Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assets Liabilities (Debt) & Equity
Assets Liabilities (Debt) & Equity
Uploaded by
the learners club5Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assets Liabilities (Debt) & Equity
Assets Liabilities (Debt) & Equity
Uploaded by
the learners club5Copyright:
Available Formats
FIN 440 LECTURE 3
REVIEW OF BASIC CONCEPTS contd…
CHAPTER REFERENCE – CHP 2 & 3
Q. What is the letter to stockholders?
Q. What are the 4 key financial statements?
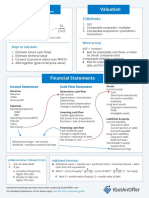
INCOME STATEMENT
SALES
- Cost of Goods Sold
GROSS PROFIT OPERATING ACTIVITIES
- Operating Expenses
OPERATING INCOME (EBIT)
- Interest Expense
EARNINGS BEFORE TAXES (EBT)
- Income Taxes
EARNINGS AFTER TAXES (EAT) FINANCING ACTIVITIES
- Preferred Stock Dividends
- NET INCOME AVAILABLE
TO COMMON STOCKHOLDERS
BALANCE SHEET
Assets Liabilities (Debt) & Equity
Current Assets Current Liabilities
Cash Accounts Payable
Marketable Securities Accrued Expenses
Accounts Receivable Short-term notes
Inventories Long-Term Liabilities
Prepaid Expenses Long-term notes
Fixed Assets Mortgages
Machinery & Equipment Equity
Buildings and Land Preferred Stock
Other Assets Common Stock (Par value)
Investments & patents Paid in Capital
Retained Earnings
• Current Assets: assets that are relatively liquid, and are expected to be converted to cash within a year.
- Cash, marketable securities, accounts receivable, inventories, prepaid expenses.
• Fixed Assets: machinery and equipment, buildings, and land.
• Other Assets: any asset that is not a current asset or fixed asset.
- Intangible assets such as patents and copyrights
• Net Working Capital (NWC) = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
• Capital Structure => Liabilities Vs Equity
• Capital Intensity => In general, higher the investment in fixed assets, higher is the risk of the company /
project
• Liquidity: Higher the NWC, higher is the liquidity, lower are the returns at lower risk and vice versa.
• Debt Capital: financing provided by a creditor.
• Short-term debt: borrowed money that must be repaid within the next 12 months.
– Accounts payable, other payables such as interest or taxes payable, accrued expenses, short-term
notes.
• Long-term debt: loans from banks or other sources that lend money for longer than 12 months.
• Equity Capital: shareholders’ investment in the firm.
• Preferred Stockholders: received fixed dividends, and have higher priority than common stockholders in
event of liquidation of the firm.
• Common Stockholders: residual owners of a business. They receive whatever is left after creditors and
preferred stockholders are paid.
Financial Analysis Components
1. Calculations: The interpretation
2. Comparisons: The comparison of the company to its past and comparison of the company to its industry
(Industry average)
3. Decision - Are our decisions maximizing shareholder wealth?
Catagories of Ratios
1. Liquidity
2. Activity
3. Debt
4. Profitability
5. Market
You might also like
- 2024 Becker CPA Financial (FAR) NotesDocument51 pages2024 Becker CPA Financial (FAR) Notescraigsappletree100% (4)
- SERIES 65 EXAM STUDY GUIDE 2021 + TEST BANKFrom EverandSERIES 65 EXAM STUDY GUIDE 2021 + TEST BANKNo ratings yet
- How To Read French Financial Statements PDFDocument4 pagesHow To Read French Financial Statements PDFJazzi SehrawatNo ratings yet
- The Giant Pool of Money NPR TranscriptDocument20 pagesThe Giant Pool of Money NPR Transcript498274929100% (1)
- Notes On Pledge, Mortgage, Chattel Mortgage and AntichresisDocument21 pagesNotes On Pledge, Mortgage, Chattel Mortgage and AntichresisJanetGraceDalisayFabrero80% (20)
- Accounting For ManagerDocument202 pagesAccounting For ManagerKHAWAJA MUHAMMAD HUZAIFA100% (1)
- Engineering Economics Reviewer Part 1 PDFDocument88 pagesEngineering Economics Reviewer Part 1 PDFagricultural and biosystems engineeringNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Ag Eng Revised 2011Document95 pagesPart 1 Ag Eng Revised 2011Zrrah Changitan0% (1)
- Cash Budgeting Examples.Document21 pagesCash Budgeting Examples.Muhammad azeem83% (6)
- Chapter 10PPTBBDocument49 pagesChapter 10PPTBBAnihaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document64 pagesLecture 6Zixin Gu100% (1)
- FinnanceDocument17 pagesFinnanceبكرة جاىNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet - Ratio AnalysisDocument49 pagesBalance Sheet - Ratio AnalysisKarishmaAshuNo ratings yet
- 1 Balance SheeetDocument15 pages1 Balance SheeetAdnan RizviNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 2 Laporan KeuanganDocument33 pagesKuliah 2 Laporan KeuanganAnanda SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document27 pagesSession 2I don't knowNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Book of Accountancy: Brilliant ProblemsDocument7 pagesUltimate Book of Accountancy: Brilliant ProblemsPramod Vasudev100% (1)
