Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Photorespiration
Photorespiration
Uploaded by
Anis AzwaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Tutorial 4Document2 pagesTutorial 4Anis AzwaNo ratings yet
- PhotorespirationDocument16 pagesPhotorespirationMoa ArmyNo ratings yet
- The Calvin CycleDocument8 pagesThe Calvin CycleVaan ChinNo ratings yet
- C4 PathwayDocument8 pagesC4 PathwayInnocent mugumeNo ratings yet
- Photosynthetic Adaptations: C Cycle and CAM: Prepared By: Group 7 (Cabatingan, Ocaya, Cardente, Guillermo, and Andamon)Document8 pagesPhotosynthetic Adaptations: C Cycle and CAM: Prepared By: Group 7 (Cabatingan, Ocaya, Cardente, Guillermo, and Andamon)Una Kaya CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Photorespiration: The Assignment Submitted by Mumtahin Ul KousarDocument11 pagesPhotorespiration: The Assignment Submitted by Mumtahin Ul KousarJunaid MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 PhotorespirationDocument12 pagesBio 11 PhotorespirationBik WodeNo ratings yet
- Revision Chapter 6 Photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)Document6 pagesRevision Chapter 6 Photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)MOHAMAD SAHIMI BIN MAHAT MoeNo ratings yet
- Calvin Cycle (Dark Reactions / Light Independent Reaction)Document47 pagesCalvin Cycle (Dark Reactions / Light Independent Reaction)L'ya Lieslotte100% (2)
- Alternative Carbon FixationDocument18 pagesAlternative Carbon Fixationlady ann apple colipanoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Prof. S. Dutta GuptaDocument41 pagesPhotosynthesis: Prof. S. Dutta Guptahimanshu_agraNo ratings yet
- Activity10answers PDFDocument6 pagesActivity10answers PDFMuthu LakshmiNo ratings yet
- C6 (Photosynthesis)Document16 pagesC6 (Photosynthesis)nurhasinahabrahimNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesissteven7 IsaacsNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS PATHWAYS - rePORTDocument22 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS PATHWAYS - rePORTGarry Michael Tarroma SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Comparing and Contrasting C3, C4, CAM - AP BiologyDocument1 pageComparing and Contrasting C3, C4, CAM - AP BiologyFVCproductionsNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument11 pagesCalvin CycleELVIRA L. ABULOKNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Fundamentals Fundamentals of Crop Science of Crop Science of Crop ScienceDocument39 pagesFundamentals Fundamentals Fundamentals of Crop Science of Crop Science of Crop ScienceAlthea DoradoNo ratings yet
- Temu Man0000Document2 pagesTemu Man0000Elijah IbsaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7th: PhotosynthesisDocument50 pagesLecture 7th: Photosynthesisfaheemyours7No ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Photosynthesis: Light Independent Reactions: How Is Chemical Energy Stored in Glucose MoleculesDocument18 pagesChapter 7: Photosynthesis: Light Independent Reactions: How Is Chemical Energy Stored in Glucose MoleculesJonard PedrosaNo ratings yet
- 18 PhotorespirationDocument21 pages18 Photorespiration黄心怡No ratings yet
- Lec4 PhotosynthesisDocument50 pagesLec4 PhotosynthesisPLANARIANo ratings yet
- Biosynthetic Pathway Dark ReactionDocument5 pagesBiosynthetic Pathway Dark ReactionspenzercadienteeNo ratings yet
- Biol1Xx7 Photosynthesis II Calvin Cycle & CO Fixation: Assoc Prof Charles WarrenDocument28 pagesBiol1Xx7 Photosynthesis II Calvin Cycle & CO Fixation: Assoc Prof Charles WarrenRachaelNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Study Material C4 Cycle OnwardsDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesis Study Material C4 Cycle OnwardsmoonyNo ratings yet
- Function of PhotosynthesisDocument58 pagesFunction of PhotosynthesisJulian ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Algae Technology Report: IndexDocument20 pagesAlgae Technology Report: IndexSteve RacoosinNo ratings yet
- Hatch and Slack CycleDocument30 pagesHatch and Slack CycleKalyani SreejithNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesChapter-4 Photosynthesiskavitaruby1980No ratings yet
- 10 Icse - Biology: Photosynthesis - Summary NotesDocument5 pages10 Icse - Biology: Photosynthesis - Summary NotesKUMAWAT DEEPIKANo ratings yet
- Day 5 Cam, C3, C4Document50 pagesDay 5 Cam, C3, C4Bruh MomentNo ratings yet
