithium, alkaline
manganese, and mercury. Recycling batteries should be a standard practice for a
technician.
Monitors contain up to 4 pounds of lead, as well as rare earth metals. Monitors must be
disposed of in compliance with environmental regulations.
Used printer toner kits and printer cartridges must be disposed of properly or recycled.
PCHS Trainer Marikina Polytechnic College, Marikina City Lesson 3
Danilo S. Ibarrola Personal Computer Hardware Servicing Page 3
Safety Precautions
Contact the local sanitation company to learn how and where to dispose of the chemicals
and solvents used to clean computers.
Proper Use of Antistatic Wrist Strap
Connect the cable to the metal chassis of the computer
Wrap the strap around your wrist
The connection will keep your body at the same voltage (potential) as the computer
Attach the wire on the same side of the equipment as the arm wearing the antistatic wrist
strap to keep the wire out of the way while you are working.
CAUTION: Never wear an antistatic wrist strap if you are repairing a monitor or CRT.
Proper Use of Hand Tools
Use the proper type and size of screwdriver by matching it to the screw. Phillips, Flat Head
and Hex are the most common types.
Do not over tighten screws because the threads may become stripped.
Caution: If excessive force is needed to remove or add a component, something may be
wrong.
Caution: Magnetized tools should not be used around electronic devices.
Caution: Pencils should not be used inside the computer because the pencil lead can act as
a conductor and may damage the computer components.
Proper Use of Cleaning Materials
To clean computers and accessories:
Use mild cleaning solution and lint-free cloth to clean computer cases, outside of monitor,
LCD screen, CRT screen, and mouse.
Use compressed air to clean heat sinks.
Use Isopropyl alcohol and lint-free swabs to clean RAM.
Use hand-held vacuum cleaner with a brush attachment to clean a keyboard.
CAUTION: Before cleaning any device, turn it off and unplug the device from the power
source.
PCHS Trainer Marikina Polytechnic College, Marikina City Lesson 3
Danilo S. Ibarrola Personal Computer Hardware Servicing Page 4
You might also like
- Ultimate Guide: Wiring, 8th Updated EditionFrom EverandUltimate Guide: Wiring, 8th Updated EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- MEP Site Construction FlowchartDocument5 pagesMEP Site Construction FlowchartAlaa AnwerNo ratings yet
- Comp Ed 1 Module 1 Week 1Document11 pagesComp Ed 1 Module 1 Week 1jennifer abadNo ratings yet
- CC 213 Week 1 StudentDocument10 pagesCC 213 Week 1 Studenthsjhs100% (1)
- Chapter 2 - Safe Lab Procedures and Tool UseDocument10 pagesChapter 2 - Safe Lab Procedures and Tool UseDharanya VNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Occupational Health and Safety Policies and ProceduresDocument5 pagesLesson 7 - Occupational Health and Safety Policies and ProceduresDyck Andre RoblesNo ratings yet
- Module 1 and 3Document12 pagesModule 1 and 3CABADONGA, Justin M.No ratings yet
- Install Computer Systems and NetworksDocument125 pagesInstall Computer Systems and NetworksMarlene G Padigos80% (5)
- APM100 Outdoor Power Supply System User Manual (V1.3)Document58 pagesAPM100 Outdoor Power Supply System User Manual (V1.3)Stephane70No ratings yet
