Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Heart Revision Notes: The Circulatory System's Main Function Is To
The Heart Revision Notes: The Circulatory System's Main Function Is To
Uploaded by
Michael DongCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- BLS TRAINING MANUAL Second Edition PDF 2023-1 - 240226 - 093323Document93 pagesBLS TRAINING MANUAL Second Edition PDF 2023-1 - 240226 - 093323mohdnor29No ratings yet
- Clinical Focus: Emergency RoomDocument12 pagesClinical Focus: Emergency Roomnokolip90% (21)
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseLouie Kem Anthony Babaran50% (8)
- Critical Care Model MCQsDocument1 pageCritical Care Model MCQssacabona100% (1)
- Pulmonary Circulation 4th Edition (2016) (PDF) (UnitedVRG) PDFDocument773 pagesPulmonary Circulation 4th Edition (2016) (PDF) (UnitedVRG) PDFpvs5155No ratings yet
- The Circulatory System PDFDocument22 pagesThe Circulatory System PDFbilly sauraNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument28 pagesCirculatory SystemMaria Theresa DemeterioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 by Jaskirat KaurDocument18 pagesLecture 3 by Jaskirat KaurmparineetNo ratings yet
- Intro To The Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesIntro To The Circulatory Systemapi-656424610No ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Transporting Gases, Nutrients, Wastes, and HormonesDocument44 pagesCirculatory System: Transporting Gases, Nutrients, Wastes, and HormonesDawn Regile MorilloNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Transporting Gases, Nutrients, Wastes, and HormonesDocument22 pagesCirculatory System: Transporting Gases, Nutrients, Wastes, and HormonesMariella SingsonNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument12 pagesCirculatory SystemKeyur SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Cardiovascular SystemDocument49 pages2.2 Cardiovascular SystemPratham ChopraNo ratings yet
- Human Body Circulatory SystemDocument41 pagesHuman Body Circulatory SystemFrancis MacasioNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument17 pagesCirculatory Systemkatefoskin2008No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Shoaib AlamDocument28 pagesCardiovascular System: Shoaib AlamUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of The HeartDocument2 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of The Heartjoycee01No ratings yet
- Module 3Document43 pagesModule 3Sharanya BasakNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument31 pagesCirculatory SystemKalev MaricqNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of HeartDocument42 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of HeartSANJAY SNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology (Cardio)Document1 pageAnatomy and Physiology (Cardio)Eunice LazaroNo ratings yet
- System Is An: ArteriesDocument4 pagesSystem Is An: ArteriesPinasti Aprilia PutriNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Biology Chapter 6 Term 1 ST 1Document27 pagesCirculatory System: Biology Chapter 6 Term 1 ST 1Pranati SharmaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 1.3 LessonDocument31 pagesScience 9 1.3 LessonHdisbdbd NfjdnbdncNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesCirculatory SystemDaniica MacaranasNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System 3500Document24 pagesThe Circulatory System 3500tarickbatshon03No ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Sbi3u The Circulatory System Introduction and Human Circulatory SystemDocument39 pagesDokumen - Tips - Sbi3u The Circulatory System Introduction and Human Circulatory Systempacheco TimeNo ratings yet
- Cardio NewDocument204 pagesCardio NewHaleema SaadiaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory Systemvedansh duttNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andDocument62 pagesCirculatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andBlister CountNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andDocument62 pagesCirculatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andBlister Count100% (1)
- BiologyDocument7 pagesBiologyMaria MubasshiraNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesThe Circulatory SystemJavier Serrano MatuteNo ratings yet
- Lecture in Circulatory SystemDocument14 pagesLecture in Circulatory SystemGailNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument20 pagesThe Circulatory Systemhanatabbal19No ratings yet
- IV.C. Nutrient and Waste Transport SystemDocument18 pagesIV.C. Nutrient and Waste Transport SystemDarwin NoolNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As ADocument6 pagesCardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As AMalaquias VallejosNo ratings yet
- Life Processes, Class XDocument31 pagesLife Processes, Class XPiyushNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument27 pagesCirculatory SystemAngel JD PelovelloNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - First Quarter Reviewer: Biology 9Document33 pagesScience 9 - First Quarter Reviewer: Biology 9Ace AligoraNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument25 pagesCirculatory SystemIan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System REVISEDDocument11 pagesCirculatory System REVISEDKim GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Transportation in AnimalsDocument14 pagesTransportation in AnimalsCREATIVING TAMILANNo ratings yet
