Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Midterm Exam Ee Electives Ramos Alyssa Maren Pipo
Midterm Exam Ee Electives Ramos Alyssa Maren Pipo
Uploaded by
Alyssa Ramos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesProtective relays are devices that detect abnormal or dangerous conditions on power systems and initiate control actions. They are not necessary for normal operation but are important for responding to faults. When applying protective relays, a balance must be struck between reliability and security. Relay performance is difficult to evaluate but can generally be categorized as correct operation, incorrect operation, or inconclusive. Power systems divide protection into zones like generators, transformers, lines, and loads, with each having primary protective devices. Engineers follow checklists covering system diagrams, equipment details, existing protection issues, and more to properly apply protective relays. Utilities are responsible for applying, designing, testing, and maintaining relays within their territories from generation to customer interfaces. New
Original Description:
Original Title
MIDTERM EXAM EE ELECTIVES RAMOS ALYSSA MAREN PIPO
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentProtective relays are devices that detect abnormal or dangerous conditions on power systems and initiate control actions. They are not necessary for normal operation but are important for responding to faults. When applying protective relays, a balance must be struck between reliability and security. Relay performance is difficult to evaluate but can generally be categorized as correct operation, incorrect operation, or inconclusive. Power systems divide protection into zones like generators, transformers, lines, and loads, with each having primary protective devices. Engineers follow checklists covering system diagrams, equipment details, existing protection issues, and more to properly apply protective relays. Utilities are responsible for applying, designing, testing, and maintaining relays within their territories from generation to customer interfaces. New
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesMidterm Exam Ee Electives Ramos Alyssa Maren Pipo
Midterm Exam Ee Electives Ramos Alyssa Maren Pipo
Uploaded by
Alyssa RamosProtective relays are devices that detect abnormal or dangerous conditions on power systems and initiate control actions. They are not necessary for normal operation but are important for responding to faults. When applying protective relays, a balance must be struck between reliability and security. Relay performance is difficult to evaluate but can generally be categorized as correct operation, incorrect operation, or inconclusive. Power systems divide protection into zones like generators, transformers, lines, and loads, with each having primary protective devices. Engineers follow checklists covering system diagrams, equipment details, existing protection issues, and more to properly apply protective relays. Utilities are responsible for applying, designing, testing, and maintaining relays within their territories from generation to customer interfaces. New
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
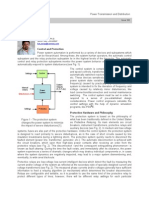
POWER SYSTEM PROTECTION 1
PROTECTIVE RELAY
Protective relay as “a relay whose function is to detect
defective lines or apparatus or other power system conditions of an
abnormal or dangerous nature and to initiate appropriate control
circuit action” (IEEE 100). Relaying is nonprofit, non
revenue-producing item that is not necessary in the normal operation
of an electrical power unless there is a faulty situation occurred.
Decision making ability must be used while applying a protective
relaying in order to balance between solidity and security.
As it was said in the Powerpoint , it is hard to evaluate an
individual relay’s performance. Performing relay operations may be
categorized as, correct (95% to 99%), incorrect (failure to trip or
false tripping and no conclusion. The six categories of the
protection zones are generators and generator-transformer unit,
transformers, buses, lines (transmission, subtransmission, and
distribution), utilization equipments (motors, static loads, or other),
and lastly the capacitor or reactor banks ( when separately
protected). Each category have their own designed primary
protection. Each protection have their own process to protect the
adjacent equipment.
There’s a check list produced to guide the consultants,
manufacturer, and other engineers. It was developed for so many
years to assist. The information for applications are as follows, (1)
Single-line diagram of the system or area involved, (2) Impedance
and connections of the power equipments, system frequency, voltage,
and phase sequence, (3) unless new, existing protection and
problems, (4) Operating procedures, and practices affecting the
protection, (5) Importance of the protection; pilot, nonpilot, and so on,
(6) System fault study, (7) Maximum load and system swing limits, (8)
CT and VT locations, connections and ratios, (9) Future expansions
expected or anticipated. These are very useful for the operating
personnel in order for them to know the cause and to prevent the
re-occurence.
