Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PH Against Rate of Amylase Reaction
PH Against Rate of Amylase Reaction
Uploaded by
using formeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- BIOM Laboratory ReportDocument7 pagesBIOM Laboratory Reportzubin33333No ratings yet
- QCVN 6-1,2010 BYT (Eng)Document15 pagesQCVN 6-1,2010 BYT (Eng)Huynh le ManNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- BTC4305 Lab Report 1Document11 pagesBTC4305 Lab Report 1Jerry Caldwell100% (1)
- Concentration Phet Weblab - Use HTML 5/surface: Part 1: Concentration Calculations Using Molarity Formula - ProcedureDocument6 pagesConcentration Phet Weblab - Use HTML 5/surface: Part 1: Concentration Calculations Using Molarity Formula - ProcedureAndrew GiambattistaNo ratings yet
- Concentration Phet Weblab - Use HTML 5/chromebooksDocument4 pagesConcentration Phet Weblab - Use HTML 5/chromebooksAlma Janella TOSINONo ratings yet
- EN 571 Homework 5Document2 pagesEN 571 Homework 5kelsi chanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Words and CultureDocument13 pagesChapter 9 - Words and CultureYesicha Ryona100% (1)
- Experiment 3: Factors Affecting Enzymes Reaction: School of Industrial Technology Faculty of Applied SciencesDocument5 pagesExperiment 3: Factors Affecting Enzymes Reaction: School of Industrial Technology Faculty of Applied SciencesnajwaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Biochemistry (BIO 462)Document4 pagesLab Report Biochemistry (BIO 462)Iman FarhaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab - Enzyme Activity (Corpuz, R)Document7 pagesBiochem Lab - Enzyme Activity (Corpuz, R)Reynand MaelNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Kinetic LabDocument13 pagesEnzyme Kinetic LabRACHAELNo ratings yet
- Effects of Enzyme Concentration On Rate of ReactionDocument2 pagesEffects of Enzyme Concentration On Rate of Reactionmigire kennedyNo ratings yet
- JJDocument4 pagesJJEureca ParraNo ratings yet
- Mahima Sikdar Enzymes Lab Report Outline Done Week 6Document7 pagesMahima Sikdar Enzymes Lab Report Outline Done Week 6Mahima SikdarNo ratings yet
- Jassia AssignmntDocument7 pagesJassia AssignmntSundas MehreenNo ratings yet
- Biology PND EnzymeDocument4 pagesBiology PND EnzymeVishmeta SeenarineNo ratings yet
- Effect of PH in Fenton-Like OxidationDocument2 pagesEffect of PH in Fenton-Like OxidationDexSobNo ratings yet
- Esterification of Ethanol in A Batch Reactor in Presence of H2SO4Document17 pagesEsterification of Ethanol in A Batch Reactor in Presence of H2SO4MD.Khairul EducationNo ratings yet
- Note: in Planning The Control of The Experiment, Explain Is The Control, and Is The Control Carried Out.Document2 pagesNote: in Planning The Control of The Experiment, Explain Is The Control, and Is The Control Carried Out.Amami RantaroNo ratings yet
- Absolute Amounts of Glucose Vs A540: DiscussionDocument3 pagesAbsolute Amounts of Glucose Vs A540: DiscussionMalek Marry AnneNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Temperature and PH On The Enzymatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseDocument33 pagesThe Effects of Temperature and PH On The Enzymatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseCherisse TuazonNo ratings yet
- Western Methods Assignment DeanDocument6 pagesWestern Methods Assignment Deantrz45k8grqNo ratings yet
- The Resulting Effect When Lactase Enzyme Is Subjected To Differences Substrate Concentration, Temperature and PHDocument6 pagesThe Resulting Effect When Lactase Enzyme Is Subjected To Differences Substrate Concentration, Temperature and PHjustusNo ratings yet