- Chapter 3-Accrual Accounting and The Balance SheetDocument2 pagesChapter 3-Accrual Accounting and The Balance SheetPriyanka KambleNo ratings yet
- Session 1 and 2 Introduction To FMDocument29 pagesSession 1 and 2 Introduction To FMPrachi PragyaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Slides - Introducing Financial StatementsDocument12 pagesModule 2 - Slides - Introducing Financial StatementsElizabethNo ratings yet
- 1/ The Balance Sheet: Financial Statements and Cash FlowDocument10 pages1/ The Balance Sheet: Financial Statements and Cash FlowBẢO NGUYỄN HUYNo ratings yet
- FABM2 (1st)Document3 pagesFABM2 (1st)7xnc4st2g8No ratings yet
- FINC6021 - Financial StatementsDocument126 pagesFINC6021 - Financial Statements尹米勒No ratings yet
- Format & ListDocument2 pagesFormat & ListJyotirmoy Chowdhury100% (1)
- Basic Principles of Accounting CH # 1Document7 pagesBasic Principles of Accounting CH # 1sameerdsportsmanNo ratings yet
- Accounting Finals 1 ReviewerDocument5 pagesAccounting Finals 1 ReviewerlaurenNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Global Accounting StandardsDocument16 pagesBenefits of Global Accounting StandardsJones EdombingoNo ratings yet
- The Analysis of The Balance Sheet and The Income StatementDocument42 pagesThe Analysis of The Balance Sheet and The Income Statementmusafir7777No ratings yet
- Balance Sheet: Mehwish KiranDocument28 pagesBalance Sheet: Mehwish KiranAlina ZubairNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument11 pagesIntroductionGokul BansalNo ratings yet
- solution-1412972Document3 pagessolution-1412972CA Sneha Gogad KothariNo ratings yet
- Overview 1Document23 pagesOverview 1Ismail MarzukiNo ratings yet
- Finance For Non Finance ExecutivesDocument48 pagesFinance For Non Finance ExecutivesKaneNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting: The Four Basic Financial StatementsDocument32 pagesFinancial Accounting: The Four Basic Financial StatementsMinto MathewNo ratings yet
- Financial InstrumentDocument62 pagesFinancial InstrumentNoor fatimaNo ratings yet
- A Balance Sheet:: More On Financial Statements ChapterDocument25 pagesA Balance Sheet:: More On Financial Statements ChapterCNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet: - Assets - Liabilities - Stockholder's EquityDocument11 pagesBalance Sheet: - Assets - Liabilities - Stockholder's EquitySASWAT MISHRANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NLKTDocument58 pagesChapter 2 NLKTPhan Lê Anh Đào100% (1)
- Introducción A Las FinanzasDocument47 pagesIntroducción A Las FinanzasLeslyNo ratings yet
- Understanding Financial Statements, Taxes, and Cash Flows Ch. 3 - Evaluating A Firm's Financial PerformanceDocument53 pagesUnderstanding Financial Statements, Taxes, and Cash Flows Ch. 3 - Evaluating A Firm's Financial PerformanceDhinar Ardhy SutrisnoNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument40 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisImtiaz MasroorNo ratings yet
- CH3 1Document64 pagesCH3 1Amanu WorkuNo ratings yet
- Topic 2Document48 pagesTopic 2Marie JulienNo ratings yet
- (Total Expenses) (Treasury Shares at Cost-Ordinary) (Dividends)Document2 pages(Total Expenses) (Treasury Shares at Cost-Ordinary) (Dividends)lykajbmNo ratings yet
- Balance SheetDocument1 pageBalance SheetKimm HuntNo ratings yet
- BF3326 Corporate Finance: Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument33 pagesBF3326 Corporate Finance: Introduction To Financial ManagementAmy LimnaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 (I)Document44 pagesUnit 2 (I)martaNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Book of AccountancyDocument8 pagesUltimate Book of AccountancyPramod VasudevNo ratings yet
- Listof AccountDocument2 pagesListof AccountNathalie MarNo ratings yet
- SFP ClasificationDocument3 pagesSFP ClasificationCygresy GomezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Understanding The Balance SheetDocument54 pagesChapter 2 - Understanding The Balance SheetNguyễn Yến NhiNo ratings yet
- Securities & Financial StatementsDocument4 pagesSecurities & Financial StatementsMuhammad Istiyansyah IdrisNo ratings yet
- Session 1 An Overview of Corporate FinanceDocument16 pagesSession 1 An Overview of Corporate Financekrishna priyaNo ratings yet
- A212 - Topic 2 - Slides (Part I)Document24 pagesA212 - Topic 2 - Slides (Part I)Teo ShengNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet s8 Shared 2021Document18 pagesBalance Sheet s8 Shared 2021nikhil gangwarNo ratings yet
