Professional Documents
Culture Documents
From Relatively Benign Disease To Rapidly Progressive and Even
From Relatively Benign Disease To Rapidly Progressive and Even
Uploaded by
diaa skam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesAutoimmunity results from a breakdown of immune tolerance that allows the immune system to attack self-antigens. Tolerance mechanisms normally distinguish self from non-self and prevent autoreactive immune cells from developing or differentiating. Failure of these tolerance mechanisms can lead to autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune disorders range from organ-specific diseases targeting a single tissue to systemic diseases affecting multiple tissues. Treatment of autoimmune diseases includes medications like NSAIDs, corticosteroids, DMARDs, and biologics, as well as procedures like plasmapheresis and surgery.
Original Description:
Original Title
abstact micro 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAutoimmunity results from a breakdown of immune tolerance that allows the immune system to attack self-antigens. Tolerance mechanisms normally distinguish self from non-self and prevent autoreactive immune cells from developing or differentiating. Failure of these tolerance mechanisms can lead to autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune disorders range from organ-specific diseases targeting a single tissue to systemic diseases affecting multiple tissues. Treatment of autoimmune diseases includes medications like NSAIDs, corticosteroids, DMARDs, and biologics, as well as procedures like plasmapheresis and surgery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesFrom Relatively Benign Disease To Rapidly Progressive and Even
From Relatively Benign Disease To Rapidly Progressive and Even
Uploaded by
diaa skamAutoimmunity results from a breakdown of immune tolerance that allows the immune system to attack self-antigens. Tolerance mechanisms normally distinguish self from non-self and prevent autoreactive immune cells from developing or differentiating. Failure of these tolerance mechanisms can lead to autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune disorders range from organ-specific diseases targeting a single tissue to systemic diseases affecting multiple tissues. Treatment of autoimmune diseases includes medications like NSAIDs, corticosteroids, DMARDs, and biologics, as well as procedures like plasmapheresis and surgery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Abstract
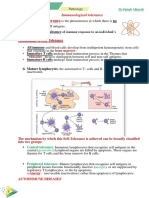
Autoimmunity is an adaptive immune response to self-antigens leading to
production of autoantibodies and self-reactive T cells attacking the self-molecule
due to a breakdown of immune tolerance to auto-reactive immune cells which may
causes autoimmune diseases.
Tolerance mechanisms have evolved to distinguish self and non-self, and block
the development of growth, or differentiation of autoreactive lymphocytes.
Immunological tolerance to different autoantigens may be induced when immature
lymphocytes recognize these antigens in the generative (central) lymphoid organs,
a process called central tolerance, or when mature lymphocytes encounter
autoantigens in peripheral (secondary) lymphoid organs or peripheral tissues,
called peripheral tolerance. Tolerance induction and maintenance mechanisms vary
between the B and T cells and the central and peripheral lymphoid. The failure of
that auto-tolerance may result in autoimmune disease.
Factors that evolve into autoimmune disease include genetic predisposition,
structural modification of tissue protein, cross reactivity and breakdown in the
immune network.
Autoimmune disorders are a spectrum of diseases ranging from organ-specific
diseases in which antibodies and T cells respond to self-antigens found in a single
specific tissue (such autoimmune thyroid diseases: Grave’s disease, myxedema and
Hashimoto's disease) to systemic diseases characterized by reactivity to a common
antigen or antigens distributed across the body's various tissues (such that occurs in
SLE and rheumatoid arthritis).
In Rheumatoid arthritis, the pathogenesis of such disease is complex with
multiple genetic, environmental, immunologic, and other factors contributing to
the development and expression of disease. Diagnosis of Rheumatoid arthritis
disease can be done by blood test, imaging tests, ELISA Test and Multiplex
cytofluorimetric test which is more sensitive and specific.
In Graves' disease, there is a generalized over-activity of the entire thyroid gland
caused by auto-antibodies to TSHR. B-cells and T-cells play an important role in
such cases. Diagnosis of Grave’s disease is done by Physical examinations to the
eye and thyroid gland, blood tests, radioactive iodine uptake, Ultrasound waves
and Imaging tests.
In Systemic lupus erythematosus, it is characterized by the production of
autoreactive antibodies and cytokines. It may be due to genetic or environmental
causes. It ranges from relatively benign disease to rapidly progressive and even
fatal disease. IL-1, Gelatinase B or MMP-9 and antibody play a significant role in
such disease.