- C4 Carbon Fixation - WikipediaDocument55 pagesC4 Carbon Fixation - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Outline Electron Transport Chain in PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesOutline Electron Transport Chain in PhotosynthesisspenzercadienteeNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument55 pagesPhotosynthesischezkanoelleangeliebalolongNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 c4 and CAMDocument15 pagesBio 11 c4 and CAMBik WodeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Dark ReactionDocument14 pagesLecture 9 - Dark ReactionAtika ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- C2 C3 C4 & Cam Variations On The Theme of PhotosynthesisDocument20 pagesC2 C3 C4 & Cam Variations On The Theme of PhotosynthesisKoons KoonsNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide in Organisms and Ecosystems EssayDocument2 pagesCarbon Dioxide in Organisms and Ecosystems EssayDavidIsmailBarkerNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis:: Variations On The ThemeDocument22 pagesPhotosynthesis:: Variations On The ThemeHaq ChandioNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesisthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy Assignment 1Document3 pagesPlant Anatomy Assignment 1anon_711152134No ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants: Very Short Answers QuestionsDocument10 pagesChapter-4 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants: Very Short Answers QuestionsPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Ch. 8 Photosynthesis F17Document70 pagesCh. 8 Photosynthesis F17bae loonaNo ratings yet
- Alternative Pathways Oi PalmDocument14 pagesAlternative Pathways Oi PalmbenzzzxNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis WorksheetDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis WorksheetAshley JohnsNo ratings yet
- Ikh 209 HG JW7 QW Ivv DRF WDocument15 pagesIkh 209 HG JW7 QW Ivv DRF Waanyapandey102No ratings yet
- Energy Variations PracticeDocument3 pagesEnergy Variations Practiceapi-522847737No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesisbluemonkeymei4921100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Reading Questions-1-1Document2 pagesChapter 7 Reading Questions-1-1Default AccountNo ratings yet
- Light Independent Reaction - BiologyDocument3 pagesLight Independent Reaction - BiologyHidayah SakinahNo ratings yet
- Assignment of C3 PATHWAYDocument4 pagesAssignment of C3 PATHWAYWorld FootballNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Reading QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 7 Reading QuestionsDefault AccountNo ratings yet
- Carbon Fixation Activity SheetDocument2 pagesCarbon Fixation Activity SheetLesley BoultonNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Leaf StructureDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis: Leaf StructureMonica Sario PolicinaNo ratings yet
- C4 Carbon Fixation - WikipediaDocument28 pagesC4 Carbon Fixation - WikipediaLalit ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Finals Gen Physio Lab ExamDocument3 pagesFinals Gen Physio Lab ExamShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 13 PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesBiology Chapter 13 PhotosynthesisSokuntheary SrunNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 Sample Problem AnswersDocument1 pageLecture 14 Sample Problem Answerssonicdragon100% (1)
- Crop Ecology - Productivity and Management in Agricultural Systems - (2011) Queensland Recomendation-275-295Document21 pagesCrop Ecology - Productivity and Management in Agricultural Systems - (2011) Queensland Recomendation-275-295CarolinaNo ratings yet
- CHM131 General Chemistry Tutorial 4B: Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesCHM131 General Chemistry Tutorial 4B: Chemical BondingAnis AzwaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6Document2 pagesTutorial 6Anis AzwaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial chm131Document3 pagesTutorial chm131Anis AzwaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2aDocument1 pageTutorial 2aAnis AzwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MAT238 PDFDocument16 pagesChapter 2 MAT238 PDFAnis AzwaNo ratings yet
Photorespiration
Photorespiration
Uploaded by
Anis AzwaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Photorespiration
Photorespiration
Uploaded by
Anis AzwaCopyright:
Available Formats
NUR ANIS AZWA BINTI MD ROBAI 2019273012
1. When does the photorespiration occur?
Photorespiration occurs during hot and dry days where plants close their stomata. The
concentration of carbon dioxide is low and concentration of oxygen is high. This is because
enzyme name rubisco fix oxygen as substrate instead of carbon dioxide.
2. What happen to O2 and CO2 during photorespiration?
Oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) will compete with each other for the same active site on
RuBP oxygenase-carboxylase (Rubisco). As the concentration of oxygen is higher than carbon
dioxide, oxygen will act as competitive inhibitor and RuBP carboxylase will fix to RuBP instead of
carbon dioxide.
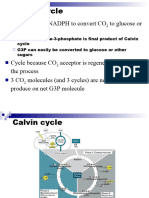
3. Why does C3 plant produce less sugar during photorespiration?
This is because the declining level of CO2 in the leaf starves the Calvin cycle.
