Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oct2020feb2021-Tutorial CHM524 Chapter 2 A
Oct2020feb2021-Tutorial CHM524 Chapter 2 A
Uploaded by
sitiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oct2020feb2021-Tutorial CHM524 Chapter 2 A
Oct2020feb2021-Tutorial CHM524 Chapter 2 A
Uploaded by
sitiCopyright:
Available Formats
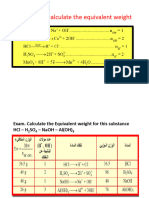
CHM 524-TUTORIAL-CHAPTER 2-A
1. The resistance of 0.01 M NaCl solution in a conductivity cell was found to be 210Ω.
The specific conductance of this solution is 4.5 x 10–3 S cm–1. What is the cell
constant of the cell? 0.945 cm–1
2. Calculate ⋀° m NH4OH from the following values. ⋀
° m for Ba(OH)2 , BaCl2, NH4Cl
are 257.6, 240.6, 129.8 Scm2 mol-1 respectively. 238.3 Scm2 mol-1
3. Calculate the molar conductivity at infinite dilution for CH3COOH if the molar
conductivities at infinite dilution for NaCl, HCl and CH3COONa are 126.45, 426.16
cm2 mol–1
and 91.0 ohm–1 cm2 mol–1 respectively.390.71 ohm–1
4. At 25°C, the molar conductance of propanoic acid at infinite dilution is 386.6 S cm2
mol-1. If its ionization constant is 1.4 x 10-5, Calculate molar conductance of 0.05 M
propanoic acid solution at 25°C? 6.47 S cm2 mol-1
5. Molar conductivities at infinite dilution at 25°C of NH4Cl, NaOH and NaCl are 129.8,
217.4 & 108.9 S cm2 mol-1. For 0.01 M NH4OH molar conductance is 9.33 S cm2
mol-1. Calculate ionization constant of NH4OH. 1.6 x 10-5
6. The molar conductivity of a weak monobasic acid at infinite dilution is 387 ohm–1
cm2 mol–1. The 0.02M solution of the same acid has a specific conductivity of
3.3 x 10–4 ohm–1 cm2 mol–1. Calculate the degree of dissociation of the acid at the
given concentration.0.0426
7. Find the ionic strength of a 0.020 M Na2SO4 solution? 0.060 M
8. Calculate the ionic strength of a 0.060 M solution of KCl.0.060 M
You might also like
- Molar Conductivity at Infinite Dilution of Electrolytes Lab ReportDocument14 pagesMolar Conductivity at Infinite Dilution of Electrolytes Lab ReportMay Lee85% (13)
- Lab 4 - 555Document12 pagesLab 4 - 555ZawanahNo ratings yet
- LMS Solutions ElectrochemistryDocument200 pagesLMS Solutions ElectrochemistrySai Rithvik Kanakamedala80% (10)
- QC1: Problem SetsDocument4 pagesQC1: Problem SetsYsabel Salvador Dychinco100% (1)
- Ch7 HM 3 1Document2 pagesCh7 HM 3 1Najmul Puda PappadamNo ratings yet
- Worksheet ElectroChemistry-2Document2 pagesWorksheet ElectroChemistry-2Rishi ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- ConductanceDocument2 pagesConductanceaviationforce204No ratings yet
- Worksheet On ElectrochemistryDocument1 pageWorksheet On Electrochemistryzakhulk2468No ratings yet
- The Molar Conductivity of A 1Document1 pageThe Molar Conductivity of A 1iliasNo ratings yet
- Numerical Problems 2ND YearDocument9 pagesNumerical Problems 2ND Yeardhanushdhanup178No ratings yet
- Electro Chemistry Numericals - 065546Document10 pagesElectro Chemistry Numericals - 065546YOGA SAI GUHANNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic ConductanceDocument8 pagesElectrolytic Conductancevijaye36100% (1)
- Worksheet ElectrochemistryDocument18 pagesWorksheet Electrochemistryyatan kapoorNo ratings yet
- GMDocument18 pagesGMVivek GusainNo ratings yet
- CHM524 Chapter 2 Part B TutoDocument1 pageCHM524 Chapter 2 Part B TutoAnis SofeaNo ratings yet
- Holiday HW-01Document3 pagesHoliday HW-01Amiyo SarkarNo ratings yet
- Experiment I1 Preparation of Some Cobaltammine ComplexesDocument7 pagesExperiment I1 Preparation of Some Cobaltammine ComplexesIftitah HauriyahNo ratings yet
- Try Electrochemistry Worksheet 13Document3 pagesTry Electrochemistry Worksheet 13falmupklNo ratings yet
- Kohlrausch Law Chemistry Questions With SolutionsDocument7 pagesKohlrausch Law Chemistry Questions With SolutionsAdugnaw BiksNo ratings yet