- Tissues and Intro To Circulation 2014 2Document51 pagesTissues and Intro To Circulation 2014 2Chantae JulienNo ratings yet
- Human HeartDocument16 pagesHuman HeartDelfin Jr UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulation-DmDocument32 pagesBlood Circulation-DmMathews showsNo ratings yet
- Question #1 Explain Femure With Structure? DefinitionDocument6 pagesQuestion #1 Explain Femure With Structure? DefinitionAmjad BhattiNo ratings yet
- THR Circulatory System (HSB)Document37 pagesTHR Circulatory System (HSB)levilevandreaNo ratings yet
- B1+ Student BookDocument60 pagesB1+ Student BookKimsun DalinNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument19 pagesCirculatory SystemСоня КропельницкаяNo ratings yet
- Nutrients and Waste Transport System: By: Jeston LetacDocument30 pagesNutrients and Waste Transport System: By: Jeston LetacJoshkorro GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and CirculatoryDocument4 pagesRespiratory and CirculatoryHeaNo ratings yet
- CVS/ The Blood Vessels: by DR - Ahmed Avdel MandaniDocument27 pagesCVS/ The Blood Vessels: by DR - Ahmed Avdel MandaniSerwan J AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Transport System in AnimalsDocument21 pagesTransport System in Animalssonia sonNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1: Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesMODULE 1: Respiratory and Circulatory SystemHeaNo ratings yet
- Vascular SystemDocument20 pagesVascular SystemHama HamidNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System - PPTDocument16 pagesThe Circulatory System - PPTrenztheoapuliNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Sci 6Document26 pagesCirculatory System Sci 6Regin BaguioNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument1 pageThe Circulatory SystemAkeeyuki WongNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument16 pagesCirculatory Systemkenneth vergaraNo ratings yet
- Animal TransportDocument20 pagesAnimal TransportFeranmi AkinboboyeNo ratings yet
- HUman Circulatory SystemDocument19 pagesHUman Circulatory SystemPrisha ChhedaNo ratings yet
- Vertebrate Circulatory System #1Document36 pagesVertebrate Circulatory System #1Josephine Ivy JumalaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument46 pagesCirculatory Systemmirasol1206100% (1)
- 2020 HSC PdhpeDocument18 pages2020 HSC PdhpemultieevNo ratings yet
- Dysrhythmia Advance Content Outline A1 - 2020.1.2Document3 pagesDysrhythmia Advance Content Outline A1 - 2020.1.2Kimberly Whiteside50% (2)
- Cadiac Cycle, Heart Sound, ECG, HypertensionDocument110 pagesCadiac Cycle, Heart Sound, ECG, HypertensionNilesh100% (1)
- Ix StrokeDocument6 pagesIx StrokeWayne MacrohonNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Heart FailureDocument33 pagesDrugs Used in Heart FailureLynx Kee Bayating100% (1)
- LP1ncm109 YboaDocument21 pagesLP1ncm109 YboaMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- Syncope ShockDocument39 pagesSyncope ShockBunga Erlita RosaliaNo ratings yet
- ECG Definition: - PurposeDocument2 pagesECG Definition: - PurposeJustine Karl Pablico100% (1)
- SABER IM PrometricDocument71 pagesSABER IM Prometricisra zaidNo ratings yet
- MSDocument12 pagesMSMary Claire AbenidoNo ratings yet
- Coronary Heart DiseaseDocument12 pagesCoronary Heart DiseaseAji Prima Putra67% (3)
- Role of Pets in Enhancing Human Well-Being PDFDocument16 pagesRole of Pets in Enhancing Human Well-Being PDFKanchan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Kardiogenik SyokDocument43 pagesKardiogenik SyokGalih Arief Harimurti WawolumajaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Past Question PapersDocument72 pagesAnalysis of Past Question PapersShamaNo ratings yet
- DM Critical Care Medicine PDFDocument23 pagesDM Critical Care Medicine PDFArun Sahaya RajaNo ratings yet
- Practice Worksheets - Cardiac PhysiologyDocument5 pagesPractice Worksheets - Cardiac PhysiologyrickNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Catheterization - 4Document2 pagesCardiac Catheterization - 4Indranil SinhaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Aortic RegurgitationDocument8 pagesAssessment of Aortic RegurgitationKhurram NadeemNo ratings yet
- Pulsus Paradoxus - Wikip PDFDocument4 pagesPulsus Paradoxus - Wikip PDFAniket MittalNo ratings yet
- IAS AneurysmDocument13 pagesIAS AneurysmE'len HamidahNo ratings yet
- Truncus ArteriosusDocument9 pagesTruncus ArteriosusAkang KurniawanNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument6 pagesCardioGrace GurdielNo ratings yet
- IT Sci F3 Topical Test 2 (E)Document6 pagesIT Sci F3 Topical Test 2 (E)Nad RamliNo ratings yet
- A Review On Dengue and Treatments 13 23Document3 pagesA Review On Dengue and Treatments 13 23Karina Mega WNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Septal DefectDocument17 pagesVentricular Septal DefectWasim IqbalNo ratings yet
The Heart Revision Notes: The Circulatory System's Main Function Is To
The Heart Revision Notes: The Circulatory System's Main Function Is To
Uploaded by
Michael DongOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Heart Revision Notes: The Circulatory System's Main Function Is To
The Heart Revision Notes: The Circulatory System's Main Function Is To
Uploaded by
Michael DongCopyright:
Available Formats
The Heart Revision Notes
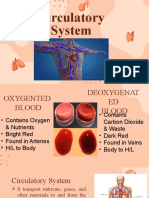
The circulatory system’s main function is to:
- carry oxygen and nutrients to the cells
- remove wastes and carbon dioxide from the cells.