- KimiaaaaaaDocument11 pagesKimiaaaaaaaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry PRC 2 Data Analysis EnzymeDocument4 pagesBiochemistry PRC 2 Data Analysis EnzymeSARAH SAFIAH TAJUL ARIFFINNo ratings yet
- JCPR 3 1 529 535Document7 pagesJCPR 3 1 529 535innoxyzNo ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetics Power Point Part 1 1Document25 pagesReaction Kinetics Power Point Part 1 1이수연No ratings yet
- 4.8 - Gel Electrophoresis - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument5 pages4.8 - Gel Electrophoresis - Chemistry LibreTextsCharm AngelesNo ratings yet
- Determination of Reaction Rate ConstantDocument7 pagesDetermination of Reaction Rate ConstantJoyce VicenteNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Outline - Exercise 7Document6 pagesLaboratory Outline - Exercise 7Majestic RavenNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument17 pagesCombinepdfNaresh GanisonNo ratings yet
- Degradation of Fluoroquinolone-Based Pollutants and Bacterial Inactivation by Visible-Light-Active Aluminum-Doped TiO2 NanoflakesDocument12 pagesDegradation of Fluoroquinolone-Based Pollutants and Bacterial Inactivation by Visible-Light-Active Aluminum-Doped TiO2 NanoflakesAkashdeep DeNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Exam1Document2 pagesAnswer Key Exam1MJ TarhiniNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Analysis of Amylase Using Quantitative BenDocument4 pagesKinetic Analysis of Amylase Using Quantitative BenCarlin NauNo ratings yet
- Taller Bioquimica Punto 5Document10 pagesTaller Bioquimica Punto 5Jesús Miguel Comas AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Chem r3p0rtDocument5 pagesChem r3p0rtDonghyuck ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nutri Meta Lab 2 CombinedDocument16 pagesNutri Meta Lab 2 CombinedvlcjNo ratings yet
- Draft Acid Flow Back Study Aug 2018Document15 pagesDraft Acid Flow Back Study Aug 2018Azizi Org Yang LuhurNo ratings yet
- Cloruro FerricoDocument8 pagesCloruro FerricoMario GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Enzyme Lab ReportDocument3 pagesAP Biology Enzyme Lab ReportPatrick100% (6)
- Reaction KineticsDocument15 pagesReaction KineticsSadiaShoaibNo ratings yet
- Practica 8 AdsorcionDocument7 pagesPractica 8 AdsorcionMónica MedinaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Characterization of Serine Proteases: GBE 302 Biochemistry Ii LaboratoryDocument8 pagesExperiment 7 Characterization of Serine Proteases: GBE 302 Biochemistry Ii LaboratoryDeniz YılmazNo ratings yet
- Fin 00253Document10 pagesFin 00253ayat arahmanNo ratings yet
- Rate Reaction Lloaana 2020Document8 pagesRate Reaction Lloaana 2020Lloaana 12No ratings yet
- Enzyme Activity Online LabDocument5 pagesEnzyme Activity Online LabJohn BuzzerioNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Rate of ReactionDocument2 pagesMeasuring The Rate of ReactionNathan KearnsNo ratings yet
- Apparent Molal Volume Vs Square Root of Molality For Trial 1Document3 pagesApparent Molal Volume Vs Square Root of Molality For Trial 1Geneva OrañoNo ratings yet
- AAS Data AnalysisDocument2 pagesAAS Data AnalysisGian MeniaNo ratings yet
- Cre I TkietDocument5 pagesCre I Tkiet259Katkar PrathmeshNo ratings yet
- DPAR Partial Molar VolumeDocument22 pagesDPAR Partial Molar VolumeFritz FestejoNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometric Study of Complexes by Job's Method: Report of The Minor UGC Project EntitledDocument19 pagesSpectrophotometric Study of Complexes by Job's Method: Report of The Minor UGC Project EntitledM Irfan Khan100% (1)