- ConductometryDocument9 pagesConductometryMuhammad FahmiNo ratings yet
- Expected Questions For Board Examination 2013Document34 pagesExpected Questions For Board Examination 2013Harsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Home Work CheDocument3 pagesHome Work CheShree PinnintiNo ratings yet
- Class XII Assignments (Complete) Chootiya Ho TumDocument35 pagesClass XII Assignments (Complete) Chootiya Ho TumpranavNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab Exp 5Document3 pagesChem Lab Exp 5Bernadette Virola CuevasNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ExamplesDocument13 pagesOrganic Chemistry Examplestalbkhfajy4No ratings yet
- Conductivity ExerciseDocument1 pageConductivity ExerciseMr. Gamingo ChallengiNo ratings yet
- MCQ Test ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesMCQ Test Electrochemistryyatan kapoorNo ratings yet
- AssignmentforSundayTest - D24 Jun 2023Document44 pagesAssignmentforSundayTest - D24 Jun 2023aadityabhagchandaniNo ratings yet
- Conductometry Lec PDFDocument11 pagesConductometry Lec PDFgamer lionNo ratings yet
- Advanced Electrochemistry 2Document24 pagesAdvanced Electrochemistry 2Ahemdi BahmanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document4 pagesExperiment 5idaayudwitasariNo ratings yet
- Question 1399058Document8 pagesQuestion 1399058rajputabhishek71708No ratings yet
- Sainik School-Amaravathinagar: 2019-20: Assignment For Summer VacationDocument5 pagesSainik School-Amaravathinagar: 2019-20: Assignment For Summer VacationSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 12 - ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument2 pagesChemistry Class 12 - ELECTROCHEMISTRYYash TyagiNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry WorksheetDocument3 pagesElectrochemistry Worksheetvsbackup261No ratings yet
- Chemistry 251 Review Questions Exam I WordDocument2 pagesChemistry 251 Review Questions Exam I WordDavid Chambergo0% (2)
- +2 Chem Ultimate Question BankDocument253 pages+2 Chem Ultimate Question Bankflex93948No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Adugnaw BiksNo ratings yet
- GravimetriaDocument1 pageGravimetriaDario PiñeresNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument21 pagesElectrochemistryessaNo ratings yet
- Redox Lab Report CompleteDocument15 pagesRedox Lab Report CompleteJackson KasakuNo ratings yet
- Holiday Homework Class Xii 2023-24, PDFDocument3 pagesHoliday Homework Class Xii 2023-24, PDFbanerjeeakshay003No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssignment 1Leo PalNo ratings yet
- 11c PDFDocument44 pages11c PDFHunnyNo ratings yet
- Chem F5C3 Thermokimia Note 4Document3 pagesChem F5C3 Thermokimia Note 4YashwinieNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document14 pagesExperiment 3hasmar78% (27)
- Ashwani Tyagi: (Code: ATJEE)Document2 pagesAshwani Tyagi: (Code: ATJEE)tarunNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument5 pagesElectrochemistryNeel SiddhpuraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Electrochem CMT555Document10 pagesExperiment 4 Electrochem CMT555Amar Safwan100% (1)
- ConductivityDocument6 pagesConductivitydrag000nNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2saranshsood74No ratings yet
- SR Ipe Chem QB Final 2023-24Document14 pagesSR Ipe Chem QB Final 2023-24bhnv83No ratings yet
- 02 Solved ProblemsDocument16 pages02 Solved ProblemsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- LAb Report 7Document3 pagesLAb Report 7Faisal MumtazNo ratings yet
- Question Bank em - FINAL PDF 2024Document9 pagesQuestion Bank em - FINAL PDF 2024dhrumilkaushalmaheriyaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsFrom EverandElectrochemical Processes in Biological SystemsAndrzej LewenstamNo ratings yet