Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.1 Lecture 8 - Orders Driving Prices (Level1 - Level2 - Time and Sales) PDF
2.1 Lecture 8 - Orders Driving Prices (Level1 - Level2 - Time and Sales) PDF
Uploaded by
UDAYAN SHAHOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.1 Lecture 8 - Orders Driving Prices (Level1 - Level2 - Time and Sales) PDF
2.1 Lecture 8 - Orders Driving Prices (Level1 - Level2 - Time and Sales) PDF
Uploaded by
UDAYAN SHAHCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 8
Orders Driving Prices
Example of orders driving prices:
Company name:
Ticker:
Listing exchange:
Shares outstanding:
Float:
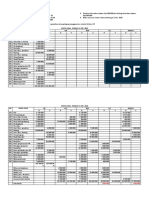
Market participant current positions:
Participants Participant Type Position
1 40,000
2 10,000
3 2,000
4 0
5 2,000
6 5,000
7 1,000
8 0
9 10,000
10 5,000
Market participant orders
Participants Side Quantity Order Type Price
1 Buy 3000 Limit 41
2 Buy 5000 Limit 39
2 Sell 5000 Limit 55
2 Sell 5000 Limit 59
3 Sell 2000 Limit 52
4 - - - -
5 Buy 1000 Limit 50
6 Buy 2000 Limit 48
7 Sell 1000 Limit 51
8 Buy 5000 Limit 46
9 Sell 5000 Market NA
10 Buy 5000 Limit 53
Example of orders driving prices(continued):
Ticker: Combination of letters that represent a particular company that is listed on
an exchange.
Bid: (or bid price) Is the highest price that a buyer/bidder is willing to pay for a prod-
uct.
Ask: (or ask price or offer) Is the lowest price that a seller is willing to receive for a
product.
Spread: Difference between the ask price to the bid price.
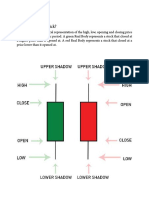
Level1: Displays the bid and ask prices as well as quantities. This also displays the last
trade executed.
NBBO (National Best Bid and Offer): This represents the highest bid and lowest
ask available on the market.
Time and Sales: Displays every single execution that happens on the market. The
executions are displayed real-time and include information like: time, direction, quan-
tity traded and exchange traded on.
Level2 / Order book: Electronic list of buy and sell orders for a stock. This list is
ordered by price and then by time. The order book lists the number of shares on the
bid and ask at every price point.
You might also like
- Beer Game Reflective ReportDocument7 pagesBeer Game Reflective Reportcancer6100% (1)
- FINC6015 Week 3 QuestionsDocument5 pagesFINC6015 Week 3 QuestionsFrank Liu100% (1)
- BestBooks Agent 2 PDFDocument3 pagesBestBooks Agent 2 PDFLindaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18 Relative Strength Index RSI PDFDocument1 pageLecture 18 Relative Strength Index RSI PDFbraetto_1x1100% (1)
- Lecture 13 Candlesticks PDFDocument5 pagesLecture 13 Candlesticks PDFbraetto_1x1No ratings yet
- Almonds - Feasibility Study For Processing PlanDocument15 pagesAlmonds - Feasibility Study For Processing Planbraetto_1x1No ratings yet
- NestleDocument16 pagesNestlegopikaNo ratings yet
- InvoiceDocument1 pageInvoiceAbhijeet Kumar MeenaNo ratings yet
- Book Presentation:: The Fifth Discipline The Art & Practice of The Learning OrganizationDocument41 pagesBook Presentation:: The Fifth Discipline The Art & Practice of The Learning OrganizationEmerita Modesto100% (3)
- Barilla Spa Case FinalDocument6 pagesBarilla Spa Case FinalRohitHarikrishnanNo ratings yet
- HUL Rural MarketingDocument22 pagesHUL Rural Marketingtoto04858100% (1)
- All LecturesDocument50 pagesAll LecturesSrinivasan BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- PARTE1 FinancialMarketDocument54 pagesPARTE1 FinancialMarketBeltrán ZamoranoNo ratings yet