Each utility owned have there own protection, which
exist within their territory, which included generating plants,
transmission and distribution system, down to the point of interface
with the customer. The utility are the ones who are responsible for
the application, design, construction, settings, testing, and the
maintenance. It was said in the Powerpoint that the power industry
doesn’t change the technical and practical aspect that are related to
the application of the power system protection, but it does have an
impact when the protection process was carried out. If they present
out a new protection system this things must be considered
resources, must be familiar with the concept of the power system
planning process, power industries must have good documentation
and an exchange in information in order to conduct studies and to
verify the information, hazard must be identified and have an
appropriate protection system applied, uniform design must be
implemented.
Given the significant structural changes in the power
industry , the standards and procedures must be develop to facilitate
efficient market operation and ensuring the system operation.
Protection requirements regarding issues related to the reliability
and safety of the electrical system must be develop as part of the
procedure. Although damage to equipment can be costly to the
owner, these failures also present challenges to the reliability of
operation of the electrical system. Minimizing the range and are of
failure. Ensure that faults are detected and fixing in in time as the
electrical system must remain stable.
RAMOS, ALYSSA MAREN P.
EE ELECTIVES
You might also like
- Training - Power System Protection - AREVADocument461 pagesTraining - Power System Protection - AREVAMallikarjun Reddy100% (52)
- Introduction To Protection Switchgear & Protection Unit 1Document150 pagesIntroduction To Protection Switchgear & Protection Unit 1padmajasiva100% (19)
- 01 - Overview of Protection FundamentalsDocument28 pages01 - Overview of Protection FundamentalsM Kumar MarimuthuNo ratings yet
- Protection CoordinationSiemensIncDocument3 pagesProtection CoordinationSiemensIncMarcWorldNo ratings yet
- Reliabilty of Protection Systems What Are The Real ConcernsDocument16 pagesReliabilty of Protection Systems What Are The Real ConcernsZunairaNazirNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Power System Protection in The Post-Restructuring EraDocument7 pagesAspects of Power System Protection in The Post-Restructuring ErakhkamalNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection PDFDocument12 pagesPower System Protection PDFBala MNo ratings yet
- Protection SettingsDocument33 pagesProtection SettingsirfanWPK100% (1)
- Design Protection SystemDocument147 pagesDesign Protection SystemchcrrNo ratings yet
- Protective Relay Maintenance and Application Guide: BackgroundDocument226 pagesProtective Relay Maintenance and Application Guide: BackgroundManeqyNo ratings yet
- Training Power System Protection AREVA PDFDocument461 pagesTraining Power System Protection AREVA PDFhiralalnhpc100% (4)
- 01b - Fundamentals of ProtectionDocument38 pages01b - Fundamentals of ProtectionAbdul MoizNo ratings yet
- Issues of Reliability and Security in Distributed Autonomous Power SystemsDocument17 pagesIssues of Reliability and Security in Distributed Autonomous Power SystemsHarjit Singh MangatNo ratings yet
- Development of A Cost-Effective, Smart Early Warning System For Improving The Reliability of Electrical SubstationsDocument5 pagesDevelopment of A Cost-Effective, Smart Early Warning System For Improving The Reliability of Electrical Substationsmayalasan1No ratings yet
- Important Considerations When Design Protection System.: B - Over Current and Earth FaultDocument16 pagesImportant Considerations When Design Protection System.: B - Over Current and Earth FaultShafeek GhreebNo ratings yet
