Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Manufacturing Engineering-19
Manufacturing Engineering-19
Uploaded by
SameerChauhanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Manufacturing Engineering-26Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-26SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Operation Process P. 1. Q. 2. R. 3. S. 4. 5. 6.: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageOperation Process P. 1. Q. 2. R. 3. S. 4. 5. 6.: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-16Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-16SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- A Study On PDC Drill Bits QualityDocument18 pagesA Study On PDC Drill Bits QualityAzri HamimNo ratings yet
- ME 505 Lab Exam July Dec 2020 Part 3Document2 pagesME 505 Lab Exam July Dec 2020 Part 3Shweta raiNo ratings yet
- Ghousia College of Engineering Ramanagaram: I Internal AssessmentDocument1 pageGhousia College of Engineering Ramanagaram: I Internal AssessmentSyedZameerNo ratings yet
- Objective QuestionsDocument73 pagesObjective QuestionsRajesh ShahNo ratings yet
- ME Manufacturing-Engineering PDFDocument73 pagesME Manufacturing-Engineering PDFpankajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (45-70)Document26 pagesChapter 3 (45-70)chaib boudabNo ratings yet
- Modern Machining ProcessesDocument4 pagesModern Machining ProcessesGangadhar TallaNo ratings yet
- HP347D HP457D: GB Si Al BG HR MK Ro RS Rus UaDocument60 pagesHP347D HP457D: GB Si Al BG HR MK Ro RS Rus UaAdi MNo ratings yet
- 2017 Dec Intermediate 2 Exam ME IDocument2 pages2017 Dec Intermediate 2 Exam ME IshanthakumargcNo ratings yet
- Ies 1997 - II ScanDocument21 pagesIes 1997 - II ScanK.v.SinghNo ratings yet
- Projek Sarjana Muda 1 (SMJ 4912) 10 MAY 2009: Universiti Technology Malaysia Faculti Kejuruteraan MekanikalDocument24 pagesProjek Sarjana Muda 1 (SMJ 4912) 10 MAY 2009: Universiti Technology Malaysia Faculti Kejuruteraan MekanikalKamarul NizamNo ratings yet
- Question Bank (PPII)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank (PPII)Udaiyar BarathadhithyaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-8 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-8 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- ME - Manufacturing Engineering 1Document6 pagesME - Manufacturing Engineering 1Vijay KumarNo ratings yet
- 6117 0 128 PDFDocument71 pages6117 0 128 PDFAngga Fajar SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Effect of Spindle Speed and Feed Rate On Surface Roughness and Material Removal Rate of AA6063A in CNC Turning Using Response Surface MethodologyDocument5 pagesEffect of Spindle Speed and Feed Rate On Surface Roughness and Material Removal Rate of AA6063A in CNC Turning Using Response Surface MethodologyFikri SiplhoNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Leak and Break Behavior in A Failure Assessment Diagram For Carbon Steel PipesDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Leak and Break Behavior in A Failure Assessment Diagram For Carbon Steel Pipesjhon ortizNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing ChallengesDocument45 pagesManufacturing ChallengesMohammad JoharNo ratings yet
- Precision Frequency Generation PDFDocument111 pagesPrecision Frequency Generation PDFwrite2arshad_mNo ratings yet
- ESCALIERSDocument12 pagesESCALIERSabdelmaleklatreche133No ratings yet
- Gate Solved Paper - Me: Manufacturing EngineeringDocument72 pagesGate Solved Paper - Me: Manufacturing EngineeringVHemendra NaiduNo ratings yet
- 7 Process-Parameter Optimization: 7.1 Definition of Process and Target ParametersDocument2 pages7 Process-Parameter Optimization: 7.1 Definition of Process and Target ParametersErick EstradaNo ratings yet
- MT 2labDocument32 pagesMT 2labPRINCE MATHEWNo ratings yet
- Effect of Cutting Speed, Feed Rate and Depth of Cut On Surface Roughness of Mild Steel in Turning OperationDocument6 pagesEffect of Cutting Speed, Feed Rate and Depth of Cut On Surface Roughness of Mild Steel in Turning OperationSourav PatilNo ratings yet
- Gear Agma IIDocument49 pagesGear Agma IInathNo ratings yet
- M 1 Gtaw Smaw d1 1 2015 PQR Form PDFDocument4 pagesM 1 Gtaw Smaw d1 1 2015 PQR Form PDFAyaz ShixaliNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements Project: Topic: Two-Stage Reduction GearboxDocument9 pagesDesign of Machine Elements Project: Topic: Two-Stage Reduction GearboxRam CharanNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture: D.K. Shanmugam, J. Wang, H. LiuDocument8 pagesInternational Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture: D.K. Shanmugam, J. Wang, H. LiuTony starkNo ratings yet