- Micro Eco, Ch-6Document20 pagesMicro Eco, Ch-6Umma Tanila RemaNo ratings yet
- Acccob3 k48 Hw4 Valdez NeoDocument6 pagesAcccob3 k48 Hw4 Valdez NeoneovaldezNo ratings yet
- Folio Dashboard: PolarisDocument28 pagesFolio Dashboard: PolarisJeniffer RayenNo ratings yet
- IFM-Chap 8 - Options - 3.11.2019Document44 pagesIFM-Chap 8 - Options - 3.11.2019Son VuNo ratings yet
- Servies Items 05Document1 pageServies Items 05SIPAN KURDINo ratings yet
- 2-2: Volksmaschine: Kevin: 32 Sumegh: 28 Atul: 04 Sanjay: 17 Gayatri: 25Document19 pages2-2: Volksmaschine: Kevin: 32 Sumegh: 28 Atul: 04 Sanjay: 17 Gayatri: 25Sanjay GhodadraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7.1 - DPB10013 Perfect CompetitionDocument40 pagesChapter 7.1 - DPB10013 Perfect CompetitionSuzana binti ithnain - PNSNo ratings yet
- P5-6a & P - 6.5aDocument8 pagesP5-6a & P - 6.5aShahriar HaqueNo ratings yet
- Litepaper YpredictDocument1 pageLitepaper YpredictSharon NwozaNo ratings yet
- CVP Analysis Q.1-10Document28 pagesCVP Analysis Q.1-10James WisleyNo ratings yet
- Topic01-Orders C6gF8Document43 pagesTopic01-Orders C6gF8Chika Nwogu-AgbakuruNo ratings yet
- My Forex Journey: By: Adonis C CorowanDocument14 pagesMy Forex Journey: By: Adonis C CorowanAdonis CorowanNo ratings yet
- Market Structures: (Mankiw, Chapter 14,15,16,17)Document34 pagesMarket Structures: (Mankiw, Chapter 14,15,16,17)Tonny NguyenNo ratings yet
- Futures Part 1Document24 pagesFutures Part 1Biswajit SarmaNo ratings yet
- TYBBA A - Group 1Document8 pagesTYBBA A - Group 1Harjas anandNo ratings yet
- Oroya Corporation - Oroya SegregationDocument8 pagesOroya Corporation - Oroya SegregationJULLIE CARMELLE H. CHATTONo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Market Structure - 1 - 2020Document31 pagesChapter 9 - Market Structure - 1 - 2020abcNo ratings yet
- Satyam 116 400 46400 320.16 46720.16 Satyam 50 400 20000 138 20138Document74 pagesSatyam 116 400 46400 320.16 46720.16 Satyam 50 400 20000 138 20138jitendrasmaliNo ratings yet
- Futures 1Document56 pagesFutures 1Rajat KatariaNo ratings yet
- Options Bull BearDocument6 pagesOptions Bull BearRaunaq KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - SD - 11 Sep 2022Document12 pagesTopic 3 - SD - 11 Sep 2022Shubham DagaNo ratings yet
- Buy StraddleDocument2 pagesBuy StraddleAKSHAYA AKSHAYANo ratings yet
- Economics Tutorial 7Document30 pagesEconomics Tutorial 7LI SIEN CHEW100% (1)
- PSE New Trading RulesDocument3 pagesPSE New Trading RulesknightshaloNo ratings yet
- Market StructureDocument31 pagesMarket StructureAnuj SachdevNo ratings yet
- Fixed Costs Inhouse Sales Executives: Number of Sales Reps Required (Rounded Off) 3Document4 pagesFixed Costs Inhouse Sales Executives: Number of Sales Reps Required (Rounded Off) 3Tanveer GagnaniNo ratings yet
- Textbook - STPP 13c 7 56 21 48Document28 pagesTextbook - STPP 13c 7 56 21 48aba22deepakNo ratings yet
- Accounts PayableDocument13 pagesAccounts Payableanurag vermaNo ratings yet
- FX VolDocument11 pagesFX VolCocoa ManNo ratings yet
- MERCHANDISING ENTITY - Docx NO ANSWERSDocument7 pagesMERCHANDISING ENTITY - Docx NO ANSWERSmartinez2331999No ratings yet
- Chapter 08 5th Edn Revised by JHDocument53 pagesChapter 08 5th Edn Revised by JHVy Tran LinhNo ratings yet
- Session7 PerfectCompetitionDocument57 pagesSession7 PerfectCompetitionShreyas DixitNo ratings yet
- MaterialDocument5 pagesMaterialmajid aliNo ratings yet
- Futures 1Document66 pagesFutures 1shivaNo ratings yet
- w1 TuteDocument4 pagesw1 TuteDylan AdrianNo ratings yet
