Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SGSN Logical Interfaces
SGSN Logical Interfaces
Uploaded by
Ali AshkarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SGSN Logical Interfaces
SGSN Logical Interfaces
Uploaded by
Ali AshkarCopyright:
Available Formats
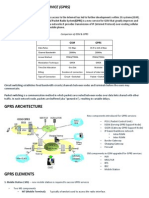
SGSN Logical Network Interfaces
The SGSN provides IP-based transport on all RAN and core network interfaces, in addition to
the standard IP-based interfaces (Ga, Gn, Gp, Iu-PS). This means enhanced performance, future-
proof scaling and reduction of inter-connectivity complexity. The all-IP functionality is key to
facilitating evolution to the next generation technology requirements.
The SGSN provides the following functions over the logical network interfaces illustrated above:
Ga: The SGSN uses the Ga interface with GPRS Transport Protocol Prime (GTPP) to
communicate with the charging gateway (CG, also known as CGF) and/or the GTPP storage
server (GSS). The interface transport layer is typically UDP over IP but can be configured as
TCP over IP for:
o One or more Ga interfaces per system context, and
o An interface over Ethernet 10/100 or Ethernet 1000 interfaces
The charging gateway handles buffering and pre-processing of billing records and the GSS
provides storage for Charging Data Records (CDRs). For additional information regarding SGSN
charging, refer to the Charging section.
IuPS: The SGSN provides an IP over ATM (IP over AAL5 over ATM) interface between the
SGSN and the RNCs in the 3G UMTS radio access network (UTRAN). RANAP is the control
protocol that sets up the data plane (GTP-U) between these nodes. SIGTRAN (M3UA/SCTP) or
QSAAL (MTP3B/QSAAL) handle IuPS-C (control) for the RNCs.
Some of the procedures supported across this interface are:
o Control plane based on M3UA/SCTP
o Up to 128 Peer RNCs per virtual SGSN. Up to 256 peers per physical chassis
o SCTP Multi-Homing supported to facilitate network resiliency
o M3UA operates in and IPSP client/server and single/double-ended modes
o Multiple load shared M3UA instances for high-performance and redundancy
o Works over Ethernet and ATM (IPoA) interfaces
o Facilitates SGSN Pooling
o RAB (Radio Access Bearer) Assignment Request
o RAB Release Request
o Iu Release Procedure
o SGSN-initiated Paging
o Common ID
o Security Mode Procedures
o Initial MN Message
o Direct Transfer
o Reset Procedure
o Error Indication
o SRNS relocation
Gb: This is the SGSN's interface to the base station system (BSS) in a 2G radio access network
(RAN). It connects the SGSN via UDP/IP via an Ethernet interface or Frame Relay via a
Channelized SDH or SONET interface (only available on an ASR 5000 chassis). Gb-IP is the
preferred interface as it improves control plane scaling as well as facilitates the deployment of
SGSN Pools.
Some of the procedures supported across this interface are:
o BSS GSM at 900/1800/1900 MHz
o BSS Edge
o Frame Relay congestion handling
o Traffic management per Frame Relay VC
o NS load sharing
o NS control procedures
o BVC management procedures
o Paging for circuit-switched services
o Suspend/Resume
o Flow control
o Unacknowledged mode
o Acknowledged mode
Gn/Gp: The Gn/Gp interfaces, comprised of GTP/UDP/IP-based protocol stacks, connect the
SGSNs and GGSNs to other SGSNs and GGSNs within the same public land mobile network
(PLMN) - the Gn - or to GGSNs in other PLMNs - the Gp.