- Gear ShavingDocument6 pagesGear ShavingRuchira Chanda InduNo ratings yet
- MS Tech1Document5 pagesMS Tech1ashishNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Analysis of Blast Loads For IN 791 Project: Anirudh Saboo August 13, 2018 Department of Civil EngineeringDocument20 pagesPreliminary Analysis of Blast Loads For IN 791 Project: Anirudh Saboo August 13, 2018 Department of Civil EngineeringAnirudh SabooNo ratings yet
- Quality Management: Department of Mechanical Engineering, MNIT JaipurDocument6 pagesQuality Management: Department of Mechanical Engineering, MNIT JaipurAnonymous SinghNo ratings yet
- R15-MayJune 2017 Kinematics of MachinesDocument2 pagesR15-MayJune 2017 Kinematics of MachinesPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Analisis Penggunaan Bit For ChevronDocument15 pagesAnalisis Penggunaan Bit For Chevronfaishal hafizhNo ratings yet
- 2022-May ME-322 109Document2 pages2022-May ME-322 109Sidhant SadyalNo ratings yet
- Acsr Conductor SpecificationDocument34 pagesAcsr Conductor SpecificationrajensamaNo ratings yet
- Autos Rejection Formate NazakatDocument4 pagesAutos Rejection Formate NazakatM ALI RajaNo ratings yet
- Procedure Qualification Record (PQR) : 1-2mm 2-5mmDocument26 pagesProcedure Qualification Record (PQR) : 1-2mm 2-5mmDHANEESH VELLILAPULLINo ratings yet
- Rdme 51Document6 pagesRdme 51adarshgitamNo ratings yet
- Prueba Inspector Soldadura 2021Document33 pagesPrueba Inspector Soldadura 2021harangoeNo ratings yet
- List-I (Equipment) List-II (Process) P. 1. Q. 2. R. 3. S. 4. 5Document1 pageList-I (Equipment) List-II (Process) P. 1. Q. 2. R. 3. S. 4. 5SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Gating System For SB-CNC Tail Stock Base CastingDocument5 pagesDesign and Analysis of Gating System For SB-CNC Tail Stock Base CastingtabibkarimNo ratings yet
- Blank Sample PQR Form (GMAW & FCAW - Page 1) Procedure Qualification Record (PQR)Document2 pagesBlank Sample PQR Form (GMAW & FCAW - Page 1) Procedure Qualification Record (PQR)Mirza FahleviNo ratings yet
- Test Reports: SL - No Description Results / ObservationsDocument3 pagesTest Reports: SL - No Description Results / ObservationsAROCKIA STEPHAN SESUMANINo ratings yet
- Jsir 69 (8) 606-612Document7 pagesJsir 69 (8) 606-612Vijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Systematic Design Procedure of SwitchedDocument14 pagesSystematic Design Procedure of SwitchedEduardo BittencourtNo ratings yet
- (MCB) MCB - RCD - Catalog - EN - 202202Document64 pages(MCB) MCB - RCD - Catalog - EN - 202202Eddy W Mendoza TrujilloNo ratings yet
- Design Process of Rotating Electrical MachinesDocument28 pagesDesign Process of Rotating Electrical MachinesAli HashemiNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modelling and Experimental Validation of Micro-Ball-EndDocument15 pagesAnalytical Modelling and Experimental Validation of Micro-Ball-EndChoy Hau YanNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument11 pages1 PDFmahendraNo ratings yet
- A New Dynamic Model For Drilling and Reaming Processes Yang2002Document13 pagesA New Dynamic Model For Drilling and Reaming Processes Yang2002RihabChommakhNo ratings yet
- Good 1Document19 pagesGood 118P202 - AJAY SIVARAMAN ANo ratings yet
- QuickGuide SurftestDocument2 pagesQuickGuide SurftestHeineken Ya PraneetpongrungNo ratings yet
- Vibrations of Machine Foundations: Richard P. Ray, PH.D., P.EDocument63 pagesVibrations of Machine Foundations: Richard P. Ray, PH.D., P.E고병준100% (1)
- Presented For CMA Analytical Workshop 2012 Neal LeddyDocument55 pagesPresented For CMA Analytical Workshop 2012 Neal LeddygprjesNo ratings yet
- Measurement While Drilling: Signal Analysis, Optimization and DesignFrom EverandMeasurement While Drilling: Signal Analysis, Optimization and DesignNo ratings yet
