Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A.Rhetoric-how Is It Conveyed Standard Process of
A.Rhetoric-how Is It Conveyed Standard Process of
Uploaded by
Joanna TamanoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A.Rhetoric-how Is It Conveyed Standard Process of
A.Rhetoric-how Is It Conveyed Standard Process of
Uploaded by
Joanna TamanoCopyright:
Available Formats
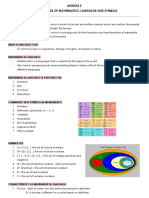
MMW Connectives (operations)- to link nos.
and symbols
Angle Bisector yung Punctuations(grouping symbols)-to gather & cluster
tawag sa dashed line a group of nos. and symbols.
L1/ L2 (smaller part of 2. Concise- non-ambiguous, never rambles
the triangle) =1.618 extraneous/ unnecessary info.
L/L1= L1/L2 Example: well-stated definition
L= total lengths A rectangle is a quadrilateral all four angles of w/c are
L1= larger length all right angles.
3. Precise- is systematic; uses symbols to make it
Pentagram= Star accurate and exact.
- Made up of Example: use the pi symbol rather than 3.14; 1/3 rather
peripheral/ than 0.33; the symbol phi rather than 1.618
golden 4. Powerful- can be applied in each and every field
triangles. Theories in physics, economics, biology, engineering,
and other fields are stated in the language of
Logarithmic Spiral mathematics.
Is generated by using golden triangles. It forms 5. Non-temporal- has no tense of verbs
logarithmic spiral (also known equiangular spiral) The “is” 2000 years ago is still “is” today.
to trace the vertices of the
golden triangles. Mathematical Expression (phrase in English language)
- The subject in ordinary language
Examples: 5+2; 3x+4y
Mathematical Sentence- statement of mathematical
expressions forming a complete thought; can be true of
false.
Example: 5+2= square root of 49
Lesson 4
Mathematics as a Language
Progression in mathematics= abstraction
We have to learn the symbols in mathematics to
learn the language of mathematics.
Structure of Mathematical Language has its own form
A.Rhetoric- how is it conveyed; standard process of
presenting a mathematical concept.
1. Definition
2. Theorem- a general result; absolute truths;
(other terms: proposition, lemma, corollary)
3. Proof- to prove the result
B. Grammar and Syntax
- Symbols and words put together to form a
complete thought.
C. Logic- soundness of thought and reasoning.
Characteristics of Mathematical Language
1. Comprehensive- mathematical language has a
set of vocabulary and parts of speech.
Noun (numbers)-represent quantities
Pronouns(variables)-letters/symbols
Verbs (relation symbols)- for comparison/relations
You might also like
- 2 Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument30 pages2 Mathematical Language and SymbolsEunice Bumanglag100% (6)
- Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument4 pagesMathematics in The Modern WorldMae AbonalNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Language and SymbolsDocument52 pagesMathematics Language and SymbolsPrince Kerwin50% (2)
- Mathematical Languages and SymbolsDocument2 pagesMathematical Languages and SymbolsJoyce Salamat100% (6)
- Strategies For Unlocking Word MeaningsDocument3 pagesStrategies For Unlocking Word MeaningsChema Paciones100% (1)
- The Art of Subtitling: Before WatchingDocument1 pageThe Art of Subtitling: Before WatchingБибаNo ratings yet
- PatpatDocument5 pagesPatpatoepe.saniana.uiNo ratings yet
- GEC-4 Chapter 2 - Lesson 1Document4 pagesGEC-4 Chapter 2 - Lesson 1Koleen Lhyte T. UYNo ratings yet
- Copy Lecture Guide GEC004 PDFDocument35 pagesCopy Lecture Guide GEC004 PDFRachel Peters0% (1)
- Lesson 1:: TransformationDocument6 pagesLesson 1:: TransformationAPRIL JOY MANZANILLANo ratings yet
- Module 2Document7 pagesModule 2Edrick G. EsparraguerraNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Mathematical LanguageDocument4 pagesModule 2 Mathematical LanguageErizza JavierNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document17 pagesChapter 2brynidea232425No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Part 1 MMWDocument13 pagesChapter 2 Part 1 MMWJob Dave ToledoNo ratings yet
- MATH 101 MODULE 2 Mathematical Language and SymbolDocument6 pagesMATH 101 MODULE 2 Mathematical Language and SymbolMaria Izabelle QuemiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Mathematical Language & Symbols - Part 1Document37 pagesLesson 2 - Mathematical Language & Symbols - Part 1ENGR. ADRIEL MARASIGANNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 4Document16 pagesModule 1 Lesson 4alex medinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 2.1Document6 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 2.1Shereen MendizabalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument32 pagesChapter 2 - Mathematical Language and SymbolsAlthea Faye Rabanal100% (1)