Treatment of autoimmune disease includes NSAIDs, Corticosteroids, Disease-
modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), Biologics (A relatively new class of
DMARDs made of synthetic proteins), Intravenous Immunoglobulin,
Plasmapheresis (a process that clears the plasma from autoantibodies) and Surgery
to cope with certain autoimmune disease complications.
You might also like
- Practical Answers DCPIPDocument98 pagesPractical Answers DCPIPSanad BashirNo ratings yet
- Immunology - Website QuestionsDocument100 pagesImmunology - Website QuestionsMohammed AlMujaini75% (12)
- Harrison SLEDocument11 pagesHarrison SLEpazucenaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Autoimmune Disease PDFDocument18 pagesUnderstanding Autoimmune Disease PDFLiz TaylorNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune-Disorders PDF Divya Mam PracticalDocument44 pagesAutoimmune-Disorders PDF Divya Mam Practicaltariqahmeda34No ratings yet
- Presentation Auto 2Document33 pagesPresentation Auto 2mlllNo ratings yet
- Копия Autoimmunity-and-Autoimmune-disordersDocument38 pagesКопия Autoimmunity-and-Autoimmune-disordersManav VyasNo ratings yet
- Hypersensitivity Diseases: Autoimmune Disease-1Document27 pagesHypersensitivity Diseases: Autoimmune Disease-1fakhirNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Diseases of Oral CavityDocument52 pagesAutoimmune Diseases of Oral Cavitylakshmi k sNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Reading Materials (Supplementary)Document5 pagesModule 5 Reading Materials (Supplementary)Luis MunozNo ratings yet
- Low-Level AutoimmunityDocument13 pagesLow-Level AutoimmunityBeeBee SethNo ratings yet
- What Is An Autoimmune DiseaseDocument7 pagesWhat Is An Autoimmune DiseaseBISHOP MBILINo ratings yet
- Autoimmune DiseaseDocument38 pagesAutoimmune DiseaseGustiandari FidhyaNo ratings yet
- Envhper00522 0014Document5 pagesEnvhper00522 0014Afaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Autoimmunity and Autoimmune DisordersDocument39 pagesAutoimmunity and Autoimmune DisordersSireeshasenapathi Sireesha SenapathiNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disease - : Immune DeficienciesDocument34 pagesAutoimmune Disease - : Immune Deficienciesahana roy100% (1)
- Discipline: B. Tech (Biotech) Module: BT 501 IV Semester: VDocument6 pagesDiscipline: B. Tech (Biotech) Module: BT 501 IV Semester: VsauravsarkarNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune DiseasesDocument4 pagesAutoimmune Diseasesnizam syedNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disorders - AgungDocument40 pagesAutoimmune Disorders - AgungalgutNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue Disease LectureDocument99 pagesConnective Tissue Disease Lectureconfuzzledfreak100% (1)
- Autoimmune Disorders - MicrobiologyDocument6 pagesAutoimmune Disorders - MicrobiologyAll in oneNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 7 AUTOIMMUNITY AND AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE Part1 PDFDocument20 pagesLECTURE 7 AUTOIMMUNITY AND AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE Part1 PDFMAYANo ratings yet
- Tolerance & Autoimmune DiseaseDocument18 pagesTolerance & Autoimmune Diseasefafyfskhan251kmfNo ratings yet
- Immunopathology Lec 4Document11 pagesImmunopathology Lec 4zaharNo ratings yet
- Cojocaru-Et-Al 08 - (Autoimmune Diseases and Their Environmental Triggers)Document6 pagesCojocaru-Et-Al 08 - (Autoimmune Diseases and Their Environmental Triggers)Luana DiEmmeNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Immune System Part 2Document47 pagesDiseases of Immune System Part 2KundaNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Diseases - MicroDocument30 pagesAutoimmune Diseases - Microdiaa skamNo ratings yet
- The Role of Viral Infections in The Onset of Autoimmune DiseaseDocument31 pagesThe Role of Viral Infections in The Onset of Autoimmune DiseaseLuis RiveraNo ratings yet