4. Why photorespiration considered as a wasteful process?
This is because photosynthetic rate will reduce. Firstly, unlike normal respiration (produce ATP),
photorespiration produce no ATP in fact it consume more ATP. Next, unlike photosynthesis
(produce sugar), photorespiration does not produce sugar or organic molecule instead it
decrease photosynthetic output by using organic material for Calvin cycle.
5. Write the reaction equation in photorespiration.
O2 + RuBP ---- Gycolate (2C)
rubisco
6. How does plant minimize photorespiration?
Plant can minimize photorespiration by increase the concentration of CO2 in the leaves so that
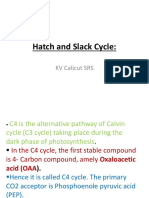
RuBP carboxylase is less likely to produce glycolate through reaction with O2. Next is alternative
mechanism of carbon fixation. First, hatch and slack C4 plant to fix different cells by capture CO2
in mesophyll cells and release it to the bundle sheath cells, where CO2 concentration is low.
Secondly, Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM) to fix CO2 different time by allows absorption of
CO2 to take place at night so that stomata can be close during the day to prevent water loss.
You might also like
- Tutorial 4Document2 pagesTutorial 4Anis AzwaNo ratings yet
- PhotorespirationDocument16 pagesPhotorespirationMoa ArmyNo ratings yet
- The Calvin CycleDocument8 pagesThe Calvin CycleVaan ChinNo ratings yet
- C4 PathwayDocument8 pagesC4 PathwayInnocent mugumeNo ratings yet
- Photosynthetic Adaptations: C Cycle and CAM: Prepared By: Group 7 (Cabatingan, Ocaya, Cardente, Guillermo, and Andamon)Document8 pagesPhotosynthetic Adaptations: C Cycle and CAM: Prepared By: Group 7 (Cabatingan, Ocaya, Cardente, Guillermo, and Andamon)Una Kaya CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Photorespiration: The Assignment Submitted by Mumtahin Ul KousarDocument11 pagesPhotorespiration: The Assignment Submitted by Mumtahin Ul KousarJunaid MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 PhotorespirationDocument12 pagesBio 11 PhotorespirationBik WodeNo ratings yet
- Revision Chapter 6 Photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)Document6 pagesRevision Chapter 6 Photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)MOHAMAD SAHIMI BIN MAHAT MoeNo ratings yet
- Calvin Cycle (Dark Reactions / Light Independent Reaction)Document47 pagesCalvin Cycle (Dark Reactions / Light Independent Reaction)L'ya Lieslotte100% (2)
- Alternative Carbon FixationDocument18 pagesAlternative Carbon Fixationlady ann apple colipanoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Prof. S. Dutta GuptaDocument41 pagesPhotosynthesis: Prof. S. Dutta Guptahimanshu_agraNo ratings yet
- Activity10answers PDFDocument6 pagesActivity10answers PDFMuthu LakshmiNo ratings yet
- C6 (Photosynthesis)Document16 pagesC6 (Photosynthesis)nurhasinahabrahimNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesissteven7 IsaacsNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS PATHWAYS - rePORTDocument22 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS PATHWAYS - rePORTGarry Michael Tarroma SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Comparing and Contrasting C3, C4, CAM - AP BiologyDocument1 pageComparing and Contrasting C3, C4, CAM - AP BiologyFVCproductionsNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument11 pagesCalvin CycleELVIRA L. ABULOKNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Fundamentals Fundamentals of Crop Science of Crop Science of Crop ScienceDocument39 pagesFundamentals Fundamentals Fundamentals of Crop Science of Crop Science of Crop ScienceAlthea DoradoNo ratings yet
- Temu Man0000Document2 pagesTemu Man0000Elijah IbsaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7th: PhotosynthesisDocument50 pagesLecture 7th: Photosynthesisfaheemyours7No ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Photosynthesis: Light Independent Reactions: How Is Chemical Energy Stored in Glucose MoleculesDocument18 pagesChapter 7: Photosynthesis: Light Independent Reactions: How Is Chemical Energy Stored in Glucose MoleculesJonard PedrosaNo ratings yet
- 18 PhotorespirationDocument21 pages18 Photorespiration黄心怡No ratings yet
- Lec4 PhotosynthesisDocument50 pagesLec4 PhotosynthesisPLANARIANo ratings yet
- Biosynthetic Pathway Dark ReactionDocument5 pagesBiosynthetic Pathway Dark ReactionspenzercadienteeNo ratings yet
- Biol1Xx7 Photosynthesis II Calvin Cycle & CO Fixation: Assoc Prof Charles WarrenDocument28 pagesBiol1Xx7 Photosynthesis II Calvin Cycle & CO Fixation: Assoc Prof Charles WarrenRachaelNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Study Material C4 Cycle OnwardsDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesis Study Material C4 Cycle OnwardsmoonyNo ratings yet