- Glucose Concentr Ation (MG/L) Absorba Nce (A) : Glucose Concentration Vs AbsorbanceDocument6 pagesGlucose Concentr Ation (MG/L) Absorba Nce (A) : Glucose Concentration Vs Absorbancesyahirah shamsudinNo ratings yet
- Lab Bio462 - Experiment 3Document6 pagesLab Bio462 - Experiment 3BalqishNo ratings yet
- Vibration Amplitude Over TimeDocument1 pageVibration Amplitude Over TimePaulo ConciNo ratings yet
- Research SampleDocument11 pagesResearch SampleosamaNo ratings yet
- 21B2043 Rusydi SC2243 Exp2Document7 pages21B2043 Rusydi SC2243 Exp2raniyaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Volatile Toxic Substances Using Headspace GC/MS Part.2 - Cyanide and AzideDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Volatile Toxic Substances Using Headspace GC/MS Part.2 - Cyanide and AzideBilal KilaniNo ratings yet
- BIO 462 Experiment 2Document6 pagesBIO 462 Experiment 2Nurul Farhah RadzuwanNo ratings yet
- Activity Number 2Document9 pagesActivity Number 2Mariella SingsonNo ratings yet
- Bio462 - Experiment 6Document1 pageBio462 - Experiment 6using formeNo ratings yet
- Bio462 - Experiment 7Document3 pagesBio462 - Experiment 7using formeNo ratings yet
- BIO462 - Result Practical 2Document1 pageBIO462 - Result Practical 2using formeNo ratings yet
- Bio 462 - Experiment 4Document3 pagesBio 462 - Experiment 4using formeNo ratings yet
- Clinical ChemistryDocument10 pagesClinical ChemistryChristina AtefNo ratings yet
- Blepharoplasty: Anatomy, Planning, Techniques, and Safety: Mohammed Alghoul, MD, FACSDocument19 pagesBlepharoplasty: Anatomy, Planning, Techniques, and Safety: Mohammed Alghoul, MD, FACSfahrulrozyNo ratings yet
- Salt IodateDocument2 pagesSalt IodateRKMNo ratings yet
- 10 1126@science Abb2491Document9 pages10 1126@science Abb2491venkatavamsibharadwajNo ratings yet
- Aloevera PDFDocument9 pagesAloevera PDFDeimer OrtizNo ratings yet
- Somacy-SP006 (Promotional Material)Document7 pagesSomacy-SP006 (Promotional Material)Karen Claire HorcaNo ratings yet
- 1 SM PDFDocument8 pages1 SM PDFjihan safNo ratings yet
- S8 Q4 Week-4Document10 pagesS8 Q4 Week-4joan marie PeliasNo ratings yet
- Inter Molecular ForcesDocument47 pagesInter Molecular ForcesSladjana TeslićNo ratings yet
- TERLIPRESSINDocument6 pagesTERLIPRESSINAnil Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences p1 Nov 2021 PDFDocument17 pagesLife Sciences p1 Nov 2021 PDFAkhonaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Module 11: Pre-Natal PeriodDocument42 pagesUNIT 1 Module 11: Pre-Natal PeriodJenno Lloyd Samaniego DariaNo ratings yet
- Lynch Nejm2018Document10 pagesLynch Nejm2018alomeletyNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle StudentDocument30 pagesCell Cycle StudentKarthikgayan (Karthik) VicneswaranNo ratings yet
- EARTH AND LIFE SUMMATIVE TEST 2 2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesEARTH AND LIFE SUMMATIVE TEST 2 2nd QuarterMars John BanatasaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5, Measuring Dental FluorosisDocument3 pagesLecture 5, Measuring Dental FluorosisJustDen09No ratings yet
- 05 Petrucci10e CSMDocument45 pages05 Petrucci10e CSMAlexNo ratings yet
- Serology & Immunology - INTRODUCTION (SC)Document31 pagesSerology & Immunology - INTRODUCTION (SC)Aira Kim ReotutarNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and Peptides SlidesDocument19 pagesAmino Acids and Peptides Slidesraanja2No ratings yet