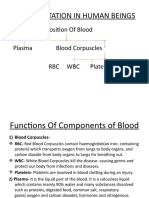
Blood consists of four main parts:
- red blood cells
- white blood cells
- platelets
- plasma
Red Blood Cells:
• Carry oxygen from lungs to the cells (attached to chemical called haemoglobin).
• Blood lacking oxygen is darker in colour (and is sometimes referred to as blue
blood,).
• Red blood cells are biconcave discs.
• Live from 1 – 4 months before being broken down in the liver.
• Made in the bone marrow
• Born with a nucleus that dissolves soon after
White Blood Cells:
• Carry oxygen from lungs to the cells (attached to chemical called haemoglobin).
• Blood lacking oxygen is darker in colour (and is sometimes referred to as blue
blood,).
• Red blood cells are biconcave discs.
• Live from 1 – 4 months before being broken down in the liver.
• Made in the bone marrow
• Born with a nucleus that dissolves soon after
Plasma:
• Liquid part of the blood. Largely water with some dissolved substances; eg. salt,
nutrients and/or wastes.
• Carries dissolved carbon dioxide from cells to lungs.
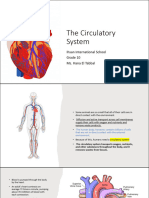
The Heart:
• is slightly larger than the fist of the owner
• sits inside a thin sac mounted just slightly left of centre of the chest
• A very strong muscular pump comprising four chambers (top-left and right atria and
bottom-left and right ventricles) surrounded by muscle.
Right Atrium
• Receives blood from the body via the superior (from upper body) and inferior (from
lower body) vena cava. Blood can only enter when atrium muscles relax.
• Blood entering is lacking oxygen, but carries carbon dioxide instead.
Right Ventricle:
• When right atrium has filled, it contracts, forcing blood into the right ventricle, past
the tricuspid valves (three flaps of strong tissue whose job is to prevent back flow
from the right ventricle into the right atrium). When the right ventricle contracts, the
tricuspid valves close, leaving the blood with only one exit, out through the
pulmonary artery to the lungs. The blood is prevented from returning by a set of
pocket valves, also called semi-lunar valves.
Left Atrium
• Blood returning from the lungs is rich in oxygen and enters the left atrium through the
pulmonary vein. Blood can only enter when atrium muscles relax.
Left Ventricle
• When the left atrium contracts it forces blood past the bicuspid valves into the left
ventricle, which has relaxed its muscle walls. When the left ventricle contracts, the
bicuspid valves close, leaving the blood with only one exit, out through the aorta
(main artery) to the body. The blood is prevented from returning by a set of pocket
valves, also called semi-lunar valves.