- Diseases in Your Discussion (2 To 4 Pages Single Spaced)Document5 pagesDiseases in Your Discussion (2 To 4 Pages Single Spaced)GeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 27: Hypersensitivity Reactions: Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesLesson 27: Hypersensitivity Reactions: Learning Objectives99manu99No ratings yet
- Immunology Unit 1Document6 pagesImmunology Unit 1Morrison GeorgeNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Molecular Mimicry As A Mechanism of Autoimmune DiseaseDocument16 pagesNIH Public Access: Molecular Mimicry As A Mechanism of Autoimmune DiseaseCarla Andrea Iturralde RamosNo ratings yet
- Experiment 12: Rheumatoid Factor Determination (Latex Slide Test)Document2 pagesExperiment 12: Rheumatoid Factor Determination (Latex Slide Test)Marjorie ColtingNo ratings yet
- Immunological Factors in Disease-) - AutoimmunityDocument49 pagesImmunological Factors in Disease-) - AutoimmunityDr anas AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Diseases of The Immune SystemDocument3 pagesChapter 6 - Diseases of The Immune SystemTurinawe Bin ByensiNo ratings yet
- Autoimmunity: Presented by DR .Esther Priyadarshini.SDocument24 pagesAutoimmunity: Presented by DR .Esther Priyadarshini.SLavanya KalapalaNo ratings yet
- Autoimmunity: Dr.C.Meenakshisundaram.,MDDocument66 pagesAutoimmunity: Dr.C.Meenakshisundaram.,MDChockalingam Meenakshisundaram100% (1)
- Immunity, Autoimmunity - QsDocument5 pagesImmunity, Autoimmunity - QsMaedehNo ratings yet
- JCI78088Document6 pagesJCI78088Ardian AshadiNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disease - Why and Where It OccursDocument7 pagesAutoimmune Disease - Why and Where It OccursdNo ratings yet
- Peran Pola Hidup Dan Faktor Lingkungan Dalam Patogenesis Penyakit AutoimunDocument7 pagesPeran Pola Hidup Dan Faktor Lingkungan Dalam Patogenesis Penyakit AutoimunShevamykolayovychshevchenko MilaniztyonlymilanelloNo ratings yet
- Autoimmunity: 1 Semester DMLTDocument11 pagesAutoimmunity: 1 Semester DMLTTepfi TepsNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Disorders: CausesDocument11 pagesAutoimmune Disorders: CausesJenalyn Pilapil SumaelNo ratings yet
- Auto ImmunityDocument38 pagesAuto ImmunityMau studioNo ratings yet
- Autoimmunityvarghx 180301134104Document74 pagesAutoimmunityvarghx 180301134104misdduaaNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument38 pagesFinalsandeep agarwalNo ratings yet
- Immune Regulation: Antibodies and T-Cell Receptors (TCRS)Document43 pagesImmune Regulation: Antibodies and T-Cell Receptors (TCRS)fakhirNo ratings yet
- Patophysiology Oral Q 1Document134 pagesPatophysiology Oral Q 1TijanaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Immune System: Allergic DiseasesDocument2 pagesDisorders of The Immune System: Allergic DiseasesElisha RosalynNo ratings yet
- 2022 Brad Spectrum of Autoreactivity in Autoimmune DiseaseDocument2 pages2022 Brad Spectrum of Autoreactivity in Autoimmune DiseaseRaul ReyesNo ratings yet
- Microbial Triggers in Autoimmunity, Severe Allergy, and AutoallergyDocument16 pagesMicrobial Triggers in Autoimmunity, Severe Allergy, and AutoallergyMystero RasicoNo ratings yet
- Microbial Triggers in Autoimmunity, Severe Allergy, and AutoallergyDocument16 pagesMicrobial Triggers in Autoimmunity, Severe Allergy, and AutoallergyMystero RasicoNo ratings yet
- Bad Loe 2017Document16 pagesBad Loe 2017Mystero RasicoNo ratings yet
- Triggers of AutoimmunityDocument13 pagesTriggers of AutoimmunityFrancisco Ibañez IrribarraNo ratings yet
- Auto ImmunityDocument73 pagesAuto ImmunitymisdduaaNo ratings yet
- Fimmu 06 00550 PDFDocument14 pagesFimmu 06 00550 PDFMurti NopitasariNo ratings yet
- Kuby5 20 AutoImmunity PDFDocument19 pagesKuby5 20 AutoImmunity PDFASDASDDD2No ratings yet