This implementation supports:
o GTPv0 and GTPv1, with the capability to auto-negotiate the version to be used with any
particular peer
o GTP-C (control plane) and GTP-U (user plane)
o Transport over ATM/STM-1Optical (only available with an ASR 5000 chassis), Fast Ethernet,
and Ethernet 1000 line cards/QGLCs)
o One or more Gn/Gp interfaces configured per system context
As well, the SGSN can support the following IEs from later version standards:
o IMEI-SV
o RAT TYPE
o User Location Information
o Extended PDP Type (Release 9)
o Extended RNC ID (Release 9)
Ge: This is the interface between the SGSN and the SCP that supports the CAMEL service. It
supports both SS7 and SIGTRAN and uses the CAP protocol.
Gr: This is the interface to the HLR. It supports SIGTRAN (M3UA/SCTP/IP) over Ethernet.
Some of the procedures supported by the SGSN on this interface are:
o Send Authentication Info
o Update Location
o Insert Subscriber Data
o Delete Subscriber Data
o Cancel Location
o Purge
o Reset
o Ready for SM Notification
o SIGTRAN based interfaces M3UA/SCTP
o Peer connectivity can be through an intermediate SGP or directly depending on whether the peer
(HLR, EIR, SMSC, GMLC) is SIGTRAN enabled or not
o SCTP Multi-Homing supported to facilitate network resiliency
o M3UA operates in IPSP client/server and single/double-ended modes
o Multiple load shared M3UA instances for high-performance and redundancy
o Works over Ethernet (IPoA) interface
Gs: This is the interface used by the SGSN to communicate with the visitor location register
(VLR) or mobile switching center (MSC) to support circuit switching (CS) paging initiated by
the MSC. This interface uses Signaling Connection Control Part (SCCP) connectionless service
and BSSAP+ application protocols.
Gd: This is the interface between the SGSN and the SMS Gateway (SMS-GMSC / SMS-
IWMSC) for both 2G and 3G technologies through multiple interface mediums. Implementation
of the Gd interface requires purchase of an additional license.
Gf: Interface is used by the SGSN to communicate with the equipment identity register (EIR)
which keeps a listing of UE (specifically mobile phones) being monitored. The SGSN's Gf
interface implementation supports functions such as:
o International Mobile Equipment Identifier-Software Version (IMEI-SV) retrieval
o IMEI-SV status confirmation
Lg: This is a Mobile Application Part (MAP) interface, between the SGSN and the gateway
mobile location center (GMLC), supports 3GPP standards-compliant LoCation Services (LCS)
for both 2G and 3G technologies. Implementation of the Lg interface requires purchase of an
additional license.
S3:On the S4-SGSN, this interface provides a GTPv2-C signaling path connection between the
EPC mobility management entity (MME) and the SGSN. This functionality is part of the S4
interface feature license.
S4: On the S4-SGSN, this interface provides a data and signaling interface between the EPC S-
GW and the S4-SGSN for bearer plane transport (GTPv1-U). The S4-SGSN communicates with
the P-GW via the S-GW. A separate feature license is required for S4 interface support.
S6d: On the SGSN, this is the S6d interface between the SGSN and the HSS. This enables the
SGSN to get subscription details of a user from the HSS when a user tries to register with the
SGSN. A separate feature license is required for S6d Diameter interface support.
S13': The SGSN supports the S13' interface between the SGSN and the EIR. This enables the
SGSN to communicate with an Equipment Identity Registry (EIR) via the Diameter protocol to
perform the Mobile Equipment (ME) identity check procedure between the SGSN and EIR.
Performing this procedure enables the SGSN to verify the equipment status of the Mobile
Equipment. A separate feature license is required for S13' interface support.
S16:On the S4-SGSN, this interface provides a GTPv2 path to a peer S4-SGSN. Support for this
interface is provided as part of the S4 interface license.
