Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer Sheet: Academic Year:2012 EC, Year: 2
Answer Sheet: Academic Year:2012 EC, Year: 2
Uploaded by
samuel debebeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer Sheet: Academic Year:2012 EC, Year: 2
Answer Sheet: Academic Year:2012 EC, Year: 2
Uploaded by
samuel debebeCopyright:
Available Formats
Furra College Hawassa campuse
Department of Accounting & Finance
Final examination for the course of Cost& Management Accounting I (Regular)
Academic year :2012 EC, Year : 2nd Time allowed: 2:00hr Instructor : Gurmu Ephrem
ANSWER SHEET
Name ______________________________Id. No. __________________ Sec. _____ Sign. __________
Program: Regular Extension Week End Year: 2nd Department
______
Part One: Multiple choices (20 %)
1._______2._______3.________4.________5._______6.______7.______8._______9.______
10._______11.______12._______13.______14.______15.______16._____17._____18.______
19._______20.______
Part I:True/false (10%) :1._______2._______3._____4._______5._____6._____7.______8.______
9._________10._________
Part III Work out: use attached paper (15%) use the attached paper
Part I: Multiple choose
Instruction: select correct answer and write your answer choice on the Space provided
above
1. When a job is complete:
A. Work-in-Process Control is debited
B. Finished Goods Control is credited
C. the cost of the job is transferred to Manufacturing Overhead Control
D. actual direct materials, actual direct manufacturing labor, and allocated
manufacturing overhead will comprise the total cost of the job
2. All of the following items are debited to Work-in-Process EXCEPT:
A. allocated manufacturing overhead
B. completed goods being transferred out of the plant
C. direct labor consumed
D. direct materials consumed
3. Which of the following statements about normal costing is true?
A. Direct costs and indirect costs are traced using an actual rate.
B. Direct costs and indirect costs are traced using budgeted rates.
C. Direct costs are traced using a budgeted rate, and indirect costs are allocated using
an actual rate.
D. Direct costs are traced using an actual rate, and indirect costs are allocated using a
budgeted rate.
4. In a normal costing system, the Manufacturing Overhead Control account:
A. is increased by allocated manufacturing overhead
B. is credited with amounts transferred to Work-in-Process
C. is decreased by allocated manufacturing overhead
D. is debited with actual overhead costs
5. A job-cost record uses information from:
A. a materials requisition record to record raw material purchases from suppliers
B. a receiving report that indicates the type and quantity of each item received in an
order from a supplier
C. a labor-time card to record an employee's wage rate and hours spent on a
particular job
D. All of these answers are correct.
6. The predetermined rate of indirect-cost rate for each cost pool is computed as
A. budgeted annual indirect costs divided by budgeted annual quantity of cost
allocation base.
B. budgeted annual quantity of cost allocation base divided by budgeted annual
indirect costs.
C. actual annual indirect costs divided by budgeted annual quantity of cost allocation
base.
D. budgeted annual indirect costs divided by budgeted actual quantity of cost
allocation base
7. Job-costing may only be used by:
A. service companies
B. merchandising companies
C. manufacturing companies
D. All of these may use job-costing.
8. Jacobs Company's Assembly Department has materials cost at $4 per unit and
conversion cost at $8 per unit. There are 9,000 units in ending work in process, all of
which are 70% complete as to conversion costs. What are the total costs assigned to
inventory?
A. $50,400 B) $86,400 C) $75,600 D) $108,000
9. If beginning work in process is 2,000 units, ending work in process is 1,000 units, and
the units accounted for equals 5,000 units, what are the units started into production?
A. 7,000 B) 6,000 C) 3,000 D) 4,000
10. Which of the following would not appear as a debit in the Work in Process account of a
second department in a two stage production process?
A. Materials used C) Labor assigned
B. Cost of products transferred out D) Overhead applied
11. One characteristic of products that are mass-produced in a continuous production
process is that
A. The products are identical or very similar in nature.
B. They are grouped in batches.
C. They are produced at the time an order is received.
D. Their costs are accumulated on job cost sheets
12. Which of the following would not appear as a debit in the Work in Process account of a
second department in a two stage production process?
A. Materials used B) Overhead applied
B. Labor assigned D) cost of products transferred out
13. A process cost accounting system is most appropriate when
A. A variety of different products are produced, each one requiring different types of
materials, labor, and overhead.