- Function of PhotosynthesisDocument58 pagesFunction of PhotosynthesisJulian ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Algae Technology Report: IndexDocument20 pagesAlgae Technology Report: IndexSteve RacoosinNo ratings yet
- Hatch and Slack CycleDocument30 pagesHatch and Slack CycleKalyani SreejithNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesChapter-4 Photosynthesiskavitaruby1980No ratings yet
- 10 Icse - Biology: Photosynthesis - Summary NotesDocument5 pages10 Icse - Biology: Photosynthesis - Summary NotesKUMAWAT DEEPIKANo ratings yet
- Day 5 Cam, C3, C4Document50 pagesDay 5 Cam, C3, C4Bruh MomentNo ratings yet
- C4 Carbon Fixation - WikipediaDocument55 pagesC4 Carbon Fixation - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Outline Electron Transport Chain in PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesOutline Electron Transport Chain in PhotosynthesisspenzercadienteeNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument55 pagesPhotosynthesischezkanoelleangeliebalolongNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 c4 and CAMDocument15 pagesBio 11 c4 and CAMBik WodeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Dark ReactionDocument14 pagesLecture 9 - Dark ReactionAtika ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- C2 C3 C4 & Cam Variations On The Theme of PhotosynthesisDocument20 pagesC2 C3 C4 & Cam Variations On The Theme of PhotosynthesisKoons KoonsNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide in Organisms and Ecosystems EssayDocument2 pagesCarbon Dioxide in Organisms and Ecosystems EssayDavidIsmailBarkerNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis:: Variations On The ThemeDocument22 pagesPhotosynthesis:: Variations On The ThemeHaq ChandioNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesisthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy Assignment 1Document3 pagesPlant Anatomy Assignment 1anon_711152134No ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants: Very Short Answers QuestionsDocument10 pagesChapter-4 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants: Very Short Answers QuestionsPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Ch. 8 Photosynthesis F17Document70 pagesCh. 8 Photosynthesis F17bae loonaNo ratings yet
- Alternative Pathways Oi PalmDocument14 pagesAlternative Pathways Oi PalmbenzzzxNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis WorksheetDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis WorksheetAshley JohnsNo ratings yet
- Ikh 209 HG JW7 QW Ivv DRF WDocument15 pagesIkh 209 HG JW7 QW Ivv DRF Waanyapandey102No ratings yet
- Energy Variations PracticeDocument3 pagesEnergy Variations Practiceapi-522847737No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesisbluemonkeymei4921100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Reading Questions-1-1Document2 pagesChapter 7 Reading Questions-1-1Default AccountNo ratings yet
- Light Independent Reaction - BiologyDocument3 pagesLight Independent Reaction - BiologyHidayah SakinahNo ratings yet
- Assignment of C3 PATHWAYDocument4 pagesAssignment of C3 PATHWAYWorld FootballNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Reading QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 7 Reading QuestionsDefault AccountNo ratings yet
- Carbon Fixation Activity SheetDocument2 pagesCarbon Fixation Activity SheetLesley BoultonNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Leaf StructureDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis: Leaf StructureMonica Sario PolicinaNo ratings yet
- C4 Carbon Fixation - WikipediaDocument28 pagesC4 Carbon Fixation - WikipediaLalit ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Finals Gen Physio Lab ExamDocument3 pagesFinals Gen Physio Lab ExamShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 13 PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesBiology Chapter 13 PhotosynthesisSokuntheary SrunNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 Sample Problem AnswersDocument1 pageLecture 14 Sample Problem Answerssonicdragon100% (1)
- Crop Ecology - Productivity and Management in Agricultural Systems - (2011) Queensland Recomendation-275-295Document21 pagesCrop Ecology - Productivity and Management in Agricultural Systems - (2011) Queensland Recomendation-275-295CarolinaNo ratings yet
- CHM131 General Chemistry Tutorial 4B: Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesCHM131 General Chemistry Tutorial 4B: Chemical BondingAnis AzwaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6Document2 pagesTutorial 6Anis AzwaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial chm131Document3 pagesTutorial chm131Anis AzwaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2aDocument1 pageTutorial 2aAnis AzwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MAT238 PDFDocument16 pagesChapter 2 MAT238 PDFAnis AzwaNo ratings yet