- Module 2Document14 pagesModule 2basanjelica018No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Part 1Document7 pagesChapter 2 - Part 1Sharmain AbotNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2: Mathematical Language and Symbol (9 Hours)Document7 pagesUNIT 2: Mathematical Language and Symbol (9 Hours)Ell VNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument10 pagesReviewer in Mathematics in The Modern Worldlei liieeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Mathematecal LanguageDocument25 pagesChapter 2 Mathematecal LanguageririricelNo ratings yet
- Module 2-Mathematical Language and Symbols Except LAsDocument26 pagesModule 2-Mathematical Language and Symbols Except LAsAngel PicazoNo ratings yet
- Language of MathematicsDocument5 pagesLanguage of MathematicsNestor Gutiza Jr.No ratings yet
- Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument8 pagesMathematical Language and SymbolsJAVIER, KISSIE CZARINNENo ratings yet
- Christine V. Mollejon: Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument17 pagesChristine V. Mollejon: Mathematical Language and SymbolsKervi RiveraNo ratings yet
- MMWDocument5 pagesMMWPrecious ViterboNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1 Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument8 pagesChapter 2.1 Mathematical Language and SymbolsC J A SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 LM 2Document6 pagesChapter 2 LM 2Liandysan23No ratings yet
- Mathematical Language 2Document27 pagesMathematical Language 2Althea Faye RabanalNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument5 pagesMathematics in The Modern WorldElvira Monica SayoNo ratings yet
- Midterm Reviewer ModmathDocument9 pagesMidterm Reviewer ModmathAaron AbareNo ratings yet
- Unit I - B (Part 1)Document13 pagesUnit I - B (Part 1)Angelo Rebayla OribiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Day 1Document32 pagesUnit 2 - Day 1JCG XIIINo ratings yet
- Symbolic Language of MathematicsDocument3 pagesSymbolic Language of MathematicsMernotz MakuletNo ratings yet
- MMW Lec3Document14 pagesMMW Lec3Shinneth Cris Salvador WapilleNo ratings yet
- Math 0 - Module 1.2 PolynomialsDocument11 pagesMath 0 - Module 1.2 PolynomialsWhelance TomboconNo ratings yet
- Tmk1 Pbis4428 Diananggraeni 042078496Document6 pagesTmk1 Pbis4428 Diananggraeni 042078496reza mahardhiNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Quennie Kent Rosal DaguilNo ratings yet
- A Self-Instructional Module On Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument29 pagesA Self-Instructional Module On Mathematics in The Modern WorldGeorge Vincent SismarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MATHDocument36 pagesChapter 2 MATHllae92892No ratings yet
- Central Bicol State University of Agriculture: Module in Gec 2: Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument24 pagesCentral Bicol State University of Agriculture: Module in Gec 2: Mathematics in The Modern WorldHazel Castillo Delos AngelesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document14 pagesChapter 2LIGAWAD, MELODY P.No ratings yet
- Math 1. Unit 1.module 1-2Document25 pagesMath 1. Unit 1.module 1-2Chen HaoNo ratings yet
- Math21 - Chapter 2Document40 pagesMath21 - Chapter 2Jessica SergioNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledKyla RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Module 2 MMWDocument28 pagesModule 2 MMWJAN HENRYCK RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Gned 03 ReviewerDocument13 pagesGned 03 ReviewerRosemary MarquezNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument8 pagesModule 2 - Mathematical Language and SymbolsJala, Jan Kylle B.No ratings yet
- Chap 2 StudentsDocument40 pagesChap 2 Studentsmauvegreige8No ratings yet
- Math in The Modern World ReviewerDocument7 pagesMath in The Modern World Reviewerivy saludesNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument72 pagesMathematical Language and SymbolsJurren Valderama Pigao100% (1)
- Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument18 pagesMathematical Language and SymbolsMaricel CarreonNo ratings yet
- Math in The Modern World ReviewerDocument31 pagesMath in The Modern World ReviewerJAY CEE SACRONo ratings yet