B. The focus of attention is on a particular job or order.
C. Similar products are mass-produced.
D. Individual products are custom made to the specification of customers
14. Which of the following cost elements occurs in a process costing system?
A. Direct materials B) Direct labor C) Manufacturing overhead D) All of these
The following data apply to questions 12& 14
Watkins Company had the following production for the month of June:
Units
Work in process, June 1 6,000
Started during June 24,000
Completed and transferred to finished goods 18,000
Abnormal spoilage incurred 3,000
Work in process, June 30 9,000
Materials are added at the beginning of the process. As to conversion cost, work in process was
20% complete at the beginning and 70% complete at the end of the month. Spoilage is detected
at the end of the process.
15. Using the weighted-average method, the equivalent units for June, with respect to
conversion cost, were
A. 23,700. B) 24,300. C) 27,300. D)30,000.
16. Using the first-in, first out (FIFO) method, the equivalent units for June, with respect
to conversion cost, were
A. 19,500. B) 22,500. C) 23,100. D) 26,100.
17. The sale of scrap from a manufacturing process usually would be recorded as a(n)
A. Increase in manufacturing overhead control.
B. Increase in finished goods control.
C. Decrease in manufacturing overhead control
D. Decrease in finished goods control
18. True about working in process
A. The production is continuous and
B. Mass production and the final product is the result of departments.
C. Costs are accumulated by processes or operations or department.
D. All
19. A cost which doesn’t increase the working in process account
A. DM B. DL C. MOH control D. applied MOH
20. A cost of a product which increased the WIP without taking a time
A. DM B) DL C) FOH D) none
Part II : True / false question
Instruction : say True for correct statement and false for incorrect statement
1. Textile factory used Job order costing method for its cost of product determination
2. Manufacture overhead control account used for recording of Estimated cost of indirect
cost a product
3. Cost added for product under process costing recorded for product
4. process costing used for homogenous product producing company
5. Job order costing used for heterogonous type of product producing company
6. If FOH control is less than applied FOH the difference is called under applied
7. Normal loss cost is avoidable
8. Equivalent cost means a per unit cost that added by a job
9. Cost that may not added by each department is labor cost
10. Direct labor cost is a part of FOH cost
Part III: Work out
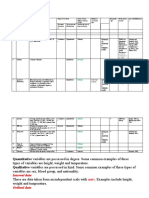
1. By using the following data prepare production cost report the equivalent product of
material ,Labor and FOH and equivalent unit cost
Departme Unit Processed and Remain in Normal Added cost for Cost of
nt start to transfer to WIP( 1/3 of lost WIP product
process Testing labor ,1/3 FOH Labor FOH transfer
department from
pervious
Testing 45,000u 40,000u 3,000U 2,000u 37,310 32,800 Br 1.72
2. Using the under given information find the requires questions
Raw material Labor FOH WIP FG
Beginning Br 30,000 Br 4,000 Br 12,000
Purchase 10,000
Used ? 21,000 28,800
Ending 6,000.00 39,800 24,000
Requires
A. Material used
B. Total Manufacturing cost
C. Cost of produced
D. Cost of Goods Sold
You might also like
- Research Methods in Accounting and Finance (Acfn3101) Assignment - Ayalnesh TibebuDocument13 pagesResearch Methods in Accounting and Finance (Acfn3101) Assignment - Ayalnesh TibebumengistuNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian Tax SystemDocument75 pagesEthiopian Tax Systemyared100% (1)
- Lesson Plan: Unit 7: Describing People and ThingsDocument102 pagesLesson Plan: Unit 7: Describing People and Thingsapi-609271900No ratings yet
- Worksheet For Government and Non-Profit AcctDocument6 pagesWorksheet For Government and Non-Profit AcctYonas100% (10)
- PERSONNEL MANAGEMENT The Human Resources Glossary The Complete Desk Reference For HR Executives, PDFDocument841 pagesPERSONNEL MANAGEMENT The Human Resources Glossary The Complete Desk Reference For HR Executives, PDFGeorgiana Petcu100% (1)
- Civil Engineering Documentation 3A 2021 Learner GuideDocument9 pagesCivil Engineering Documentation 3A 2021 Learner GuidedwdNo ratings yet
- Assignment Chapter 5Document2 pagesAssignment Chapter 5Nati AlexNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 - Costing Methods The Costing of Resource OutputsDocument27 pagesChapter3 - Costing Methods The Costing of Resource OutputsNetsanet Belay100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Plant Asset PDFDocument20 pagesChapter 2 Plant Asset PDFWonde Biru100% (1)
- Chapter-5-Accounting For Partnerships in EthiopiaDocument17 pagesChapter-5-Accounting For Partnerships in EthiopiaYasin100% (1)
- Unit 4: Capital Project FundsDocument20 pagesUnit 4: Capital Project FundsMuktar jiboNo ratings yet
- Fa Ii Final ExamDocument4 pagesFa Ii Final ExamIfa100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Cost IDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Cost Iyebegashet100% (1)
- All Model Exit Exam by UoGDocument69 pagesAll Model Exit Exam by UoGZeki HD100% (1)
- Or Individual Assignment 2023Document4 pagesOr Individual Assignment 2023Misganew NegaNo ratings yet
- Public Finance and Taxation (ch-1)Document26 pagesPublic Finance and Taxation (ch-1)yebegashet50% (2)
- Fair Value Measurement: Prepared By: Michael Wells Date: June 13-17, 2016 Addis AbabaDocument60 pagesFair Value Measurement: Prepared By: Michael Wells Date: June 13-17, 2016 Addis AbabaGere Tassew100% (2)
- Govt Test IDocument2 pagesGovt Test ICreate Ed100% (1)
- Advanced Financial Accounting (Acfn3151)Document2 pagesAdvanced Financial Accounting (Acfn3151)alemayehu100% (4)
- Chapter Three Accounting For General and Special Revenue FundsDocument22 pagesChapter Three Accounting For General and Special Revenue Fundshabtamu tadesse100% (3)
- Accounting For Capital Project FundsDocument8 pagesAccounting For Capital Project FundsMekonnen MekuriaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 CM Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis, Absorption, and Variable CostingDocument15 pagesCH 1 CM Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis, Absorption, and Variable CostingOROM VINE100% (5)
- Public Final ExamDocument5 pagesPublic Final Examsenbetotilahun8No ratings yet
- Accounting Information Systems: An Overview: Addis Ababa University School of CommerceDocument20 pagesAccounting Information Systems: An Overview: Addis Ababa University School of Commercealemayehu100% (2)
- Final EXIT 2015Document110 pagesFinal EXIT 2015naolmeseret22No ratings yet
- Chapter2 - Cost Determination The Cost of Resource InputsDocument11 pagesChapter2 - Cost Determination The Cost of Resource InputsNetsanet Belay100% (4)
- Development of Accounting Principles and Professional PracticeDocument61 pagesDevelopment of Accounting Principles and Professional Practiceesubalew yayena100% (2)
- Chapter 2 The Auditing ProfessionDocument56 pagesChapter 2 The Auditing ProfessionNigussie Berhanu100% (1)
- BAC312 - Management Accounting ModuleDocument129 pagesBAC312 - Management Accounting ModuleBashi Taizya100% (1)
- Unit 3: General Fund & Special Revenue FundsDocument28 pagesUnit 3: General Fund & Special Revenue Fundsayele gebremichael75% (4)
- ACFN 342 Auditing Principles IIDocument2 pagesACFN 342 Auditing Principles IItemedebere50% (2)
- OM Assignment NewDocument37 pagesOM Assignment NewBisrat nigusuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Project Preparation and Analysis - 2Document54 pagesChapter 4 Project Preparation and Analysis - 2Aida Mohammed100% (1)
- Cma - Chapter OneDocument19 pagesCma - Chapter OneKiya AbdiNo ratings yet
- Final Exam of PF 2012 (Infolink)Document5 pagesFinal Exam of PF 2012 (Infolink)samuel debebe100% (1)
- Adv. Fin. Acct Test-2Document4 pagesAdv. Fin. Acct Test-2Samuel DebebeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Accounting For Plant Assets and Depreciation. ContentsDocument46 pagesChapter 6: Accounting For Plant Assets and Depreciation. ContentsSimon MollaNo ratings yet
- Cost Accaunting 2Document12 pagesCost Accaunting 2ዝምታ ተሻለNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Financial Markets in The Financial SystemDocument66 pagesChapter Four Financial Markets in The Financial SystemMikias DegwaleNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting 2 Final ExamDocument6 pagesCost Accounting 2 Final ExamCynthia Yeung100% (1)
- GNP CH 3 MCQ 1-10 From Text BookDocument4 pagesGNP CH 3 MCQ 1-10 From Text Booksamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Current Liability PayrollDocument39 pagesChapter 3 Current Liability PayrollAbdi Mucee Tube100% (1)
- 3chapter Three FM ExtDocument19 pages3chapter Three FM ExtTIZITAW MASRESHANo ratings yet
- Project Analysis and Evaluation 1Document3 pagesProject Analysis and Evaluation 1tewodros bayisa100% (2)
- Test Bank Public Finance DR - Ali UpdateDocument51 pagesTest Bank Public Finance DR - Ali UpdateMahmoud Ayoub Goda100% (2)
- Public Finance and Taxation AssignemetDocument3 pagesPublic Finance and Taxation AssignemetEmebet TesemaNo ratings yet
- MCQs - Relevant Information For Decision MakingDocument7 pagesMCQs - Relevant Information For Decision MakingVy Hua100% (4)
- Advanced Public Finance & Taxation: Ethiopian Civil Service University College of Finance, Management and DevelopmentDocument28 pagesAdvanced Public Finance & Taxation: Ethiopian Civil Service University College of Finance, Management and DevelopmentWagner Adugna100% (4)
- Chapter 2 Cost IDocument13 pagesChapter 2 Cost IHussen AbdulkadirNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Accounting Ii Final ModuleDocument174 pagesFundamental Accounting Ii Final ModuleFanuel Derese100% (2)
- Auditing Principles and Practices II Assignment AnswerDocument6 pagesAuditing Principles and Practices II Assignment Answerbona birra67% (3)
- Plant Asset QuizDocument3 pagesPlant Asset QuizFami Famz100% (1)
- Lecture 3 Public Finance in EthiopiaDocument11 pagesLecture 3 Public Finance in Ethiopiadejenkibr100% (1)
- Lecturenote - 1573170473OR MODULE MengistuDocument163 pagesLecturenote - 1573170473OR MODULE MengistuZena Selfu100% (5)
- Model Exam 1Document25 pagesModel Exam 1rahelsewunet0r37203510No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Joint Arrangements & PEDocument36 pagesChapter 1 Joint Arrangements & PEMati MeseretNo ratings yet
- Bedri Operation Management AssignmentDocument40 pagesBedri Operation Management AssignmentBedri M Ahmedu100% (1)
- Accounting For Public Sector and Civil Society-1Document147 pagesAccounting For Public Sector and Civil Society-1Zeki HDNo ratings yet
- Test Blue Print Detail Table For ACCOUNTING & FINANCE 1Document19 pagesTest Blue Print Detail Table For ACCOUNTING & FINANCE 1maledaamsalu1100% (3)
- At 5Document9 pagesAt 5Joshua GibsonNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz Semifinal SolDocument7 pagesLong Quiz Semifinal SolJohn RoaNo ratings yet
- Cost I Final ExtDocument6 pagesCost I Final ExtGetu WeyessaNo ratings yet
- 2ndyr - 1stF - Cost Accounting and Control - 2223Document28 pages2ndyr - 1stF - Cost Accounting and Control - 2223rylNo ratings yet
- Benefits and Challenges of Pooled Financial Accounting System in Public Sectors: A Case Study of Hawassa City AdministrationDocument1 pageBenefits and Challenges of Pooled Financial Accounting System in Public Sectors: A Case Study of Hawassa City Administrationsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- FM-II Course OutlineDocument2 pagesFM-II Course Outlinesamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment@FM IIDocument2 pagesGroup Assignment@FM IIsamuel debebe100% (1)
- Individual Assignem (Minyichel)Document16 pagesIndividual Assignem (Minyichel)samuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Declaration and Table of ContentDocument6 pagesDeclaration and Table of Contentsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- C-5 Dividend Policy 3rdDocument12 pagesC-5 Dividend Policy 3rdsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Declaration and Table of ContentDocument6 pagesDeclaration and Table of Contentsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- CH17Document10 pagesCH17samuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Research Methods Course Outline GeFs 512Document5 pagesResearch Methods Course Outline GeFs 512samuel debebeNo ratings yet
- What Is An Installment Sale?: Revenue ExpenseDocument8 pagesWhat Is An Installment Sale?: Revenue Expensesamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- UNIT ONE Introduction To ResearchDocument49 pagesUNIT ONE Introduction To Researchsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- 20th July, 2020Document8 pages20th July, 2020samuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Swot Scheme 1Document4 pagesSwot Scheme 1samuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Ersonal InformationDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Ersonal Informationsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Unit I: Introduction To Research Lecture NotesDocument36 pagesUnit I: Introduction To Research Lecture Notessamuel debebe100% (5)
- Aplca. LeterDocument1 pageAplca. Letersamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Research EthicsDocument17 pagesChapter 4 Research Ethicssamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Variables: Informati On Innovatio N Adoption ModelDocument3 pagesVariables: Informati On Innovatio N Adoption Modelsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Investmment Chapter TwoDocument10 pagesInvestmment Chapter Twosamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- College of Social Scinences and Humanities Department of Bussines and ManagmenetDocument19 pagesCollege of Social Scinences and Humanities Department of Bussines and Managmenetsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Background 1.1: Meaning of InvestmentDocument12 pagesIntroduction and Background 1.1: Meaning of Investmentsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Investement ASSignt ELIOCDocument42 pagesInvestement ASSignt ELIOCsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Decision MakingDocument14 pagesChapter Three Decision Makingsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Security Analysis: The Business Cycle:-The Economy Recurrently Experiences Periods of Expansion andDocument4 pagesChapter Five Security Analysis: The Business Cycle:-The Economy Recurrently Experiences Periods of Expansion andsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Foreign Currency Translation - Modified.aDocument71 pagesForeign Currency Translation - Modified.asamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Management Fundamentals (Introduction) : 1) Meaning and Definition of ManagementDocument19 pagesManagement Fundamentals (Introduction) : 1) Meaning and Definition of Managementsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Intrio To MGMTDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 7 Intrio To MGMTsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- ICCP Code of EthicsDocument1 pageICCP Code of EthicsThe PieonicBritzNo ratings yet
- Subject English-Test Book Let (A) - 108345Document23 pagesSubject English-Test Book Let (A) - 108345medhanshu0% (1)
- Standard Ii: Talent Search Examination - 2021-22Document17 pagesStandard Ii: Talent Search Examination - 2021-22Sowmya Sandeep100% (2)
- Why Cheating Is Not Good For StudentDocument3 pagesWhy Cheating Is Not Good For StudentRebecca Rosauly Siringo RingoNo ratings yet
- 06062019-PG Bulletin2019-20Document142 pages06062019-PG Bulletin2019-20Ravi SinghNo ratings yet
- Students Instruction - PPMDocument4 pagesStudents Instruction - PPMDeepak PooranachandranNo ratings yet
- MSW SyllabusDocument8 pagesMSW SyllabusSuman Chakraborty100% (1)
- Personal Statement SamplesDocument11 pagesPersonal Statement SamplesAshfaque HussainNo ratings yet
- IELTSDocument2 pagesIELTSPramays Shella0% (1)
- Web Development Series Brochure PDFDocument3 pagesWeb Development Series Brochure PDFCristiano MottaNo ratings yet
- Recruitment Process Group 6Document11 pagesRecruitment Process Group 6Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Development of Item Banks: The Techne Group, IncDocument6 pagesGuidelines For The Development of Item Banks: The Techne Group, IncYossi Indra KusumaNo ratings yet
- Admissions Application King Solomon UniversityDocument20 pagesAdmissions Application King Solomon Universityapi-303090562No ratings yet
- Pare InvoDocument7 pagesPare InvoShanthala RaoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus in Kitchen EssentialsDocument7 pagesSyllabus in Kitchen EssentialsCrizz Oracion Medija100% (1)
- Effects of Computers On AuditingDocument26 pagesEffects of Computers On Auditingnagarajuvcc123No ratings yet
- CONTENT SYLLABUS (3) PERSONAL DATA SHEET Pg. 7 EDU-201-202 FALL 2021-1-1Document8 pagesCONTENT SYLLABUS (3) PERSONAL DATA SHEET Pg. 7 EDU-201-202 FALL 2021-1-1Bianca SegerNo ratings yet
- HEC Approved Policy Guidelines On Semester Examination SystemDocument12 pagesHEC Approved Policy Guidelines On Semester Examination System__qasimk100% (3)
- Cidtt The GuideDocument268 pagesCidtt The GuideAbdul Shameem100% (1)
- Skills & Its AssessmentDocument20 pagesSkills & Its AssessmentFrank NobodNo ratings yet
- Aa FASS - HANDBOOK PDFDocument47 pagesAa FASS - HANDBOOK PDFYemi AdetayoNo ratings yet
- Construction Technology Course OutlineDocument8 pagesConstruction Technology Course Outlineapi-268401961No ratings yet
- 0417 m18 3 1 MsDocument11 pages0417 m18 3 1 MsJishnu SinghNo ratings yet
- Writing Skills Scheme of WorkDocument14 pagesWriting Skills Scheme of WorkWinnie D' Fap0% (1)
- 7010 Computer Studies: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2012 SeriesDocument12 pages7010 Computer Studies: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2012 SeriesSadaf ZaheerNo ratings yet
- 4Document24 pages4MAIRA ALEJANDRA BLANCO TORRESNo ratings yet
- BSC ZoologyDocument172 pagesBSC ZoologyJamesNo ratings yet