You might also like
- BLS TRAINING MANUAL Second Edition PDF 2023-1 - 240226 - 093323Document93 pagesBLS TRAINING MANUAL Second Edition PDF 2023-1 - 240226 - 093323mohdnor29No ratings yet
- Clinical Focus: Emergency RoomDocument12 pagesClinical Focus: Emergency Roomnokolip90% (21)
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseLouie Kem Anthony Babaran50% (8)
- Critical Care Model MCQsDocument1 pageCritical Care Model MCQssacabona100% (1)
- Pulmonary Circulation 4th Edition (2016) (PDF) (UnitedVRG) PDFDocument773 pagesPulmonary Circulation 4th Edition (2016) (PDF) (UnitedVRG) PDFpvs5155No ratings yet
- The Circulatory System PDFDocument22 pagesThe Circulatory System PDFbilly sauraNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument28 pagesCirculatory SystemMaria Theresa DemeterioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 by Jaskirat KaurDocument18 pagesLecture 3 by Jaskirat KaurmparineetNo ratings yet
- Intro To The Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesIntro To The Circulatory Systemapi-656424610No ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Transporting Gases, Nutrients, Wastes, and HormonesDocument44 pagesCirculatory System: Transporting Gases, Nutrients, Wastes, and HormonesDawn Regile MorilloNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Transporting Gases, Nutrients, Wastes, and HormonesDocument22 pagesCirculatory System: Transporting Gases, Nutrients, Wastes, and HormonesMariella SingsonNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument12 pagesCirculatory SystemKeyur SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Cardiovascular SystemDocument49 pages2.2 Cardiovascular SystemPratham ChopraNo ratings yet
- Human Body Circulatory SystemDocument41 pagesHuman Body Circulatory SystemFrancis MacasioNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument17 pagesCirculatory Systemkatefoskin2008No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Shoaib AlamDocument28 pagesCardiovascular System: Shoaib AlamUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of The HeartDocument2 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of The Heartjoycee01No ratings yet
- Module 3Document43 pagesModule 3Sharanya BasakNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument31 pagesCirculatory SystemKalev MaricqNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of HeartDocument42 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of HeartSANJAY SNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology (Cardio)Document1 pageAnatomy and Physiology (Cardio)Eunice LazaroNo ratings yet
- System Is An: ArteriesDocument4 pagesSystem Is An: ArteriesPinasti Aprilia PutriNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Biology Chapter 6 Term 1 ST 1Document27 pagesCirculatory System: Biology Chapter 6 Term 1 ST 1Pranati SharmaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 1.3 LessonDocument31 pagesScience 9 1.3 LessonHdisbdbd NfjdnbdncNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesCirculatory SystemDaniica MacaranasNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System 3500Document24 pagesThe Circulatory System 3500tarickbatshon03No ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Sbi3u The Circulatory System Introduction and Human Circulatory SystemDocument39 pagesDokumen - Tips - Sbi3u The Circulatory System Introduction and Human Circulatory Systempacheco TimeNo ratings yet
- Cardio NewDocument204 pagesCardio NewHaleema SaadiaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory Systemvedansh duttNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andDocument62 pagesCirculatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andBlister CountNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andDocument62 pagesCirculatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andBlister Count100% (1)
- BiologyDocument7 pagesBiologyMaria MubasshiraNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesThe Circulatory SystemJavier Serrano MatuteNo ratings yet
- Lecture in Circulatory SystemDocument14 pagesLecture in Circulatory SystemGailNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument20 pagesThe Circulatory Systemhanatabbal19No ratings yet
- IV.C. Nutrient and Waste Transport SystemDocument18 pagesIV.C. Nutrient and Waste Transport SystemDarwin NoolNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As ADocument6 pagesCardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As AMalaquias VallejosNo ratings yet
- Life Processes, Class XDocument31 pagesLife Processes, Class XPiyushNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument27 pagesCirculatory SystemAngel JD PelovelloNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - First Quarter Reviewer: Biology 9Document33 pagesScience 9 - First Quarter Reviewer: Biology 9Ace AligoraNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument25 pagesCirculatory SystemIan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System REVISEDDocument11 pagesCirculatory System REVISEDKim GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Transportation in AnimalsDocument14 pagesTransportation in AnimalsCREATIVING TAMILANNo ratings yet