- MMW Midterm ReviewerDocument10 pagesMMW Midterm ReviewerSean NaresNo ratings yet
- Symbolic Language of MathematicsDocument3 pagesSymbolic Language of MathematicsJr DiazNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Language: GEC 002 - Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument13 pagesMathematical Language: GEC 002 - Mathematics in The Modern WorldCherolyn Abajeto LawaniNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Language Is PreciseDocument2 pagesMathematical Language Is Precisesunghoon best boyNo ratings yet
- Essential Elements of Architectural AcousticsDocument4 pagesEssential Elements of Architectural AcousticsJoanna TamanoNo ratings yet
- Objectives of A BuildingDocument7 pagesObjectives of A BuildingJoanna TamanoNo ratings yet
- Re100 - Dimensions - TamanoDocument8 pagesRe100 - Dimensions - TamanoJoanna TamanoNo ratings yet
- Reaction PaperDocument8 pagesReaction PaperJoanna TamanoNo ratings yet
- Universidad Popular Del Cesar: UNIT 3: It Was Painted by Bansky! Group: Upc06Document2 pagesUniversidad Popular Del Cesar: UNIT 3: It Was Painted by Bansky! Group: Upc06Anha Noriega BarrazaNo ratings yet
- RC-AKICFI Preliminary Pages TemplateDocument10 pagesRC-AKICFI Preliminary Pages TemplateAbudani GoteNo ratings yet
- Partitive in Italian Giusti 2021Document44 pagesPartitive in Italian Giusti 2021PamNo ratings yet
- Class 4 Eng Grammar Lesson 6 The Noun NumberDocument5 pagesClass 4 Eng Grammar Lesson 6 The Noun NumberKaruna VermaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: Business English Success Esforay GMBHDocument6 pagesReported Speech: Business English Success Esforay GMBHNadri KulturaNo ratings yet
- 3 IC Varieties and Registers of Spoken and Written LanguageDocument69 pages3 IC Varieties and Registers of Spoken and Written LanguageLiane BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Third Conditional Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesThird Conditional Lesson Planaliciacg67No ratings yet
- Think BE SB 4Document11 pagesThink BE SB 4supergiuz1986No ratings yet
- Improving Students Speaking Ability Through Repetition DrillDocument10 pagesImproving Students Speaking Ability Through Repetition DrillRoyana Joy FuentesNo ratings yet
- Teaching Rare DetailedDocument11 pagesTeaching Rare DetailedpetitlutinNo ratings yet
- LESSON-EXEMPLAR-IN-ENGLISH-4-CO1-2021-3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesLESSON-EXEMPLAR-IN-ENGLISH-4-CO1-2021-3rd QuarterBEVERLY ROSETENo ratings yet
- Present Form: (Simple / Continuous / Perfect Simple) Will / Be Going To / Imperative / Modal InfinitiveDocument4 pagesPresent Form: (Simple / Continuous / Perfect Simple) Will / Be Going To / Imperative / Modal InfinitiverosarioNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Unit 1 Language Sách Global Success L P 10Document12 pagesLesson Plan Unit 1 Language Sách Global Success L P 10Thuong NgoNo ratings yet
- Asking Giving SuggestionDocument30 pagesAsking Giving Suggestionhermanelly ramadhani100% (1)
- Interrogative Question Sentences Learn English Grammar RajeeveltDocument9 pagesInterrogative Question Sentences Learn English Grammar RajeeveltmarikaNo ratings yet
- My Mother Are CookingDocument80 pagesMy Mother Are CookingKate FernandezNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1 Patterns of CitationDocument1 pagePractical Research 1 Patterns of CitationChad CadizalNo ratings yet
- Logic of English Spelling RulesDocument4 pagesLogic of English Spelling RulesArturo Gallardo100% (1)
- Translating: Dita Septi Andini Yuniharti KhoirunisaDocument37 pagesTranslating: Dita Septi Andini Yuniharti KhoirunisaYuniharti KhoirunisaNo ratings yet
- Class V Eng KeyDocument5 pagesClass V Eng KeyNouzeen AhmedNo ratings yet
- CAE Students HandbookDocument12 pagesCAE Students HandbookDavid CastroNo ratings yet
- Gos ImtihonDocument84 pagesGos ImtihonstalkeremptiNo ratings yet
- Mastermind 1 Unit 11 Grammar 1Document11 pagesMastermind 1 Unit 11 Grammar 1Mauricio Martinez GambaNo ratings yet
- 1994 - Bloom - Language Acquisition: Core ReadingsDocument46 pages1994 - Bloom - Language Acquisition: Core ReadingsCarolina RochaNo ratings yet
- Portfolio - TKT Practice - Students'Document4 pagesPortfolio - TKT Practice - Students'Miguel Alberto Anabalón TorresNo ratings yet
- Larimerla 2 1Document3 pagesLarimerla 2 1api-706267136No ratings yet
- 4 кл ктп 2022-2023Document8 pages4 кл ктп 2022-2023Бектемисова КуляндаNo ratings yet
- Simple Present and Frequency Adve3rbsDocument14 pagesSimple Present and Frequency Adve3rbsKevinNo ratings yet