- Advances in Ceramic Armor XIFrom EverandAdvances in Ceramic Armor XIJerry C. LaSalviaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-52Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-52SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-53Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-53SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- F D T D T: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageF D T D T: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Processes Associated State of Stress P. 3. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 4Document1 pageProcesses Associated State of Stress P. 3. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 4SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-54Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-54SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-55Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-55SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-48Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-48SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-51Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-51SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- For Metal: Atomic Weight Valency The Metal Removal Rate: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageFor Metal: Atomic Weight Valency The Metal Removal Rate: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Column I Column II P. 4. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 3.: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageColumn I Column II P. 4. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 3.: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-45Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-45SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-40Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-40SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-46Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-46SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- ADE Δ θ DE x x θ x x Z d x: Visit us at: www.nodia.co.inDocument1 pageADE Δ θ DE x x θ x x Z d x: Visit us at: www.nodia.co.inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- A N B N VT A VT B VT: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageA N B N VT A VT B VT: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- α 12c t t φ r r α α t φ φ: Machining process Mechanism of material removal P. 2. Q. 3. R. 4. S. 1Document1 pageα 12c t t φ r r α α t φ φ: Machining process Mechanism of material removal P. 2. Q. 3. R. 4. S. 1SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-38Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-38SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-28 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-28 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- 175 MM 200 MM 200 MM 10 MM 10 / Ms : Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 page175 MM 200 MM 200 MM 10 MM 10 / Ms : Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Solution: Metal Forming Process Types of Stress 1. S. Compressive 2. P. Tensile 3. Q. Shear 4. R. Tensile and CompressiveDocument1 pageSolution: Metal Forming Process Types of Stress 1. S. Compressive 2. P. Tensile 3. Q. Shear 4. R. Tensile and CompressiveSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-31 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-31 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-29 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-29 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-34Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-34SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-30 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-30 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
Manufacturing Engineering-19
Manufacturing Engineering-19
Uploaded by
SameerChauhanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Manufacturing Engineering-19
Manufacturing Engineering-19
Uploaded by
SameerChauhanCopyright:
Available Formats
www.gatehelp.
com
CHAP 10 MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING PAGE 445
MCQ 10.86 If each abrasive grain is viewed as a cutting tool, then which of the following
represents the cutting parameters in common grinding operations ?
(A) Large negative rake angle, low shear angle and high cutting speed
(B) Large positive rake angle, low shear angle and high cutting speed
(C) Large negative rake angle, high shear angle and low cutting speed
(D) Zero rake angle, high shear angle and high cutting speed
MCQ 10.87 Arrange the processes in the increasing order of their maximum material
removal rate.
Electrochemical Machining (ECM)
Ultrasonic Machining (USM)
Electron Beam Machining (EBM)
Laser Beam Machining (LBM) and
Electric Discharge Machining (EDM)
(A) USM, LBM, EBM, EDM, ECM
(B) EBM, LBM, USM, ECM, EDM
(C) LBM, EBM, USM, ECM, EDM
(D) LBM, EBM, USM, EDM, ECM
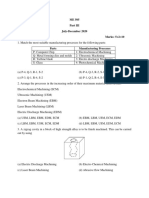
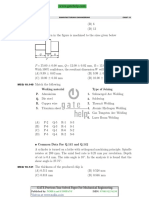
MCQ 10.88 Match the items in columns I and II.