You might also like
- Implementing IP and Ethernet on the 4G Mobile NetworkFrom EverandImplementing IP and Ethernet on the 4G Mobile NetworkRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- h12-711 Hcia-Security Qn12 29qnDocument9 pagesh12-711 Hcia-Security Qn12 29qnEDWARD KIWALABYENo ratings yet
- LTE and Mobile InternetDocument1 pageLTE and Mobile InternetAlex HunterNo ratings yet
- Ericsson GPRSDocument7 pagesEricsson GPRSvelayyaNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Part 1 LTE Technology Overview V2mailersDocument45 pagesDay 1 Part 1 LTE Technology Overview V2mailersmahendras7786No ratings yet
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandFrom EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNo ratings yet
- EDGEDocument43 pagesEDGEPramod RaiNo ratings yet
- Gprs Architecture: General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Document6 pagesGprs Architecture: General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Vam ArmodiaNo ratings yet
- SGSN Admin ChapterDocument94 pagesSGSN Admin ChapterAbhilash BrahmaNo ratings yet
- 3G Core NewDocument46 pages3G Core NewPaul Joseph100% (1)
- VASDocument50 pagesVASPrashant BediNo ratings yet
- GPRS Core NetworkDocument6 pagesGPRS Core NetworkJince KappanNo ratings yet
- Lte Optimization IntroductionDocument87 pagesLte Optimization IntroductionScribduser160100% (2)
- GPRS Chap7Document43 pagesGPRS Chap7Shailesh PathakNo ratings yet
- GPRS Logical ArchitectureDocument4 pagesGPRS Logical ArchitectureFaran Ul GhaniNo ratings yet
- For RADCOM Analyzers GPRS Network Support: HighlightsDocument2 pagesFor RADCOM Analyzers GPRS Network Support: HighlightsAnonymous Ie0oEXP2eNo ratings yet
- AdigsmDocument12 pagesAdigsmAdarsh PattarNo ratings yet
- 3G SGSN 0 4Document15 pages3G SGSN 0 4Anoop SharmaNo ratings yet
- E2E Insight, Analytics & Customer Experience: Masterclaw MonitoringDocument1 pageE2E Insight, Analytics & Customer Experience: Masterclaw MonitoringIsroGeNo ratings yet
- GPRS For 2 Hours TrainingDocument105 pagesGPRS For 2 Hours Trainingh_hadidiNo ratings yet
- Sisco PDFDocument19 pagesSisco PDFinside121No ratings yet
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Document44 pagesGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Mubassir PatelNo ratings yet
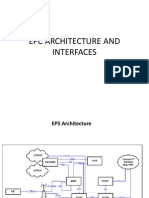
- EPS ArchitectureDocument12 pagesEPS ArchitectureLokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Gtp-U & GTP-CDocument9 pagesGtp-U & GTP-CiAZHTONNo ratings yet
- LTE ProtocolDocument6 pagesLTE Protocolhakrajput50% (2)
- Assignment 1: Wireless and Mobile CommunicationDocument8 pagesAssignment 1: Wireless and Mobile CommunicationMuhammad Rizwan TariqNo ratings yet
- LTE Interfaces NDocument14 pagesLTE Interfaces NHrishikesh TripathiNo ratings yet
- SIGTRAN Analysis and SimulationDocument45 pagesSIGTRAN Analysis and SimulationJesus Choque EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- LTE Interface and Protocol StacksDocument12 pagesLTE Interface and Protocol StacksJung Hyun JeongNo ratings yet
- GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) : ArchitectureDocument7 pagesGPRS (General Packet Radio Service) : ArchitectureSrinivas KaratlapelliNo ratings yet
- ITU PSTN-to-NGNDocument19 pagesITU PSTN-to-NGNjack22345No ratings yet