- CIE Biology GCSE: 9 - Transport in AnimalsDocument104 pagesCIE Biology GCSE: 9 - Transport in AnimalsSavage YNo ratings yet
- SHSA G12 PART 1 General Knowledge English Math Science PDFDocument6 pagesSHSA G12 PART 1 General Knowledge English Math Science PDFBessie Sotero100% (1)
- Introduction To MycologyDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Mycologyapi-19969058100% (1)
- Morphology Notes-2023-24 Updated For ExamDocument8 pagesMorphology Notes-2023-24 Updated For Examsaanvika100% (1)
- Locomotion and Postural BehaviourDocument17 pagesLocomotion and Postural BehaviourMiguel LessaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Plant MorphologyDocument5 pagesLab 1 Plant MorphologyNabilah SyahirahNo ratings yet
- Copy of Sex Linked Practice ProblemsDocument8 pagesCopy of Sex Linked Practice ProblemsmishineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14.2 - Cardiovascular System - The HeartDocument32 pagesChapter 14.2 - Cardiovascular System - The HeartMichael PeraltaNo ratings yet
- 978-3-642-67913-1 - 10) Monty, Claude - Phanerozoic Stromatolites Possible Microbial Accretions in Cenomanian Mounds, S.E. France PDFDocument13 pages978-3-642-67913-1 - 10) Monty, Claude - Phanerozoic Stromatolites Possible Microbial Accretions in Cenomanian Mounds, S.E. France PDFMoezNo ratings yet
PH Against Rate of Amylase Reaction
PH Against Rate of Amylase Reaction
Uploaded by
using formeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PH Against Rate of Amylase Reaction
PH Against Rate of Amylase Reaction
Uploaded by
using formeCopyright:
Available Formats
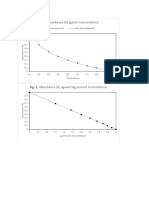
Part A
: Effect of pH on the activity of amylase in breaking down of starch
Table 1: Effects of pH on amylase activity
Time needed for Rate of amylase
colour change reaction (1/time
pH
from blue-black to needed for colour
brown (min) change)
3 11 0.09
5 3 0.33
7 1 1
9 15 0.07
pH against Rate of amylase reaction
1.2
1
Rate of amylase reaction
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
3 5 7 9
pH
Enzyme that works optimally at an acidic pH = Pepsin
Part B: Effect of substrate concentration on amylase activity
Table 2: Effect of substrate concentration of amylase activity at pH7
Amount of substrate Time needed for colour change
Amount of enzyme (mL)
(mL) from blue-black to brown (min)
1 1 1
5 1 1
10 1 2
15 1 3
20 1 9
25 1 16
Time needed for color change against Amount of substrate
30
25
Amount of substrate (mL)
20
15
10
0
1 2 3 9 16
Time needed for color change (min)
What happened at higher concentration of substrate that caused the rate of reaction to
become steady?
Enzymes become saturated when the substrate concentration is high
Suggest how can you increase the rate of reaction.
Add more enzyme
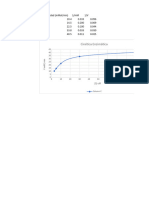
Part C: Effect of enzyme concentration on amylase activity
Table 3: Effect of enzyme concentration of amylase activity
Amount of
Time needed for colour change from Rate of amylase reaction (1/time
enzyme
blue-black to brown (min) needed for colour change)
(mL)
0.2 10 0.10
0.4 8 0.13
0.6 6 0.17
0.8 4 0.25
1.0 3 0.33
1.2 3 0.33
Amount of enzyme against Rate of amylase reaction
0.35
0.3
Rate of amylase reaction
0.25
0.2
0.15
0.1
0.05
0
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2
Amount of enzyme (mL)
Can the reaction still happen when no enzyme is added? Explain your answer.
The reaction still can happen but these reaction would take place slowly because enzyme are
proteins that control the speed of chemical reactions.