Column I Column II
P. Charpy test 1. Fluidity
Q. Knoop test 2. Microhardness
R. Spiral test 3. Formability
S. Cupping test 4. Toughness
5. Permeability
(A) P-4, Q-5, R-3, S-2
(B) P-3, Q-5, R-1, S-4
(C) P-2, Q-4, R-3, S-5
(D) P-4, Q-2, R-1, S-3
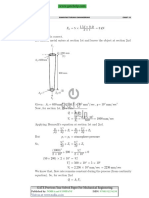
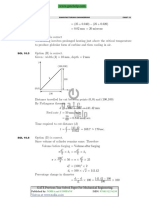
• Common Data For Q.89, 90 and Q.91
In an orthogonal machining operation :
Uncut thickness = 0.5 mm
Cutting speed = 20 m/min
Rake angel = 15c
Width of cut = 5 mm Chip thickness = 0.7 mm
GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
You might also like
- Manufacturing Engineering-26Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-26SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Operation Process P. 1. Q. 2. R. 3. S. 4. 5. 6.: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageOperation Process P. 1. Q. 2. R. 3. S. 4. 5. 6.: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-16Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-16SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- A Study On PDC Drill Bits QualityDocument18 pagesA Study On PDC Drill Bits QualityAzri HamimNo ratings yet
- ME 505 Lab Exam July Dec 2020 Part 3Document2 pagesME 505 Lab Exam July Dec 2020 Part 3Shweta raiNo ratings yet
- Ghousia College of Engineering Ramanagaram: I Internal AssessmentDocument1 pageGhousia College of Engineering Ramanagaram: I Internal AssessmentSyedZameerNo ratings yet
- Objective QuestionsDocument73 pagesObjective QuestionsRajesh ShahNo ratings yet
- ME Manufacturing-Engineering PDFDocument73 pagesME Manufacturing-Engineering PDFpankajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (45-70)Document26 pagesChapter 3 (45-70)chaib boudabNo ratings yet
- Modern Machining ProcessesDocument4 pagesModern Machining ProcessesGangadhar TallaNo ratings yet
- HP347D HP457D: GB Si Al BG HR MK Ro RS Rus UaDocument60 pagesHP347D HP457D: GB Si Al BG HR MK Ro RS Rus UaAdi MNo ratings yet
- 2017 Dec Intermediate 2 Exam ME IDocument2 pages2017 Dec Intermediate 2 Exam ME IshanthakumargcNo ratings yet
- Ies 1997 - II ScanDocument21 pagesIes 1997 - II ScanK.v.SinghNo ratings yet
- Projek Sarjana Muda 1 (SMJ 4912) 10 MAY 2009: Universiti Technology Malaysia Faculti Kejuruteraan MekanikalDocument24 pagesProjek Sarjana Muda 1 (SMJ 4912) 10 MAY 2009: Universiti Technology Malaysia Faculti Kejuruteraan MekanikalKamarul NizamNo ratings yet
- Question Bank (PPII)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank (PPII)Udaiyar BarathadhithyaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-8 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-8 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- ME - Manufacturing Engineering 1Document6 pagesME - Manufacturing Engineering 1Vijay KumarNo ratings yet
- 6117 0 128 PDFDocument71 pages6117 0 128 PDFAngga Fajar SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Effect of Spindle Speed and Feed Rate On Surface Roughness and Material Removal Rate of AA6063A in CNC Turning Using Response Surface MethodologyDocument5 pagesEffect of Spindle Speed and Feed Rate On Surface Roughness and Material Removal Rate of AA6063A in CNC Turning Using Response Surface MethodologyFikri SiplhoNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Leak and Break Behavior in A Failure Assessment Diagram For Carbon Steel PipesDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Leak and Break Behavior in A Failure Assessment Diagram For Carbon Steel Pipesjhon ortizNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing ChallengesDocument45 pagesManufacturing ChallengesMohammad JoharNo ratings yet
- Precision Frequency Generation PDFDocument111 pagesPrecision Frequency Generation PDFwrite2arshad_mNo ratings yet
- ESCALIERSDocument12 pagesESCALIERSabdelmaleklatreche133No ratings yet
- Gate Solved Paper - Me: Manufacturing EngineeringDocument72 pagesGate Solved Paper - Me: Manufacturing EngineeringVHemendra NaiduNo ratings yet
- 7 Process-Parameter Optimization: 7.1 Definition of Process and Target ParametersDocument2 pages7 Process-Parameter Optimization: 7.1 Definition of Process and Target ParametersErick EstradaNo ratings yet
- MT 2labDocument32 pagesMT 2labPRINCE MATHEWNo ratings yet