- Agilent Testing GPRS SignallingDocument24 pagesAgilent Testing GPRS SignallingPrasant KumarNo ratings yet
- Gprs PosterDocument1 pageGprs PostermathcueiNo ratings yet
- Gsc11 Joint 32r1 3GPP LTE SAEDocument14 pagesGsc11 Joint 32r1 3GPP LTE SAEJorge R Genes ForcadellNo ratings yet
- GPRS OverviewDocument57 pagesGPRS OverviewDeepak BhattNo ratings yet
- CAMEL in GPRS Prepaid ServiceDocument32 pagesCAMEL in GPRS Prepaid ServiceImranNo ratings yet
- Evolution of The GSM: General Packet Radio System (GPRS)Document5 pagesEvolution of The GSM: General Packet Radio System (GPRS)Simranbir SinghNo ratings yet
- Yateucn DatasheetDocument3 pagesYateucn DatasheetajdCruiseNo ratings yet
- c655eGPRS 1Document61 pagesc655eGPRS 1Tushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- GprsDocument25 pagesGprsYuvraj TjNo ratings yet
- GSM P&O Training Material For Skill Certificate-GPRS Basic PrincipleDocument87 pagesGSM P&O Training Material For Skill Certificate-GPRS Basic PrincipleObaid RaoNo ratings yet
- Gprs Qos and Parameters - AlcatelDocument316 pagesGprs Qos and Parameters - AlcatelOcira OyaroNo ratings yet
- Mod1 SlideDocument22 pagesMod1 Slide2020ecpriyanshnigambNo ratings yet
- GPRS Signalling IntroductionDocument18 pagesGPRS Signalling IntroductionRodrigo Abrego100% (1)
- Presentation Topic: GPRS (General Packet Radio Service)Document26 pagesPresentation Topic: GPRS (General Packet Radio Service)Anonymous xsK0G4INo ratings yet
- What Are LTE InterfacesDocument2 pagesWhat Are LTE InterfacesDhiraj SinghNo ratings yet
- UMTS Networks StandardizationDocument10 pagesUMTS Networks StandardizationsurvivalofthepolyNo ratings yet
- 4G Asr5000Document42 pages4G Asr5000Sri VagiralaNo ratings yet
- GPRS Basic PrincipleDocument90 pagesGPRS Basic PrincipleMahim GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Diameter Signaling: A Whitepaper July 2012Document7 pagesThe Evolution of Diameter Signaling: A Whitepaper July 2012m.alnabhani9097No ratings yet
- GSM/GPRS: Dr. Anil Kumar Intel CorporationDocument53 pagesGSM/GPRS: Dr. Anil Kumar Intel CorporationIsoQuantic100% (1)
- Mobile & Wireless Networking: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) (Schiller, Section 4.4)Document33 pagesMobile & Wireless Networking: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) (Schiller, Section 4.4)sadzvokoraNo ratings yet
- Versatile Routing and Services with BGP: Understanding and Implementing BGP in SR-OSFrom EverandVersatile Routing and Services with BGP: Understanding and Implementing BGP in SR-OSNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- External Alarm Monitoring For The DWDM (OSN 8800)Document9 pagesExternal Alarm Monitoring For The DWDM (OSN 8800)Ali AshkarNo ratings yet
- Database Error 10 Rectification GuideDocument5 pagesDatabase Error 10 Rectification GuideAli AshkarNo ratings yet
- Syriatel Optical / Transport Network Mofification Document Damascus OPNETDocument6 pagesSyriatel Optical / Transport Network Mofification Document Damascus OPNETAli AshkarNo ratings yet
- Product Documentation: NM Configuration ReferenceDocument4 pagesProduct Documentation: NM Configuration ReferenceAli AshkarNo ratings yet
- AUX Jumper FOR Different VersionDocument4 pagesAUX Jumper FOR Different VersionAli AshkarNo ratings yet