You might also like
- BIOM Laboratory ReportDocument7 pagesBIOM Laboratory Reportzubin33333No ratings yet
- QCVN 6-1,2010 BYT (Eng)Document15 pagesQCVN 6-1,2010 BYT (Eng)Huynh le ManNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- BTC4305 Lab Report 1Document11 pagesBTC4305 Lab Report 1Jerry Caldwell100% (1)
- Concentration Phet Weblab - Use HTML 5/surface: Part 1: Concentration Calculations Using Molarity Formula - ProcedureDocument6 pagesConcentration Phet Weblab - Use HTML 5/surface: Part 1: Concentration Calculations Using Molarity Formula - ProcedureAndrew GiambattistaNo ratings yet
- Concentration Phet Weblab - Use HTML 5/chromebooksDocument4 pagesConcentration Phet Weblab - Use HTML 5/chromebooksAlma Janella TOSINONo ratings yet
- EN 571 Homework 5Document2 pagesEN 571 Homework 5kelsi chanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Words and CultureDocument13 pagesChapter 9 - Words and CultureYesicha Ryona100% (1)
- Experiment 3: Factors Affecting Enzymes Reaction: School of Industrial Technology Faculty of Applied SciencesDocument5 pagesExperiment 3: Factors Affecting Enzymes Reaction: School of Industrial Technology Faculty of Applied SciencesnajwaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Biochemistry (BIO 462)Document4 pagesLab Report Biochemistry (BIO 462)Iman FarhaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab - Enzyme Activity (Corpuz, R)Document7 pagesBiochem Lab - Enzyme Activity (Corpuz, R)Reynand MaelNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Kinetic LabDocument13 pagesEnzyme Kinetic LabRACHAELNo ratings yet
- Effects of Enzyme Concentration On Rate of ReactionDocument2 pagesEffects of Enzyme Concentration On Rate of Reactionmigire kennedyNo ratings yet
- JJDocument4 pagesJJEureca ParraNo ratings yet
- Mahima Sikdar Enzymes Lab Report Outline Done Week 6Document7 pagesMahima Sikdar Enzymes Lab Report Outline Done Week 6Mahima SikdarNo ratings yet
- Jassia AssignmntDocument7 pagesJassia AssignmntSundas MehreenNo ratings yet
- Biology PND EnzymeDocument4 pagesBiology PND EnzymeVishmeta SeenarineNo ratings yet
- Effect of PH in Fenton-Like OxidationDocument2 pagesEffect of PH in Fenton-Like OxidationDexSobNo ratings yet
- Esterification of Ethanol in A Batch Reactor in Presence of H2SO4Document17 pagesEsterification of Ethanol in A Batch Reactor in Presence of H2SO4MD.Khairul EducationNo ratings yet
- Note: in Planning The Control of The Experiment, Explain Is The Control, and Is The Control Carried Out.Document2 pagesNote: in Planning The Control of The Experiment, Explain Is The Control, and Is The Control Carried Out.Amami RantaroNo ratings yet
- Absolute Amounts of Glucose Vs A540: DiscussionDocument3 pagesAbsolute Amounts of Glucose Vs A540: DiscussionMalek Marry AnneNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Temperature and PH On The Enzymatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseDocument33 pagesThe Effects of Temperature and PH On The Enzymatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseCherisse TuazonNo ratings yet
- Western Methods Assignment DeanDocument6 pagesWestern Methods Assignment Deantrz45k8grqNo ratings yet
- The Resulting Effect When Lactase Enzyme Is Subjected To Differences Substrate Concentration, Temperature and PHDocument6 pagesThe Resulting Effect When Lactase Enzyme Is Subjected To Differences Substrate Concentration, Temperature and PHjustusNo ratings yet
- KimiaaaaaaDocument11 pagesKimiaaaaaaaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry PRC 2 Data Analysis EnzymeDocument4 pagesBiochemistry PRC 2 Data Analysis EnzymeSARAH SAFIAH TAJUL ARIFFINNo ratings yet
- JCPR 3 1 529 535Document7 pagesJCPR 3 1 529 535innoxyzNo ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetics Power Point Part 1 1Document25 pagesReaction Kinetics Power Point Part 1 1이수연No ratings yet