- Chapter 28 (Aim Disorders)Document9 pagesChapter 28 (Aim Disorders)Vince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- Immunological Tolerance: UnresponsivenessDocument31 pagesImmunological Tolerance: UnresponsivenessBasher BasherNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Autoimmunity and Immunodeficiency StatesDocument76 pagesMechanisms of Autoimmunity and Immunodeficiency Statesogenyisam300No ratings yet
- Complementary and Alternative Medical Lab Testing Part 14: ImmunologyFrom EverandComplementary and Alternative Medical Lab Testing Part 14: ImmunologyNo ratings yet
- Choose The CORRECT AnswerDocument2 pagesChoose The CORRECT Answerdiaa skamNo ratings yet
- Choose The Correct AnswerDocument2 pagesChoose The Correct Answerdiaa skamNo ratings yet
- Choose The Correct Answer:-: 1-Acute Localized Otitis Externa (Furuncle) Is Caused byDocument2 pagesChoose The Correct Answer:-: 1-Acute Localized Otitis Externa (Furuncle) Is Caused bydiaa skamNo ratings yet
- Choose The Correct Answer::-1-Otogenic Brain Abscess NecessitatesDocument2 pagesChoose The Correct Answer::-1-Otogenic Brain Abscess Necessitatesdiaa skamNo ratings yet
- Choose The CORRECT Answer:-: ENT Department Time Allowed Name NumberDocument3 pagesChoose The CORRECT Answer:-: ENT Department Time Allowed Name Numberdiaa skamNo ratings yet
- Choose The CORRECT AnswerDocument2 pagesChoose The CORRECT Answerdiaa skamNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and PoisonsDocument1 pageCommon Drugs and Poisonsdiaa skamNo ratings yet
- Choose The CORRECT Answer:-1 - Watery Ear Discharge Is Seen inDocument2 pagesChoose The CORRECT Answer:-1 - Watery Ear Discharge Is Seen indiaa skamNo ratings yet
- Toxicology and Sudden DeathDocument1 pageToxicology and Sudden Deathdiaa skamNo ratings yet
- Environmental Toxicology: Arsenic PoisoningDocument1 pageEnvironmental Toxicology: Arsenic Poisoningdiaa skamNo ratings yet
- Clinical Feature: (Pathology Department Book)Document6 pagesClinical Feature: (Pathology Department Book)diaa skamNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Diseases - MicroDocument30 pagesAutoimmune Diseases - Microdiaa skamNo ratings yet
- Zamecnik 2019Document9 pagesZamecnik 2019diaa skamNo ratings yet
- Acute Otitis Media (English)Document8 pagesAcute Otitis Media (English)diaa skamNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Chagas' Disease: Pregnancy and Congenital TransmissionDocument11 pagesReview Article: Chagas' Disease: Pregnancy and Congenital Transmissiondiaa skamNo ratings yet
- ToxocologyDocument1 pageToxocologydiaa skamNo ratings yet
- Burnett 2019Document15 pagesBurnett 2019diaa skamNo ratings yet
- Effects of Malaria During Pregnancy On Infant Mortality in An Area of Low Malaria TransmissionDocument7 pagesEffects of Malaria During Pregnancy On Infant Mortality in An Area of Low Malaria Transmissiondiaa skamNo ratings yet
- Congenital Parasitic Infections A Review PDFDocument16 pagesCongenital Parasitic Infections A Review PDFdiaa skamNo ratings yet
- (From The Surgical Laboratory of The Peter Bent Brigkara Hospital, and The Laboratory (Or Surgical Research, Harvard Medical Sckool)Document12 pages(From The Surgical Laboratory of The Peter Bent Brigkara Hospital, and The Laboratory (Or Surgical Research, Harvard Medical Sckool)diaa skamNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasma Gondii Infection in PregnantDocument5 pagesToxoplasma Gondii Infection in Pregnantdiaa skamNo ratings yet
- Etiology of Autoimmune Disease: Past, Present and Future: CommentaryDocument3 pagesEtiology of Autoimmune Disease: Past, Present and Future: Commentarydiaa skamNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Toxoplasma Gondii: EditorialcommentaryDocument3 pagesPrenatal Toxoplasma Gondii: Editorialcommentarydiaa skamNo ratings yet