- EGALLA Lec AssignmentDocument5 pagesEGALLA Lec AssignmentDerek C. EgallaNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 - Safe Lab Procedures and Tool UseDocument12 pagesChapter2 - Safe Lab Procedures and Tool UseCyril Jean GulmaticoNo ratings yet
- ECE102 Electronic Lab II Manual IIU MalaysiaDocument57 pagesECE102 Electronic Lab II Manual IIU Malaysiasteiner68100% (2)
- Lesson 1 PRACTICE OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY PROCEDURESDocument7 pagesLesson 1 PRACTICE OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY PROCEDURESKrizaleih QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Electronics Lab ManualDocument57 pagesElectronics Lab ManualaravindmalkajiNo ratings yet
- Testing TET113 NOTE 111Document16 pagesTesting TET113 NOTE 111bello musaNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet No 1Document7 pagesInformation Sheet No 1Froz WorksNo ratings yet
- Precautions: 1.1 Safety WarningDocument4 pagesPrecautions: 1.1 Safety WarningAngel BorsaniNo ratings yet
- ACTURA Flex 48330 PDFDocument96 pagesACTURA Flex 48330 PDFturand100No ratings yet
- Ricoh Aficio FX16 S - Ac104Document142 pagesRicoh Aficio FX16 S - Ac104RostocanieNo ratings yet
- Xerox WorkCentre PE16 Service ManualDocument132 pagesXerox WorkCentre PE16 Service Manualkarl_frederickNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.1 2Document8 pagesInformation Sheet 1.1 2ALLAN GABRIEL GOJOCONo ratings yet
- Module 2Document38 pagesModule 2WilfNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Safe Procedures & Tool UseDocument19 pagesChapter 2 - Safe Procedures & Tool UseamandegiNo ratings yet
- OHS Policies & ProceduresDocument7 pagesOHS Policies & ProceduresMark Emerson BernabeNo ratings yet
- G10 Safety PrecautionsDocument34 pagesG10 Safety PrecautionsJhoncarlo AliadoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 Occupational Safety and Health Module 1Document9 pagesLESSON 1 Occupational Safety and Health Module 1MELCHOR CASTRONo ratings yet
- Saftey MeasurmentDocument13 pagesSaftey MeasurmentHira IqbalNo ratings yet
- PPT01 ElectricalSafetyWSHrequirementsDocument29 pagesPPT01 ElectricalSafetyWSHrequirementsJohn TanNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual ECE1201Document56 pagesLab Manual ECE1201de_stanszaNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health and SafetyDocument3 pagesOccupational Health and SafetyErwin BenitezNo ratings yet
- User Manual Thermbox Lot5Document26 pagesUser Manual Thermbox Lot5andy_krskNo ratings yet
- Service Manual For Samsung MFP SCX 4016F 4216FDocument135 pagesService Manual For Samsung MFP SCX 4016F 4216FalephzeroNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Sec A1 & A2Document34 pagesElectrical Safety Sec A1 & A2jaganmohan20347No ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronics Lab Safety: DET 4313 Electric TechnologyDocument16 pagesElectrical & Electronics Lab Safety: DET 4313 Electric TechnologyKesalan TerasaNo ratings yet
- CSSQ3HANDTOOLSDocument21 pagesCSSQ3HANDTOOLSlouiskalixyNo ratings yet
- Lab SafetyDocument3 pagesLab SafetyAshrafAtallaNo ratings yet
- FP104 Computer Hardware Chapter 3 Computer Maintenance and Troubleshooting Part 1: Understand Safe Working ConditionsDocument20 pagesFP104 Computer Hardware Chapter 3 Computer Maintenance and Troubleshooting Part 1: Understand Safe Working ConditionsKali DasNo ratings yet
- PS48600-3-2900 Power Supply System User ManualDocument130 pagesPS48600-3-2900 Power Supply System User ManualFabricio IzaNo ratings yet