- Effect of Cutting Speed, Feed Rate and Depth of Cut On Surface Roughness of Mild Steel in Turning OperationDocument6 pagesEffect of Cutting Speed, Feed Rate and Depth of Cut On Surface Roughness of Mild Steel in Turning OperationSourav PatilNo ratings yet
- Gear Agma IIDocument49 pagesGear Agma IInathNo ratings yet
- M 1 Gtaw Smaw d1 1 2015 PQR Form PDFDocument4 pagesM 1 Gtaw Smaw d1 1 2015 PQR Form PDFAyaz ShixaliNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements Project: Topic: Two-Stage Reduction GearboxDocument9 pagesDesign of Machine Elements Project: Topic: Two-Stage Reduction GearboxRam CharanNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture: D.K. Shanmugam, J. Wang, H. LiuDocument8 pagesInternational Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture: D.K. Shanmugam, J. Wang, H. LiuTony starkNo ratings yet
- Gear ShavingDocument6 pagesGear ShavingRuchira Chanda InduNo ratings yet
- MS Tech1Document5 pagesMS Tech1ashishNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Analysis of Blast Loads For IN 791 Project: Anirudh Saboo August 13, 2018 Department of Civil EngineeringDocument20 pagesPreliminary Analysis of Blast Loads For IN 791 Project: Anirudh Saboo August 13, 2018 Department of Civil EngineeringAnirudh SabooNo ratings yet
- Quality Management: Department of Mechanical Engineering, MNIT JaipurDocument6 pagesQuality Management: Department of Mechanical Engineering, MNIT JaipurAnonymous SinghNo ratings yet
- R15-MayJune 2017 Kinematics of MachinesDocument2 pagesR15-MayJune 2017 Kinematics of MachinesPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Analisis Penggunaan Bit For ChevronDocument15 pagesAnalisis Penggunaan Bit For Chevronfaishal hafizhNo ratings yet
- 2022-May ME-322 109Document2 pages2022-May ME-322 109Sidhant SadyalNo ratings yet
- Acsr Conductor SpecificationDocument34 pagesAcsr Conductor SpecificationrajensamaNo ratings yet
- Autos Rejection Formate NazakatDocument4 pagesAutos Rejection Formate NazakatM ALI RajaNo ratings yet
- Procedure Qualification Record (PQR) : 1-2mm 2-5mmDocument26 pagesProcedure Qualification Record (PQR) : 1-2mm 2-5mmDHANEESH VELLILAPULLINo ratings yet
- Rdme 51Document6 pagesRdme 51adarshgitamNo ratings yet
- Prueba Inspector Soldadura 2021Document33 pagesPrueba Inspector Soldadura 2021harangoeNo ratings yet
- List-I (Equipment) List-II (Process) P. 1. Q. 2. R. 3. S. 4. 5Document1 pageList-I (Equipment) List-II (Process) P. 1. Q. 2. R. 3. S. 4. 5SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Gating System For SB-CNC Tail Stock Base CastingDocument5 pagesDesign and Analysis of Gating System For SB-CNC Tail Stock Base CastingtabibkarimNo ratings yet
- Blank Sample PQR Form (GMAW & FCAW - Page 1) Procedure Qualification Record (PQR)Document2 pagesBlank Sample PQR Form (GMAW & FCAW - Page 1) Procedure Qualification Record (PQR)Mirza FahleviNo ratings yet
- Test Reports: SL - No Description Results / ObservationsDocument3 pagesTest Reports: SL - No Description Results / ObservationsAROCKIA STEPHAN SESUMANINo ratings yet
- Jsir 69 (8) 606-612Document7 pagesJsir 69 (8) 606-612Vijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Systematic Design Procedure of SwitchedDocument14 pagesSystematic Design Procedure of SwitchedEduardo BittencourtNo ratings yet
- (MCB) MCB - RCD - Catalog - EN - 202202Document64 pages(MCB) MCB - RCD - Catalog - EN - 202202Eddy W Mendoza TrujilloNo ratings yet
- Design Process of Rotating Electrical MachinesDocument28 pagesDesign Process of Rotating Electrical MachinesAli HashemiNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modelling and Experimental Validation of Micro-Ball-EndDocument15 pagesAnalytical Modelling and Experimental Validation of Micro-Ball-EndChoy Hau YanNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument11 pages1 PDFmahendraNo ratings yet
- A New Dynamic Model For Drilling and Reaming Processes Yang2002Document13 pagesA New Dynamic Model For Drilling and Reaming Processes Yang2002RihabChommakhNo ratings yet
- Good 1Document19 pagesGood 118P202 - AJAY SIVARAMAN ANo ratings yet
- QuickGuide SurftestDocument2 pagesQuickGuide SurftestHeineken Ya PraneetpongrungNo ratings yet