- Basic of Protection SystemsDocument36 pagesBasic of Protection SystemsguntadiNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Relays For Overhead Line ProtecDocument8 pagesAdaptive Relays For Overhead Line Protecjose_sa_3No ratings yet
- The Role of Protection Performance Audits in The Lifetime Management of Protection SystemsDocument10 pagesThe Role of Protection Performance Audits in The Lifetime Management of Protection Systemssno-koneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - INTRODUCTIONDocument7 pagesChapter 1 - INTRODUCTIONMark Loyd ColoniaNo ratings yet
- Ect 148Document20 pagesEct 148Aceel FitchNo ratings yet
- X Paper 19Document17 pagesX Paper 19mohdfirdausNo ratings yet
- Power System RelayingDocument22 pagesPower System RelayingKhairul AshrafNo ratings yet
- Coordination of Relays, Reclosers, and Sectionalizing Fuses For Overhead Lines in The Oil PatchDocument8 pagesCoordination of Relays, Reclosers, and Sectionalizing Fuses For Overhead Lines in The Oil PatchluhusapaNo ratings yet
- ProposalDocument4 pagesProposaldattrinh2204No ratings yet
- Protection of Synchronous GeneratorsDocument117 pagesProtection of Synchronous GeneratorsprotectionworkNo ratings yet
- PNNL 24843Document196 pagesPNNL 24843FabSan21No ratings yet
- Study of Impedance Relay: Mr. Nilesh Pangare, Mr. R. S. DesaiDocument7 pagesStudy of Impedance Relay: Mr. Nilesh Pangare, Mr. R. S. DesaierpublicationNo ratings yet
- Study Committee B5 Colloquium 2007 October 15-20 Madrid, SPAINDocument13 pagesStudy Committee B5 Colloquium 2007 October 15-20 Madrid, SPAINraghavendran raghuNo ratings yet
- Do Utilities Still Need Stand Alone Disturbance Recorders?Document7 pagesDo Utilities Still Need Stand Alone Disturbance Recorders?Akhtar CoolNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Adaptative Overcurrent Protection Scheme Applied To An Industrial Plant With Cogeneration UnitsDocument5 pagesCase Study: Adaptative Overcurrent Protection Scheme Applied To An Industrial Plant With Cogeneration UnitsAlexander ToyoNo ratings yet
- Protection of Electrical SystemDocument34 pagesProtection of Electrical SystemDan C. LabagnoyNo ratings yet
- 26 Relay Testing Techniques, Requirements, Considerations MDocument8 pages26 Relay Testing Techniques, Requirements, Considerations Mgagan0312No ratings yet
- Industrial SafetyDocument7 pagesIndustrial SafetymuneebNo ratings yet
- Narrative On General Practice RelayDocument7 pagesNarrative On General Practice RelaySasquatchCornNo ratings yet
- PROTMAN2Document9 pagesPROTMAN2David DuncanNo ratings yet
- Australian Protection Symposium 2013: Add Your Voice To The Future of Electrical ProtectionDocument4 pagesAustralian Protection Symposium 2013: Add Your Voice To The Future of Electrical ProtectionMuruganNo ratings yet
- Paper ID 120Document4 pagesPaper ID 120Sanjay ShelarNo ratings yet
- 6156 WPRC DynamicSimulations 20031002 WebDocument34 pages6156 WPRC DynamicSimulations 20031002 WebYM6BNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Fuzzy Evaluation Algorithm For Power System Protection Security AssessmentDocument8 pagesHybrid Fuzzy Evaluation Algorithm For Power System Protection Security Assessmentpaisul pareeNo ratings yet
- CIGRE 2010: 21, Rue D'artois, F-75008 PARISDocument8 pagesCIGRE 2010: 21, Rue D'artois, F-75008 PARISkponramNo ratings yet
- Relay Coordination 1 PDFDocument5 pagesRelay Coordination 1 PDFNikhil SainiNo ratings yet
- Final - Version - Buscano, Jon Hermie AlobDocument23 pagesFinal - Version - Buscano, Jon Hermie Alobapi-20012905No ratings yet
- Integrati On Ensí G Timing, Etc.: 1.2 Typical Protective Relays and Relay SystemsDocument3 pagesIntegrati On Ensí G Timing, Etc.: 1.2 Typical Protective Relays and Relay Systemsbryan eduardo villegas carrascoNo ratings yet