- Precautions: 1.1 Warning For SafetyDocument4 pagesPrecautions: 1.1 Warning For SafetyRostocanieNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 - Week1 OHS Policies and ProceduresDocument2 pagesGrade 10 - Week1 OHS Policies and ProceduresPurificacion, AnabeaNo ratings yet
- Observe Safety Rules When Working Inside The System and When Handling Computer Components. Avoid Electric Shock or Personal Injury by Observing The Following WarningDocument23 pagesObserve Safety Rules When Working Inside The System and When Handling Computer Components. Avoid Electric Shock or Personal Injury by Observing The Following WarningKent Erl Uson EmiuhcNo ratings yet
- Ict - CSS 10Document18 pagesIct - CSS 10Puche MaraNo ratings yet
- Instruction ManualDocument40 pagesInstruction ManualFORYOUMANo ratings yet
- 2.1.2 Safety MeasuresDocument3 pages2.1.2 Safety MeasuresLisha De LeonNo ratings yet
- Emerson ECM1500Document34 pagesEmerson ECM1500cristachedinuNo ratings yet
- 10 Dumb ThingsDocument2 pages10 Dumb ThingsKrishna KhandigeNo ratings yet
- Advanced Automotive Electronics and Electrical: TANG, Austine C. Betech - Maet 2BDocument4 pagesAdvanced Automotive Electronics and Electrical: TANG, Austine C. Betech - Maet 2BAustine TangNo ratings yet
- Netsure 2100 Series User ManualDocument29 pagesNetsure 2100 Series User ManualOrlee FranciscoNo ratings yet
- 01.-SAFETY. ElectronicsDocument3 pages01.-SAFETY. ElectronicsChillie Bronzal UllamotNo ratings yet
- Sierra Sable PCC671Document11 pagesSierra Sable PCC671Phany ValeciaNo ratings yet
- ACTURA OPTIMA 48200 (PS48165/3200) Power Supply System User ManualDocument46 pagesACTURA OPTIMA 48200 (PS48165/3200) Power Supply System User Manualtienhiep100% (1)
- Topic 2-Safe Lab Procedures and Tool Use PDFDocument24 pagesTopic 2-Safe Lab Procedures and Tool Use PDFPONDRICHE -TICIU CRISTIANNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety and Guidlines - ELECTRICAL INSTALLATIONDocument3 pagesElectrical Safety and Guidlines - ELECTRICAL INSTALLATIONTuhafeni HailekaNo ratings yet
- NetSure 731 A41 - UserManual - V1.3 - 20151022Document38 pagesNetSure 731 A41 - UserManual - V1.3 - 20151022TuanNguyenVanNo ratings yet
- Practical ElexDocument67 pagesPractical ElexAnthony SisonNo ratings yet
- Safety Requirement in Marine EngineeringDocument24 pagesSafety Requirement in Marine EngineeringR.W. SaputraNo ratings yet
- Quarter-1 Module-1 G10 CSSDocument12 pagesQuarter-1 Module-1 G10 CSSRhonalyn Angel GalanoNo ratings yet
- Netsure 801 Series Power Supply System User ManualDocument133 pagesNetsure 801 Series Power Supply System User ManualJavier RojoNo ratings yet
- Electricity Unplugged: A Beginner's Guide to Electrical SafetyFrom EverandElectricity Unplugged: A Beginner's Guide to Electrical SafetyNo ratings yet
- Socket AM2+: Stvep-Cbc TVE Specialization Lesson 9b Noveline C. TacataDocument4 pagesSocket AM2+: Stvep-Cbc TVE Specialization Lesson 9b Noveline C. TacataryekeaanNo ratings yet
- Computer Motherboard: Socket Type Manufacturer Status Processor TypesDocument4 pagesComputer Motherboard: Socket Type Manufacturer Status Processor TypesryekeaanNo ratings yet
- Computer Motherboard: Data Exchange in The MotherboardDocument4 pagesComputer Motherboard: Data Exchange in The MotherboardryekeaanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 System CaseDocument5 pagesLesson 7 System CaseryekeaanNo ratings yet