- 4.8 - Gel Electrophoresis - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument5 pages4.8 - Gel Electrophoresis - Chemistry LibreTextsCharm AngelesNo ratings yet
- Determination of Reaction Rate ConstantDocument7 pagesDetermination of Reaction Rate ConstantJoyce VicenteNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Outline - Exercise 7Document6 pagesLaboratory Outline - Exercise 7Majestic RavenNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument17 pagesCombinepdfNaresh GanisonNo ratings yet
- Degradation of Fluoroquinolone-Based Pollutants and Bacterial Inactivation by Visible-Light-Active Aluminum-Doped TiO2 NanoflakesDocument12 pagesDegradation of Fluoroquinolone-Based Pollutants and Bacterial Inactivation by Visible-Light-Active Aluminum-Doped TiO2 NanoflakesAkashdeep DeNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Exam1Document2 pagesAnswer Key Exam1MJ TarhiniNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Analysis of Amylase Using Quantitative BenDocument4 pagesKinetic Analysis of Amylase Using Quantitative BenCarlin NauNo ratings yet
- Taller Bioquimica Punto 5Document10 pagesTaller Bioquimica Punto 5Jesús Miguel Comas AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Chem r3p0rtDocument5 pagesChem r3p0rtDonghyuck ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nutri Meta Lab 2 CombinedDocument16 pagesNutri Meta Lab 2 CombinedvlcjNo ratings yet
- Draft Acid Flow Back Study Aug 2018Document15 pagesDraft Acid Flow Back Study Aug 2018Azizi Org Yang LuhurNo ratings yet
- Cloruro FerricoDocument8 pagesCloruro FerricoMario GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Enzyme Lab ReportDocument3 pagesAP Biology Enzyme Lab ReportPatrick100% (6)
- Reaction KineticsDocument15 pagesReaction KineticsSadiaShoaibNo ratings yet
- Practica 8 AdsorcionDocument7 pagesPractica 8 AdsorcionMónica MedinaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Characterization of Serine Proteases: GBE 302 Biochemistry Ii LaboratoryDocument8 pagesExperiment 7 Characterization of Serine Proteases: GBE 302 Biochemistry Ii LaboratoryDeniz YılmazNo ratings yet
- Fin 00253Document10 pagesFin 00253ayat arahmanNo ratings yet
- Rate Reaction Lloaana 2020Document8 pagesRate Reaction Lloaana 2020Lloaana 12No ratings yet
- Enzyme Activity Online LabDocument5 pagesEnzyme Activity Online LabJohn BuzzerioNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Rate of ReactionDocument2 pagesMeasuring The Rate of ReactionNathan KearnsNo ratings yet
- Apparent Molal Volume Vs Square Root of Molality For Trial 1Document3 pagesApparent Molal Volume Vs Square Root of Molality For Trial 1Geneva OrañoNo ratings yet
- AAS Data AnalysisDocument2 pagesAAS Data AnalysisGian MeniaNo ratings yet
- Cre I TkietDocument5 pagesCre I Tkiet259Katkar PrathmeshNo ratings yet
- DPAR Partial Molar VolumeDocument22 pagesDPAR Partial Molar VolumeFritz FestejoNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometric Study of Complexes by Job's Method: Report of The Minor UGC Project EntitledDocument19 pagesSpectrophotometric Study of Complexes by Job's Method: Report of The Minor UGC Project EntitledM Irfan Khan100% (1)
- Glucose Concentr Ation (MG/L) Absorba Nce (A) : Glucose Concentration Vs AbsorbanceDocument6 pagesGlucose Concentr Ation (MG/L) Absorba Nce (A) : Glucose Concentration Vs Absorbancesyahirah shamsudinNo ratings yet
- Lab Bio462 - Experiment 3Document6 pagesLab Bio462 - Experiment 3BalqishNo ratings yet
- Vibration Amplitude Over TimeDocument1 pageVibration Amplitude Over TimePaulo ConciNo ratings yet
- Research SampleDocument11 pagesResearch SampleosamaNo ratings yet
- 21B2043 Rusydi SC2243 Exp2Document7 pages21B2043 Rusydi SC2243 Exp2raniyaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Volatile Toxic Substances Using Headspace GC/MS Part.2 - Cyanide and AzideDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Volatile Toxic Substances Using Headspace GC/MS Part.2 - Cyanide and AzideBilal KilaniNo ratings yet