- Examination of Electromechanical Over-Current Relay Characteristics by Using Experimental and ANN MethodsDocument6 pagesExamination of Electromechanical Over-Current Relay Characteristics by Using Experimental and ANN MethodsAsad AliNo ratings yet
- Protection, Discrimination and Restricted Earth Fault (REF) StudiesDocument4 pagesProtection, Discrimination and Restricted Earth Fault (REF) Studiescloobpsp100% (1)
- Wide Area ProtectionDocument27 pagesWide Area ProtectionRamesh KannanNo ratings yet
- Securoty Analysis and OptimizationDocument22 pagesSecuroty Analysis and Optimizationanoopeluvathingal100No ratings yet
- Differential Protection and Distance Protection SelectivityDocument3 pagesDifferential Protection and Distance Protection SelectivityBogdan BogdanNo ratings yet
- Nerc Guideline: Security Guidelines For The Electricity Sector: Physical SecurityDocument9 pagesNerc Guideline: Security Guidelines For The Electricity Sector: Physical SecurityshreeNo ratings yet
- Practical Control of Electric Machines: Model-Based Design and SimulationFrom EverandPractical Control of Electric Machines: Model-Based Design and SimulationNo ratings yet
- Safe Use of Smart Devices in Systems Important to Safety in Nuclear Power PlantsFrom EverandSafe Use of Smart Devices in Systems Important to Safety in Nuclear Power PlantsNo ratings yet
- Industrial Network Security, Second EditionFrom EverandIndustrial Network Security, Second EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Use of Voltage Stability Assessment and Transient Stability Assessment Tools in Grid OperationsFrom EverandUse of Voltage Stability Assessment and Transient Stability Assessment Tools in Grid OperationsSarma (NDR) NuthalapatiNo ratings yet
- Process Control for Sheet-Metal Stamping: Process Modeling, Controller Design and Shop-Floor ImplementationFrom EverandProcess Control for Sheet-Metal Stamping: Process Modeling, Controller Design and Shop-Floor ImplementationNo ratings yet
- Electrician's Troubleshooting and Testing Pocket Guide, Third EditionFrom EverandElectrician's Troubleshooting and Testing Pocket Guide, Third EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guide for Asset Integrity Managers: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategies, Practices and BenchmarkingFrom EverandGuide for Asset Integrity Managers: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategies, Practices and BenchmarkingNo ratings yet
- Ramos - Alyssa Maren - Indelex - HW04Document2 pagesRamos - Alyssa Maren - Indelex - HW04Alyssa RamosNo ratings yet
- Industrial ElexDocument204 pagesIndustrial ElexAlyssa RamosNo ratings yet
- Ee - Elective 1: Power System Protection 1Document22 pagesEe - Elective 1: Power System Protection 1Alyssa RamosNo ratings yet
- Ramos Logic Circuits Number System Common Number SystemDocument8 pagesRamos Logic Circuits Number System Common Number SystemAlyssa RamosNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines 1: DC MachineryDocument10 pagesElectrical Machines 1: DC MachineryAlyssa RamosNo ratings yet
- Essential Elements of Society BiosocialsocioculturalsystemsDocument16 pagesEssential Elements of Society BiosocialsocioculturalsystemsAlyssa RamosNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Morality and ReligionDocument21 pagesRelationship Between Morality and ReligionAlyssa RamosNo ratings yet
- 10 The Philippine Revolution1Document12 pages10 The Philippine Revolution1Alyssa RamosNo ratings yet
- Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument43 pagesCorporate Social ResponsibilityAlyssa RamosNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductiontoProtectionv1 PDFDocument62 pages1 IntroductiontoProtectionv1 PDFAlyssa RamosNo ratings yet
- Capitalism PDFDocument1 pageCapitalism PDFAlyssa RamosNo ratings yet
- Prelim Exam ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesPrelim Exam ThermodynamicsAlyssa RamosNo ratings yet