- Ent Model MCQ 2007 - 2Document9 pagesEnt Model MCQ 2007 - 2diaa skamNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Nature or Nurture?Document8 pagesPathophysiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Nature or Nurture?diaa skamNo ratings yet
- What Is Cardiomyopathy?Document11 pagesWhat Is Cardiomyopathy?ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- MeniereDocument5 pagesMeniereMayls Sevilla CalizoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Biotechnology (BT) : Engineering MathematicsDocument2 pagesSyllabus For Biotechnology (BT) : Engineering MathematicsManoj SkNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid Gland Diseases: Primary Hyperparathyroidism HypoparathyroidismDocument25 pagesParathyroid Gland Diseases: Primary Hyperparathyroidism HypoparathyroidismZahrah El FaradisaNo ratings yet
- Cytochrome P450 Structure, Mechanism, and Biochemistry 3rd Edition by Paul R. Ortiz de MontellanoDocument702 pagesCytochrome P450 Structure, Mechanism, and Biochemistry 3rd Edition by Paul R. Ortiz de MontellanoBrittanie MouzonNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Sensitivity To Chlorhexidine, Voriconazole and ItraconazoleDocument7 pagesEvaluation of The Sensitivity To Chlorhexidine, Voriconazole and ItraconazoleNurul JannahNo ratings yet
- Understanding Motor Neuron DiseaseDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Motor Neuron Diseasemasa eNo ratings yet
- Congenital Hips DislocationDocument6 pagesCongenital Hips DislocationMar OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- FELASA Recommendation For Health Monitoring of Mouse, Rat, Hamster, Guinea Pig and RabbitDocument15 pagesFELASA Recommendation For Health Monitoring of Mouse, Rat, Hamster, Guinea Pig and RabbitRamanaReddyNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Habbatussauda Sebagai NefroprotectiveDocument6 pagesJurnal Habbatussauda Sebagai Nefroprotectivenoni wahyuniNo ratings yet
- Understanding Biology Kenneth Mason Et Al Ebook Full ChapterDocument51 pagesUnderstanding Biology Kenneth Mason Et Al Ebook Full Chapterjoshua.mayer789100% (5)
- Charmanta Sambo CV UpdatedDocument2 pagesCharmanta Sambo CV Updatedapi-625293707No ratings yet
- Genetic CounsellingDocument3 pagesGenetic Counsellingavinash dhameriyaNo ratings yet
- JAT - CHT 13Document68 pagesJAT - CHT 13j_smith24No ratings yet
- Blood Cells - eDocument3 pagesBlood Cells - eTai Yin LAMNo ratings yet
- Covid ReportDocument5 pagesCovid Reportraojip1232No ratings yet
- The World Federation of Adhd GuideDocument134 pagesThe World Federation of Adhd GuideolNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity1 - LoboseaDocument21 pagesLab Activity1 - LoboseaJosh Buenafe MacapallagNo ratings yet
- The Functions of Human Saliva - A ReviewDocument12 pagesThe Functions of Human Saliva - A ReviewRaúl Ernesto Quispe CórdovaNo ratings yet
- Psyc 100 NotesDocument157 pagesPsyc 100 NotesJi Wook HwangNo ratings yet
- Quillen Quirks 2013Document85 pagesQuillen Quirks 2013Anand SahaNo ratings yet
- OsteomalaciaDocument28 pagesOsteomalaciaReginette Pisalbo ChanNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Pediatric FlatfootDocument33 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Pediatric FlatfootIfrim MihaiNo ratings yet
- Calcium HomeostasisDocument2 pagesCalcium HomeostasisyunisasinagaNo ratings yet
- Current Status and Challenges of Stem Cell Treatment For Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument19 pagesCurrent Status and Challenges of Stem Cell Treatment For Alzheimer's DiseaseHelical Nail FemurNo ratings yet
- Draft Circular LIC's Cancer Cover - 28.09.17Document10 pagesDraft Circular LIC's Cancer Cover - 28.09.17bbbbbbNo ratings yet
- EFTand FibromyalgiaDocument6 pagesEFTand Fibromyalgiacharliesangel2012No ratings yet
- (Smtebooks - Com) A Century of Geneticists - Mutation To Medicine 1st EditionDocument322 pages(Smtebooks - Com) A Century of Geneticists - Mutation To Medicine 1st Editiondehbash20No ratings yet