- How To Measure The Receiving/Transmitting Optical PowerDocument2 pagesHow To Measure The Receiving/Transmitting Optical PowerAli AshkarNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual To Chapter 02Document2 pagesSolution Manual To Chapter 02Arpit JainNo ratings yet
- Assesment 3 AnswersDocument4 pagesAssesment 3 AnswersMaja ChagorskyNo ratings yet
- Problems: TCP and UDPDocument2 pagesProblems: TCP and UDPmayur jabareNo ratings yet
- Sip LogDocument491 pagesSip LogGina JohnNo ratings yet
- SCTP and Diameter PArameter PDFDocument111 pagesSCTP and Diameter PArameter PDFRavi RaiNo ratings yet
- hwk3 F 11 3 Sol 2Document8 pageshwk3 F 11 3 Sol 2Min LiNo ratings yet
- Data Link LayerDocument9 pagesData Link LayerFarhana AijazNo ratings yet
- 05-Wireshark TCP Solution July 22 2007Document16 pages05-Wireshark TCP Solution July 22 2007Sobi100% (2)
- h16568 MP 7800b Switches SsDocument6 pagesh16568 MP 7800b Switches SsNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Official Documentation (Ws Apache Org) - Axis2 - Part 2Document80 pagesOfficial Documentation (Ws Apache Org) - Axis2 - Part 2Fede100% (9)
- SRAN Transport Template NPO Global Service v1Document64 pagesSRAN Transport Template NPO Global Service v1balajisk007No ratings yet
- Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)Document11 pagesBorder Gateway Protocol (BGP)Msambili NdagaNo ratings yet
- Saswata Basu 20mid0035 DCCN Lab 1Document7 pagesSaswata Basu 20mid0035 DCCN Lab 1Alina HasanNo ratings yet
- ASUS U5A Rev2.0 Schematic DiagramDocument58 pagesASUS U5A Rev2.0 Schematic DiagramADAMO PATRICIO O'BYRNE RIVERANo ratings yet
- MTCRE OutlineDocument1 pageMTCRE Outlinerabbi_mit34No ratings yet
- CCNPv7 ROUTE Lab3-3 OSPFv3-Address-Families InstructorDocument26 pagesCCNPv7 ROUTE Lab3-3 OSPFv3-Address-Families InstructorHuanChiHuaNo ratings yet
- 01 Halaman 1 - 43Document42 pages01 Halaman 1 - 43Anta MasimmoNo ratings yet
- TCP Three-Way Handshake As A Pedagogical ToolDocument8 pagesTCP Three-Way Handshake As A Pedagogical Toolfree bishoNo ratings yet
- 3GPP TR 23.715: Technical ReportDocument39 pages3GPP TR 23.715: Technical ReportnvilochanNo ratings yet
- Enterasys ® B-Series B5 Firmware Version 6.71.02.0008 July 2013Document26 pagesEnterasys ® B-Series B5 Firmware Version 6.71.02.0008 July 2013Sergio AcunaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 CS 2204 AssignmentDocument2 pagesUnit 6 CS 2204 AssignmentZodwa MngometuluNo ratings yet
- WiresharkDocument8 pagesWiresharkwelcomeuser66No ratings yet
- F3x36 Industrial Router Technical Specification: GeneralDocument5 pagesF3x36 Industrial Router Technical Specification: GeneralFasop UP2DLampungNo ratings yet
- RG-ES200 Series Cloud Managed Switch DatasheetDocument12 pagesRG-ES200 Series Cloud Managed Switch Datasheetruijie medanNo ratings yet
- Vxlan Evpn 10 5 0 0 - en Us 1Document129 pagesVxlan Evpn 10 5 0 0 - en Us 1nguyenkha_1605No ratings yet
- The Network+ Cram Sheet: Networking ConceptsDocument4 pagesThe Network+ Cram Sheet: Networking ConceptsISTAKHAR UDDIN AHAMED100% (1)
- Gigabyte Ga-H61m-Ds2 Rev. 2.01Document30 pagesGigabyte Ga-H61m-Ds2 Rev. 2.01Adriano Araújo Amaral100% (2)
- Schem 8520Document19 pagesSchem 8520Adryan Ersan PratamaNo ratings yet
- Ch2 Questions With SolutionsDocument18 pagesCh2 Questions With Solutionsraghad mejeedNo ratings yet