- Ramos ALYSSAMAREN INDELEX MOD2 HW04Document1 pageRamos ALYSSAMAREN INDELEX MOD2 HW04Alyssa RamosNo ratings yet
- Emergency Rescue and TransferDocument31 pagesEmergency Rescue and TransferJhoana Rose Joaquin Santos95% (20)
- Awareness and Practices Regarding Biomedical Waste.1Document5 pagesAwareness and Practices Regarding Biomedical Waste.1doremonblue01No ratings yet
- Panel Saw Model DS: User ManualDocument25 pagesPanel Saw Model DS: User ManualIng Admir MatoshiNo ratings yet
- What Is HappinessDocument8 pagesWhat Is HappinessAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- IARC STP-158 Dec-2012Document2 pagesIARC STP-158 Dec-2012Thayse AlvesNo ratings yet
- Surgical Hip Dislocation Is More Powerful Than Arthro - 2019 - Orthopaedics - TRDocument6 pagesSurgical Hip Dislocation Is More Powerful Than Arthro - 2019 - Orthopaedics - TRIuliana MoiseNo ratings yet
- Personality by Five ElementsDocument4 pagesPersonality by Five ElementsWaylon CahiligNo ratings yet
- Clinical HypnosisDocument6 pagesClinical Hypnosisyazhini sasiNo ratings yet
- Best IVF Training Center - Medline AcademicsDocument4 pagesBest IVF Training Center - Medline AcademicsMedline AcademicsNo ratings yet
- CM Infant Weighing Scale PPDocument16 pagesCM Infant Weighing Scale PPMani DhamodharanNo ratings yet
- University of Kansas Full Senate Minutes Oct. 9Document7 pagesUniversity of Kansas Full Senate Minutes Oct. 9KUStudentSenateNo ratings yet
- Final 1Document5 pagesFinal 1khansha ComputersNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Gynecologic Surgical Pathology, 4th EditionDocument4 pagesAtlas of Gynecologic Surgical Pathology, 4th EditionWilmer Zambrano GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Occupational Therapy's Role in Bariatric CareDocument2 pagesOccupational Therapy's Role in Bariatric CareThe American Occupational Therapy AssociationNo ratings yet
- Cbse Sample Paper For Class 8 English FA 1Document3 pagesCbse Sample Paper For Class 8 English FA 1SoumitraBag100% (1)
- Multiple IntelligencesDocument4 pagesMultiple IntelligencesChrista Liane CasimiroNo ratings yet
- CPG 1Document21 pagesCPG 1Jennifer ConradNo ratings yet
- Sun PDFDocument17 pagesSun PDFAmanda MillerNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet Week 1 Pe 8Document2 pagesAnswer Sheet Week 1 Pe 8Riza LeeNo ratings yet
- GAL ReimbursementRejectionLetter CLMG 2020 151115 0709507 1583485932639 PDFDocument2 pagesGAL ReimbursementRejectionLetter CLMG 2020 151115 0709507 1583485932639 PDFhiteshmohakar15No ratings yet
- Azadirachta Indica A. Juss. in Vivo Toxicity-An Updated ReviewDocument21 pagesAzadirachta Indica A. Juss. in Vivo Toxicity-An Updated ReviewEdwin ThomasNo ratings yet
- 4life Transfer Factor CardioDocument1 page4life Transfer Factor CardioHimawan Sigit NugrohoNo ratings yet
- RTC Strengthening Article PDFDocument14 pagesRTC Strengthening Article PDFineedsheetzNo ratings yet
- Orar ClaseDocument12 pagesOrar ClaseStan Nicolae-MariusNo ratings yet
- Odontectomy: Name: Hani Afdaliah Arifin K NIM: J014171010 Supervisor: Drg. M. Irfan Rasul, Sp. BMDocument31 pagesOdontectomy: Name: Hani Afdaliah Arifin K NIM: J014171010 Supervisor: Drg. M. Irfan Rasul, Sp. BMDjuanri ThioritzNo ratings yet
- 06 Ra Abdominal TuberculosisDocument10 pages06 Ra Abdominal TuberculosisMade Oka HeryanaNo ratings yet
- DWC 25Document18 pagesDWC 25Yenitze PerezNo ratings yet
- Tarlac State UniversityDocument11 pagesTarlac State UniversityJenica DancilNo ratings yet
- Kamlshkumr KKSEPLDocument25 pagesKamlshkumr KKSEPLraj355No ratings yet
- Kazire Health Products Limited Is A Company Deeply Committed To Improving The Health and Well Being of People and Their CommunitiesDocument5 pagesKazire Health Products Limited Is A Company Deeply Committed To Improving The Health and Well Being of People and Their CommunitiesGgayi JosephNo ratings yet