- BIO 462 Experiment 2Document6 pagesBIO 462 Experiment 2Nurul Farhah RadzuwanNo ratings yet
- Activity Number 2Document9 pagesActivity Number 2Mariella SingsonNo ratings yet
- Bio462 - Experiment 6Document1 pageBio462 - Experiment 6using formeNo ratings yet
- Bio462 - Experiment 7Document3 pagesBio462 - Experiment 7using formeNo ratings yet
- BIO462 - Result Practical 2Document1 pageBIO462 - Result Practical 2using formeNo ratings yet
- Bio 462 - Experiment 4Document3 pagesBio 462 - Experiment 4using formeNo ratings yet
- Clinical ChemistryDocument10 pagesClinical ChemistryChristina AtefNo ratings yet
- Blepharoplasty: Anatomy, Planning, Techniques, and Safety: Mohammed Alghoul, MD, FACSDocument19 pagesBlepharoplasty: Anatomy, Planning, Techniques, and Safety: Mohammed Alghoul, MD, FACSfahrulrozyNo ratings yet
- Salt IodateDocument2 pagesSalt IodateRKMNo ratings yet
- 10 1126@science Abb2491Document9 pages10 1126@science Abb2491venkatavamsibharadwajNo ratings yet
- Aloevera PDFDocument9 pagesAloevera PDFDeimer OrtizNo ratings yet
- Somacy-SP006 (Promotional Material)Document7 pagesSomacy-SP006 (Promotional Material)Karen Claire HorcaNo ratings yet
- 1 SM PDFDocument8 pages1 SM PDFjihan safNo ratings yet
- S8 Q4 Week-4Document10 pagesS8 Q4 Week-4joan marie PeliasNo ratings yet
- Inter Molecular ForcesDocument47 pagesInter Molecular ForcesSladjana TeslićNo ratings yet
- TERLIPRESSINDocument6 pagesTERLIPRESSINAnil Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences p1 Nov 2021 PDFDocument17 pagesLife Sciences p1 Nov 2021 PDFAkhonaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Module 11: Pre-Natal PeriodDocument42 pagesUNIT 1 Module 11: Pre-Natal PeriodJenno Lloyd Samaniego DariaNo ratings yet
- Lynch Nejm2018Document10 pagesLynch Nejm2018alomeletyNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle StudentDocument30 pagesCell Cycle StudentKarthikgayan (Karthik) VicneswaranNo ratings yet
- EARTH AND LIFE SUMMATIVE TEST 2 2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesEARTH AND LIFE SUMMATIVE TEST 2 2nd QuarterMars John BanatasaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5, Measuring Dental FluorosisDocument3 pagesLecture 5, Measuring Dental FluorosisJustDen09No ratings yet
- 05 Petrucci10e CSMDocument45 pages05 Petrucci10e CSMAlexNo ratings yet
- Serology & Immunology - INTRODUCTION (SC)Document31 pagesSerology & Immunology - INTRODUCTION (SC)Aira Kim ReotutarNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and Peptides SlidesDocument19 pagesAmino Acids and Peptides Slidesraanja2No ratings yet
- CIE Biology GCSE: 9 - Transport in AnimalsDocument104 pagesCIE Biology GCSE: 9 - Transport in AnimalsSavage YNo ratings yet
- SHSA G12 PART 1 General Knowledge English Math Science PDFDocument6 pagesSHSA G12 PART 1 General Knowledge English Math Science PDFBessie Sotero100% (1)
- Introduction To MycologyDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Mycologyapi-19969058100% (1)
- Morphology Notes-2023-24 Updated For ExamDocument8 pagesMorphology Notes-2023-24 Updated For Examsaanvika100% (1)
- Locomotion and Postural BehaviourDocument17 pagesLocomotion and Postural BehaviourMiguel LessaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Plant MorphologyDocument5 pagesLab 1 Plant MorphologyNabilah SyahirahNo ratings yet
- Copy of Sex Linked Practice ProblemsDocument8 pagesCopy of Sex Linked Practice ProblemsmishineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14.2 - Cardiovascular System - The HeartDocument32 pagesChapter 14.2 - Cardiovascular System - The HeartMichael PeraltaNo ratings yet
- 978-3-642-67913-1 - 10) Monty, Claude - Phanerozoic Stromatolites Possible Microbial Accretions in Cenomanian Mounds, S.E. France PDFDocument13 pages978-3-642-67913-1 - 10) Monty, Claude - Phanerozoic Stromatolites Possible Microbial Accretions in Cenomanian Mounds, S.E. France PDFMoezNo ratings yet