- Vibrations of Machine Foundations: Richard P. Ray, PH.D., P.EDocument63 pagesVibrations of Machine Foundations: Richard P. Ray, PH.D., P.E고병준100% (1)
- Presented For CMA Analytical Workshop 2012 Neal LeddyDocument55 pagesPresented For CMA Analytical Workshop 2012 Neal LeddygprjesNo ratings yet
- Measurement While Drilling: Signal Analysis, Optimization and DesignFrom EverandMeasurement While Drilling: Signal Analysis, Optimization and DesignNo ratings yet
- Advances in Ceramic Armor XIFrom EverandAdvances in Ceramic Armor XIJerry C. LaSalviaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-52Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-52SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-53Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-53SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- F D T D T: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageF D T D T: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Processes Associated State of Stress P. 3. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 4Document1 pageProcesses Associated State of Stress P. 3. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 4SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-54Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-54SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-55Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-55SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-48Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-48SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-51Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-51SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- For Metal: Atomic Weight Valency The Metal Removal Rate: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageFor Metal: Atomic Weight Valency The Metal Removal Rate: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Column I Column II P. 4. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 3.: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageColumn I Column II P. 4. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 3.: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-45Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-45SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-40Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-40SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-46Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-46SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- ADE Δ θ DE x x θ x x Z d x: Visit us at: www.nodia.co.inDocument1 pageADE Δ θ DE x x θ x x Z d x: Visit us at: www.nodia.co.inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- A N B N VT A VT B VT: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageA N B N VT A VT B VT: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- α 12c t t φ r r α α t φ φ: Machining process Mechanism of material removal P. 2. Q. 3. R. 4. S. 1Document1 pageα 12c t t φ r r α α t φ φ: Machining process Mechanism of material removal P. 2. Q. 3. R. 4. S. 1SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-38Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-38SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-28 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-28 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- 175 MM 200 MM 200 MM 10 MM 10 / Ms : Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 page175 MM 200 MM 200 MM 10 MM 10 / Ms : Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Solution: Metal Forming Process Types of Stress 1. S. Compressive 2. P. Tensile 3. Q. Shear 4. R. Tensile and CompressiveDocument1 pageSolution: Metal Forming Process Types of Stress 1. S. Compressive 2. P. Tensile 3. Q. Shear 4. R. Tensile and CompressiveSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-31 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-31 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-29 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-29 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-34Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-34SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-30 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-30 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet