Professional Documents
Culture Documents
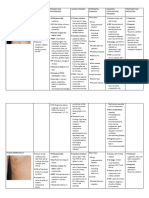
Name of Infection/virus Acquired at What Time How To Test For It Likely S/s HSV
Name of Infection/virus Acquired at What Time How To Test For It Likely S/s HSV
Uploaded by
C RCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Dermatology Condition Description Signs/symptoms DDX Viral InfectionsDocument40 pagesDermatology Condition Description Signs/symptoms DDX Viral InfectionsWaseem Ullah100% (1)
- Treatment:: Most LikelyDocument4 pagesTreatment:: Most LikelyRichlie Magtulis IINo ratings yet
- 2.congenital TORCH InfDocument24 pages2.congenital TORCH Infelka.kgmaNo ratings yet
- Inrauterine InfectionsDocument83 pagesInrauterine Infectionsahmad aminNo ratings yet
- TORCHDocument42 pagesTORCHKarla RosadoNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease in PregnancyDocument21 pagesInfectious Disease in PregnancyLauren McrobertsNo ratings yet
- CytomegalovirusDocument33 pagesCytomegalovirusAnggi Tridinanti PutriNo ratings yet
- Parvovirus: Transient Aplastic CrisisDocument2 pagesParvovirus: Transient Aplastic CrisisJayde TabanaoNo ratings yet
- Viral Infections of The Skin and Mucus MembranesDocument54 pagesViral Infections of The Skin and Mucus MembranesVikaNo ratings yet
- Infections in Pregnancy & NewbornDocument70 pagesInfections in Pregnancy & NewbornmbbsclerkingNo ratings yet
- TORCH Repro 2012Document44 pagesTORCH Repro 2012Ibnu SyahNo ratings yet
- InfectionDocument11 pagesInfectionHero StoreNo ratings yet
- MicroPara Report HandoutsDocument9 pagesMicroPara Report HandoutsKyla RamonesNo ratings yet
- Double-Stranded DNA VirusesDocument9 pagesDouble-Stranded DNA VirusesLoc NguyenNo ratings yet
- Viral Infection Summary 1Document4 pagesViral Infection Summary 1Richlie Magtulis IINo ratings yet
- Viral Exanthem in PregnancyDocument3 pagesViral Exanthem in PregnancyCatherine Blanche LeeNo ratings yet
- Varicella/Herpes Zoster: Communicable Disease Management ProtocolDocument5 pagesVaricella/Herpes Zoster: Communicable Disease Management Protocolyuliyanto.efendiNo ratings yet
- Exanthematous Viral DiseasesDocument64 pagesExanthematous Viral DiseasesHoc Lim SeeNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Opportunistic Infections in Children Living With HIV Part 2 - Viral & Protozoal OIs and HIV-TB Co-InfectionDocument54 pages8.3 Opportunistic Infections in Children Living With HIV Part 2 - Viral & Protozoal OIs and HIV-TB Co-Infectiondawalgari srivanireddyNo ratings yet
- MEASLESDocument68 pagesMEASLESMonysyha AtriNo ratings yet
- 8 Viral Exanthems of ChildhoodDocument9 pages8 Viral Exanthems of ChildhoodErik OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Compiled Pedia Eye DiseasesDocument17 pagesCompiled Pedia Eye DiseasesJudy Ignacio EclarinoNo ratings yet
- DiseaseDocument5 pagesDiseaseinzegi96No ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 18Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 18JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Swine 5&6Document57 pagesSwine 5&6Keegan McElroyNo ratings yet
- UP PGH 2019 Interns Review 2 Gyne InfectionsDocument39 pagesUP PGH 2019 Interns Review 2 Gyne InfectionsTrisNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted InfectionDocument11 pagesSexually Transmitted Infectionmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Infections - Dr. R. Adhi Teguh SpA (K)Document65 pagesCongenital Infections - Dr. R. Adhi Teguh SpA (K)syak turNo ratings yet
- Myco Viro Hand Out Batch2 UpdatedDocument10 pagesMyco Viro Hand Out Batch2 UpdatedMark jay LlanoNo ratings yet
- VaricellaDocument15 pagesVaricellaPrabhat RanjanNo ratings yet
- Calici Viri DaeDocument5 pagesCalici Viri DaeGabrielle IsnardNo ratings yet
- Block 4B 2023 Viral Exanthems Part 2Document29 pagesBlock 4B 2023 Viral Exanthems Part 2Sabelo VictorNo ratings yet
- Herpes Viruses LectureDocument46 pagesHerpes Viruses Lectureapi-19969058100% (1)
- PATHO Infectious DiseasesDocument3 pagesPATHO Infectious DiseasesamheartsssNo ratings yet
- Infections in PregnancyDocument124 pagesInfections in Pregnancyxzfdf2mwvxNo ratings yet
- German MeaslesDocument25 pagesGerman MeaslesVysakhi PVNo ratings yet
- Viral and Protozoal Infection in PregnancyDocument58 pagesViral and Protozoal Infection in Pregnancyjyoti kunduNo ratings yet
- Pediatria 2021Document34 pagesPediatria 2021Bryan MelendezNo ratings yet
- AAD BF Cutaneous Manifestations of HIV InfectionsDocument2 pagesAAD BF Cutaneous Manifestations of HIV Infectionskahkashanahmed065No ratings yet
- Infeksi Virus Pada KehamilanDocument43 pagesInfeksi Virus Pada KehamilanAgungwiraNo ratings yet
- Rubella, Science DirectDocument11 pagesRubella, Science DirectFebby OktaviantiNo ratings yet
- CYRUSSDocument13 pagesCYRUSSRienna Marie HentoloroNo ratings yet
- Pir 37-12 Enterovirus PPT Final PDFDocument10 pagesPir 37-12 Enterovirus PPT Final PDFbentoeNo ratings yet
- Pir 37-12 Enterovirus PPT Final PDFDocument10 pagesPir 37-12 Enterovirus PPT Final PDFbentoeNo ratings yet
- Syphillis, Herpes, Hepatitis, and HPV: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and TreatmentDocument43 pagesSyphillis, Herpes, Hepatitis, and HPV: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and TreatmentsgolbariNo ratings yet
- Virology: Herpesviruses II: Herpes SimplexDocument4 pagesVirology: Herpesviruses II: Herpes SimplexJaz CNo ratings yet
- Paediatrics MCQ PointsDocument117 pagesPaediatrics MCQ PointstharikaneelawathuraNo ratings yet
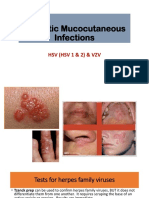
- Herpetic Mucocutaneous Infections: HSV (HSV 1 & 2) & VZVDocument32 pagesHerpetic Mucocutaneous Infections: HSV (HSV 1 & 2) & VZVJaneNo ratings yet
- Measles and Scarlet Fever Kawasaki Disease: Fatin & EileenDocument30 pagesMeasles and Scarlet Fever Kawasaki Disease: Fatin & EileenbyteNo ratings yet
- HIVDocument5 pagesHIVsarguss14100% (1)
- MIC 211 Papillomavirus Polyomavirus and Parvovirus IBD MergedDocument14 pagesMIC 211 Papillomavirus Polyomavirus and Parvovirus IBD MergedJack Ortega PuruggananNo ratings yet
- Epi Reportable PractitionersDocument1 pageEpi Reportable Practitionerspauloantoniolima450No ratings yet
- Krizia Joy Borromeo-Galve, MD: Bulacan Medical Center, Department of PediatricsDocument84 pagesKrizia Joy Borromeo-Galve, MD: Bulacan Medical Center, Department of PediatricsTara Oliveros Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS Maternal LecDocument3 pagesSEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS Maternal LecRomm JacobNo ratings yet
- Hiv Aids in PediatricsDocument60 pagesHiv Aids in Pediatricsmy Lord JesusNo ratings yet
- KHMH Obs Gyn Infections 2022Document31 pagesKHMH Obs Gyn Infections 2022rigo montejoNo ratings yet
- Torch Infection: Reporter: Zhao Meiling (Alice) Date: April.10.2019Document35 pagesTorch Infection: Reporter: Zhao Meiling (Alice) Date: April.10.2019Hilary WangNo ratings yet
- Rubella (German Measles) : Sabah Mohsin Al-Maamuri MDDocument2 pagesRubella (German Measles) : Sabah Mohsin Al-Maamuri MDnadyaszahraaaaNo ratings yet
- Viral DiseasesDocument54 pagesViral Diseasesapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Report BioinfoDocument6 pagesReport BioinfoAkash semwalNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical TestDocument9 pages1st Periodical TestJezzaMay TambauanNo ratings yet
- Bio PhysioDocument587 pagesBio Physioسامي التريكيNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14:: Skin Barrier:: Akiharu Kubo & Masayuki AmagaiDocument21 pagesChapter 14:: Skin Barrier:: Akiharu Kubo & Masayuki Amagaililis nur faridaNo ratings yet
- Morphology of HematologyDocument11 pagesMorphology of HematologyChabNo ratings yet
- Blood Product Transfusion in Adults: Indications, Adverse Reactions, and ModificationsDocument9 pagesBlood Product Transfusion in Adults: Indications, Adverse Reactions, and ModificationsYeseniaNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Microbiology 09-10Document5 pagesSynopsis Microbiology 09-10ikepo adeyeriNo ratings yet
- GentamicinDocument2 pagesGentamicinMiguel Sanico0% (2)
- Creutzfeldt JakobDocument6 pagesCreutzfeldt JakobErnesto Ochoa MonroyNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 3 Edexcel (A) Biology A-Level PDFDocument8 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 3 Edexcel (A) Biology A-Level PDFmohammedNo ratings yet
- Cle Len Terralin Protect ProdDocument2 pagesCle Len Terralin Protect ProdIura FlorinNo ratings yet
- DigitalPharmacologyBundle170Pages CompressedDocument170 pagesDigitalPharmacologyBundle170Pages Compressed98b5jc5hgtNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Culture of Primary Glioblastoma Cells Form Human Tumor SpecimensDocument13 pagesIsolation and Culture of Primary Glioblastoma Cells Form Human Tumor SpecimensPatricia GomesNo ratings yet
- 2.9-Specialized CellsDocument2 pages2.9-Specialized CellsPatrick KamelNo ratings yet
- Oral Viral Infections Diagnosis and ManagementDocument13 pagesOral Viral Infections Diagnosis and ManagementhunarsandhuNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure + Function 12-1Document31 pagesDNA Structure + Function 12-1Jalajarani AridassNo ratings yet
- An Short HistoryDocument33 pagesAn Short HistoryJeanneNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing and Managing Tubercular MeningitisDocument23 pagesDiagnosing and Managing Tubercular MeningitisAstie NomleniNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY111Document60 pagesANAPHY111Gerlyn MortegaNo ratings yet
- Ag Ab ReactionsDocument92 pagesAg Ab ReactionsKavi GawliNo ratings yet
- Quinolone AntibioticsDocument21 pagesQuinolone Antibioticsergrt hdfhdhNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell CycleDocument31 pages1 Cell CycleAkshit BindhaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document17 pagesChapter 3Anna CortiNo ratings yet
- 476 MCB 409 Environmental MicrobiologyDocument26 pages476 MCB 409 Environmental MicrobiologyAbdulkadir HassanNo ratings yet
- GlomerulonephritisDocument39 pagesGlomerulonephritisCheska TumulakNo ratings yet
- Placental PathologyDocument62 pagesPlacental Pathologymaskurniawan100% (2)
- Notes: Vaccines, Abortion, & Fetal TissueDocument5 pagesNotes: Vaccines, Abortion, & Fetal Tissuejdm81No ratings yet
- Prometric Questions: Reviewed By:dr - Mohamed Soliman Call: +201016640110Document215 pagesPrometric Questions: Reviewed By:dr - Mohamed Soliman Call: +201016640110Mallu StreamerNo ratings yet
- Biofire FilmArray Full Panel Menu Info SheetDocument3 pagesBiofire FilmArray Full Panel Menu Info SheetAnne Jillian Castillo100% (1)
- Disease Emergence and Resurgence: The Wildlife-Human ConnectionDocument402 pagesDisease Emergence and Resurgence: The Wildlife-Human ConnectionMaíra100% (1)
Name of Infection/virus Acquired at What Time How To Test For It Likely S/s HSV
Name of Infection/virus Acquired at What Time How To Test For It Likely S/s HSV
Uploaded by
C ROriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Name of Infection/virus Acquired at What Time How To Test For It Likely S/s HSV
Name of Infection/virus Acquired at What Time How To Test For It Likely S/s HSV
Uploaded by
C RCopyright:
Available Formats
Name of Acquired at what time How to test for it Likely s/s
infection/virus
HSV Intrapartum, via infected PCR of CSF and Skin Vesicular lesions on
vaginal canal presenting part, CNS
abnormality
HIV Time of delivery, lesser DNA PCR at first then Recurrent Infections
degree from BF RNA PCR to follow
treatment efficacy
Toxoplasmosis Risk of infection increases IgM Diffuse intracranial
with GA, but worse if calcifications; delayed
contracted early chorioretinitis
Chlamydia At birth Tissue culture (gold Most common cause of
standard) -because it an conjunctivitis at 4-14
intracellular organism days after birth; eyelid
swelling and purulent
discharge; treat with
erythromycin 14 days
Gonorrhea Peripartum, or exposure to Gram stain and Eye infection by 1-4 days
lesions conjunctival scrapings; of life, purulent; eye
blood culture edema; arthritis
Ceftriaxone 25-50mg/kg
IV or PO (not to exceed
125mg) x1 for
conjunctivitis; 7 days for
invasive ds; 14 days for
meningitis
Syphilis Correlates largely with VDRL CSF, and PCR Rash on soles and palms,
duration of maternal blood snuffles, blue/red/white
infection; 1st and 2nd stage CBC, platelets cord; PCN G x10 for
of syphilis transmits X-rays confirmed and likely, and
~100% 1 dose for less likely and
unlikely infection
CMV With primary infection PCR of urine or saliva Periventricular
transmission is highest (gold standard) calcifications,
(very rarely occur PCR of blood if negative chorioretinitis; Early and
perinatally or postnatally) may still be positive late hearing loss
Varicella Weeks 7-20 or 5 days Presence of lesions and Typical vesicular rash
before or 2 days after birth +maternal diagnosis; that becomes into
of maternal infection PCR of fetal blood or cicatricial scars; 60%
amniotic fluid with CNS symptoms
VZIG or IVIG
Rubella 1-12 weeks risk of severe Isolation of virus from Cataracts, SNHL, CHD
anomalies highest, but rate oropharynx, (pulmonary artery
of transmission is highest conjunctival scrapings, stenosis and PDA are
last month of gestation urine, CSF; rubella most common)
specific IgM in cord or
blood (less reliable after
3 months of age)
You might also like
- Dermatology Condition Description Signs/symptoms DDX Viral InfectionsDocument40 pagesDermatology Condition Description Signs/symptoms DDX Viral InfectionsWaseem Ullah100% (1)
- Treatment:: Most LikelyDocument4 pagesTreatment:: Most LikelyRichlie Magtulis IINo ratings yet
- 2.congenital TORCH InfDocument24 pages2.congenital TORCH Infelka.kgmaNo ratings yet
- Inrauterine InfectionsDocument83 pagesInrauterine Infectionsahmad aminNo ratings yet
- TORCHDocument42 pagesTORCHKarla RosadoNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease in PregnancyDocument21 pagesInfectious Disease in PregnancyLauren McrobertsNo ratings yet
- CytomegalovirusDocument33 pagesCytomegalovirusAnggi Tridinanti PutriNo ratings yet
- Parvovirus: Transient Aplastic CrisisDocument2 pagesParvovirus: Transient Aplastic CrisisJayde TabanaoNo ratings yet
- Viral Infections of The Skin and Mucus MembranesDocument54 pagesViral Infections of The Skin and Mucus MembranesVikaNo ratings yet
- Infections in Pregnancy & NewbornDocument70 pagesInfections in Pregnancy & NewbornmbbsclerkingNo ratings yet
- TORCH Repro 2012Document44 pagesTORCH Repro 2012Ibnu SyahNo ratings yet
- InfectionDocument11 pagesInfectionHero StoreNo ratings yet
- MicroPara Report HandoutsDocument9 pagesMicroPara Report HandoutsKyla RamonesNo ratings yet
- Double-Stranded DNA VirusesDocument9 pagesDouble-Stranded DNA VirusesLoc NguyenNo ratings yet
- Viral Infection Summary 1Document4 pagesViral Infection Summary 1Richlie Magtulis IINo ratings yet
- Viral Exanthem in PregnancyDocument3 pagesViral Exanthem in PregnancyCatherine Blanche LeeNo ratings yet
- Varicella/Herpes Zoster: Communicable Disease Management ProtocolDocument5 pagesVaricella/Herpes Zoster: Communicable Disease Management Protocolyuliyanto.efendiNo ratings yet
- Exanthematous Viral DiseasesDocument64 pagesExanthematous Viral DiseasesHoc Lim SeeNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Opportunistic Infections in Children Living With HIV Part 2 - Viral & Protozoal OIs and HIV-TB Co-InfectionDocument54 pages8.3 Opportunistic Infections in Children Living With HIV Part 2 - Viral & Protozoal OIs and HIV-TB Co-Infectiondawalgari srivanireddyNo ratings yet
- MEASLESDocument68 pagesMEASLESMonysyha AtriNo ratings yet
- 8 Viral Exanthems of ChildhoodDocument9 pages8 Viral Exanthems of ChildhoodErik OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Compiled Pedia Eye DiseasesDocument17 pagesCompiled Pedia Eye DiseasesJudy Ignacio EclarinoNo ratings yet
- DiseaseDocument5 pagesDiseaseinzegi96No ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 18Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 18JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Swine 5&6Document57 pagesSwine 5&6Keegan McElroyNo ratings yet
- UP PGH 2019 Interns Review 2 Gyne InfectionsDocument39 pagesUP PGH 2019 Interns Review 2 Gyne InfectionsTrisNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted InfectionDocument11 pagesSexually Transmitted Infectionmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Infections - Dr. R. Adhi Teguh SpA (K)Document65 pagesCongenital Infections - Dr. R. Adhi Teguh SpA (K)syak turNo ratings yet
- Myco Viro Hand Out Batch2 UpdatedDocument10 pagesMyco Viro Hand Out Batch2 UpdatedMark jay LlanoNo ratings yet
- VaricellaDocument15 pagesVaricellaPrabhat RanjanNo ratings yet
- Calici Viri DaeDocument5 pagesCalici Viri DaeGabrielle IsnardNo ratings yet
- Block 4B 2023 Viral Exanthems Part 2Document29 pagesBlock 4B 2023 Viral Exanthems Part 2Sabelo VictorNo ratings yet
- Herpes Viruses LectureDocument46 pagesHerpes Viruses Lectureapi-19969058100% (1)
- PATHO Infectious DiseasesDocument3 pagesPATHO Infectious DiseasesamheartsssNo ratings yet
- Infections in PregnancyDocument124 pagesInfections in Pregnancyxzfdf2mwvxNo ratings yet
- German MeaslesDocument25 pagesGerman MeaslesVysakhi PVNo ratings yet
- Viral and Protozoal Infection in PregnancyDocument58 pagesViral and Protozoal Infection in Pregnancyjyoti kunduNo ratings yet
- Pediatria 2021Document34 pagesPediatria 2021Bryan MelendezNo ratings yet
- AAD BF Cutaneous Manifestations of HIV InfectionsDocument2 pagesAAD BF Cutaneous Manifestations of HIV Infectionskahkashanahmed065No ratings yet
- Infeksi Virus Pada KehamilanDocument43 pagesInfeksi Virus Pada KehamilanAgungwiraNo ratings yet
- Rubella, Science DirectDocument11 pagesRubella, Science DirectFebby OktaviantiNo ratings yet
- CYRUSSDocument13 pagesCYRUSSRienna Marie HentoloroNo ratings yet
- Pir 37-12 Enterovirus PPT Final PDFDocument10 pagesPir 37-12 Enterovirus PPT Final PDFbentoeNo ratings yet
- Pir 37-12 Enterovirus PPT Final PDFDocument10 pagesPir 37-12 Enterovirus PPT Final PDFbentoeNo ratings yet
- Syphillis, Herpes, Hepatitis, and HPV: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and TreatmentDocument43 pagesSyphillis, Herpes, Hepatitis, and HPV: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and TreatmentsgolbariNo ratings yet
- Virology: Herpesviruses II: Herpes SimplexDocument4 pagesVirology: Herpesviruses II: Herpes SimplexJaz CNo ratings yet
- Paediatrics MCQ PointsDocument117 pagesPaediatrics MCQ PointstharikaneelawathuraNo ratings yet
- Herpetic Mucocutaneous Infections: HSV (HSV 1 & 2) & VZVDocument32 pagesHerpetic Mucocutaneous Infections: HSV (HSV 1 & 2) & VZVJaneNo ratings yet
- Measles and Scarlet Fever Kawasaki Disease: Fatin & EileenDocument30 pagesMeasles and Scarlet Fever Kawasaki Disease: Fatin & EileenbyteNo ratings yet
- HIVDocument5 pagesHIVsarguss14100% (1)
- MIC 211 Papillomavirus Polyomavirus and Parvovirus IBD MergedDocument14 pagesMIC 211 Papillomavirus Polyomavirus and Parvovirus IBD MergedJack Ortega PuruggananNo ratings yet
- Epi Reportable PractitionersDocument1 pageEpi Reportable Practitionerspauloantoniolima450No ratings yet
- Krizia Joy Borromeo-Galve, MD: Bulacan Medical Center, Department of PediatricsDocument84 pagesKrizia Joy Borromeo-Galve, MD: Bulacan Medical Center, Department of PediatricsTara Oliveros Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS Maternal LecDocument3 pagesSEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS Maternal LecRomm JacobNo ratings yet
- Hiv Aids in PediatricsDocument60 pagesHiv Aids in Pediatricsmy Lord JesusNo ratings yet
- KHMH Obs Gyn Infections 2022Document31 pagesKHMH Obs Gyn Infections 2022rigo montejoNo ratings yet
- Torch Infection: Reporter: Zhao Meiling (Alice) Date: April.10.2019Document35 pagesTorch Infection: Reporter: Zhao Meiling (Alice) Date: April.10.2019Hilary WangNo ratings yet
- Rubella (German Measles) : Sabah Mohsin Al-Maamuri MDDocument2 pagesRubella (German Measles) : Sabah Mohsin Al-Maamuri MDnadyaszahraaaaNo ratings yet
- Viral DiseasesDocument54 pagesViral Diseasesapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Report BioinfoDocument6 pagesReport BioinfoAkash semwalNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical TestDocument9 pages1st Periodical TestJezzaMay TambauanNo ratings yet
- Bio PhysioDocument587 pagesBio Physioسامي التريكيNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14:: Skin Barrier:: Akiharu Kubo & Masayuki AmagaiDocument21 pagesChapter 14:: Skin Barrier:: Akiharu Kubo & Masayuki Amagaililis nur faridaNo ratings yet
- Morphology of HematologyDocument11 pagesMorphology of HematologyChabNo ratings yet
- Blood Product Transfusion in Adults: Indications, Adverse Reactions, and ModificationsDocument9 pagesBlood Product Transfusion in Adults: Indications, Adverse Reactions, and ModificationsYeseniaNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Microbiology 09-10Document5 pagesSynopsis Microbiology 09-10ikepo adeyeriNo ratings yet
- GentamicinDocument2 pagesGentamicinMiguel Sanico0% (2)
- Creutzfeldt JakobDocument6 pagesCreutzfeldt JakobErnesto Ochoa MonroyNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 3 Edexcel (A) Biology A-Level PDFDocument8 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 3 Edexcel (A) Biology A-Level PDFmohammedNo ratings yet
- Cle Len Terralin Protect ProdDocument2 pagesCle Len Terralin Protect ProdIura FlorinNo ratings yet
- DigitalPharmacologyBundle170Pages CompressedDocument170 pagesDigitalPharmacologyBundle170Pages Compressed98b5jc5hgtNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Culture of Primary Glioblastoma Cells Form Human Tumor SpecimensDocument13 pagesIsolation and Culture of Primary Glioblastoma Cells Form Human Tumor SpecimensPatricia GomesNo ratings yet
- 2.9-Specialized CellsDocument2 pages2.9-Specialized CellsPatrick KamelNo ratings yet
- Oral Viral Infections Diagnosis and ManagementDocument13 pagesOral Viral Infections Diagnosis and ManagementhunarsandhuNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure + Function 12-1Document31 pagesDNA Structure + Function 12-1Jalajarani AridassNo ratings yet
- An Short HistoryDocument33 pagesAn Short HistoryJeanneNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing and Managing Tubercular MeningitisDocument23 pagesDiagnosing and Managing Tubercular MeningitisAstie NomleniNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY111Document60 pagesANAPHY111Gerlyn MortegaNo ratings yet
- Ag Ab ReactionsDocument92 pagesAg Ab ReactionsKavi GawliNo ratings yet
- Quinolone AntibioticsDocument21 pagesQuinolone Antibioticsergrt hdfhdhNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell CycleDocument31 pages1 Cell CycleAkshit BindhaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document17 pagesChapter 3Anna CortiNo ratings yet
- 476 MCB 409 Environmental MicrobiologyDocument26 pages476 MCB 409 Environmental MicrobiologyAbdulkadir HassanNo ratings yet
- GlomerulonephritisDocument39 pagesGlomerulonephritisCheska TumulakNo ratings yet
- Placental PathologyDocument62 pagesPlacental Pathologymaskurniawan100% (2)
- Notes: Vaccines, Abortion, & Fetal TissueDocument5 pagesNotes: Vaccines, Abortion, & Fetal Tissuejdm81No ratings yet
- Prometric Questions: Reviewed By:dr - Mohamed Soliman Call: +201016640110Document215 pagesPrometric Questions: Reviewed By:dr - Mohamed Soliman Call: +201016640110Mallu StreamerNo ratings yet
- Biofire FilmArray Full Panel Menu Info SheetDocument3 pagesBiofire FilmArray Full Panel Menu Info SheetAnne Jillian Castillo100% (1)
- Disease Emergence and Resurgence: The Wildlife-Human ConnectionDocument402 pagesDisease Emergence and Resurgence: The Wildlife-Human ConnectionMaíra100% (1)