- Faster Internet and Network Connections Thru Hidden Windows TweaksDocument3 pagesFaster Internet and Network Connections Thru Hidden Windows TweaksryekeaanNo ratings yet
- OB2301W On BrightElectronicsDocument11 pagesOB2301W On BrightElectronicsIlago BenignoNo ratings yet
- As Built Plan: General NotesDocument1 pageAs Built Plan: General NotesBryll Jude Calaor MartinezNo ratings yet
- Manual de OperacionDocument102 pagesManual de OperacionGustavo HuertasNo ratings yet
- Standards For Cable Testing - 03 2015Document22 pagesStandards For Cable Testing - 03 2015Junior Ramirez Reyes100% (1)
- HIPASE-E 002-CP-300 Processor BoardDocument7 pagesHIPASE-E 002-CP-300 Processor BoardChi PhamNo ratings yet
- LG Package CatalogueDocument7 pagesLG Package CatalogueTechnical OfficeNo ratings yet
- Diamond DA40NG - ChecklistDocument26 pagesDiamond DA40NG - ChecklistJoão SantosNo ratings yet
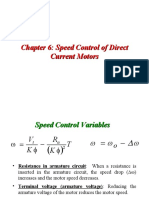
- Chapter6 Speed Control DCDocument36 pagesChapter6 Speed Control DCAzmi Shah Alias KhooNo ratings yet
- Pse - Fire AlarmDocument5 pagesPse - Fire AlarmArif KusumariyadiNo ratings yet
- XS650 PDFDocument215 pagesXS650 PDFphilNo ratings yet
- Outdoor Lighting Control Details SKi Village-ModelDocument1 pageOutdoor Lighting Control Details SKi Village-ModelAmr EidNo ratings yet
- RAMPAS DIY - DiySkateDocument80 pagesRAMPAS DIY - DiySkateC0STNo ratings yet
- Digital VLSI Design: About MeDocument2 pagesDigital VLSI Design: About Meavstar001No ratings yet
- Book Parts B-T1201C INGDocument45 pagesBook Parts B-T1201C INGricardo assaf marcheti100% (1)
- Rail-Road Shunting Vehicle - WINDHOFFDocument3 pagesRail-Road Shunting Vehicle - WINDHOFFKhhg AgddsNo ratings yet
- Tyco CSJA Data SheetDocument2 pagesTyco CSJA Data SheetDiego SantaNo ratings yet
- Uei DL39 Instruction ManualDocument7 pagesUei DL39 Instruction ManualBlue AlienNo ratings yet
- Kaise-Kb1270s - 12V 7ahDocument2 pagesKaise-Kb1270s - 12V 7ahcecilicastro60No ratings yet
- Richards Lock Up Kit For 2016+200Document7 pagesRichards Lock Up Kit For 2016+200chrisNo ratings yet
- Intel 8086: Atanu ShomeDocument23 pagesIntel 8086: Atanu Shomequasi paskiNo ratings yet
- Mos Integrated Circuit: Data SheetDocument62 pagesMos Integrated Circuit: Data SheetdgdNo ratings yet
- Xerox Phaser 8400 Parts & ServiceDocument335 pagesXerox Phaser 8400 Parts & ServiceBarry Paul SolywodaNo ratings yet
- TI Format LEDVANCE - Performance Solar StreetlightDocument7 pagesTI Format LEDVANCE - Performance Solar StreetlightSeno W. CahyadiNo ratings yet
- Appliance DiagnosisDocument76 pagesAppliance Diagnosisjergreen6100% (1)
- 1997 Harley Davidson Softail Models Parts CatalogDocument498 pages1997 Harley Davidson Softail Models Parts CatalogcoyoteassasinNo ratings yet
- The Effects of System Grounding & Probability of Arc Flash Reduction - I-Gard - Ajit Bapat - October 27 2014Document81 pagesThe Effects of System Grounding & Probability of Arc Flash Reduction - I-Gard - Ajit Bapat - October 27 2014add8742No ratings yet
- Specification Ranger DX800Document4 pagesSpecification Ranger DX800Nugraha SandyNo ratings yet
- Computer SkillsDocument99 pagesComputer SkillsBridget KarimiNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Resistant and Ultra-Pure Rotameters For Accurate Measurement of Liquids and GasesDocument18 pagesCorrosion Resistant and Ultra-Pure Rotameters For Accurate Measurement of Liquids and GasesMagin Idelfonso TorreblancaNo ratings yet