- Supply and Demand I: How Markets WorkDocument72 pagesSupply and Demand I: How Markets WorkRashmeet AroraNo ratings yet
- FINS2624 Lecture 1: Asset Classes, Trading, and Investment CompaniesDocument54 pagesFINS2624 Lecture 1: Asset Classes, Trading, and Investment CompaniesChenyu WangNo ratings yet
- Pasicolan, Mark Joshua BSA 3206: Absorption CostingDocument6 pagesPasicolan, Mark Joshua BSA 3206: Absorption CostingMark Joshua PasicolanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument33 pagesChapter 4 PDFAdda KadhilaNo ratings yet
- Selesaikan Kertas Kerja - Catatan Untuk Penyesuaian Persediaan Barang Dagang Menggunakan Metode Ikhtisar L/RDocument5 pagesSelesaikan Kertas Kerja - Catatan Untuk Penyesuaian Persediaan Barang Dagang Menggunakan Metode Ikhtisar L/RRebel ChannelNo ratings yet
- Option Trading StrategiesDocument2 pagesOption Trading StrategiesAKSHAYA AKSHAYANo ratings yet
- Market Competition Actual1123Document27 pagesMarket Competition Actual1123oshimo.tokuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Economic Assignment (Submitted by Group (6) )Document9 pagesIntroduction To Economic Assignment (Submitted by Group (6) )Khun Zwe Man MyintNo ratings yet
- EBook - YouTube HandbookDocument29 pagesEBook - YouTube Handbookditiromandewo14No ratings yet
- Perfect Competition: Key Concepts Practice Quiz Internet ExercisesDocument95 pagesPerfect Competition: Key Concepts Practice Quiz Internet ExercisesGabe ParkerNo ratings yet
- Perfect Competition: Key Concepts Practice Quiz Internet ExercisesDocument95 pagesPerfect Competition: Key Concepts Practice Quiz Internet ExercisesGabe ParkerNo ratings yet
- Derivatives Crux Notes LDRDocument11 pagesDerivatives Crux Notes LDRjobsoutsource1001No ratings yet
- Beginner's Guide To CFDs 1.1-1.3Document7 pagesBeginner's Guide To CFDs 1.1-1.3pmlsimoesNo ratings yet
- Class Notes 2 Securities Trading: 2.1 Two Basic Concepts in Financial EconomicsDocument12 pagesClass Notes 2 Securities Trading: 2.1 Two Basic Concepts in Financial EconomicsMohamed MadyNo ratings yet
- Tradex Data (Since April 2016)Document73 pagesTradex Data (Since April 2016)Neeraj KrNo ratings yet
- AP 5904Q InvestmentsDocument6 pagesAP 5904Q InvestmentsRhea NograNo ratings yet
- Zero Rupee Marketing WorksheetDocument7 pagesZero Rupee Marketing WorksheetSharveshNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument6 pagesAnswerMyron BrandwineNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument6 pagesAnswerMyron BrandwineNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Capital Markets: Products, Strategies, ParticipantsFrom EverandAn Introduction to Capital Markets: Products, Strategies, ParticipantsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 31 Confirmation Bias PDFDocument1 pageLecture 31 Confirmation Bias PDFbraetto_1x1No ratings yet
- Lecture 24 Money Management PDFDocument2 pagesLecture 24 Money Management PDFbraetto_1x1No ratings yet
- Lecture 30 Anchoring Effect PDFDocument1 pageLecture 30 Anchoring Effect PDFbraetto_1x1No ratings yet
- Lecture 22 Batting Average Win Loss Ratio PDFDocument1 pageLecture 22 Batting Average Win Loss Ratio PDFbraetto_1x1No ratings yet
- Chart Patterns: Head and ShouldersDocument6 pagesChart Patterns: Head and Shouldersbraetto_1x1No ratings yet
- Loss Aversion: How Itaff Ects Our TradingDocument1 pageLoss Aversion: How Itaff Ects Our Tradingbraetto_1x1No ratings yet
- Lecture 12 Charts Candlesticks PDFDocument1 pageLecture 12 Charts Candlesticks PDFbraetto_1x1No ratings yet