- Tissues and Intro To Circulation 2014 2Document51 pagesTissues and Intro To Circulation 2014 2Chantae JulienNo ratings yet
- Human HeartDocument16 pagesHuman HeartDelfin Jr UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulation-DmDocument32 pagesBlood Circulation-DmMathews showsNo ratings yet
- Question #1 Explain Femure With Structure? DefinitionDocument6 pagesQuestion #1 Explain Femure With Structure? DefinitionAmjad BhattiNo ratings yet
- THR Circulatory System (HSB)Document37 pagesTHR Circulatory System (HSB)levilevandreaNo ratings yet
- B1+ Student BookDocument60 pagesB1+ Student BookKimsun DalinNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument19 pagesCirculatory SystemСоня КропельницкаяNo ratings yet
- Nutrients and Waste Transport System: By: Jeston LetacDocument30 pagesNutrients and Waste Transport System: By: Jeston LetacJoshkorro GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and CirculatoryDocument4 pagesRespiratory and CirculatoryHeaNo ratings yet
- CVS/ The Blood Vessels: by DR - Ahmed Avdel MandaniDocument27 pagesCVS/ The Blood Vessels: by DR - Ahmed Avdel MandaniSerwan J AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Transport System in AnimalsDocument21 pagesTransport System in Animalssonia sonNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1: Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesMODULE 1: Respiratory and Circulatory SystemHeaNo ratings yet
- Vascular SystemDocument20 pagesVascular SystemHama HamidNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System - PPTDocument16 pagesThe Circulatory System - PPTrenztheoapuliNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Sci 6Document26 pagesCirculatory System Sci 6Regin BaguioNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument1 pageThe Circulatory SystemAkeeyuki WongNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument16 pagesCirculatory Systemkenneth vergaraNo ratings yet
- Animal TransportDocument20 pagesAnimal TransportFeranmi AkinboboyeNo ratings yet
- HUman Circulatory SystemDocument19 pagesHUman Circulatory SystemPrisha ChhedaNo ratings yet
- Vertebrate Circulatory System #1Document36 pagesVertebrate Circulatory System #1Josephine Ivy JumalaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument46 pagesCirculatory Systemmirasol1206100% (1)
- 2020 HSC PdhpeDocument18 pages2020 HSC PdhpemultieevNo ratings yet
- Dysrhythmia Advance Content Outline A1 - 2020.1.2Document3 pagesDysrhythmia Advance Content Outline A1 - 2020.1.2Kimberly Whiteside50% (2)
- Cadiac Cycle, Heart Sound, ECG, HypertensionDocument110 pagesCadiac Cycle, Heart Sound, ECG, HypertensionNilesh100% (1)
- Ix StrokeDocument6 pagesIx StrokeWayne MacrohonNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Heart FailureDocument33 pagesDrugs Used in Heart FailureLynx Kee Bayating100% (1)
- LP1ncm109 YboaDocument21 pagesLP1ncm109 YboaMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- Syncope ShockDocument39 pagesSyncope ShockBunga Erlita RosaliaNo ratings yet
- ECG Definition: - PurposeDocument2 pagesECG Definition: - PurposeJustine Karl Pablico100% (1)
- SABER IM PrometricDocument71 pagesSABER IM Prometricisra zaidNo ratings yet
- MSDocument12 pagesMSMary Claire AbenidoNo ratings yet
- Coronary Heart DiseaseDocument12 pagesCoronary Heart DiseaseAji Prima Putra67% (3)
- Role of Pets in Enhancing Human Well-Being PDFDocument16 pagesRole of Pets in Enhancing Human Well-Being PDFKanchan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Kardiogenik SyokDocument43 pagesKardiogenik SyokGalih Arief Harimurti WawolumajaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Past Question PapersDocument72 pagesAnalysis of Past Question PapersShamaNo ratings yet
- DM Critical Care Medicine PDFDocument23 pagesDM Critical Care Medicine PDFArun Sahaya RajaNo ratings yet
- Practice Worksheets - Cardiac PhysiologyDocument5 pagesPractice Worksheets - Cardiac PhysiologyrickNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Catheterization - 4Document2 pagesCardiac Catheterization - 4Indranil SinhaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Aortic RegurgitationDocument8 pagesAssessment of Aortic RegurgitationKhurram NadeemNo ratings yet
- Pulsus Paradoxus - Wikip PDFDocument4 pagesPulsus Paradoxus - Wikip PDFAniket MittalNo ratings yet
- IAS AneurysmDocument13 pagesIAS AneurysmE'len HamidahNo ratings yet
- Truncus ArteriosusDocument9 pagesTruncus ArteriosusAkang KurniawanNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument6 pagesCardioGrace GurdielNo ratings yet
- IT Sci F3 Topical Test 2 (E)Document6 pagesIT Sci F3 Topical Test 2 (E)Nad RamliNo ratings yet
- A Review On Dengue and Treatments 13 23Document3 pagesA Review On Dengue and Treatments 13 23Karina Mega WNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Septal DefectDocument17 pagesVentricular Septal DefectWasim IqbalNo ratings yet