- Commercial AccountingDocument16 pagesCommercial AccountingAaditya Pandey AmritNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke - 3 SOFPDocument2 pagesPertemuan Ke - 3 SOFPTommyNo ratings yet
- DCF Valuation: Formula: 3 MethodsDocument1 pageDCF Valuation: Formula: 3 Methodsmadhav madhavNo ratings yet
- Internal Control of Fixed Assets: A Controller and Auditor's GuideFrom EverandInternal Control of Fixed Assets: A Controller and Auditor's GuideRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Financial Accounting and Reporting Study Guide NotesFrom EverandFinancial Accounting and Reporting Study Guide NotesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Financial Analysis 101: An Introduction to Analyzing Financial Statements for beginnersFrom EverandFinancial Analysis 101: An Introduction to Analyzing Financial Statements for beginnersNo ratings yet
- FIN 440 Financial Forecasting, Planning, and Budgeting Chapter Reference - CHP 4Document4 pagesFIN 440 Financial Forecasting, Planning, and Budgeting Chapter Reference - CHP 4the learners club5100% (1)
- Suggested Ratios For Banks Deposit RatiosDocument5 pagesSuggested Ratios For Banks Deposit Ratiosthe learners club5No ratings yet
- Lab Assignment 4: Submitted in Group byDocument4 pagesLab Assignment 4: Submitted in Group bythe learners club5No ratings yet
- Assignment On Air Pollution and Thermal ExpansionDocument6 pagesAssignment On Air Pollution and Thermal Expansionthe learners club5No ratings yet
- Iceland Assignment 1Document11 pagesIceland Assignment 1sanchkNo ratings yet
- Personal Propert Security Act OutlineDocument1 pagePersonal Propert Security Act OutlineMJ CreceNo ratings yet
- Villareal Vs Ramirez - DigestDocument2 pagesVillareal Vs Ramirez - DigestRay John Uy-Maldecer AgregadoNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Auditing With Answer UcpDocument7 pagesFinal Exam Auditing With Answer UcpJelyn RuazolNo ratings yet
- Pledge: Section 172 The Indian Contract Act 1872 Defines The Contract of Pledge AsDocument14 pagesPledge: Section 172 The Indian Contract Act 1872 Defines The Contract of Pledge AsTARUN RAJANINo ratings yet
- BCTA UJ Question PaperDocument14 pagesBCTA UJ Question PaperFresh LoverzzNo ratings yet
- Accepted For Value RulesDocument6 pagesAccepted For Value RulesChad Lange97% (29)
- Economy (2011-21) Prelims QuestionsDocument36 pagesEconomy (2011-21) Prelims QuestionsChinmay JenaNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis On Optcl, BBSRDocument47 pagesRatio Analysis On Optcl, BBSRSusmita Nayak100% (1)
- "Debt Free Living God's Way": The E-BookDocument63 pages"Debt Free Living God's Way": The E-BookTushaliNo ratings yet
- #52 PCIB vs. FrancoDocument2 pages#52 PCIB vs. FrancoHarry Dave Ocampo PagaoaNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Financial ManagementDocument16 pagesApproaches To Financial Managementarko banerjeeNo ratings yet
- BDK Engineering Industries Put LTD HubliDocument80 pagesBDK Engineering Industries Put LTD HubliRuishabh RunwalNo ratings yet
- Ch05 P24 Build A ModelDocument5 pagesCh05 P24 Build A ModelKatarína HúlekováNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Financing: An: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument20 pagesLong-Term Financing: An: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinPhạm Đăng KhoaNo ratings yet
- Sec D CMA Part 2.Document2 pagesSec D CMA Part 2.shreemant muniNo ratings yet
- DataDocument396 pagesDataCésar ChávezNo ratings yet
- Reyes v. SierraDocument2 pagesReyes v. SierraGabe RuaroNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Financial Accounting TheoryDocument13 pagesTest Bank Financial Accounting TheoryPhilip Castro100% (3)
- SRK Food Products Private Limited (In Liquidation) Public Announcement For E-AuctionDocument1 pageSRK Food Products Private Limited (In Liquidation) Public Announcement For E-AuctionSneha AdepuNo ratings yet
- 3 (A) - History of Stock Markets, Players, FundsDocument2 pages3 (A) - History of Stock Markets, Players, FundsAneesh KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Financial Management: Week 1Document314 pagesFinancial Management: Week 1Hien NguyenNo ratings yet
- 5 6125287842781331528Document15 pages5 6125287842781331528Anuj SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio AnalysisDocument2 pagesFinancial Ratio AnalysisFayad CalúNo ratings yet
- Government Security MarketDocument18 pagesGovernment Security MarketHarsh SenNo ratings yet
- BNU1501 - Assessment 4-Semester 2-2023Document7 pagesBNU1501 - Assessment 4-Semester 2-2023bonokuhledlamini60No ratings yet
- BÀI TẬP Ở NHÀ SỐ 4 - PHẦN II-CHƯƠNG 4-UNDERSTANDING INTEREST RATEDocument2 pagesBÀI TẬP Ở NHÀ SỐ 4 - PHẦN II-CHƯƠNG 4-UNDERSTANDING INTEREST RATENguyen KhanhNo ratings yet