- Lecture 26 The Importance of Psychology PDFDocument1 pageLecture 26 The Importance of Psychology PDFbraetto_1x1No ratings yet
- Lecture 20 Expectancy PDFDocument2 pagesLecture 20 Expectancy PDFbraetto_1x1No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 What Is A Stock PDFDocument1 pageLecture 3 What Is A Stock PDFbraetto_1x1No ratings yet
- Lecture 16 Volume PDFDocument1 pageLecture 16 Volume PDFbraetto_1x1No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 What Is A Market PDFDocument1 pageLecture 4 What Is A Market PDFbraetto_1x1No ratings yet
- S02 3G RPLS2 - v2-0 The Physical LayerDocument74 pagesS02 3G RPLS2 - v2-0 The Physical LayerginnboonyauNo ratings yet
- Channel DecisionsDocument30 pagesChannel Decisionsuzmatabassum1996No ratings yet
- Solutions To End of Mankiw 4 SolproblemsDocument1 pageSolutions To End of Mankiw 4 SolproblemsNatasha VaniaNo ratings yet
- Nature Scope SCM 1Document24 pagesNature Scope SCM 1Parmeet kaurNo ratings yet
- Marketing Mix 27psDocument3 pagesMarketing Mix 27psMOHAMMAD SAIFUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- LDocument34 pagesLharisankar sureshNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Supermarket Information Management SystemDocument59 pagesDesign and Implementation of Supermarket Information Management SystemAyinde AbiodunNo ratings yet
- NC5 - Procurement and Supply StakeholdersDocument3 pagesNC5 - Procurement and Supply StakeholdersHus NiaNo ratings yet
- Distribution Channels of KMFDocument13 pagesDistribution Channels of KMFvenucoldNo ratings yet
- Demo Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesDemo Lesson PlangviolaNo ratings yet
- Tour OperatorsDocument9 pagesTour OperatorsKoechNo ratings yet
- Final Marketing Strategy Surf ExcelDocument35 pagesFinal Marketing Strategy Surf Exceltalhahpatel100% (8)
- Topic 8 - Accounting For Merchandising OperationDocument36 pagesTopic 8 - Accounting For Merchandising Operationdenixng100% (2)
- Ikea Assembles $1.4bn China Expansion Drive - Financial TimesDocument2 pagesIkea Assembles $1.4bn China Expansion Drive - Financial TimeshvsbouaNo ratings yet
- In Re Keurig Green Mountain Antitrust PDFDocument99 pagesIn Re Keurig Green Mountain Antitrust PDFMark JaffeNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER3 - Channel Analysis Auditing Marketing Channels PDFDocument10 pagesCHAPTER3 - Channel Analysis Auditing Marketing Channels PDFPramod PatilNo ratings yet
- 1 India Family Mart ReportDocument29 pages1 India Family Mart Reportठाकुर निशांत सिंहNo ratings yet
- Learning Insight CH 4 Buisness Markets and Business Buying BehaviorDocument6 pagesLearning Insight CH 4 Buisness Markets and Business Buying BehaviorMonette Calpe AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Costco Wholesale Corporation PaperDocument7 pagesCostco Wholesale Corporation Paperdian ratnasariNo ratings yet
- Cadbury Final 1Document28 pagesCadbury Final 1shwetaadlakha16No ratings yet
- Supply Curve Ppt-1Document18 pagesSupply Curve Ppt-1mansi mehtaNo ratings yet
- Funskool Domestic Catalog 2017Document6 pagesFunskool Domestic Catalog 2017Smita Sawant BholeNo ratings yet
- Operational McqsDocument59 pagesOperational McqsADNAN ABBASNo ratings yet
- Kimball's Restaurant Ch. 9Document4 pagesKimball's Restaurant Ch. 9Nabeela MushtaqNo ratings yet
- 1520954299311Document1 page1520954299311AlokNo ratings yet
- Shelly Field - Career Opportunities in The Retail and Wholesale Industry, 2nd Edition (2009)Document351 pagesShelly Field - Career Opportunities in The Retail and Wholesale Industry, 2nd Edition (2009)fdlskfjNo ratings yet